Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Internal Anatomy of A Bony Fish
Încărcat de
maryxtelDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Internal Anatomy of A Bony Fish
Încărcat de
maryxtelDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Internal anatomy of a bony fish: finned aquatic vertebrates animal with skin covered with scales.
It lives in water and is usually oviparous. Brain: seat of the mental faculties of a fish. Esophagus: part of the digestive tract connecting the mouth to the stomach. Dorsal aorta: vessel in the back that carries blood from the heart to the organs. Stomach: part of the digestive tract between the esophagus and the intestine. Air bladder: pocket in which urine collects. Spinal cord: part of the nervous system that connects the brain to all other parts of a fish. Kidney: blood-purifying organ. Urinary orifice: opening for eliminating urine. Genital Orifice: opening related to the genital organs. Anus: end of the digestive tract. Gonad: hormone-secreting sexual gland of a fish. Intestine: last part of the digestive tract. Pyloric cecum: cul-de-sac related to the intestine. Gall bladder: small sac containing the bile. Liver: bile-producing digestive gland. Heart: blood-pumping organ. Gills: respiratory organ of a fish. Tooth: hard organ of a fish used to shred food. Eye: sight organ of a fish. Olfactory bulb: bulging part of the smell organ of smell of a fish.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
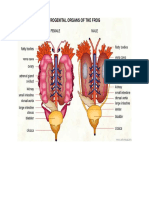
- Urogenital Organs of The FrogDocument4 paginiUrogenital Organs of The FrogApril Zonio AlisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy NewDocument46 paginiAnatomy NewhalimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animals, Respiration and Digestion Study SheetDocument9 paginiAnimals, Respiration and Digestion Study SheetcohensoobÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Trouts Anatomy-WebDocument2 paginiA Trouts Anatomy-WebDiaconu DragosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vocabulary Ingles MédicoDocument14 paginiVocabulary Ingles MédicoMayra LandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Parts of A Frog and It's FunctionsDocument3 paginiBody Parts of A Frog and It's FunctionsMichael ChuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOL223-Lab 8Document29 paginiBIOL223-Lab 8chicken friesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Organs For The ExamDocument5 paginiBody Organs For The ExamrayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dalgo, Alpha Joy A. Bs Pych I-C: Respiratory OrgansDocument2 paginiDalgo, Alpha Joy A. Bs Pych I-C: Respiratory OrgansAlphajoy Aguli DalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FishdissectionnewDocument45 paginiFishdissectionnewdqmprenticeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Reviewer: - Left AtriumDocument14 paginiScience Reviewer: - Left AtriumJasmineLouiseEspañolÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOLOGY ReviewerDocument18 paginiBIOLOGY ReviewerAngela Nicole ManasÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIO Notes Class 12Document14 paginiBIO Notes Class 12Marwa KhotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Parts of A FishDocument2 paginiInternal Parts of A FishBohna FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fauziatul Riyada 2210070100104 Bahasa InggrisDocument4 paginiFauziatul Riyada 2210070100104 Bahasa InggrisFauziatul RiyadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human System MateriaLDocument57 paginiHuman System MateriaLSalma AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frog-Str Organization in Animals PDFDocument27 paginiFrog-Str Organization in Animals PDFAÎncă nu există evaluări
- StemchartDocument8 paginiStemchartapi-297052087Încă nu există evaluări
- Functions and Anatomy of Human Body GK Notes in PDFDocument14 paginiFunctions and Anatomy of Human Body GK Notes in PDFreenajoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Systems AnatomyDocument9 paginiBody Systems AnatomyDeepikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Vertebrates SystemsDocument3 paginiTypes of Vertebrates SystemsMauricio LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System PartsDocument3 paginiDigestive System PartsDaniel DadzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frog External Anatomy RevDocument18 paginiFrog External Anatomy RevMike DelivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accessory OrgansDocument18 paginiAccessory OrgansDaniel AtiehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organ Systems of Some Animal StudentsDocument2 paginiOrgan Systems of Some Animal StudentsAdrian Santos IdananÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODULE 2 Ichthyology - SECTION 5 Shark Anatomy and Dogfish Dissection PDFDocument27 paginiMODULE 2 Ichthyology - SECTION 5 Shark Anatomy and Dogfish Dissection PDFElishae SamonteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frog PartsDocument1 paginăFrog Partstony montanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Digestive System of Fish Consists ofDocument6 paginiThe Digestive System of Fish Consists ofPurity MoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Systems Unit Objectives: 1. Chapter 40: Animal Form and FunctionDocument3 paginiAnimal Systems Unit Objectives: 1. Chapter 40: Animal Form and FunctionBob SchneiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Part of The BodyDocument2 paginiInternal Part of The Bodykevynj35Încă nu există evaluări
