Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lesson Plan Math 5
Încărcat de
Ronan SibbalucaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lesson Plan Math 5
Încărcat de
Ronan SibbalucaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Give the place value of each digit in a 6 or more digit number.
Read and write numbers through billions in figures and in words correctly. Psychomotor: Write numbers through billions in figures and in words. Affective: Observe accuracy in reading and writing numbers through billions in figures and in words. Reading and writing numbers through billions in figures and in words Ref: BEC-PELC 1.A.1 Mat: Place value Chart, number cards Value: Alertness, accuracy A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Writing numbers in expanded form. 2. Review Reading smaller group of numbers written on reusable materials B. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 3 (See Lesson Guide, p. 2) 2. Generalization How many periods are there in a billion? What are the periods in a billion? Application 1. Write the following numbers in words? a) 2 750 000 b) 3 726 513 c) 43 000 210
II.
III.
C.
IV.
Write the value of the underlined digit in each number 1. 2 750 423 000 2. 9 287 600 3. 412 876 010 051 4. 17 386 001 000 5. 234 126 143
V. In the numeral 927 814 760, write each digit in the proper place according to value _________ Thousands _________ hundred millions _________ Billions
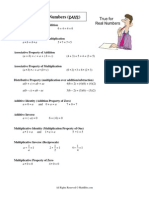
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Identify the properties of addition used in an equation. Add numbers using the properties. Psychomotor: Write the sum of a given set of numbers. Affective: Appreciation for the use of the properties of addition. Using the properties of Addition to help find the Sum Ref: BEC-PELC I.A.2.a. Mat: Flashcards Value: Appreciation for beauty/ Be clean and orderly A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Writing numbers in expanded form. 2. Review Reading smaller group of numbers written on reusable materials Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 4-5) 2. Generalization What are the properties of addition? What is the commutative property of addition? Associative property? Identity property? Application Name the properties used. 1. (7 + 8) + 2 = 7 + (8 + 2) 2. 3+9=9+3 3. 4 + (7 + 6) = (4 + 6) + 7
II.
III.
B.
C.
____________________ ____________________ ____________________
IV.
Find each missing addend. Name the properties you used. 1. (12 + 3) + 5 = ____ + (3 + 5) ______________ 2. 35 + 0 + ____ = 35 + 9 + 0 ______________ 3. 27 + _____ = 27 ______________ Use the properties to complete each sentence. 1. 24 + 12 + 6 = _____ 2. 33 + 10 + 7 = _____ 3. 65 + 20 + 115 = _____
V.
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Identify the properties of multiplication. Find the product using the properties of multiplication. Psychomotor: Write the equation and the answer illustrating the properties of multiplication. Affective: Be alert in every activity Identifying and showing the Properties of Multiplication. Reference : BEC-PELC I.A.2.b Mat: counters Values. Cooperation, active participation A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Name the properties used. a. (5 + 7) + 4 = 5 + (7 + 4) b. 6+3=3+6 2. Checking of assignment Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 1(See Lesson Guide, p. 6-7) 2. Generalization What are the properties of multiplication?
II.
III.
B.
IV.
Identify the property of multiplication illustrated. 1. 4 761 x 0 = 0 2. 8 x 27 = 27 x 8 3. 8 x (4 x 9) = (8 x 4) x 9 Write true or false. If true , identify the property of multiplication illustrated. 1. 8x4=4x8 2. 5 x (2 x 6) = (5 x 2) x (6 x 5) 3. (3 x 4)+ (4 x 5) = (3 x 4) x 5
V.
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Round off numbers to the nearest indicated place value. Psychomotor: Write numbers rounded to the indicated place value. Affective: Demonstrate consciousness too much food wastage Rounding numbers to the nearest tens, hundreds, thousands, ten thousands, etc. Reference: Math textbook, BEC-PELC I.A.3 Materials: flashcards, place value charts Value: Consciousness of too much food wastage A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Drill on reading Numbers through Billions 2. Review Strategy 1: Show me card Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 1(See Lesson Guide, p. 10) 2. Generalization How do we round off numbers? Application Name the place value where the numbers are rounded. 1. 890 2. 700 000 000 3. 456 000
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Round the numbers to the nearest Tens 1. 4 315 652 2. 7 354 754 3. 6 812 563 Hundreds Thousands
V.
