Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
NCP Format 3 (CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus Nephropathy)
Încărcat de
John Christopher CelestinoDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NCP Format 3 (CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus Nephropathy)
Încărcat de
John Christopher CelestinoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
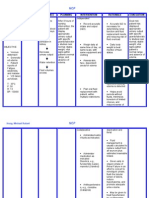
Patients Diagnosis: CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE probably secondary to DM Nephropathy
Short Background: Chronic kidney disease (CKD) occurs when one suffers from gradual and usually permanent loss of kidney function over time. With loss of kidney function, there is an accumulation of water; waste; and toxic substances, in the body, that are normally excreted by the kidney. Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR), the measure of the kidney's function, determines the severity or stage of the disease (whereas Stage 5 CKD is considered Renal Failure due to gradual loss of GFR, GFR < 15: needs dialysis). CKD often develops from 1Diabetes (stenosis/ischemic), 2Hypertension (microvascular damage), 3Glomerulonephritis (post-infection), or 4Nephrotoxicity (medications).
Assessment
Subjective: Patient is not able to verbalize.
Nursing Diagnosis
Ineffective Breathing Pattern r/t impending pulmonary congestion d/t impaired GFR and fluid retention or respiratory muscle weakness d/t physical stress.
Scientific Explanation of the Problem
Impaired GFR results into fluid overload. With fluid volume excess, venous pressure is more likely to cause both circulatory and pulmonary congestion. The patient may possibly manifests fatigue, dyspnea, tachypnea, muscle weakness (including diaphragm), or sputum production that are related to pulmonary congestion. Physical stress also impacts pulmonary functioning. Diabetic, there is a possibility that sugar crystallization has occurred and leads to renal artery stenosis or a microvascular complication due to viscosity.
Planning
Goal: Establish Spontaneous, nonLabored Breathing Short Term: After 4 hours of nursing interventions, patient will be able to reduce labored and difficult breathing and establish a respiratory rate of less than 30cpm. Long Term: After 5 days of nursing interventions, patient will be able to demonstrate nonlabored and spontaneous breathing.
Interventions
Collaborative: 1. Administer humid Oxygen (8-10Lpm) as ordered. 2. Assist in Manual Ventilation via ET Tube.
Rationale
Evaluation
1. To help patient get adequate oxygen despite of DOB. 2. To assist patient on respiration and to ensure adequate tidal volume.
Objective:
> Deep, fast, noisy breathing > RR 33cpm > Crackles heard on inspiration > SaO2 99% > BP 140/100mmhg > PR 80bpm > T 37.0 C > Diaphoretic, cold clammy skin > Unresponsive; may be due to fatigue/weakness. > Increased respiratory secretions.
Independent: 1. Monitor and record vital signs. 2. Assess for lung sounds.
1. To check and reassess vital function changes (Respiration). 2. To identify extent of fluid accumulation in the respiratory system. 3. To facilitate gravitational expansion of the lungs to decrease inspiratory effort. 4. To avoid stressors and let patient regain strength by manipulation of environment. 5. To facilitate airway clearance and reduce effort from DOB.
3. Position on moderate high back rest.
4. Maintain calm and nonstimulating environment.
5. Suction secretions PRN.
CELESTINO, JOHN CHRISTOPHER S. WUP SN13 senior block 04
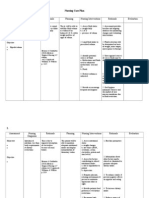
Patients Diagnosis: CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE probably secondary to DM Nephropathy
Priority Problem: (Priority 1) Ineffective Breathing Pattern
Assessment
Subjective: Patient is not able to verbalize.
Nursing Diagnosis
Fluid Volume Excess R/T decrease Glomerular filtration Rate and sodium retention.
