Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Condensation and Hydrolysis and Their Importance in Biology
Încărcat de
Bridie WildDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Condensation and Hydrolysis and Their Importance in Biology
Încărcat de
Bridie WildDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
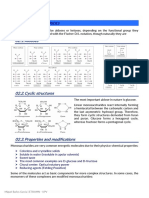
Condensation and Hydrolysis and their importance in Biology Carbohydrates: Monomers form polymers through a series of condensation polymerisation
reactions, forming a glycosidic bond. Forming polysaccharides makes the molecule insoluble as it is so large. Hydrolysis is used to break the glycosidic bond, releasing monosaccharides from a disaccharide. Polysaccharides are found in plants as small granules or grains, for example chloroplasts. Sucrase hydrolyses the single glycosidic bond in a sucrose molecule to produce glucose and fructose. Glucose is then available for use in respiration where it is broken down to produce ATP. Respiration: Glycolysis is the activation of glucose by phosphorylation. The phosphate molecules come from the hydrolysis of two ATP molecules to ADP, providing energy to activate glucose. Amino Acids: Amino acids combine together to make a polypeptide through a series of condensation reactions. This produces the primary structure of proteins, determining the ultimate shape and function of the protein. The proteins which are enzymes require a specific shape to function properly. Muscular Relaxation: When nervous stimulation ceases, calcium ions are actively transported back into the endoplasmic reticulum using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- K.kothandaraman Offer LetterDocument1 paginăK.kothandaraman Offer LetterSupriya NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Submit Website On Blog Directory Submission SitesDocument7 paginiHow To Submit Website On Blog Directory Submission SitesDigitalPediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shiva Mantra GhanapaathaDocument2 paginiShiva Mantra GhanapaathaTruth Be100% (1)
- What Risks Are You Taking With Your Money?: The Renminbi On The Verge of A Major BreakdownDocument76 paginiWhat Risks Are You Taking With Your Money?: The Renminbi On The Verge of A Major BreakdownravibehlÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8th Square and Square Root 8th CubeDocument3 pagini8th Square and Square Root 8th CubeMorgan ThomasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Talk Delta HelpDocument58 paginiTalk Delta HelpRocks JitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ranking Report Email TemplateDocument1 paginăRanking Report Email TemplateChristian LlorcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Off Page SEO Activities - Off Page SEO Techniques 2020 - DMIRDocument12 paginiOff Page SEO Activities - Off Page SEO Techniques 2020 - DMIRsanjay mishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cascading Style Sheet: Nazia Hameed Comsats Institute of Information Technology IslamabadDocument45 paginiCascading Style Sheet: Nazia Hameed Comsats Institute of Information Technology IslamabadAqib KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- IoT Based Health Monitoring SystemDocument11 paginiIoT Based Health Monitoring SystemakashlogicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commodity Market: Presented By: Akhilesh Gadkar PG-13-14 Pritesh Shah PG-13-50 Arpit Shah PG-13-59Document37 paginiCommodity Market: Presented By: Akhilesh Gadkar PG-13-14 Pritesh Shah PG-13-50 Arpit Shah PG-13-59Laura ButlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gann Square of 9 CalculatorDocument15 paginiGann Square of 9 CalculatorSantosh ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inr 4.74LDocument49 paginiInr 4.74LtamaldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predicting EarthquakesDocument12 paginiPredicting EarthquakesGauravMalhotraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blue White Simple Copy Editor CVDocument2 paginiBlue White Simple Copy Editor CVMehak ShehzadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Painting Spec - MechanicalDocument22 paginiPainting Spec - MechanicalMansoor Ahamed AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8a Food Digestion Science QuizDocument42 pagini8a Food Digestion Science QuizAmarpreet KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astrological Trade Recommendations For The Components of The S&P100 IndexDocument2 paginiAstrological Trade Recommendations For The Components of The S&P100 Indexapi-139665491Încă nu există evaluări
- Strategic Role Product ManagementDocument35 paginiStrategic Role Product ManagementShankar Ram SivaswamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comparative Study On Vaastu Shastra An PDFDocument20 paginiA Comparative Study On Vaastu Shastra An PDFRaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental AnalysisDocument28 paginiFundamental AnalysisAjitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manually Directory SubmissionDocument5 paginiManually Directory Submissionarun11nov85Încă nu există evaluări