List down at least 2 numbers that can rounded off to the nearest: 1. hundreds 2. thousands 3. hundred millions 4. millions 5. billions
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Review the process of adding and solving large numbers with and without regrouping. Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of whole numbers. Psychomotor: Write numbers in column properly. Affective: Persevere in working with large numbers. Reviewing the process of adding and solving large numbers with and without regrouping Addition and subtraction of large number with and without regrouping. Reference: Math textbook, BEC-PELC I.A.4.a Materials: flashcards, counters Value: Perseverance, cooperation A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Basic addition and subtraction facts. 2. Review Review on identity property of addition. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 13-14) 2. Generalization How do we add/subtract large numbers with regrouping? Without regrouping? Application Do the indicated operation. 1. 638 431 + 972 302 + 439 166 = 2. 906 382 529 495 =
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Solve the following correctly. 1. From 189 860 take away 56 780. 2. What is the total of 143 321 478 939 and 113 026 788 519? 3. What is 299 749 123 increased by 187 894 091? Complete the chart. Write the sum and difference of the numbers indicated? Sum Difference
V.
Numbers 1. 984 207 542 263 481 563 2. 725 983 654 336 343 459
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Review the process of multiplying whole numbers. Psychomotor: Write the correct solution in multiplying whole numbers. Affective: Persevere in ones work. Reviewing the process of multiplying whole numbers Reference: Math textbook, BEC-PELC I.A.4.b Materials: flashcards, counters Value : Patience A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Basic facts in multiplication through flash cards. 2. Mental Computation. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 16-17) 2. Generalization How do we multiply whole numbers? Application Multiply. 1. 5 629 x 47 = 2. 31 695 x 43 =
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV. V.
Find the product of the following. 1. 40 306 2. 37 715 3. 45 681 x 27 x 53 x 13 Read each problem. Write the mathematical sentence then solve. 1. Mr. Rico sold 2 321 copies of mathematics books. Mr. Pazsold 12 times as many. How many mathematics books did Mr. Paz sold?
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V
Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Review the process of dividing whole numbers. Psychomotor: Find the quotient of given numbers. Affective: Perform the operation with speed and accuracy. Dividing whole numbers Reference: Math textbook, BEC-PELC I.A.4.c Materials: flashcards, counters Value : Speed and accuracy A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Basic facts on division through flash cards. 2. Mental Computation. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 1(See Lesson Guide, p. 18-19) 2. Generalization How will you divide whole numbers? Application Divide. 1. 1359 23 = 2. 7332 52 =
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Find the quotient of the following. 1. 13248 24 = _____ 2. 15184 24 = _____ 3. 239708 48 = _____ Read each problem and solve. 1. Mang Berto gathered 1 350 mangoes from his orchard. Before selling the mangoes, he placed them equally in 6 kaings. many mangoes were placed in each kaing?
V. How
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V
Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Solve 1-step word problem using any of the four fundamental operations. Psychomotor: Solve accurately and correctly 1-step word problems. Affective: Develop critical thinking in analyzing and solving word problems. Solving one step word problems using any of the four fundamental operations Reference: BEC-PELC I.A.5.a Materials: Charts, flashcards Value: Thoughtfulness, critical thinking A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Drill on the basic addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. 2. Review Review the steps in problem solving. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 1(See Lesson Guide, p. 21) 2. Generalization What are the steps in solving word problems? Application Solve the following problems. 1. Mr. Sison sold 41 000 kilograms of copra in January and another 29 368 kilograms in June. How many more kilograms of he sell in January than in June?
II.
III.
B.
C.
copra did IV.
Solve for the following problems. 1. Omar collected 31 242 eggs. He sold 19 568 eggs to store owners. How many eggs were left unsold? 2. There were 4 grade levels which joined the parade at Luneta. Each grade level had 42 pupils. How many pupils in all joined the parade? V. girl Solve the following problem. Miss Lorenzo distributed 3 264 squares of cloth equally among her 16 girls to make a table cover. How many squares of cloth did each receive?
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V
Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Solve 2-3-step word problem using any of the four fundamental operations. Psychomotor: Solve 2- to 3- word problems correctly. Affective: Solve 2-3-step word problem using any of the four fundamental operations with accuracy. Solving 2-3 step word problems using any of the four fundamental operations Reference: BEC-PELC I.A.5.b Materials: Charts, flashcards Values: Accuracy , alertness, cooperation A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Drill on the basic addition facts, subtraction facts, multiplication facts and division facts through the use of flash cards. 2. Checking of assignments. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 23 - 24) 2. Generalization What are the steps you should follow in solving word problems? What is the most important thing to consider in problem solving? Application Solve the following problems. Each of the 4 officials of the Sports Club contributed P 1 032.00 for the basketball uniforms. How much was raised for the basketball
II.
