Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer System
Încărcat de
Nuj Wehtam InairamDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
5 Basic Operations Performed by Computer System
Încărcat de
Nuj Wehtam InairamDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
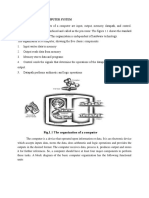
Basic Computer Organization Basic operations of a computer 1.
Inputting- The process of entering the data and instruction in the computer system. 2. Processing- Performing arithmetic operations or logical on data to convert them into useful information 3. Outputting- The process of producing the useful information or result for the user such as a printed report or visual display 4. Storing- Storing data and instruction to make them readily available for initial or additional processing whenever required. 5. Controlling- Directing the manner or sequence in which all of the above operation are performed. Basic computer of organization system
Input unit: Input unit links the external environment with the computer system. Data and instruction must be entered to the computer before performing any competition. Data or instructions can be entered through input devices
eg. Key board, or any other input devices. Input unit transferred this data into binary coded in short input unit performs the following function: -It accepts data or instructions from external world. -It converts these instructions and data in computer acceptable form. -It supplies the converted instruction & data to the computer for further processing. Output unit: The job of output unit it is just the viewers of that any input unit it provides information reasons of computation to the output of the world. Output unit links the computer with the external world. A computer prepares results in binary code. Output unit converts these results into human acceptable forms. In short perform the following functions. -It accepts the result produced by the computer. -It converts these coded results to human acceptable form. -It supplies the converted to the outside world. Storage unit: Before actual processing start, data & instructions entered to the computer must be stored inside the computer. Similarly, results produced by the computer are required to be stored before being passed to the output unit. The intermedial result produced by the computer must also be stored for further processing. In short the function of storage unit: -It stores all the data to be process. -It stores intermedial results. -It stores final result are realize an output device. Types of storage used in a computer system Primary Computer Storage Devices Primary storage refers to the computer's memory, which connects directly to the computer's CPU. The computer's memory evolved into what is now known as random access memory (RAM) which is a volatile form of storage. Volatile storage means that you totally lose data when you switch the system off. Secondary Computer Storage Devices
These storage devices are external in nature and non-volatile as compared to primary storage devices. Secondary storage devices do not lose data even when they are turned off. Hence, they are the ideal back-up and data storage devices. Tertiary Computer Storage Devices This type of computer storage device is not as popular as the other two storage device types. Its main use is for storing data at a very large-scale. This includes optical jukeboxes and tape libraries. Tertiary storage devices require a database to organize the data that are stored in them, and the computer needs to go through the database to access those data. Offline Storage Offline or disconnected storage is not directly connected to the computer and is used as a transfer medium only. Offline storage devices are remotely located and accessed as per need only. This storage device also needs human intervention to be read properly by the main computer system. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): ALU is the place where actual execution of the instructions takes places during the processing operations. All calculations & comparisons are made in the ALU. The data and instructions stored in the primary storage are transferred as where required. Intermedial results are also transferred back to the ALU for the final processing. After completion of processing the final results are send to storage units from ALU. Number of arithmetic & logical operation that a computer can perform is determined by the design to perform the four basic arithmetic operations. They are +,-,*,/. The logic operations like <,=,>. Control unit (CU): ALU does not know what should be done with the data likewise; output unit does not know when the result should be displayed. By selecting, interning and seeing to the execution of the program the CU is able to maintain order and direct the operations of the entire system CU doesnt perform any actual processing on data yet it is known as a central nervous system for the comforts of the computer. It manages co-ordinates the entire system.
Central Processing Unit CPU or Central Processing Unit is the heart and brains of every computer. Many of us do not know what importance it has on the whole performance of a computer.
4 primary functions of a CPU Fetch All the instructions are stored in memory. Each instruction has is address. The processor takes this address number from the program counter. Program counter is responsible for tracking what instructions CPU should execute next. So fetching basically means taking the instruction from the memory. Decode CPU understands instructions, that are written in Assembly programming language. All the programs, that must be executed, are translated to Assembly instructions. Different CPUs understand different instructions, so Assembly code must be decoded into binary instructions which are understandable to your CPU. This step is called decoding. Execute During the procedure of instruction execution, tree things can be done. Firstly, CPU can do some calculations. To execute calculations ALU is used. Secondly, CPU can move data from
one memory location to another. And thirdly, CPU can jump to different address if it is needed. So basically, one of those three options is executed during this step.