Scientific Explanation of the Problem
Renal disorder impairs glomerular filtration that resulted to fluid overload. With fluid volume excess, hydrostatic pressure is higher than the usual pushing excess fluids into the interstitial spaces, causes venous return, leading the patient to have edema, weight gain, pulmonary congestion and HPN at the same time due to decrease GFR, nephron hypertrophied leading to decrease ability of the kidney to concentrate urine and impaired excretion of fluid thus leading to oliguria/anuria. With associated DM, there is a possibility that sugar crystallization has occurred and leads to renal artery stenosis or a microvascular complication due to viscosity of blood.
Planning
Goal: Reduce Fluid Volume Excess, output more than input. Short Term: After 4 hours of nursing interventions, patient will be able to avoid recurrence of fluid excess Long Term: After 5 days of nursing intervention the patient will manifest stabilize fluid volume, I & O, normal VS, stable weight, and free from signs of edema.
Interventions
Collaborative: 1. Administer loop diuretics (Furosemide/Lasix) as ordered. 2. Assist in specimen extraction for serum analysis (Serum Electrolytes/ RBS or FBS) and urine analysis (BUN/Crea). 3. CBG Test as ordered. Independent: 1. Monitor and record vital signs 2. Auscultate breath sounds 3. Record occurrence of dyspnea
Rationale
Collaborative: 1. Diuretics reduce fluid volume by helping kidney excrete urine and sodium. 2. To prepare patient for possible lab orders.. 3. To determine the efficacy of DM regimen. Independent: 1. To check and reassess vital function changes (Circulation). 2. To determine extent of fluid excess. 3. To check possible respiratory complications (pulmonary congestion). 4.
Evaluation
Objective:
> Anuria > BP 140/100mahg > RR 27cpm > PR 80bpm > T 37.0 C > Peripheral Edema > Diaphoretic, cold clammy skin > Unresponsive; may be due to fatigue/weakness. > Increased respiratory secretions. > CBG 126mg/dL
4. Review lab data like BUN, Creatinine, Serum electrolyte.
To monitor kidney function and fluid retention (electrolyte compensation).
5. To determine fluid retention and kidney function (GFR). 6. Increasing weight may indicate fluid retention. 7. To allow patient cope with stressors naturally.
5. Record I&O accurately and calculate fluid volume balance
6. Weigh client 7. Encourage quiet, restful atmosphere. Main Problem: (Priority 2) Fluid Volume Excess CELESTINO, JOHN CHRISTOPHER S. WUP SN13 senior block 04
Patients Diagnosis: CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE probably secondary to DM Nephropathy
Manifestation Problem: (Priority 3) Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity
CELESTINO, JOHN CHRISTOPHER S. WUP SN13 senior block 04
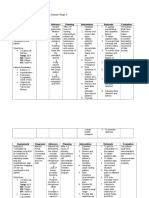
Patients Diagnosis: CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE probably secondary to DM Nephropathy
Assessment
Subjective: Patient is not able to verbalize.
Nursing Diagnosis
Risk for Impaired Skin Integrity r/t edema and prolonged bed rest d/t
Scientific Explanation of the Problem
Due to fluid retention, fluid accumulates and fluid shifts from intracellular compartment to extracellular compartment causing escape of fluid to the tissues (edema). With associated complications of anemia, skin nutrition would be crucial and may have easily broken off. DM could cause high blood sugar levels and leads to viscosity of blood that also impairs nutrition of skin or reduction of blood cells to capillaries.
Planning
Goal: Prevent Risks on Developing Skin Breakdown. Short Term: After 4 hours of nursing interventions, patient will be able to remove potential threats that may lead to poor skin integrity. Long Term: After 5 days of nursing interventions, patient will be able to identify and avoid factors that lead to skin breakdown.
Interventions
Collaborative: 1. Ferrous Sulfate (Iron supplement) as ordered. 2. Update Lab Findings for CBC (RBC, Hgb, Hct). 3. CBG T.I.D. as ordered.