III.
B.
C.
uniforms? IV. Read and solve. 1. An airplane covered the following distances in 3 trips: 1 300 miles, 972 miles and 1 580 miles. The average speed of the plane was 550 miles per hour. What was the average distance covered in the three trips? 2. An egg vendor bought 600 eggs from the Solder Farm. She paid Php. 28 per dozen. How much did she pay in all? V. Solve the following problem. The PTA donated P 39 510 to the school to buy 15 typewriters. If each typewriter costs P 3000, how much was the schools s
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Differentiate odd from even numbers Identify odd and even numbers. Psychomotor: Play actively in group games. Affective: Show alertness in playing group games. Differentiate Odd and Even Numbers Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.1 Materials : Concrete objects, number cards Value: Alertness A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Write the missing numbers. a. 20, 22, 26, 32, ____, ____, ____, 76 b. 4321, 4311, 4301, ____ 2. Review Skip Counting. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 3 (See Lesson Guide, p. 26) 2. Generalization How do you differentiate odd numbers from even numbers? Application Write odd or even on the blank before each number. ____ 1. 3104 ____ 2. 263 ____ 3. 5778
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Ring all even numbers and box all the odd numbers 1. 476 2. 1263 3. 7000 Answer each question 1. If n is an odd number and p is an even number, then p + p + n = ____
V.
10
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Give the common factor of a given number. Find the greatest common factors of given numbers. Psychomotor: Compute the GCF of given numbers using any method. Affective: Show cooperation with the group in finding factors. Finding the greatest common factor of given numbers. Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.2 Materials : Concrete objects, number cards Value: Cooperation A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Mental drill on Odd and Even numbers 2. Review Factorization Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 3 (See Lesson Guide, p. 28-29) 2. Generalization What are the methods of finding GCF of numbers? Application Give all the factors of each number. Then box the GCF. 1. 4=? 2. 12 = ? 8=? 30 = ? 20 = ?
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Express each number as a product of its prime factors. Find the GCF. 1. 18 = ? 2. 12 = ? 27 = ? 18 = ? GCF = ? 24 = ? GCF = 3. 24 = ? 30 = ? 36 = ? GCF = ? Answer each question 1. If the GCF of two numbers is 36, what are some of the prime factors of each number?
V.
11
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Identify prime and composite numbers. Psychomotor: Manipulate the given objects as directed. Affective: Appreciate the importance of little things/objects around us. Identifying Prime and Composite Numbers Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.3 Materials: pocket chart, models, cut outs Value: Cooperation A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Game 2. Review Factors of a Number 3. Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 32) Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 2 (See Lesson Guide, p. 32) 2. Generalization What are prime numbers? Composite numbers? Application List all the factors of each number. Then encircle the number if it is prime. 1. 48 2. 36 3. 53
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Write P if the number is prime and C if composite. _____ 1. 28 _____ 2. 36 _____ 3. 21 Answer the questions. 1. Name the prime numbers between 1 and 50. 2. Name the composite numbers between 50 and 100.
V.
12
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Find the prime factors of a number. Psychomotor: Write the prime factors of a given number correctly. Affective: participate actively in the discussion. Finding the prime factors of a number Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.4 Materials : Chart, flashcards Value: Alertness A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill a. What is twice the product of 4 and 5? 2. Review Tell whether the following numerals are prime or composite. a. 17 b. 3 c. 5 3. Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 35) Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 2 (See Lesson Guide, p. 36) 2. Generalization How do you find the prime factors of a number?
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Application Find the prime factors of these numbers using any method 1. 30 2. 28 3. 24 Give the prime factors of the following number using any method. 1. 78 2. 80 3. 48 Write the prime factors of the following. 1. 84 2. 60 3. 90
V.
