Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Solid Geometry Form 2
Încărcat de
graciezaynDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Solid Geometry Form 2
Încărcat de
graciezaynDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MATHEMATICS - FORM 2 SOLID GEOMETRY II
GEOMETRIC PROPERTIES OF PRISMS, PYRAMIDS, CYLINDERS, CONES AND SPHERES (A) Stating the geometric properties of prisms, pyramids, cylinders, cones and spheres 1. Prisms (a) A prism is a solid with two congruent, parallel bases which are polygons. The other faces called lateral faces are in the shape of parallelograms.
(b) A prism has a uniform cross section in the shape of a polygon. (A section if the cross sections have the same shape and area as the end faces of the solid.)
(c) A right prism is a prism in which the bases of the prism are perpendicular to the bases of the prism are perpendicular to the prism are perpendicular to the lateral faces.
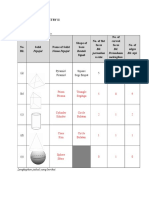
(d) The type of prism is named after the shape of its base. (i) (ii)
Triangular prism (iii) (iv)
Rectangular prism
Pentagonal prism (e) Example : A triangular building block
Hexagonal prism
2. Pyramid (a) A pyramid is a solid with a flat base in the shape of a polygon, and triangular faces that converge at a vertex. (b) A right pyramid has its vertex directly above the centre of its base.
(c) The type of pyramid is named after the shape of its base. (i) (ii)
Triangular pyramid (iii) (iv)
Square pyramid
Rectangular pyramid Hexagonal pyramid (d) Example : Pyramid of Giza, Egypt. 3. Cylinder (a) A cylinder is a solid with two parallel congruent circular bases and a curved surface.
(b) Example: A milk tin, a plastic pipe
4. Cone (a) A cone is a solid with a circular base, a curved surface and a vertex.
(b) Example: An ice cream cone, a party hat 5. Sphere (a) A sphere is a solid whereby all its points on the surface are at the same distance from the centre.
(b) Example: A football, a marble 6. The geometric solids can be categorized into three groups. (a) Solids with flat surfaces only. Example: Cubes, cuboids, prisms and pyramids (b) Solids with curved surfaces only. Example: Spheres (c) Solids with both flat and curved surfaces Example: Cones and cylinders NETS (A) Drawing Nets Net of a geometric solid is the shape in a plane that is obtained by opening up and flattening out the faces of the geometric solid. Net of a geometric solid may have many different shapes.
Draw a net for each of the following geometric solids. (a) (b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(B) Stating the Types and Constructing Models of Solid Given Their Nets
The figure shows the net of a geometric solid. (a) State the type of solid formed from the net. (b) Copy the net according to the measurements given and then construct a model of the solid.
(a) cuboid (b)
(a) Name the solid which can be formed from the net shown. (b) Construct a model of the solid according to the measurements given.
(a) A right prism (b)
(a) State the type of solid that has the net shown in the figure. (b) Construct a model of the solid according to the actual measurement given.
(a) A right cylinder (b)
SURFACE AREA (A) Stating the surface area of prisms, pyramids, cylinders and cones The surface area of a solid is the total area of all the faces of the solid. Therefore, the surface area of a solid can be calculated from its net. (a) Prism (i) Triangular prism
Surface area of a triangular prism = 2 x Area of cross section + Total area of lateral faces = 2 (Area of triangle) + Total area of 3 rectangles (ii) Hexagonal prism
Surface area of a hexagonal prism = 2 x Area of cross section + Total area of lateral faces = 2 (Area of hexagon) + total area of 6 rectangles
(b) Pyramid (i) Triangular pyramid
Surface area of a triangular pyramid = Area of base + Total area of 3 triangular faces = Area of triangular base + Total area of 3 triangles (ii) Rectangular pyramid
Surface area of a rectangular pyramid = Area of base + Total area of 4 triangular faces = Area of rectangular base + Total area of 4 triangles (c) Cylinder
(d) Cone
(B) Finding the surface area of prisms, pyramids, cylinders and cones
Calculate the surface area for each of the following.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
(e)
(f)
(C) Finding the surface area of spheres using the standard formula The surface area of a sphere can be determined by using a formula.
The radius of the earth is approximately 6 400 km. Find the surface area of the earth.
(D) Finding the dimensions of a solid given its surface area
(E) Solving problems involving surface area
The diagram shows a solid consisting of a cuboid and a right cylinder with one end of the cylinder resting on top of the cuboid. The cylinder has a diameter of 28 cm and a height of 10 cm. Determine the total surface area of the solid.