- 03 - CarbohydratesDocument6 pagini03 - CarbohydratesMiguel BañosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates IAL Edexcel ChemistryDocument17 paginiCarbohydrates IAL Edexcel ChemistryIsaa gabÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCB 201 Biosynthesis of Biomolecules - MCB - 201Document10 paginiMCB 201 Biosynthesis of Biomolecules - MCB - 201Lena HasleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Notes: Topic 1ADocument10 paginiBiology Notes: Topic 1Alaiba amirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Bio ChemistryDocument9 paginiClinical Bio ChemistrylegendofrohithÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2 Biological MoleculesDocument48 paginiCH 2 Biological Molecules9G11 Aulia KayanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. CarbohydratesDocument6 paginiI. CarbohydratescelynjasminegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 05 - The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesDocument6 paginiChapter 05 - The Structure and Function of MacromoleculesMars RaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomolecule: Carbohydrates: Philippine Christian Gospel SchoolDocument9 paginiBiomolecule: Carbohydrates: Philippine Christian Gospel SchoolTashi OngÎncă nu există evaluări
- INTRODUCTIONDocument19 paginiINTRODUCTIONVatsal BajpaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOA111 SN17 SummaryDocument6 paginiBIOA111 SN17 SummaryDorothy NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Script For BiochemDocument12 paginiScript For Biochemotep freecsÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiochemistryDocument16 paginiBiochemistryLeila JoieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 1-20Document20 paginiTopic-1A (Food and Health) (Autosaved) - 1-20lisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VojoyDocument7 paginiVojoyFerds SalvatierraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydrateDocument14 paginiCarbohydrate Classification of Carbohydrate Metabolism and Regulation of CarbohydratesukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Prof. Lenny MaterialsDocument8 paginiReview Prof. Lenny MaterialsIrvandar NurviandyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CarbohydratesDocument14 paginiCarbohydratesxubulavaxatiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingDocument9 paginiBIOMOLECULES-Any Molecules That Are Produced by A LivingRuskin Jamir AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates: MonosaccharidesDocument4 paginiCarbohydrates: MonosaccharidesMafalda CalheirosÎncă nu există evaluări
- CarbohydratesDocument22 paginiCarbohydratesSHIFA ALTAFÎncă nu există evaluări
- STPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesDocument9 paginiSTPM BIOLOGY SEMESTER 1 Chapter 1 CarbohydratesMabel Lee Shan Shan100% (3)
- BIOMOLECULESDocument8 paginiBIOMOLECULESjorel marcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 - Enzymes and The Digestive SystemDocument11 paginiUnit 2 - Enzymes and The Digestive SystemKatherine NunnÎncă nu există evaluări
- CarbohydratesDocument19 paginiCarbohydratesNaina YadavvÎncă nu există evaluări
- CarbohydratesDocument34 paginiCarbohydratesDebbie AdamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 CarbohydratesDocument10 pagini04 CarbohydratesAlbert MuswewemombeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disaccharide QuestionsDocument2 paginiDisaccharide QuestionsMichael WrightÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Molecules and EnzymesDocument16 paginiBiological Molecules and EnzymesdebbyhooiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Reviewer - FinaDocument3 paginiScience Reviewer - FinaAmamore Lorenzana PlazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDocument15 paginiBiology: Carbohydrates Lipids & ProteinsDr.CharinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Notes 2Document32 paginiBio Notes 2Sinin VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Notes 2Document32 paginiBio Notes 2Sinin VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates: Monosaccharides - Simple SugarsDocument2 paginiCarbohydrates: Monosaccharides - Simple SugarsSarah MudaliarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrolysis and Dehydration SynthesisHydrolysisDocument2 paginiHydrolysis and Dehydration SynthesisHydrolysismikey12345452863879Încă nu există evaluări