13
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. Cognitive: Identify multiples of a given numbers. Psychomotor: Write numbers legibly Affective: Demonstrate willingness in doing group activities. Identifying multiples of given numbers. Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.5 Materials: Chart, flashcards Value: Willingness to join in group activities. A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Game: Treasure Hunting 2. Review Find the prime numbers of these numbers. a. 60 b. 34 c. 150 3. Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 38) Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 39) 2. Fixing Skills List down the first 5 multiples of each pair of numbers. 1. 50 3. 20 15 40 2. 30 50 3. Generalization How do identify multiples of given numbers? Application Encircle the numbers that are not multiple of the number at the left. 1. 11 (22, 37, 44, 55, 66, 78) 2. 13 (36, 26, 39, 52, 64, 78)
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Put a check under a number at the top if the number at the left is a multiple of it. 8 1. 96 2. 117 3. 72 4. 105 5. 90 9 7 6 12 15 13
V.
Answer the following. 1. Find five multiples of 9 with a sum of 9. 2. Find two multiples of 12 with a sum of 9.
14
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ___________________ I. II. Show multiples of a number by 10, 100 Find the least multiple of a set of numbers. Value: Willingness to join group activities Showing multiples of a given number by 10, 100 Finding the least common multiples of a set of numbers Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.5 Materials : old calendar, number cards A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Drill on finding prime and composite numbers. (Distribute old calendars) 2. Checking of Assignment 3. Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 38) B. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 39) Application List down the first five multiples of each pair of numbers and then circle their LCM 1. 50 __ __ __ __ __ 15 __ __ __ __ __
III.
C.
IV.
V.
Give the LCM of each pair of numbers. 1. 6 and 9 2. 10 and 20 3. Express each number as a product of prime factors. Then find the LCM. 1. 18 , 36 2. 12 , 30
15
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: Find the least common multiple of a set of numbers Psychomotor: Write the multiples and least common multiple of a set of numbers. Affective: Work cooperatively with the other members of the group. Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of a set of numbers Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.6 Materials : flashcards, ruler Value: Cooperation A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Drill on giving numbers in sequence. 0, 3, 6, 9 , ___, ___, ___ 2. Review Find the GCF of the following using the prime factorization. a. 24 and 36 b. 15 and 40 c. 12 and 24 3. Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 41) Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 1(See Lesson Guide, p. 42) 2. Generalization What is the least common multiple (LCM) of a set numbers? Application Give the least common multiple (LCM). 1. 6 and 8 2. 3 and 6 3. 10 and 4
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Name the LCM of these set of numbers. 1. 12, 18, 36 2. 8, 12, 18 3. 8, 12, 16 Find the LCM of these sets of numbers 1. 8, 12, 30 2. 12, 20, 45
V.
16
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: State divisibility rules for 2, 5, and 10 Classify numbers as divisible by 2, 5 and 10. Psychomotor: Post the corresponding number in the correct place in Venn diagram. Affective: Participate actively in class discussion. State Divisibility Rules of 2, 5, 10 Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.7 Materials: flashcards, ruler Value: Active participation A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill 126 3 = n 522 6 = n 2. Review Give at least 5 multiples of the following numbers. a. 4 b. 3 c. 5 Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 45)
II.
III.
3. B.
Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 45-46) 2. Generalization Recall the divisibility rules for 2, 5 and 10. Application Write on the blank before each item whether the given number is divisible by 2, 5, or 10. _______ 1. 16 _______ 2. 125
C.
IV.
Put a check under each corresponding column to identify whether each given number is divisible by 2, 5, 10 2 1. 120 2. 405 5 10
V.
Put a check on the blank if the first number is divisible by the second number. X if not. 1. 864 , 2 _____ 2. 606 , 10 _____
17
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: State divisibility rules for 3, 6, and 9 Classify numbers as divisible by 3, 6 and 9. Psychomotor: Put check marks under corresponding column where divisibility rules apply. Affective: Participate actively in class discussion. State Divisibility Rules of 3, 6, and 9 Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.7 Materials : flashcards, Venn Diagram Value: Active participation A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Divide mentally 366 6 = n 148 2 = n 2. Review Encircle the number(s) which are exactly divisible by the given number before each item. 2 a. 17, 16, 20, 15 10 b. 40, 14, 25, 300 Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 48)
II.
III.
3. B.
Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 48) 2. Generalization Recall the divisibility rules for 3, 6 and 9. Application Put a check under the correct column applying the rules for divisibility. 3 6 9 120 315
C.
IV.
Identify if the number is divisible by 3. 6, or 9. Write on the blanks. 1. 630 ____ 2. 363 ____ 3. 423 ____ Encircle the numbers, which are divisible by the given number before each item. 3 1. 54, 26, 346, 84 5 2. 65, 299, 846, 627
V.