The diagram shows a closed cylindrical tank. Draw the net for the cylindrical tank.
copyright 2005 Kenshido International Sdn Bhd
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- MATHEMATICS - CIRCLES FORM 2Document22 paginiMATHEMATICS - CIRCLES FORM 2graciezayn100% (6)
- Maths Form 2 Chapter 1Document19 paginiMaths Form 2 Chapter 1Suelly Sabri100% (1)
- KSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 Polygons 4.2.4Document2 paginiKSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 Polygons 4.2.4KSSM TSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circular Measure PDFDocument6 paginiCircular Measure PDFAnna LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- KSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 PolygonsDocument2 paginiKSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 PolygonsKSSM TSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Form 3Document24 paginiMathematics Form 3Amal Sufiah82% (33)
- Circular Measure CalculationsDocument17 paginiCircular Measure CalculationsRahman AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polygons II (PMR Practice)Document5 paginiPolygons II (PMR Practice)dikwanz100% (12)
- Mathematics Form 1 Chapter 6 & 7 QuizDocument1 paginăMathematics Form 1 Chapter 6 & 7 Quizlaukhaisiang67% (3)
- Math Form 1 Paper 2Document9 paginiMath Form 1 Paper 2adelymohd100% (1)
- Exercise Chapter 1 Form 4Document15 paginiExercise Chapter 1 Form 4Siti Hajar Johari100% (4)
- Answers Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)Document2 paginiAnswers Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)compeil100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Factorisation and Algebraic FractionDocument7 paginiChapter 2 Factorisation and Algebraic FractionCiern Tan29% (7)
- Math MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)Document1 paginăMath MF2 Chapter 4 (Linear Equations I)compeil80% (5)
- Modul 5min Mathematics Form 2Document40 paginiModul 5min Mathematics Form 2yattie17607100% (1)
- Find Circle Values Form 3 Math Chapter 3Document5 paginiFind Circle Values Form 3 Math Chapter 3Afida HamsaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 3 - Chapter 15-TrigonometryDocument15 paginiForm 3 - Chapter 15-TrigonometryIlyana Ghazali0% (1)
- Lines & Angles II (PMR Practice)Document4 paginiLines & Angles II (PMR Practice)dikwanz89% (18)
- Past SPM Maths Questions on Trigonometric Equations (2003-2009Document5 paginiPast SPM Maths Questions on Trigonometric Equations (2003-2009Siti Aizatie Ramli0% (1)
- Mid Year Mathematics Form 2Document7 paginiMid Year Mathematics Form 2wahee88Încă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Form 2 - Chapter 7-Stu Ver PDFDocument30 paginiMathematics Form 2 - Chapter 7-Stu Ver PDFKoh Shi Qi50% (2)
- Chapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeDocument12 paginiChapter 4 Algebraic FormulaeCik Yana50% (2)
- KSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 PolygonsDocument6 paginiKSSM Mathematics Form 2 Chapter 4 PolygonsKSSM TSE67% (3)
- SPM Questions Transformations IIIDocument6 paginiSPM Questions Transformations IIIjuriah binti ibrahim0% (1)
- Form 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1-7Document3 paginiForm 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 1-7Kelvin100% (2)
- Maths F3 KSSM 2019Document132 paginiMaths F3 KSSM 2019蔡卷勋100% (5)
- Form 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 8Document8 paginiForm 2 Mathematics Notes +exercise by Kelvin - Chapter 8Kelvin0% (1)
- Form 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureDocument9 paginiForm 4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 8 Circular MeasureManisha Sekaran Muniandy80% (5)
- Chapter 5 5.1.5.2 WorksheetDocument6 paginiChapter 5 5.1.5.2 WorksheetKSSM TSEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Progression Past YearDocument2 paginiProgression Past YearMrJay SuperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topical Test Chapter 1 Math Form 1 Paper 2Document1 paginăTopical Test Chapter 1 Math Form 1 Paper 2syukrie3100% (2)
- Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 1 SKEMA JAWAPANDocument4 paginiMatematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 1 SKEMA JAWAPANrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Force and Motion EquationsDocument13 paginiForce and Motion EquationsniknadhiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math MF2 Chapter 9 (Loci in Two Dimensions)Document6 paginiMath MF2 Chapter 9 (Loci in Two Dimensions)compeil100% (1)
- Science Form 1 - Chapter 1.2 by KelvinDocument22 paginiScience Form 1 - Chapter 1.2 by KelvinKelvin50% (2)