- Biomolecules: Biomolecules Are Natural Polymers. These Have A Wide Range of Sizes andDocument7 paginiBiomolecules: Biomolecules Are Natural Polymers. These Have A Wide Range of Sizes andKimberly IgbalicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrates BiochemDocument4 paginiCarbohydrates Biochemsaythename.smmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wrtitten .Structure of PolysacDocument4 paginiWrtitten .Structure of PolysacDianne Joy LeybaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 980.13 Fructose, Glucose, Lactose, Maltose and Sucrose in Milk ChocolateDocument1 pagină980.13 Fructose, Glucose, Lactose, Maltose and Sucrose in Milk ChocolateJessica triana pinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: - Class: - Exercise Chapter 6.4 & 6.5 6.4 (Food Digestion) 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested FoodDocument4 paginiName: - Class: - Exercise Chapter 6.4 & 6.5 6.4 (Food Digestion) 6.5 Absorption and Assimilation of Digested Foodsylent gohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ginger Rhizomes (Zingiber Officinale) A Spice With Multiple Healthbeneficial PotentialsDocument11 paginiGinger Rhizomes (Zingiber Officinale) A Spice With Multiple Healthbeneficial PotentialsRabeea NasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dissertation PPT SampleDocument52 paginiDissertation PPT SamplePritpal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8000 GK Questions Updated CompressDocument259 pagini8000 GK Questions Updated CompresskhyallalingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approved Chemicals ListDocument7 paginiApproved Chemicals Listapi-232424041Încă nu există evaluări
- SCD Lista Alimente Permise InterziseDocument62 paginiSCD Lista Alimente Permise InterzisenicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Izumoring: A Novel and Complete Strategy For Bioproduction of Rare SugarsDocument6 paginiIzumoring: A Novel and Complete Strategy For Bioproduction of Rare SugarsFabián Camilo OtáloraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biotransformation of Spent Coffee Grounds by Fermentation WithDocument11 paginiBiotransformation of Spent Coffee Grounds by Fermentation WithDavi MouraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Term 1 Week 3 - 2021Document7 paginiLife Sciences Grade 10 Term 1 Week 3 - 2021Chelain BoucherÎncă nu există evaluări
- MacronutrientsDocument23 paginiMacronutrientsarasmus2Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology - Transport in AnimalsDocument67 paginiIgcse Biology - Transport in AnimalsYoshitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prelim Biochem Exam ReviewerDocument11 paginiPrelim Biochem Exam ReviewerCarla Marie LedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hispida Leaves. Mice of Either Sex Weighing 20 - 25 G Were Included in The Study. Alloxan Monohydrate Was GivenDocument5 paginiHispida Leaves. Mice of Either Sex Weighing 20 - 25 G Were Included in The Study. Alloxan Monohydrate Was GivenZo ThelfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systematic Analysis of Organic CompoundsDocument12 paginiSystematic Analysis of Organic CompoundsM Bharath ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study The Rates of Fermentation of Fruit or Vegetable JuicesDocument6 paginiStudy The Rates of Fermentation of Fruit or Vegetable JuicesKusumBhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 - CarbohydratesDocument26 paginiUnit 3 - CarbohydratesWinrich Louise M. MontanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Compounds in Living Things: PropertiesDocument96 paginiOrganic Compounds in Living Things: PropertiesTUĞRUL ERGÜLÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2005 - Ravno - Dealing With Dextran in TheDocument20 pagini2005 - Ravno - Dealing With Dextran in ThenghiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMGBS-Bio 11. U.2 NoteDocument77 paginiEMGBS-Bio 11. U.2 Notenafhire2021Încă nu există evaluări
- Issa Ebook RecoveryDocument25 paginiIssa Ebook RecoveryMohammed Naved100% (1)
- Revive PDFDocument6 paginiRevive PDFMarcus SouzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The First Two Years Lesson of A DoctorDocument64 paginiThe First Two Years Lesson of A DoctorWheljy Salise AmpoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2: Molecular Biology: Synthesis of UreaDocument23 paginiChapter 2: Molecular Biology: Synthesis of UreaHiya GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 36 Sydney Mangham.: Lecturer in Botany, Armstrong College, Newcastle-on-Tyne, in The University of Durham.Document6 pagini36 Sydney Mangham.: Lecturer in Botany, Armstrong College, Newcastle-on-Tyne, in The University of Durham.mallik789Încă nu există evaluări
- 6 Week Six Pack DietDocument55 pagini6 Week Six Pack DietIsaiyah Carmona100% (3)
- Organic Chemistry Notes-G10Document41 paginiOrganic Chemistry Notes-G10rana alweshah100% (1)
- Glucose EstimationDocument10 paginiGlucose EstimationZahidKhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top 100 Biology GK Questions For SSC Exams (WWW - Thegkadda.com) PDFDocument3 paginiTop 100 Biology GK Questions For SSC Exams (WWW - Thegkadda.com) PDFMi MolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Macronutrients and MicronutrientsDocument78 paginiMacronutrients and MicronutrientsPATRIZJA YSABEL REYESÎncă nu există evaluări