18
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: State divisibility rules for 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, and 10 Classify numbers as divisible by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, and 10 Psychomotor: Form numbers satisfying given conditions. Affective: Participate actively in class discussion. State divisibility rules for 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, and 10 Reference: BEC PELC I.A 5.1.7 Materials : flashcards, ruler Value: Active participation, teamwork A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill On easy division (Mental Computation) 488 8 = n 279 3 = n 2. 3. B. Review Have the pupils recall the divisibility rules taken so far. Checking of assignment. Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 50-51)
II.
III.
Developmental Activities 1. Presentation (See Lesson Guide, p. 51) 2. Generalization Recall the divisibility rules for 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9 and 10. Application Write on the blank before each item whether the given number is divisible by 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, and 10 _______ 1. 423 _______ 2. 5746 _______ 3. 3000
C.
IV.
Encircle 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 9, and 10 if the number is divisible by these numbers 1. 702 2 3 4 5 6 9 10 2. 1632 2 3 4 5 6 9 10 Put a check under each column where divisibility rules apply. 2 3 4 5 6 9 532 4554 249 10
V.
19
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: Visualize changing dissimilar fractions to similar fractions. Rename dissimilar fractions to similar fractions. Psychomotor: Illustrate or match fractions equal to a given pair of dissimilar fractions. Affective: Demonstrate helpfulness at all times by helping with the household chores. Visualize changing dissimilar fractions to similar fractions. Renaming dissimilar fractions to similar fractions. Reference: BEC PELC II.A 1 Materials : fraction cards, charts Value: Helpfulness, active participation in class activities A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Drill in finding the LCM of given numbers. 2. Review Identifying pairs of equivalent fractions. Checking of assignment. 3. Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 55) Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 1 (See Lesson Guide, p. 55-56) 2. Generalization How do we rename dissimilar fractions to similar fractions? Application Rename these dissimilar fractions to similar fractions. 1. 3/10 , 4/6 2. 5/8 , 3/4
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
Write as similar fractions 1. 2/8 , 3/10 2. 2/9 , 2/4 3. 4/10, 5/12 Rename these dissimilar fractions as similar fractions. 1. 6/8 , 2/12 2. 3/20 , 4/10 3. 7/8, 3/5
V.
20
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: Identify equal fractions. Use cross product to determine whether 2 fractions are equal. Psychomotor: Write the cross product of a given pair of fractions. Affective: Appreciate things receive. Identifying Equal Fractions. Using cross product to determine whether 2 fractions are equal. Reference: BEC PELC II.A 1.2 and 1.2.1 Materials : flashcards, fractional kit Value: Positive attitude towards sharing. A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Drill on basic multiplication facts 2. Review Answer the following. Luz and Noemi were both given one pizza by their cousin. Luz ate of her pizza while Noemi ate 5/7 of hers. Who ate more pizza? 3. Motivation (See Lesson Guide, p. 59) Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 1 (See Lesson Guide, p. 59-60) 2. Generalization How do we identify equal fractions? Application Check if the fractions are equal, use the cross product method. Then write equal or not equal. 1. 3/8 , 2/5 _______ 2. , 2/3 ______
II.
III.
B.
C.
IV.
On the blanks before each number, write YES if the pair of fractions are equal and NO if not. ___________ 1. 2/8 , 3/10 ___________ 2. , 3/12 ___________ 3. , 3/6 Write the missing numerator And denominator to make the statement correct. 1. 2 ___ 2. 1 _7 3 = 12 4 =
V.
21
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: Change fractions to lowest terms or higher terms. Psychomotor: Illustrate the process of changing fractions to lowest terms. Affective: Demonstrate diligence in doing ones schoolwork. Changing Fractions to lowest or Higher terms Reference: BEC PELC II.A 1.3 Materials : Activity sheets, cartolina strips Value: Diligence A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill Drill on basic division facts 2. Review Find the GCF of the following pairs of numbers. a. 24, 6 b. 64, 24 3. Motivation Do you love to eat cake? What kind of cake do you want to eat? B. Developmental Activities 1. Presentation Strategy 1 (See Lesson Guide, p. 63) 2. Generalization How do we change fractions to lowest terms? When do we say that a fractions is in its lowest terms? Application Box the fraction in the higher term. Transform them in the lowest terms. 1. 3/7 2. 3/9 3. 9/10
II.
III.
C.
IV.
V.