Rationale
Evaluation
Objective:
> Peripheral Edema > Prolonged bed rest > Pallor > Hgb > Diaphoretic, cold clammy skin > Unresponsive; may be due to fatigue/weakness. > CBG 126mg/dL
1. To help body regulate RBC in the absence/lacking of hormone erythropoietin. 2. To evaluate efficacy of treatment/prophylaxis for anemia regimen. 3. To determine hyperglycemia that makes blood viscous and induces the risk for infection.
Independent: 1. Assess skin appearance (color, texture, temperature). 2. Turn patient side to side every 2 hours if possible.
1. To determine edema or erythema that indicates possible bed sore. 2. To make pressure equal when lying to avoid unilateral skin tissue blood insufficiency. 3. To avoid skin irritation from crease. 4. To avoid risk for skin injury and infection.
3. Maintain crease-free bed linen. 4. Maintain a clean, therapeutic environment.
CELESTINO, JOHN CHRISTOPHER S. WUP SN13 senior block 04
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NCP - Fluid RetentionDocument3 paginiNCP - Fluid RetentionMichelle Teodoro100% (1)
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 paginiNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDocument9 paginiNursing Care Plan for a Diabetic Patient with Dehydration and FatigueDanica Salinas100% (1)
- Managing Fluid Volume for Renal FailureDocument2 paginiManaging Fluid Volume for Renal FailureMark Angelo Chan100% (13)
- NCP CKDDocument4 paginiNCP CKDljarseniorn100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan CKDDocument6 paginiNursing Care Plan CKDReylan Deo Rallo Asio100% (5)
- NCP CKDDocument6 paginiNCP CKDBenjie Dimayacyac100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan for HyperkalemiaDocument10 paginiNursing Care Plan for HyperkalemiaChamelli RobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Analysis FinalDocument29 paginiCase Analysis FinalVeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esrd NCPDocument7 paginiEsrd NCPSharmaine Camille de LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Diagnosis Scientific ExplanationDocument9 paginiNursing Diagnosis Scientific ExplanationMarisol Dizon100% (1)
- NCP For Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 paginiNCP For Diabetic KetoacidosisLovely Cacapit100% (1)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Document21 paginiChronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Kristine Anne Soriano100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Renal FailureDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan - Renal Failurederic90% (30)
- NCP: Chronic Renal FailureDocument14 paginiNCP: Chronic Renal FailureJavie77% (13)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 paginiChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESRD Secondary To Diabetic Nephropathy CASE STUDY Docx 2Document42 paginiESRD Secondary To Diabetic Nephropathy CASE STUDY Docx 2Eyerusalem100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument11 paginiNursing Care Plan Renal Failurenosevad88850% (2)
- Chronic Kidney Disease CompilationDocument33 paginiChronic Kidney Disease CompilationGwen Stefanie Lagrimas ValloyasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationChristine LebicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Failure NCPDocument3 paginiRenal Failure NCPJet Ray-Ann GaringanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Volume Excess (CRF)Document4 paginiFluid Volume Excess (CRF)NursesLabs.com100% (1)
- UGIBDocument1 paginăUGIBgarrl100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For CHFDocument7 paginiNursing Care Plan For CHFRosemarie Carpio100% (5)
- Understanding End-Stage Renal DiseaseDocument59 paginiUnderstanding End-Stage Renal DiseaseJonathan Diaz93% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For ESRDDocument8 paginiNursing Care Plan For ESRDChester Manalo94% (17)
- Case Study 18Document4 paginiCase Study 18api-271284613Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of ESRDDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of ESRDjake90210100% (1)
- CKD (F&e)Document110 paginiCKD (F&e)Al-nazer Azer Al100% (1)
- FINAL PPT of Grand Case Presentation About CKDDocument66 paginiFINAL PPT of Grand Case Presentation About CKDmaria erika94% (16)
- NCP Excess Fluid VolumeDocument4 paginiNCP Excess Fluid VolumeTrixia CamporedondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Document4 paginiMedical Diagnosis: Chronic Kidney Disease Stage 5Hadeer Mahmoud Abuslima100% (1)
- Acute Renal FailureDocument76 paginiAcute Renal Failureikemas100% (7)
