Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
NCP For Acute Coronary Syndrome
Încărcat de
sarahtotDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NCP For Acute Coronary Syndrome
Încărcat de
sarahtotDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
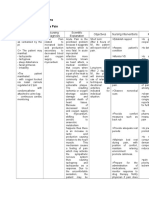
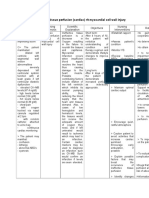
NCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome Assessment Background Diagnosis Knowledge Subjective: atherosclerosis Acute pain Sumasakit related
to ang dibdib myocardial ko , as ischemia ischemia verbalized as by the evidenced patient. angina by severe pectoris chest pain. Objective: Severe chest pain Pain scale 10/10
Planning Within 2 hours of nursing intervention the patient will experience decrease level of pain.
Interventions -Evaluate chest pain (ex. intensity, location, radiation, duration, and precipitating and alleviating factors) in order to accurately evaluate, treat, and prevent further ischemia. -Monitor effectiveness of oxygen therapy to increase oxygenation of myocardial tissue and prevent further ischemia. -Administer medications to relieve/prevent pain and ischemia to decrease anxiety and cardiac workload. -Obtain 12lead ECG during pain episode to help differentiate angina from extension of
Evaluations After 2 hours of nursing intervention the patient experienced a decreased level of pain.
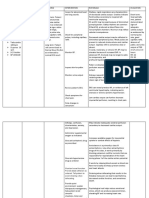
MI or pericarditis. -Monitor cardiac rhythm and rate and trends in blood pressure and hemodynamic parameters (e.g., central venous pressure and pulmonary artery wedge pressure) to monitor for hypotension and bradycardia, which may lead to hypoperfusion. Assessment Subjective: Nahihilo ako, as verbalized by the patient. Objective: PR - 85 RR - 30 BP 160/100 Background Diagnosis Knowledge Atherosclerosis Ineffective tissue oerfussion ischemia (cardiac) related to potential angina pectoris pulmonary congestion as decrease manifested blood flow by dyspnea. Planning Within 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient will be able to maintain stable vital signs. Intervention -Monitor vital signs frequently to determine baseline and ongoing changes. -Monitor for cardiac dysrhythmias, including disturbances of both rhythm and conduction, to identify and treat signi cant dysrhythmias. -Monitor respiratory evaluation After 8 hours of nursing intervention the patient had maintain stable vital signs.
status for symptoms of heart failure to maintain appropriate levels of oxygenation and observe for signs of pulmonary edema. -Monitor uid balance (e.g., intake/output, daily weight) to monitor renal perfusion and observe for uid retention. -Arrange exercise and rest periods to avoid fatigue and decrease the oxygen demand on myocardium. -instruct patient to eat low fat and low salt diet.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- NCP CADDocument31 paginiNCP CADjan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Pulmonary EmbolismDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan - Pulmonary EmbolismPui_Yee_Siow_6303100% (10)
- Decrease Cardiac OutputDocument6 paginiDecrease Cardiac OutputGerardeanne ReposarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationsweethoney220% (1)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 01Document5 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 01AgronaSlaughter0% (1)
- NCPDocument4 paginiNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 03Document6 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 03AgronaSlaughterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care Plan Unstable AnginaDocument4 paginiCare Plan Unstable Anginaالغزال الذهبي50% (6)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsDocument3 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsAjay SupanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAMPLE NCP For Angina PectorisDocument3 paginiSAMPLE NCP For Angina Pectorisseanne_may100% (4)
- NCP For Mi PainDocument2 paginiNCP For Mi PainKahMallariÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionDocument16 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionFreisanChenMandumotan100% (1)
- Myocarditis NCP 2Document8 paginiMyocarditis NCP 2astro_aaron117375% (4)
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansDocument21 pagini"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- NCP RHDDocument7 paginiNCP RHDHenry Roque Tagalag80% (5)
- NCP AnginaDocument3 paginiNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- CAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiCAD NCP Decreased Cardiac OutputLeizel Apolonio100% (3)
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output NCPbaba69baba100% (1)
- NCP Myocardial InfarctionDocument1 paginăNCP Myocardial InfarctionjamieboyRN88% (8)
- NCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYDocument4 paginiNCP Impaired Gas Exhange CHEST INJURYMa. Elaine Carla Tating100% (2)
- NCP For SVTDocument6 paginiNCP For SVTRen VillenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Afib NCPDocument3 paginiAfib NCPGen RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To CardiomyopathyDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output Related To Decreased Myocardial Contractility Secondary To Cardiomyopathywen_pil75% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionDocument7 paginiNursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionjamieboyRN88% (8)
- NCP Hypertension 2Document3 paginiNCP Hypertension 2Roseben Somido50% (2)
- NCP For AnginaDocument5 paginiNCP For Anginacarizza_bernas100% (1)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputEdrianne J.100% (2)
- NCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionDocument3 paginiNCP Inffective Tissue PerfusionPaul Cubacub0% (1)
- NCP Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 paginiNCP Cardiogenic ShockTrixia Camporedondo100% (1)
- Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument3 paginiMyocardial Infarction NCPlapistolero33% (3)
- Acute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02Document6 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome NCP 02AgronaSlaughterÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For CTTDocument1 paginăNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- NCP AfDocument3 paginiNCP AfAngelica Mercado SirotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care Planjudssalangsang86% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan - Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan - Myocardial Infarctionderic80% (10)
- NCP-Esophageal Varices Pleural EffusionDocument6 paginiNCP-Esophageal Varices Pleural Effusiontinatin98933% (3)
- NCP - TBDocument2 paginiNCP - TBPahw BaluisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output NCPmicah1318100% (2)
- Pulmonary HypertensionDocument10 paginiPulmonary HypertensionqingwenÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionDocument13 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial Infarctionbanyenye2593% (14)
- Angina Pectoris Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăAngina Pectoris Nursing Care PlanjamieboyRN86% (7)
- Activity Intolerance Related To AmeniaDocument1 paginăActivity Intolerance Related To AmeniaSiti Syazana Mohamad MogriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument2 paginiImpaired Gas ExchangeHanya Bint PotawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Acute Pain Related Myocardial IschemiaDocument2 paginiNCP - Acute Pain Related Myocardial IschemiaKian HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationDocument2 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention EvaluationCharissa Magistrado De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiNursing Care PlanJoy Callo100% (2)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiDecreased Cardiac OutputRizalyn QuindipanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For StrokeDocument4 paginiNCP For StrokeJASON OGALESCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDocument5 paginiNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- RNPIDEA-Coronary Artery Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument8 paginiRNPIDEA-Coronary Artery Disease Nursing Care PlanAngie MandeoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Management of Altered Acute Biologic CrisisDocument7 paginiPrinciples of Management of Altered Acute Biologic CrisisSam Abduhassan SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 5 PresentationDocument24 paginiGroup 5 PresentationHera Pamela Buelis BatoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial InfarctionDocument44 paginiCoronary Heart Disease: Angina Pectoris Myocardial Infarctionalejandrino_leoaugustoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac ComplicationDocument12 paginiCardiac ComplicationResa ShotsÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP HCVD (Final)Document8 paginiNCP HCVD (Final)khrizaleeh100% (1)
- Care Plan Designed For Mr. SalmanDocument2 paginiCare Plan Designed For Mr. SalmanHouda HayekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Failure Care PlanDocument5 paginiHeart Failure Care PlanJustin StuartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)Document20 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)Benjiber R. SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiogenic ShockDocument3 paginiCardiogenic Shockmerin sunilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course in The WardDocument3 paginiCourse in The WardsarahtotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument7 paginiDrug StudysarahtotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument7 paginiDrug StudysarahtotÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCCC CCC C C C C!C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCDocument1 paginăCCCC CCC C C C C!C: CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCsarahtotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Equipment Manufacturing Business Plan ExampleDocument36 paginiMedical Equipment Manufacturing Business Plan ExampleSofia Shanli San JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer Diagnosis: 1. RhythmDocument2 paginiAnswer Diagnosis: 1. RhythmSuggula Vamsi KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Vital SignsDocument5 paginiThe Vital SignsKhalid EppingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Aquatic Therapy 101 RevampedDocument39 pagini1 Aquatic Therapy 101 RevampedJaesonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition Moore Agur DalleyDocument19 paginiTest Bank Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th Edition Moore Agur DalleyMichael Burger100% (34)
- Case Study EssayDocument19 paginiCase Study EssaylecharmedenuitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q1 ExamDocument3 paginiQ1 ExamGlenda AstodilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- HypertensionDocument8 paginiHypertensionMario MorinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH11 Patho Benitado 405 - 407Document17 paginiCH11 Patho Benitado 405 - 407Joy VelascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECG Basics: Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument34 paginiECG Basics: Acute Myocardial InfarctionnengninisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Onuaguluchi1996 1Document10 paginiOnuaguluchi1996 1IkaSugihartatikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Pacing and ICD ReviewDocument21 paginiCardiac Pacing and ICD ReviewAlexander Edo Tondas100% (1)
- Rat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyDocument10 paginiRat Dissection Protocol - Intro BiologyValar Mathei PadmanadhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Us-Bing-B SMPDocument8 paginiUs-Bing-B SMPZulfan SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EKG Rest Versus ExerciseDocument9 paginiEKG Rest Versus Exercisedesiree2391744Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 The Importance of Having A Transport System in Some Multicellular OrganismsDocument27 pagini1.1 The Importance of Having A Transport System in Some Multicellular Organismsdania0% (1)
- Emergency Medicine 1st Edition - DR - Waleed (101 Papers)Document101 paginiEmergency Medicine 1st Edition - DR - Waleed (101 Papers)Mokhtar Moh100% (1)
- Septum Formation in The VentriclesDocument43 paginiSeptum Formation in The VentriclesAhsan IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- O IntegratedscienceDocument36 paginiO IntegratedscienceFarai FaustosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitral Stenosis PDFDocument3 paginiMitral Stenosis PDFshanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual EAV: The Electro-Dermal Screening TestDocument21 paginiVirtual EAV: The Electro-Dermal Screening Testmich100% (1)
- Heart Rate Design PracticalDocument13 paginiHeart Rate Design PracticalMary Elizabeth ValmoresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 20 - Cardiac EmergenciesDocument96 paginiChapter 20 - Cardiac EmergenciesAmit KlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Ana & DxticsDocument3 paginiCardiac Ana & Dxticsjames garciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Prime Post Test 1Document24 paginiMS Prime Post Test 1quidditch07Încă nu există evaluări
- IPD - KardiologiDocument124 paginiIPD - KardiologiAnis BonitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of A BiosensorDocument7 paginiParts of A BiosensorSubin TħomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waktu Tunggu Hasil Lab MutuDocument42 paginiWaktu Tunggu Hasil Lab MutuDwinoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengobatan Alternatif Untuk AritmiaDocument26 paginiPengobatan Alternatif Untuk AritmiaFerina Nadya PratamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cvs Mbbs PDFDocument57 paginiCvs Mbbs PDFAbhishekÎncă nu există evaluări