Reduce the following to lowest term. 1. 16/20 2. 14/28 3. 21/24 Complete the set of fractions 1. 1/3 , __/6 , __/9
22
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: Change fractions to lowest terms or higher terms. Psychomotor: Illustrate the process of changing fractions to lowest terms Affective: Demonstrate diligence in doing ones schoolwork. Changing Fractions to lowest or Higher terms Reference: BEC PELC II.A 1.3,Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp.68-73 Materials: Activity sheets, cartolina strips Value: Diligence 1. Drill on basic division facts 2. Review on finding the GCF Find the GCF of the following pairs of numbers. 1. 24 and 6 2. 64 and 24 3. Do you love to eat cake? What kind of cake do you want to eat? 1. Refer to Lesson Guide pp. 69-70 2. a. Give three fractions equivalent to the given 1. 3/7 _______, _________, ____________ 2. 3/9 _______, _________, ___________ b. Reduce the following fractions to their lowest term. 1. 5/15 _______ 2. 21/28 ________ 3. How do we change fraction to lowest terms? When do we say a fraction is in the lowest term? How can we identify fraction in its lowest term? Reduce the following to lowest term 1. 16/20 2. 14/28 3. 8/24 (See Lesson Guide pp72-73) A. B. Encircle the fraction which does not belong to the group. 1. 7/14 6/9 8/16 2. 3/7 1/3 5/15 4/12 Give the GCF of each fraction, then change fractions to its lowest terms. 1. 2/4 = ______ = ______ 2. 5/15 = ______ = ______ 3. 4/12 = ______ = ______
II.
III. A.
B.
IV.
V.
23
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: Estimate fractions close to 0, , or 1 Psychomotor: Draw regions and/or construct number lines to aid in estimation. Affective : Demonstrate proper attitude in winning or losing a game/contest. Estimating Fractions close to 0, , or 1 Reference: BEC PELC II.A. 2, Lesson Guide in Mathematics, pp. 73 - 78 Materials: flashcards, number line Values: Sportsmanship Drill on rounding off whole numbers Review in comparing fractions. (Group Activity) See Lesson Guide p74. Refer to Lesson Guide pp. 75-76 Round the fraction to 0, , or 1 a. 9/12 b. 7/8 c. 2/15 In estimating fractions, what are things we have to consider in numerators and denominators? Do you get a closer estimate if you round a mixed number to the nearest half or to a whole number? Explain Suppose you round down to , and your friend rounds to 1. Explain why both answers are reasonable.
II.
III. A. 1. 2. B. 1. 2.
3. C. 1. 2. IV.
Estimate the following fractions if they are close to 0, , 0r 1. Write the correct estimate on the blank. 1. ________ 2. 5/12 _______ 3. 11/13 _______ 1. 2. Draw a number line showing 1/12 to 12/12 on an illustration board or cartolina. List the fractions that are close to 0 , , 0r 1
V.
24
Lesson Plan in Mathematics V Date: ____________________ I. Cognitive: Add two to four similar fractions Psychomotor: Write the sum of the given similar factions Affective: Show proper care of ones belongings Adding two to four Similar Fractions with or without regrouping Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.1 Lesson Guide in Mathematics, pp. 79-83 Materials: Fraction cards, regions Values: Proper care of ones belongings
II.
III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on changing improper fractions to mixed number and vice versa. 2. Put a * before the number if the fraction is in the lowest terms. Simplify if it is NOT. ______ a. 9/11 ______ b. 4/6 ______ c. 7/8 3. Present the problem Trina used 3/8 m of plastic to cover her art portfolio and 2/8 m for her notebooks. How many meters of plastic cover did she use? What kind of pupil is Trina? Why is it important to take care of your things? B. 1. Refer to Lesson Guide pp. 80-82 2. Find the sum. Reduce the answers to lowest term. a. 13/30 + 5/20 b. 6/14 + 2/14 c. 2/9 + 4/9 + 1/9 3. How do you add 2 or more similar fractions? C. Find the sum. Simplify if possible. 1. You finished 1/8 of a drawing on Tuesday and 3/8 more on Wednesday. How much of the drawing did you finished? 2. A weather report states that cm of water fell on Saturday and the same amount on Sunday. How much rainwater fell on the two days? IV. Find the sum. Reduce answers to simplest form. 1. + = ________ 2. 4/8 + 1/8 = _______ 3. 8/10 + 3/10 = _______ Find the sum and give the answer in simplest form 1. 2/5 + 8/5 + 3/5 2. 11/12 + 2/12 + 1/12 3. 2/7 + 5/7 4. 4/15 + 1/15 + 5/15 5. 5/9 + 2/9 + 4/19
V.