- CKD NCPDocument4 paginiCKD NCPArlene Macatangay100% (1)
- NCP 2 Addison's DiseaseDocument4 paginiNCP 2 Addison's DiseaseRenee RoSeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument103 paginiA Case Study On Chronic Kidney DiseaseLouella Mae CoraldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Diabetic Drug Vildagliptin: Mechanism, Indication, Side Effects and Nursing CareDocument2 paginiAnti-Diabetic Drug Vildagliptin: Mechanism, Indication, Side Effects and Nursing CareChris Denver BancaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Renal FailureDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Renal FailureMark Jason Rabadan100% (1)
- Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiAcute Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanKrisianne Mae Lorenzo Francisco80% (5)
- NCP For Bladder CaDocument4 paginiNCP For Bladder CaChris Tine CaccamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Kidney Disease ManagementDocument3 paginiChronic Kidney Disease ManagementAngie MandeoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationandronicoc100% (5)
- Diabetic Neuropathy and Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument62 paginiDiabetic Neuropathy and Chronic Kidney DiseaseMae Navidas DigdiganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceDocument7 paginiCase: Liver Cirrhosis Assessment:: Nursing InferenceLovelyn GanirÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Altered Renal Tissue Perfusion Chronic Renal Renal Failure Nursing Care PlansDocument4 pagini3 Altered Renal Tissue Perfusion Chronic Renal Renal Failure Nursing Care Planssapiah raman100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Management Nursing InterventionsDocument5 paginiFluid Volume Management Nursing InterventionsMerrill HansÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathyDocument4 paginiNCP Format 3 CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus NephropathySapna thakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthDocument2 paginiNursing Diagnosis: Fatigue related to decreased muscular strengthAna Ramos LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 paginăPathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- CKD Patient at Risk for Respiratory, Fluid and Skin IssuesDocument3 paginiCKD Patient at Risk for Respiratory, Fluid and Skin IssuesMichael Baylon Dueñas100% (2)
- NCPDocument15 paginiNCPCamille PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DENGUE HEMORRHAGIC FEVER NURSING CAREDocument5 paginiDENGUE HEMORRHAGIC FEVER NURSING CAREMichaela ArellanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired kidney function nursing careDocument21 paginiImpaired kidney function nursing careKate ManalastasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Septic Shock Nursing Assessment and ManagementDocument6 paginiSeptic Shock Nursing Assessment and ManagementJenn GallowayÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 paginiNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetes Mellitus Fluid Volume DeficitDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan for Diabetes Mellitus Fluid Volume DeficitAnnisa Silvera II50% (2)
- NCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument4 paginiNCP Ineffective Tissue PerfusionKristine Maghari83% (6)
- Hanoi Medical Nursing Care Plan for Heart FailureDocument11 paginiHanoi Medical Nursing Care Plan for Heart Failurelephuongloan2601Încă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Volume Excess CRFDocument3 paginiFluid Volume Excess CRFDana Fajardo RezanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- FhtyDocument3 paginiFhtyAnthropophobe NyctophileÎncă nu există evaluări
- GastritisDocument3 paginiGastritisJohn Christopher CelestinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychiatric NursingDocument11 paginiPsychiatric NursingJohn Christopher Celestino100% (1)
- Sample FNCPDocument6 paginiSample FNCPtehkie04100% (4)
- Related Literature For Health Care PractitionersDocument29 paginiRelated Literature For Health Care PractitionersJohn Christopher CelestinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument25 paginiMaternal and Child Health Nursingmarie100% (46)