- Chapter 13 Probability: Form 2 KSSM MathematicsDocument47 paginiChapter 13 Probability: Form 2 KSSM MathematicsJenny bean100% (1)
- Science Notes Form 1Document20 paginiScience Notes Form 1Farah Asnida0% (2)
- Form 3 Maths Lesson Plan 2021Document6 paginiForm 3 Maths Lesson Plan 2021Tcer ReenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionDocument7 paginiForm 3 Chapter 4 ReproductionWan Shuhaimi Wan Ali100% (1)
- Form 3 Chapter 9Document3 paginiForm 3 Chapter 9naza9775100% (5)
- Quiz: CIRCLE (Form 2)Document4 paginiQuiz: CIRCLE (Form 2)raudatunnur87Încă nu există evaluări
- Review Exercise: (Form 2) Chapter 5 - Ratios, Rates & Proportions IDocument3 paginiReview Exercise: (Form 2) Chapter 5 - Ratios, Rates & Proportions IZulfitri Muhamad100% (6)
- Practice Makes Perfect 7 (Algebra)Document8 paginiPractice Makes Perfect 7 (Algebra)dikwanzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer All The Questions. (A) Diagram 1 (A) Shows A Number LineDocument16 paginiAnswer All The Questions. (A) Diagram 1 (A) Shows A Number LineRosmah Abdullah89% (19)
- Soalan Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 1Document2 paginiSoalan Matematik Tingkatan 1 Kertas 1afiq8586Încă nu există evaluări
- Form 2 - Chapter 13Document8 paginiForm 2 - Chapter 13Adibah AliasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 3 Chapter 3Document7 paginiForm 3 Chapter 3naza977582% (11)
- Solid Geometry 2 AnswerDocument15 paginiSolid Geometry 2 AnswerHazri Mohd HamzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add Math Mid Year Exam Form 4 Paper 1Document12 paginiAdd Math Mid Year Exam Form 4 Paper 1Rozaidi J-daiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid Geometry Form 2Document18 paginiSolid Geometry Form 2Nurin WaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 15. Visualising Solid ShapesDocument19 paginiChapter 15. Visualising Solid ShapesVRENIE JOY PEDROÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Grade Worksheets Shapes Worksheet 1Document9 pagini3rd Grade Worksheets Shapes Worksheet 1juwita ayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Term s1 MathematicsDocument62 pagini3rd Term s1 MathematicsAdelowo DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Surface Area of SolidsDocument14 paginiThe Surface Area of Solidsyarinaosu100% (1)
- 11 AreaDocument4 pagini11 AreaMohanlal PereraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Third Term SS 1 Mathematics Lesson Note 1Document3 paginiThird Term SS 1 Mathematics Lesson Note 1DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- A (C) M Radius Circle Circumscribing A Triangle With Sides (A) M, (B) M and X (M) - Find XDocument15 paginiA (C) M Radius Circle Circumscribing A Triangle With Sides (A) M, (B) M and X (M) - Find XLee Warren IntoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 9 Mathematics Worksheet - Surface Areas and VolumesDocument4 paginiCBSE Class 9 Mathematics Worksheet - Surface Areas and VolumesvenusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 Maths 12Document17 paginiClass 10 Maths 12Mallipudi SphoorthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sectional Views and Surface Development MCQsDocument8 paginiSectional Views and Surface Development MCQsraja30g100% (1)
- SCIENCE Form 3-ExcretionDocument11 paginiSCIENCE Form 3-ExcretiongraciezaynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Document4 paginiScience Form 3 Chapter 1 - Respiration (Notes)Autumn JJ40% (5)
- Directed Number Form 2Document19 paginiDirected Number Form 2graciezaynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths FractionDocument39 paginiMaths FractionSherlock Wesley ConanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordinates Form 2Document17 paginiCoordinates Form 2graciezayn100% (1)
- Polygons Form 1Document38 paginiPolygons Form 1graciezaynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Percentage Form 1Document22 paginiPercentage Form 1graciezaynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths DecimalsDocument38 paginiMaths DecimalsSherlock Wesley ConanÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATHEMATICS - UNDERSTANDING INTEGERSDocument17 paginiMATHEMATICS - UNDERSTANDING INTEGERSgraciezayn50% (2)