- Discussion Rabbit Dissection AnatomyDocument1 paginăDiscussion Rabbit Dissection AnatomyNorasyikin ZulkifliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accessory Glands of The Digestive-SystemDocument3 paginiAccessory Glands of The Digestive-SystemMarchylle Faye JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urinary Tract Infection Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument12 paginiUrinary Tract Infection Anatomy and PhysiologyPaul Anthony Centeno PimentelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class AgnathaDocument5 paginiClass AgnathaJackie Swift Funtanilla100% (1)
- Frog Organ SystemDocument33 paginiFrog Organ SystemReineil PanguitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagram of The Abdomen of A DogDocument9 paginiDiagram of The Abdomen of A DogSriram SKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mollusca LecDocument6 paginiMollusca LecPatricia HariramaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4 HandoutDocument4 paginiClass - XI - Biology - Structural Orgganization in Animals M 4 HandoutNewcomerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Organ Systems: Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument34 paginiAnimal Organ Systems: Anatomy and PhysiologybibisupergirlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hesi ADocument214 paginiHesi Ayisel56100% (6)
- Hafeezullah: Subject:Anatomy Topic: Anatomy of Excretory System Roll No: 15 Semester: 1 RepeaterDocument10 paginiHafeezullah: Subject:Anatomy Topic: Anatomy of Excretory System Roll No: 15 Semester: 1 RepeaterMuhammad ShahzaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System in FinfishDocument18 paginiCirculatory System in FinfishSalma SabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excretory System in InvertebratesDocument2 paginiExcretory System in Invertebratesihtishamulhaq1348Încă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life Science 1Document24 paginiEarth and Life Science 1John Jacob Ezekiel CaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Human Body: An Arrangement of Many Parts That Work TogetherDocument6 paginiThe Human Body: An Arrangement of Many Parts That Work TogetherSara RoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive System Anatomy & HistologyDocument7 paginiDigestive System Anatomy & HistologyAbdallah AlasalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amphibians: Amphibian EvolutionDocument8 paginiAmphibians: Amphibian EvolutionManoj Kumar UpadhyayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Notes: Excretory OrgansDocument4 paginiRevision Notes: Excretory Organskavitaruby1980Încă nu există evaluări
- Special Chordate CharacteriscticsDocument19 paginiSpecial Chordate CharacteriscticsKunica SurajÎncă nu există evaluări
- The LiverDocument7 paginiThe LiverBarrameda NegideasisÎncă nu există evaluări
- TomdDocument15 paginiTomdduinnemerriedithcastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phylum Chaetognatha: Means "Hairy Jaws" 100 SPDocument4 paginiPhylum Chaetognatha: Means "Hairy Jaws" 100 SPsomu1Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 4 Anatomy Review For Fish DiseaseDocument48 paginiLecture 4 Anatomy Review For Fish DiseasePokemongo Shu Ting100% (1)
- Definitions Module 3Document8 paginiDefinitions Module 3warrior girlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument14 paginiAnatomy and PhysiologyZhailyn Joy DumlaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RANADocument19 paginiRANAPragya SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade7 Bio Chapter10 Transportation - CW&HWDocument6 paginiGrade7 Bio Chapter10 Transportation - CW&HWTanushree RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineDe la EverandDeciphering nCoV19, Quest for Cure, Prophylaxis, and VaccineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strategic ActingDocument19 paginiStrategic ActingMuhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposal For A School of Information Management and SystemsDocument16 paginiProposal For A School of Information Management and SystemsAnabia ChodryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Class in Haiti: HistoryDocument17 paginiSocial Class in Haiti: HistoryMuhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCB FinalDocument24 paginiMCB FinalMuhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Initiation Ahmed 025Document2 paginiInitiation Ahmed 025Muhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course OutlineDocument3 paginiCourse OutlineMuhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Source: Survey DataDocument3 paginiSource: Survey DataMuhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balance Sheet As at December 31Document2 paginiBalance Sheet As at December 31Muhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiotechReserveSeatsBS 2Document1 paginăBiotechReserveSeatsBS 2Muhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industry Analysis: Market SegmentsDocument3 paginiIndustry Analysis: Market SegmentsMuhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Law?: Law Is The Body of The Principles Recognized and Applied by The Court in The Administration of JusticeDocument2 paginiWhat Is Law?: Law Is The Body of The Principles Recognized and Applied by The Court in The Administration of JusticeMuhammad Adnan ÇhÎncă nu există evaluări