- Related Literature For Health Care PractitionersDocument29 paginiRelated Literature For Health Care PractitionersJohn Christopher CelestinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicroDocument2 paginiMicroJohn Christopher CelestinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ante Part UmDocument3 paginiAnte Part UmJohn Christopher CelestinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adrenergic Agonists 2020 PDFDocument65 paginiAdrenergic Agonists 2020 PDFAlaa NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canvas Lab Exercise 12 Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 paginiCanvas Lab Exercise 12 Cardiovascular SystemJamesanne DemetriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Board Exam Pointers for SingaporeDocument18 paginiNursing Board Exam Pointers for SingaporeHegi Ann AlcalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Systems and Homeostasis Lab 1409: ObjectivesDocument21 paginiBody Systems and Homeostasis Lab 1409: ObjectivesJazmin Robles HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neoreviews 201533Document11 paginiNeoreviews 201533Dmitri KaramazovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibhre Prep 01 KeyDocument16 paginiIbhre Prep 01 Keyanon-747764100% (4)
- Calculate Target Heart Rates for TrainingDocument3 paginiCalculate Target Heart Rates for TrainingBrij Mohan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mujika2019 2Document19 paginiMujika2019 2Maria ChristodoulouÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgical Complications: Maj. Hafizur Rashid SazalDocument43 paginiSurgical Complications: Maj. Hafizur Rashid SazalHafizur RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Airway and Ventilatory ManagementDocument19 paginiAirway and Ventilatory ManagementChynthea ParamithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map TemplateDocument4 paginiConcept Map TemplateaamenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHANGES IN BLOOD AFTER DEATHDocument19 paginiCHANGES IN BLOOD AFTER DEATHKU RU RUÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hope - 3 Grade 12 Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Document5 paginiHope - 3 Grade 12 Energy System: Quarter 1 Week 1 Module 1Angelo Dela LlarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Pressure Regulation SummaryDocument42 paginiBlood Pressure Regulation SummaryLouis JinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reymart Baguio A. Iii Bsed-Science Module 4 - Fluids and Transport Module Assessment Critical Thinking QuestionsDocument13 paginiReymart Baguio A. Iii Bsed-Science Module 4 - Fluids and Transport Module Assessment Critical Thinking QuestionsReymart Anga Baguio IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carganilla - Pathophysiology - Week 1Document4 paginiCarganilla - Pathophysiology - Week 1Marjorie CarganillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copd and Pnumonia Questions With AnswersDocument5 paginiCopd and Pnumonia Questions With Answersjess_nookieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Linked to Stroke RiskDocument4 paginiHypertension Linked to Stroke RisklidawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Interesting Case of "Trigeminal Tachycardia"Document3 paginiAn Interesting Case of "Trigeminal Tachycardia"ABDULLAH ALHASANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amls Pretest BlsDocument13 paginiAmls Pretest BlsrkopecmdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mtle - Hema 1Document50 paginiMtle - Hema 1Leogene Earl FranciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Causes and Treatment of Enlarged HeartDocument23 paginiCauses and Treatment of Enlarged HeartMaulana AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patient Data From 1Document18 paginiPatient Data From 1Lalit Surykant ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nocturnal &diurnal GapfillDocument6 paginiNocturnal &diurnal GapfillSam EspinosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atif Afzal Quick HintsDocument54 paginiAtif Afzal Quick Hintssara khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NUR3111 Past Paper Care PlanDocument14 paginiNUR3111 Past Paper Care PlanliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Human Biology 15th Edition Sylvia Mader and Michael WindelspechtDocument21 paginiTest Bank For Human Biology 15th Edition Sylvia Mader and Michael Windelspechtjohnsmithysekamonit100% (22)
- History Assessment Video NCPDocument10 paginiHistory Assessment Video NCPamal abdulrahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CARDIO Intensive CareDocument6 paginiCARDIO Intensive CareDianne Erika MeguinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topics For Oral Exam Mug 2023Document3 paginiTopics For Oral Exam Mug 2023xxlolaxxgachaÎncă nu există evaluări