- Mathematics F1-Algebraic ExpressionsDocument5 paginiMathematics F1-Algebraic ExpressionsgraciezaynÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Radar and Its FunctionDocument3 paginiWhat Is Radar and Its FunctionJean Maya DiscayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 4 - Chemical Kinetics 4b - Half LifeDocument20 paginiTopic 4 - Chemical Kinetics 4b - Half LifeJoshua LaBordeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Communication & Computer NetworksDocument32 paginiData Communication & Computer NetworksMuhammad NadeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Fourier and Wavelet Transforms: 2.1. Time and Frequency Representation of SignalsDocument25 pagini2 Fourier and Wavelet Transforms: 2.1. Time and Frequency Representation of SignalszvjpÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE6010-High Voltage Direct Current TransmissionDocument12 paginiEE6010-High Voltage Direct Current Transmissionabish abish0% (1)
- Assignment No.3 Bolted JointsDocument6 paginiAssignment No.3 Bolted JointsYash SahuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Economies of Scale in Supply ChainsDocument25 paginiManaging Economies of Scale in Supply ChainsWei JunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iota Tangle 2.0: Toward A Scalable, Decentralized, Smart, and Autonomous Iot EcosystemDocument8 paginiIota Tangle 2.0: Toward A Scalable, Decentralized, Smart, and Autonomous Iot EcosystemMarcos PonceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chevalier FSG-1224ADIIIDocument12 paginiChevalier FSG-1224ADIIIOsvaldo MarinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Criteria Cogni+Ve Ap+Tude Style Free Test: AssessmentdayDocument15 paginiCriteria Cogni+Ve Ap+Tude Style Free Test: AssessmentdayRahul SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023 Key Stage 2 Mathematics Braille Transcript Paper 1 ArithmeticDocument8 pagini2023 Key Stage 2 Mathematics Braille Transcript Paper 1 ArithmeticMini WorldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Research of MRAC in Fault-Tolerant Flight ControllerDocument1 paginăApplication Research of MRAC in Fault-Tolerant Flight ControlleradcadÎncă nu există evaluări
- M.O.E.M.S Practice Packet 2013-2014 PDFDocument20 paginiM.O.E.M.S Practice Packet 2013-2014 PDFrajit kunwar72% (25)
- A-019730-1647416754604-137865-W.M.Supun Anjana DSADocument175 paginiA-019730-1647416754604-137865-W.M.Supun Anjana DSADishan SanjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kalman Filter Tutorial - PresentationDocument65 paginiKalman Filter Tutorial - Presentationcarlazar100% (2)
- D200801 Slope and Offset Adjustment For A Pressure SensorDocument4 paginiD200801 Slope and Offset Adjustment For A Pressure SensorBrian McMorrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- MK-PPT Chapter 1Document37 paginiMK-PPT Chapter 1Nicolás SánchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breathing AND Exchange of Gases MCQs PDFDocument78 paginiBreathing AND Exchange of Gases MCQs PDFJatin SinglaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clustering Methods for Data MiningDocument60 paginiClustering Methods for Data MiningSuchithra SalilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCADADocument14 paginiSCADANunna BaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental of Database: Madda Walabu University College of Computing Department of Information TechnologyDocument46 paginiFundamental of Database: Madda Walabu University College of Computing Department of Information TechnologychalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Information: Introducing The Machine Information Center (MIC) MiningDocument44 paginiProduct Information: Introducing The Machine Information Center (MIC) MiningKolo BenduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aircraft Engine InstrumentsDocument11 paginiAircraft Engine Instrumentssamuelkasoka641Încă nu există evaluări
- Research Article: Ballistic Impact Performance of Sic Ceramic-Dyneema Fiber Composite MaterialsDocument10 paginiResearch Article: Ballistic Impact Performance of Sic Ceramic-Dyneema Fiber Composite MaterialsBhasker RamagiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM4Document572 paginiDM4Axel ToelkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Efectele Pe Termen Lung Ale Alaptatului OMSDocument74 paginiEfectele Pe Termen Lung Ale Alaptatului OMSbobocraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NETZSCH NEMO BY Pumps USADocument2 paginiNETZSCH NEMO BY Pumps USAWawan NopexÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBIP draft meter standardsDocument22 paginiCBIP draft meter standardslalit123indiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3Document2 paginiAssignment 3Spring RollsÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Overview On Reliability, Availability, Maintainability and Supportability (RAMS) EngineeringDocument15 paginiAn Overview On Reliability, Availability, Maintainability and Supportability (RAMS) EngineeringKrinta AlisaÎncă nu există evaluări