25
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive : Visualize addition of dissimilar fractions without and with regrouping Psychomotor : Illustrate addition of dissimilar fractions Affective : Work harmoniously with others. II. Visualizing addition of dissimilar fractions without and with regrouping Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.2 , Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 83 - 90 Materials : Fraction cards, regions, game boards, fraction chart Values: Peace and Harmony III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on giving the LCM of given numbers 2. Review on adding similar fractions using board games (See Lesson guide pp. 84-85) 4. If you are going to combine the following musical notes ; one eight note, one quarter note and one half note, what is the combined value ? B. 1. Refer to Lesson Guide pp. 86-88 2. Use models to find the sum. Reduce the answers to lowest term. a. + 2/3 b. 3/8 + c. + 1/3 d. What is the addition sentence for the diagram below? + =
3. How can we better understand addition of dissimilar fractions? C. Application. 1. If you add two fractions whose denominators are 4 and 5, what denominator will their sum have? Write and illustrate an example an example using models. 2. How would you illustrate this, two s and three 1/3 s make a total of what number IV. Use diagrams or fraction regions to add the following. 1. 2/3 + 1/4 = ________ 2. 2/6 + 1/3 = _______ 3. 3/8 + 1/3 = _______ V. Find the sum of the following using diagrams. 6. 2/5 + 1/3 + 4/6 7. 1/12 + 2/6 + 1/3 8. 2/7 + 5/6 9. 2/15 + 1/5 + 3/10 10. 1/3 + 2/7 + 4/2
26
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive : Visualize addition of dissimilar fractions without and with regrouping Psychomotor : Illustrate addition of dissimilar fractions Affective : Work harmoniously with others. II. Visualizing addition of dissimilar fractions without and with regrouping Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.2 , Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 83 - 90 Materials : Fraction cards, regions, game boards, fraction chart Values: Peace and Harmony III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on giving the LCM of given numbers 2. Review on adding similar fractions using board games (See Lesson guide pp. 84-85) 5. If you are going to combine the following musical notes ; one eight note, one quarter note and one half note, what is the combined value ? B. 1. Refer to Lesson Guide pp. 86-88 2. Use models to find the sum. Reduce the answers to lowest term. a. + 2/3 b. 3/8 + c. + 1/3 d. What is the addition sentence for the diagram below? + =
3. How can we better understand addition of dissimilar fractions? C. Application. 1. If you add two fractions whose denominators are 4 and 5, what denominator will their sum have? Write and illustrate an example an example using models. 2. How would you illustrate this, two s and three 1/3 s make a total of what number IV. Use diagrams or fraction regions to add the following. 1. 2/3 + 1/4 = ________ 2. 2/6 + 1/3 = _______ 3. 3/8 + 1/3 = _______ V. Find the sum of the following using diagrams. 1. 2/5 + 1/3 + 4/6 2. 1/12 + 2/6 + 1/3 3. 2/7 + 5/6 4. 2/15 + 1/5 + 3/10 5. 1/3 + 2/7 + 4/2
27
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add dissimilar fractions. Psychomotor: Illustrate the steps in adding dissimilar fractions. Affective ; Form the habit of being obedient II. Adding Dissimilar Fractions Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.3, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 90-94 Materials : Fraction cards, regions Values: Obedience III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on finding the LCM of given numbers 2. Review on finding the LCM through the decomposition method 3. Faith ate 3/6 of pizza . mark ate 2/12 of the same pizza. How many 5 parts of the pizza did they eat? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide pp91-92 2. Find the sum + =
3. How do we add dissimilar fraction? C. Application 1. There are different musical notes. There are notes and 1/8 notes . How long will the sound be if two notes and three 1/8 notes are played? 1. If you sleep 8 hours in a 24-hour day and take a 2-hour nap, what fraction of the day have you been asleep? IV. Rename each fractions as similar fractions. Add then express the sum in lowest terms if possible? 1. 2/8 + = 2. 5/8 + = 3. 6/10 + = V. Find the sum and if necessary reduce the answer to its lowest form. 1. 3/6 + 4/10 = 2. 6/12 + 5/9 = 3. 6/15 + 7/10 = 4. 2/10 + = 5. 5/9 + 10/15 =
28
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add dissimilar fractions. Psychomotor: Illustrate the steps in adding dissimilar fractions. Affective ; Form the habit of being obedient II. Adding Dissimilar Fractions Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.3, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 90-94 Materials : Fraction cards, regions Values: Obedience III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on finding the LCM of given numbers 2. Review on finding the LCM through the decomposition method 3. Faith ate 3/6 of pizza . mark ate 2/12 of the same pizza. How many 5 parts of the pizza did they eat? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide pp91-92 2. Find the sum + =
3. How do we add dissimilar fraction? C. Application 1. There are different musical notes. There are notes and 1/8 notes . How long will the sound be if two notes and three 1/8 notes are played? 2.If you sleep 8 hours in a 24-hour day and take a 2-hour nap, what fraction of the day have you been asleep? IV. Rename each fractions as similar fractions. Add then express the sum in lowest terms if possible? 1. 2/8 + = 2. 5/8 + = 3. 6/10 + = V. Find the sum and if necessary reduce the answer to its lowest form. 1. 3/6 + 4/10 = 2. 6/12 + 5/9 = 3. 6/15 + 7/10 = 4. 2/10 + = 5. 5/9 + 10/15 =
29
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add dissimilar fractions and whole numbers. Psychomotor: Write the answer in a number sentence through the aid of visual representation Affective ; Appreciate the importance of putting up a small income-generating project II. Adding Dissimilar Fractions and Whole Numbers Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.4, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 94-98 Materials : Fraction cards, regions, cut-outs Values: Industry III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on finding the LCD of given numbers. 2. Review on changing dissimilar fractions as similar fractions. 3. Who among you have tasted sweet tamarind candies? Do you have an idea what ingredients they have? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 95-97 2. Find the sum 4 + 6 + 2/3 + 5/10 + 3/6 + 15 3. How do we add dissimilar fraction and whole numbers? C. Application 1. Lynette walked 2/3 km on Friday, 3/4 km on Saturday and 1 km on Sunday. What is the total distance she walked? 2. Three hamsters were weighed by a veterinarian. 3/5 kg, 2/3 kg, and 2 kg. Give the total weight. IV. Add. Express the answers in lowest terms. If possible. 1. 2/8 + + 3 + 4= 2. 5 + 5/8 + = 3. 8 + 5 + 6/10 + = V. Find the sum and if necessary reduce the answer to its lowest form. 1. 8 + 10 + 3/6 + 4/10 = 2. 6/12 + 5/9 + 6 + 4 = 3. 18 + 2 + 6/15 + 7/10 = 4. 7 + 2 + 3 + 2/10 + = 5. 12 + 2 + 5/9 + 10/15 =
30
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add dissimilar fractions and whole numbers. Psychomotor: Write the answer in a number sentence through the aid of visual representation Affective ; Appreciate the importance of putting up a small income-generating project II. Adding Dissimilar Fractions and Whole Numbers Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.4, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 94-98 Materials : Fraction cards, regions, cut-outs Values: Industry III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on finding the LCD of given numbers. 2. Review on changing dissimilar fractions as similar fractions. 3. Who among you have tasted sweet tamarind candies? Do you have an idea what ingredients they have? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 95-97 2. Find the sum 4 + 6 + 2/3 + 5/10 + 3/6 + 15 3. How do we add dissimilar fraction and whole numbers? C. Application 1. Lynette walked 2/3 km on Friday, 3/4 km on Saturday and 1 km on Sunday. What is the total distance she walked? 2. Three hamsters were weighed by a veterinarian. 3/5 kg, 2/3 kg, and 2 kg. Give the total weight. IV. Add. Express the answers in lowest terms. If possible. 1. 2/8 + + 3 + 4= 2. 5 + 5/8 + = 3. 8 + 5 + 6/10 + = V. Find the sum and if necessary reduce the answer to its lowest form. 1. 8 + 10 + 3/6 + 4/10 = 2. 6/12 + 5/9 + 6 + 4 = 3. 18 + 2 + 6/15 + 7/10 = 4. 7 + 2 + 3 + 2/10 + = 5. 12 + 2 + 5/9 + 10/15 =
31
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add whole numbers and mixed forms. Psychomotor: Illustrate addition of whole numbers and mixed forms through a diagram. Affective : Budget ones time wisely. II. Adding Whole Numbers and Mixed Forms Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.5, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 99-103 Materials : , regions, cut-outs, cartolina , pair of scissors Values: Spending time wisely III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on changing fractions to simplest form. 2. