Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Nursing Care Plan TB Meningitis
Încărcat de
deric74%(19)74% au considerat acest document util (19 voturi)
19K vizualizări2 pagini1. The client presented with headache, restlessness, and changes in motor and sensory responses with an elevated temperature of 37.7°C, pulse of 50, respiration of 12, and blood pressure of 130/90.
2. The nursing diagnosis was risk for ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to cerebral edema, with a secondary diagnosis of tuberculous mening
Descriere originală:
A free sample nursing care plan (ncp) for TB Meningitis.
Titlu original
NursingCrib.com Nursing Care Plan TB Meningitis
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest document1. The client presented with headache, restlessness, and changes in motor and sensory responses with an elevated temperature of 37.7°C, pulse of 50, respiration of 12, and blood pressure of 130/90.
2. The nursing diagnosis was risk for ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to cerebral edema, with a secondary diagnosis of tuberculous mening
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
74%(19)74% au considerat acest document util (19 voturi)
19K vizualizări2 paginiNursing Care Plan TB Meningitis
Încărcat de
deric1. The client presented with headache, restlessness, and changes in motor and sensory responses with an elevated temperature of 37.7°C, pulse of 50, respiration of 12, and blood pressure of 130/90.
2. The nursing diagnosis was risk for ineffective cerebral tissue perfusion related to cerebral edema, with a secondary diagnosis of tuberculous mening
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
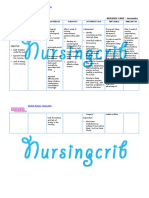
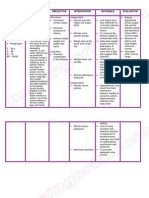
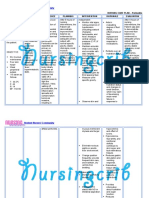
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS INFERENCE PLANNING INTERVENTION RATIONALE EVALUATION
Independent:
Subjective: • Risk for • Tuberculous • After 4 hrs. • Maintain head or • Turning head to • After 4 hrs.
ineffective meningitis is the Of nursing neck in midline or one side Of nursing
“Masakit ang ulo cerebral most severe form interventions, neutral position, compresses the intervention
ko.” as verbalized tissue of tuberculosis. It the client will support with small jugular veins s, the client
by the client. perfusion causes severe demonstrate towel rolls and and inhibits was able to
related neurologic deficits stable vital pillows. cerebral venous demonstrate
Objective: cerebral or death in more signs and drainage, stable vital
edema. than half of cases. absence of thereby signs and
• Restlessness. Tuberculois signs of increasing absence of
meningitis begins intracranial intracranial signs of
• Changes in insidiously with a pressure. pressure. intracranial
motor or gradual fluctuating • Provide rest • Continual pressure.
sensory fever, fatigue, periods between activity can
responses. weight loss, care activities and increase
behavior changes, limit duration of intracranial
• V/S taken as headache, and procedures. pressure.
follows: vomiting. This • Decrease • Provides
early phase is extraneous calming effect,
T: 37.7 followed by stimuli and reduces
P: 50 neurologic deficits, provide comfort adverse
R: 12 loss of measures like physiological
Bp: 130/90 consciousness, or back massage, response and
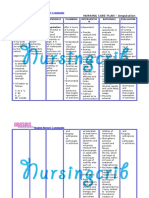
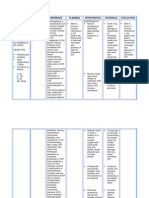
convulsions. A quiet promotes rest
dense gelatinous environment, soft to maintain or
exudate voice. lower
(outpouring) forms intracranial
and envelops the pressure.
brain arteries and • Help patient avoid • These activities
cranial nerves. It or limit coughing, increase
creates a vomiting, thoracic and
bottleneck in the straining at stool, intra-abdominal
flow of the bearing down as pressure which
cerebrospinal fluid, possible. can increase
which leads to intracranial
hydrocephalus. pressure.