Store CPU must give some feedback after executing the instruction. The output data is written to the memory. In this phase program counter is incremented Computer as a system A system is interconnected computers that share a central storage system and various peripheral devices such as a printers, scanners, or routers. Each computer connected to the system can operate independently, but has the ability to communicate with other external devices and computers. A system has following three characteristics: 1. 2. 3. A system has more than one element. All elements of a system are logically related. All elements of a system are controlled in a manner to achieve the system goal,
A computer is a system as it comprises of integrated components (input unit, output unit, storage unit, and CPU) that work together to perform the steps called for in the executing program.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Components of System UnitDocument8 paginiComponents of System Unitroger_embalsado331988% (16)
- Module 9 Living in The IT EraDocument11 paginiModule 9 Living in The IT ErakvelezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Fundamentals of Information SystemDocument64 paginiChapter 2 Fundamentals of Information SystemGanesh Thapa100% (2)
- Information System ActivitiesDocument6 paginiInformation System ActivitiesDr. Shailendra Kumar Srivastava100% (2)
- Some of This Are The FollowingDocument27 paginiSome of This Are The FollowingRalph RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 Information ManagementDocument22 paginiModule 1 Information ManagementKaelf Dave NoguerraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Living in The Information Technology EraDocument1 paginăLiving in The Information Technology EraArnold TyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IS Exam Sarvida Oct282019Document5 paginiIS Exam Sarvida Oct282019jeromme saldivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Organization and Architecture Module 1Document46 paginiComputer Organization and Architecture Module 1Assini Hussain100% (1)
- CpE Laws and Professional PracticeDocument1 paginăCpE Laws and Professional Practiceprince_kc200229% (7)
- Program Development LifecycleDocument3 paginiProgram Development LifecycleJacksonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Computers On Internal ControlDocument53 paginiEffects of Computers On Internal ControlPia SurilÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLASS 8 Information TechnologyDocument6 paginiCLASS 8 Information TechnologyKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture #1Document23 paginiLecture #1Matt FriedmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Device DriversDocument12 paginiDevice DriversFaroog fatma JafriÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Relationship Between Software and Hardware in A Computer SystemDocument27 paginiThe Relationship Between Software and Hardware in A Computer SystemIwuagwu Judith Nkechi75% (4)
- IT ERA Chapter 1Document31 paginiIT ERA Chapter 1sam peligroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Control ChallengesDocument36 paginiInformation Control Challengeskim13aimeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Early Computers: From Vacuum Tubes to MicroprocessorsDocument7 paginiEarly Computers: From Vacuum Tubes to MicroprocessorsNova Divine De la PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1 QuizDocument20 paginiWeek 1 QuizEduardo GomezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 VIRTUAL MEETINGS SMART MANAGEMENTDocument2 paginiChapter 2 VIRTUAL MEETINGS SMART MANAGEMENTJessuel Larn-epsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Book Review of Computer Fundamentals by StallingsDocument4 paginiBook Review of Computer Fundamentals by StallingsEr Rouf UlAlam BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Decision Making - The Essence of The Manager's JobDocument8 paginiChapter 6 Decision Making - The Essence of The Manager's Jobnourh-anne100% (1)
- Identify The Uses of Personal Interest ApplicationsDocument1 paginăIdentify The Uses of Personal Interest Applicationssaher QueenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Computers by Size, Technology and PurposeDocument8 paginiClassification of Computers by Size, Technology and PurposeAnkit Tiwari100% (1)
- TMP 7617 PLDT Home DSL and PLDT Home Fiber New Default Wifi Password Hack 11508993826 PDFDocument7 paginiTMP 7617 PLDT Home DSL and PLDT Home Fiber New Default Wifi Password Hack 11508993826 PDFErvin BasasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ra 10844 - PPTDocument41 paginiRa 10844 - PPTRose Jones33% (3)
- Familiarize yourself with computer hardwareDocument32 paginiFamiliarize yourself with computer hardwareSantpreet Singh Kalra83% (6)
