Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ec9 Ex11 Mathcad Formulations
Încărcat de
imotalpDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ec9 Ex11 Mathcad Formulations
Încărcat de
imotalpDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
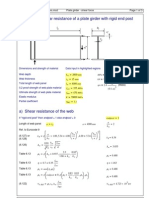
Example calculations
75
Example calculations
The calculations in the following examples are set out in detail. In most cases, the designer can make simplifications when he/she has learned by experience which checks are not usually critical.
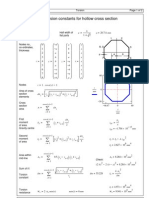
The examples are worked out in the mathematics program Mathcad, version 8. Some of the operators and notations used in the examples are explained below. x := 50.6 mm y 2.5 mm x + y = 53.1 mm a=b 0.5 c := ( 1 3 2 ) ( c d ) Definition of value Global definition Calculation result Boolean equality Decimal point must be used Row vector Vectorise operator, i.e. perform arithmetical operation on each element of a vector or matrix gives a = ( 2 12 6 ) Example: d := ( 2 4 3 ) a := ( c d ) Matrix
1 8 2 g := 3 4 7 5 6 9
c
T
Transpose, i.e. rows and columns are interchanged
Example:
1 c = 3 2
T
1 3 5 g = 8 4 6 2 7 9
T
submatrix( a , 0 , 1 , 1 , 2 )
Part of matrix ( a=matrix, 0 och 1 define rows, 1 and 2 define columns) Normally, in a matrix, the first row is numbered 0 and the first column is numbered 0 Example:
1 8 2 g = 3 4 7 5 6 9
submatrix( g , 0 , 1 , 1 , 2 ) =
8 2 4 7
augment( f , g )
Augmentation of matrices Example:
T augment( c , g ) = 3
Column Example:
1 1 8 2 3 4 7 2 5 6 9
8 1 g = 4 6
Aef A
i
Notation ( ef is not a subscript but part of variable notation) Subscript i Example: g
1, 2
=7
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 2009 - Introductory Time Series With R - Select Solutions - Aug 05Document16 pagini2009 - Introductory Time Series With R - Select Solutions - Aug 05Anonymous BZ0l8Qylp33% (3)
- UW Madison Textbook MATH 222Document138 paginiUW Madison Textbook MATH 222wvlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maths Notes P1 and P3 PDFDocument193 paginiMaths Notes P1 and P3 PDFGeofreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mushroom Growers' Handbook 2: Shiitake CultivationDocument292 paginiMushroom Growers' Handbook 2: Shiitake CultivationMilkwood93% (30)
- Computer Aided Design and Its Applications in Civil EngineeringDocument23 paginiComputer Aided Design and Its Applications in Civil EngineeringPrabagaran DeveshwaarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture2013 04 25Document4 paginiLecture2013 04 25pikachu_latias_latiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab LectureDocument6 paginiMatlab Lecturekafle_yrsÎncă nu există evaluări
- E.0.1 Introduction To MatlabDocument35 paginiE.0.1 Introduction To MatlabMesfin SisayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To MATLAB: Lecturer: Cik Sitinoor Adeib Binti Idris Room: Level 5 CONTACT NUMBER: 03-5543 6362Document27 paginiIntroduction To MATLAB: Lecturer: Cik Sitinoor Adeib Binti Idris Room: Level 5 CONTACT NUMBER: 03-5543 6362seddeswertyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Tutorial 1Document28 paginiMatlab Tutorial 1Saeed Mahmood Gul KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introducere in MatlabDocument73 paginiIntroducere in MatlabFlorin-Lucian CiubotariuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics 4330/5344 - # 3 Loops, Conditionals, Examples and ProgrammingDocument11 paginiMathematics 4330/5344 - # 3 Loops, Conditionals, Examples and ProgrammingAlthara BaldagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 LabDocument6 pagini3 LabkhawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 304 MatrixDocument5 pagini304 Matrixbuckk138Încă nu există evaluări
- AssignmentsDocument84 paginiAssignmentsPrachi TannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic MatlabDocument112 paginiBasic MatlabPrasun SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kuwait University Dept. of Chemical Engineering Spring 2017/2018Document8 paginiKuwait University Dept. of Chemical Engineering Spring 2017/2018material manÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1Document4 paginiLab 1Deepak MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro - Matlab - and - Numerical - Method Lab Full DocumentDocument75 paginiIntro - Matlab - and - Numerical - Method Lab Full DocumentEyu KalebÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATLAB Intro Tutorial (Peter Blossey)Document16 paginiMATLAB Intro Tutorial (Peter Blossey)pitchtwitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To MatlabDocument45 paginiIntroduction To MatlabSivaraman ChidambaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Short TutorialDocument45 paginiMatlab Short TutorialCan ÇamlıkÎncă nu există evaluări
- MATLAB SlidesDocument76 paginiMATLAB SlidesShwe LayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab: Window, Where The Special Prompt Appears. This Prompt Means That MATLAB Is Waiting For ADocument20 paginiMatlab: Window, Where The Special Prompt Appears. This Prompt Means That MATLAB Is Waiting For APunithkumar PuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Notes: CE 33500, Computational Methods in Civil EngineeringDocument10 paginiLab Notes: CE 33500, Computational Methods in Civil EngineeringJose Lorenzo TrujilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 MatLab Tutorial ProblemsDocument27 pagini6 MatLab Tutorial Problemsabhijeet834uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To MatlabDocument10 paginiIntroduction To MatlabHenry LimantonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Intro11.12.08 SinaDocument26 paginiMatlab Intro11.12.08 SinaBernard KendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B. Vector Operations PDFDocument6 paginiB. Vector Operations PDFPapia SultanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions To Assignment 02Document8 paginiSolutions To Assignment 02themba alex khumaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- MatlabDocument50 paginiMatlabOleg ZenderÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSD Practical MannualDocument35 paginiCSD Practical MannualitsurturnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gcse Geometry Vector Operations ExerciseDocument6 paginiGcse Geometry Vector Operations ExerciseGodfred WelbeckÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimization MATLAB ExercisesDocument157 paginiOptimization MATLAB ExercisesJosemarPereiradaSilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HPH Matlab Basic2012 3Document29 paginiHPH Matlab Basic2012 3Axmed ShirwacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction Part I: Basic Matlab StructureDocument28 paginiIntroduction Part I: Basic Matlab StructureMahreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Part 2Document52 paginiMatlab Part 2milenia andiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratorium Teknik Kimia: Fakultas Teknik Upn "Veteran" Jawa TimurDocument17 paginiLaboratorium Teknik Kimia: Fakultas Teknik Upn "Veteran" Jawa TimurNur Rokhma SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Matlab: By: Kichun Lee Industrial Engineering, Hanyang UniversityDocument34 paginiIntroduction To Matlab: By: Kichun Lee Industrial Engineering, Hanyang UniversityEvans Krypton SowahÎncă nu există evaluări
- matlabGetStart Course PDFDocument32 paginimatlabGetStart Course PDFSam JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comm. Sys Lab: SPRING 2013Document85 paginiComm. Sys Lab: SPRING 2013ahmad035Încă nu există evaluări
- Mathcad13 - New FeaturesDocument8 paginiMathcad13 - New FeaturescutefrenzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MathCAD BasicsDocument10 paginiMathCAD BasicsKrusovice15Încă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Concise Notes: Algorithms + Data Structures ProgramsDocument17 paginiMatlab Concise Notes: Algorithms + Data Structures ProgramsnorthorsouthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab TutorDocument8 paginiMatlab Tutorwferry27Încă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Lect 2Document25 paginiMatlab Lect 2Qamar AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 2065 Review Exercises For Exam IIDocument11 paginiMath 2065 Review Exercises For Exam IITri Phương NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 01 (Creating Variables & Arrays)Document94 paginiLecture 01 (Creating Variables & Arrays)Efrem HabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curs 0 Introducere in MatlabDocument73 paginiCurs 0 Introducere in MatlabCorinaPîrvuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Getting Help: Example: Look For A Function To Take The Inverse of A Matrix. Try Commands "HelpDocument24 paginiGetting Help: Example: Look For A Function To Take The Inverse of A Matrix. Try Commands "Helpsherry mughalÎncă nu există evaluări
- MECH374 Lab Class 1: Introduction: 1. How To StartDocument5 paginiMECH374 Lab Class 1: Introduction: 1. How To StartMingCheungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 121 EEE110 LabSheet01Document11 pagini121 EEE110 LabSheet01bkmmizanÎncă nu există evaluări
- محاضرة 1Document24 paginiمحاضرة 1OmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 244 Cheat SheetDocument4 pagini244 Cheat SheetGokul KalyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"De la EverandA Brief Introduction to MATLAB: Taken From the Book "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach"Evaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (2)
- Graphs with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")De la EverandGraphs with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach - Revised EditionDe la EverandMATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach - Revised EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matrices with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")De la EverandMatrices with MATLAB (Taken from "MATLAB for Beginners: A Gentle Approach")Evaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (4)
- Ec9 Ex94 Beam Column HAZDocument5 paginiEc9 Ex94 Beam Column HAZimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec9 Ex81 Torsion Open SectionDocument5 paginiEc9 Ex81 Torsion Open SectionimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure Calculation Sheet For SiloDocument1 paginăStructure Calculation Sheet For SiloimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec9 Ex82 Torsion Closed SectionDocument2 paginiEc9 Ex82 Torsion Closed SectionimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec9 Ex56 Compression OrthotropicDocument6 paginiEc9 Ex56 Compression OrthotropicimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec9 Ex61 Shear No StiffenersDocument3 paginiEc9 Ex61 Shear No StiffenersimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example 5.1. Axial Force Resistance of Member With Square Hollow SectionDocument1 paginăExample 5.1. Axial Force Resistance of Member With Square Hollow SectionimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec9 Ex44 Bending Trapez Class 4Document7 paginiEc9 Ex44 Bending Trapez Class 4imotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec9 Ex43 Bending Trapez Class 2Document7 paginiEc9 Ex43 Bending Trapez Class 2imotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec9 Ex42 Bending O SectionDocument6 paginiEc9 Ex42 Bending O SectionimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec9 Ex41 Bending I SectionDocument5 paginiEc9 Ex41 Bending I SectionimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări
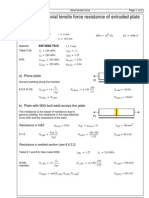
- Example 3.2. Axial Tensile Force Resistance of Extruded PlateDocument2 paginiExample 3.2. Axial Tensile Force Resistance of Extruded PlateimotalpÎncă nu există evaluări