• Observe for • Seizure can
seizure activity occur as result
and protect of cerebral
patient from irritation,
injury. hypoxia or
increase
intracranial
pressure.
Collaborative:
• Restrict fluid • Fluid restriction
intake as may be needed
indicated. to reduce
cerebral
edema.
• Administer • Reduces
supplemental hypoxemia.
oxygen as
indicated.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia NCPderic79% (133)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument8 paginiNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic87% (15)
- Nursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Ineffective Infant Feeding Pattern NCPderic71% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan For Risk For Aspiration NCPderic100% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Spiritual Well Being NCPderic83% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan For Post Trauma NCPderic82% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Peptic Ulcer NCPderic85% (46)
- Nursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPDocument14 paginiNursing Care Plan For Liver Cirrhosis NCPderic92% (12)
- Nursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Seizure NCPderic88% (40)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Rabies NCPderic100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Insomnia NCPderic83% (24)
- Nursing Care Plan (Bell's Palsy)Document3 paginiNursing Care Plan (Bell's Palsy)Yessamin Paith Roderos100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Upper Gastrointestinal Bleeding NCPderic79% (14)
- Nursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Insufficient Breastmilk NCPderic100% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Multiple Sclerosis NCPderic88% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan For AmputationDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Amputationderic80% (25)
- Nursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For AIDS/HIVderic81% (16)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Sleep NCPderic100% (2)
- Central Nervous System Nursing Care PlanDocument11 paginiCentral Nervous System Nursing Care PlanUday Kumar100% (1)
- NCP PreeclampsiaDocument2 paginiNCP Preeclampsiasteffi100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For HemodialysisDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Hemodialysisderic80% (20)
- Nursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Risk For Compromised Human Dignity NCPderic100% (2)
- Thinking Skills and Problem Solving Oum Jan 2020Document15 paginiThinking Skills and Problem Solving Oum Jan 2020Shoba ManoharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural EffusionDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan For A Patient With Pleural Effusionmac042250% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan of MeningitisDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan of MeningitisŦỏṯặ Łaẕỗzą100% (7)
- NCP TbiDocument4 paginiNCP TbiWyen CabatbatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperthyroidism N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 paginăHyperthyroidism N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- NCP. FistulectomyDocument2 paginiNCP. Fistulectomymitchelley80% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan For TonsillitisDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For TonsillitisEden Cruz50% (6)
- Intussusception Nursing Care PlanDocument7 paginiIntussusception Nursing Care PlanElli SuñgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Tissue PerfusionDocument2 paginiNCP Tissue PerfusionNiña Montejo Ealdama100% (1)
- NCP AnginaDocument3 paginiNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Smoke Poisoning NCPderic100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan For Rape Trauma Syndrome NCPderic100% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Neonatal Sepsis NCPderic67% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Interrupted Breastfeeding NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Disturbed Sleep Pattern NCPderic67% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Pedia TB MeningitisDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Pedia TB Meningitisderic100% (10)
- Bronchopneumonia Care PlanDocument6 paginiBronchopneumonia Care PlanAbhijit Soundade0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan NephritisDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Nephritisderic82% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan: General: Goals Met GenreralRomzy BasañesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan 1Document4 paginiNursing Care Plan 1Johndelle Banlasan Hernan100% (1)