- History and Generation of ComputerDocument4 paginiHistory and Generation of Computerakyadav12350% (2)
- TLE 3 - Teaching ICT As An Exploratory Course Topics and Assigned Reporters Topic 1Document2 paginiTLE 3 - Teaching ICT As An Exploratory Course Topics and Assigned Reporters Topic 1Jessa EdulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSTP Module Dr. MabalayDocument120 paginiNSTP Module Dr. Mabalayjongoks81Încă nu există evaluări
- Polytechnic University of the Philippines ExercisesDocument2 paginiPolytechnic University of the Philippines ExercisesFelix LlameraÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT in BusinessDocument33 paginiIT in BusinessJunjie Dela RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social Issues in Tech. MGMTDocument2 paginiSocial Issues in Tech. MGMTUtshav PoudelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Intro To Info. ManagementDocument9 pagini1 - Intro To Info. Managementcyka blyatÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBLM-Computer ProgrammingDocument86 paginiCBLM-Computer ProgrammingJERIKO PELIMIANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions On Operating System PartDocument24 paginiMultiple Choice Questions On Operating System Partgdeepthi100% (3)
- Mid Term ExamDocument26 paginiMid Term Examdw40412Încă nu există evaluări
- OBE Syllabus in Computer Systems Servicing NC IIDocument7 paginiOBE Syllabus in Computer Systems Servicing NC IIJayvee Cadiz Lagmay100% (1)
- The Title ProposalDocument3 paginiThe Title ProposalRobert Lee BawigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Developing An EA Management Plan: Enterprise ArchitectureDocument36 paginiDeveloping An EA Management Plan: Enterprise ArchitectureSobat KurniawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Components of Computer SystemDocument38 paginiUnit 4 Components of Computer SystemPauline TorionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principle Brief Description Keywords Quotation As A Prospective Teacher, I WillDocument3 paginiPrinciple Brief Description Keywords Quotation As A Prospective Teacher, I WillVanessa Mae NaveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of ComputerDocument13 paginiTypes of ComputerSachin TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NAME: Reneil James D. Gutierrez Section: BSIT-1C NAME: Al Francis Cortez Bake A BreadDocument11 paginiNAME: Reneil James D. Gutierrez Section: BSIT-1C NAME: Al Francis Cortez Bake A BreadAl Francis Cortez100% (1)
- Configuring of Computer Systems and NetworksDocument73 paginiConfiguring of Computer Systems and NetworksMark Michael BundocÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Microsoft PowerpointDocument5 paginiHistory of Microsoft PowerpointNuez Abeño JacobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - ERP A Manufacturing PerspectiveDocument18 paginiChapter 4 - ERP A Manufacturing PerspectiveHarold Falip100% (1)
- Basic Components of Computer SystemDocument4 paginiBasic Components of Computer SystemAnonymous u64nn35tHCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Organization & Architecture: Input UnitDocument3 paginiComputer Organization & Architecture: Input UnitTilak JethwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional units and buses in digital systemsDocument20 paginiFunctional units and buses in digital systemsDivyaanshu AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Components of A ComputerDocument5 paginiComponents of A ComputersoujanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer System Computer ArchitectureDocument7 paginiComputer System Computer ArchitectureSuman Samal MagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Computer Is An Electronic DeviceDocument10 paginiA Computer Is An Electronic Devicearvinder kaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fcpit: Familiarisation of ComputerDocument38 paginiFcpit: Familiarisation of ComputerVipin SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Functional UnitsDocument14 paginiThe Functional UnitsSiddhartha BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The 5 Basic Operations of A ComputerDocument3 paginiWhat Are The 5 Basic Operations of A ComputerShin NeulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module - 01 - Computer FundamentalsDocument18 paginiModule - 01 - Computer FundamentalsRide RelaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Organization Lab ManualDocument29 paginiComputer Organization Lab ManualAshis UgetconfusedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-I Notes PPSDocument23 paginiUnit-I Notes PPSAbhir999Încă nu există evaluări
- Import JavaDocument2 paginiImport JavaNuj Wehtam InairamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution of The ComputerDocument7 paginiEvolution of The ComputerNuj Wehtam InairamÎncă nu există evaluări
- SoftwareDocument1 paginăSoftwareNuj Wehtam InairamÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChickenDocument3 paginiChickenNuj Wehtam InairamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ComputersDocument6 paginiIntroduction To ComputersNuj Wehtam InairamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lanschool YeahDocument14 paginiLanschool YeahNuj Wehtam InairamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vosk CoinDocument1.365 paginiVosk Coinxalila8569Încă nu există evaluări
- Fujitsu M10-1 or M10-4 or M10-4S Servers Help Desk Support Consultant Online AssessmentDocument12 paginiFujitsu M10-1 or M10-4 or M10-4S Servers Help Desk Support Consultant Online AssessmentAl MamunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course StructureDocument11 paginiCourse Structuredhruvgoel1Încă nu există evaluări
- 800-4006-19 Field Engineer Handbook Vol 1 Sep2000 PDFDocument803 pagini800-4006-19 Field Engineer Handbook Vol 1 Sep2000 PDFwbergiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Addressing MODES of 8085 - Free 8085 Microprocessor NotesDocument2 paginiAddressing MODES of 8085 - Free 8085 Microprocessor NotesPawan Kumar Thakur100% (1)
- SLT Form TwoDocument5 paginiSLT Form Twocmukhongo_679153453Încă nu există evaluări
- Nuvoton ISD9xxx ICP Programmer User Guide V1.17.5182Document46 paginiNuvoton ISD9xxx ICP Programmer User Guide V1.17.5182PitarsaÎncă nu există evaluări
- InfoCaster DS1150 Hardware Specifications - 20111221Document2 paginiInfoCaster DS1150 Hardware Specifications - 20111221FrancisÎncă nu există evaluări
- TVL CSS11 Q2 M3Document18 paginiTVL CSS11 Q2 M3charmaine jornadalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer 7 ExamDocument40 paginiComputer 7 ExamAldren BarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dell Drivers ListDocument2 paginiDell Drivers ListrameshfaceÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANNAUNIVERSITY OPERATING SYSTEM Unit 1Document89 paginiANNAUNIVERSITY OPERATING SYSTEM Unit 1studentscorners100% (1)
- 2 A COAL - Final PaperDocument2 pagini2 A COAL - Final PaperMUHAMMAD AQEEL ANWAR KAMBOHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panasonic Toughbook CF-53AACHYDY Semi Rugged HD NotebookDocument2 paginiPanasonic Toughbook CF-53AACHYDY Semi Rugged HD NotebookWebAntics.com Online Shopping StoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Msy 25-3-11-PartsDocument4 paginiMsy 25-3-11-Partsmarekr57591Încă nu există evaluări
- BR Ricoh Aficio 1018D PDFDocument2 paginiBR Ricoh Aficio 1018D PDFAivars LīpenītsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 07Document47 paginiChapter 07Muhammad AzharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summative Test: Computer Systems Servicing-Ii 1 QUARTER SY:2020-2021Document7 paginiSummative Test: Computer Systems Servicing-Ii 1 QUARTER SY:2020-2021Merlie Ewican PatalotÎncă nu există evaluări
- DP Vendor 15125 DriversDocument143 paginiDP Vendor 15125 Driversviki mikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Teaching Load Allocation For Cs Spring Semester, 2011-2012Document5 paginiIndian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Teaching Load Allocation For Cs Spring Semester, 2011-2012Adithya MailaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VTSS5000 DatasheetDocument3 paginiVTSS5000 Datasheetkunene07Încă nu există evaluări
- Harga Hardware dan Aksesoris Terbaru Toko Komputer Gemilang JayaDocument3 paginiHarga Hardware dan Aksesoris Terbaru Toko Komputer Gemilang JayaFaris NuchadrinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS1358 Computer Architecture QuestionsDocument8 paginiCS1358 Computer Architecture QuestionsMarimuthu MuthaiyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ET SyllabusDocument2 paginiET SyllabusDr.S.A.SivakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASUS Fatal1ty Z68 Professional Gen3 - Moderkort PDFDocument86 paginiASUS Fatal1ty Z68 Professional Gen3 - Moderkort PDFMagnus PerssonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acer Aspire 5550 3670 (Wistron Garda-3 AG3 Discrete) PDFDocument55 paginiAcer Aspire 5550 3670 (Wistron Garda-3 AG3 Discrete) PDFMustafa AkanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory Memory Organization OrganizationDocument43 paginiMemory Memory Organization OrganizationAnonymous AFFiZnÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIBO QuickstartDocument10 paginiAIBO Quickstartevhyajah100% (1)
- 4552 2014-07-22 21.05Document665 pagini4552 2014-07-22 21.05Gilbert TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- F21 Series EN 8-29 InstructionsDocument16 paginiF21 Series EN 8-29 Instructionsjuan VillaÎncă nu există evaluări