- Furosemid Citicoline Clexane, LevofloxacinDocument9 paginiFurosemid Citicoline Clexane, Levofloxacincotyboy50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationAbdallah AlasalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge Deficit - RegorDocument3 paginiKnowledge Deficit - RegorAdrian MallarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiNursing Care PlanJoshua Pascasio100% (1)
- TB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsDocument1 paginăTB, Ineffectivbe Breathing PatternsnikkilyceeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP For Nephrotic SyndromeDocument2 paginiNCP For Nephrotic SyndromeLee Jenny100% (5)
- To Decrease Temperature by Means Through Evaporation and ConductionDocument11 paginiTo Decrease Temperature by Means Through Evaporation and Conductioniaekawa100% (6)
- CP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanDocument7 paginiCP Intestinal Obstruction Nursing Care PlanShiella Heart MalanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Pre EclampsiaDocument2 paginiNCP Pre EclampsiaFarrah Grace Birowa0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan: Risk For Ineffective Airway Clearance Related To Bleeding From Tonsillectomy Short TermErika Danalle ArceoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 paginiNursing Care PlanCris Solis33% (3)
- Stroke Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăStroke Nursing Care PlanTracy PearlÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP MeningitisDocument6 paginiNCP MeningitisSkyerex67% (3)
- NCP HydrocephalusDocument6 paginiNCP HydrocephalusgopscharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ovarian Cancer NCPDocument7 paginiOvarian Cancer NCPAsterlyn Coniendo100% (1)
- Gcic NCP Seizure PICUOSMUNDocument2 paginiGcic NCP Seizure PICUOSMUNhanyaklein100% (3)
- Hypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiHypothyroidism Nursing Care PlanRizza Mae MaglacionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsDocument3 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale EvaluationsAjay SupanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disturbed Visual Sensory Perception Related: Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiDisturbed Visual Sensory Perception Related: Nursing Care PlanMae Therese B. MAGNOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 paginiNursing Care Plankreny1050% (2)
- Role Av Aids in Clinical TeachingDocument16 paginiRole Av Aids in Clinical Teachingtankmp100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For HypoglycemiaPuteri AzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăHyperthermia Pneumonia Nursing Care Planjustin_saneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Needle Stick Injury Among The Staff NursesDocument3 paginiEffectiveness of Planned Teaching Programme On Knowledge Regarding Needle Stick Injury Among The Staff NursesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan HyperthermiaDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan Hyperthermiasamanthabox50% (2)
- NCP For LeukemiaDocument2 paginiNCP For Leukemiaخالد الغامديÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Bronchiolitis 1Document2 paginiChild Bronchiolitis 1sarooah1994100% (2)
- MYELOMENINGOCELEDocument2 paginiMYELOMENINGOCELECass Bartolome50% (2)
- NCP LaminectomyDocument4 paginiNCP LaminectomyMark Zedrix MediarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan SeizureDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Seizuretimie_reyes100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Patiients With MeningitisDocument35 paginiNursing Care Plan For Patiients With Meningitisixa_morales67% (6)
- NCP FeverDocument2 paginiNCP FeverMary Joyce LimoicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument2 paginiAssessment Diagnisis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDanica Kate GalleonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etiology of TonsillitisDocument15 paginiEtiology of TonsillitisRendy Candra100% (1)
- Aaa Adolescent NCP FinalDocument1 paginăAaa Adolescent NCP FinalJhaenelle Allyson TabiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- HydrocephalusDocument3 paginiHydrocephalusMae Arra Lecobu-anÎncă nu există evaluări
- NS3 Ncp-FdarDocument5 paginiNS3 Ncp-FdarArdiene Shallouvette GamosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP NeuroDocument20 paginiNCP NeuroNica Gaborne Navarro100% (3)
- Angina PectorisDocument22 paginiAngina Pectorismacoy08Încă nu există evaluări
- Hydrocephalus NCP - DayanghirangDocument2 paginiHydrocephalus NCP - DayanghirangEdnar DayanghirangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Pain!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Document3 paginiAcute Pain!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!ahz_kerian2Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument2 paginiNCP For Pregnancy Induced HypertensionTsu Wei Chua0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For GlaucomaDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Glaucomaderic79% (28)
- Nursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide PoisoningDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Carbon Monoxide Poisoningderic73% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPDocument4 paginiNursing Care Plan For Readiness For Enhanced Hope NCPderic100% (6)
- Nursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Peritonitis NCPderic86% (7)
- Nursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Pedia TB Meningitis NCPderic100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Overflow Urinary Incontinence NCPderic71% (7)
- TITLE: Prevention of Diarrhea: A Health Teaching PlanDocument3 paginiTITLE: Prevention of Diarrhea: A Health Teaching PlanMariel Gamalo0% (1)
- Diagnosis Banding I. BronkopneumoniaDocument20 paginiDiagnosis Banding I. BronkopneumoniaHijriah SyafitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade VII Feeling and Health ProblemsDocument4 paginiGrade VII Feeling and Health ProblemspridarikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Glomerulonephritis: Adlyanna VelascoDocument14 paginiAcute Glomerulonephritis: Adlyanna VelascoShaheed SorathiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hiv Persuasion SpeechDocument2 paginiHiv Persuasion SpeechMaxine De CastroÎncă nu există evaluări
- AFP Orientation Presentation 2022Document33 paginiAFP Orientation Presentation 2022thqhospital pasrurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xenex Effectiveness Summary Studies PDFDocument4 paginiXenex Effectiveness Summary Studies PDFREDENLAKE LTDÎncă nu există evaluări
- LGS InfographicDocument1 paginăLGS InfographicCourtney CampÎncă nu există evaluări
- History Form - Ahmad Alalmai 2Document2 paginiHistory Form - Ahmad Alalmai 2heydydÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quadrivalent Inactivated Influenza Vaccine (Vaxigriptetra™) : Expert Review of VaccinesDocument41 paginiQuadrivalent Inactivated Influenza Vaccine (Vaxigriptetra™) : Expert Review of VaccinesMarco LealiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modular Distance Learning in The New Normal Education Amidst Covid-19Document4 paginiModular Distance Learning in The New Normal Education Amidst Covid-19Michael Vincent De VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of DiseasesDocument7 paginiList of DiseasesLoveleen SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap 18 Reading WorksheetDocument3 paginiChap 18 Reading WorksheetSarahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Herpes PresentationDocument10 paginiHerpes PresentationOkafor AugustineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colon CancerDocument7 paginiColon CancerAdrian Paulo CastivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Write A Dialogue of at Least 150 Words Between A Nurse and A Patient Suffering of Earache/ An Eye ConditionDocument1 paginăWrite A Dialogue of at Least 150 Words Between A Nurse and A Patient Suffering of Earache/ An Eye ConditionLaurusAdiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ver E-Hpv-R1Document2 paginiVer E-Hpv-R1api-309082881Încă nu există evaluări
- Gas GangreneDocument6 paginiGas GangreneIwan AchmadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RubellaDocument13 paginiRubellaaminceloÎncă nu există evaluări
- (PSYCH3) 5.4 The Person With Chronic Mental IllnessDocument3 pagini(PSYCH3) 5.4 The Person With Chronic Mental IllnessDrina PaglinawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Altered Sensorium and Care of Unconscious PatientsDocument17 paginiAltered Sensorium and Care of Unconscious PatientsChhabilal BastolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hepatitis A Treatment in Pune - Kaizen Gastro CareDocument4 paginiHepatitis A Treatment in Pune - Kaizen Gastro CareKaizen Gastro CareÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCDSO Medical History QuestionnaireDocument2 paginiRCDSO Medical History QuestionnaireFusionIntenseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infectious or Communicable DiseasesDocument2 paginiInfectious or Communicable DiseasesДария КоваленкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maleria PDFDocument4 paginiMaleria PDFPravesh VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Artikel Bahasa Inggris Depresi 2Document6 paginiArtikel Bahasa Inggris Depresi 2Serli SafitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ssi (Surgical Site Infection)Document31 paginiSsi (Surgical Site Infection)tugam umarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 112 - Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD)Document4 paginiNCM 112 - Sexually Transmitted Disease (STD)Cailah Sofia SelausoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter One: 1.4.1 General ObjectiveDocument3 paginiChapter One: 1.4.1 General ObjectivejohnÎncă nu există evaluări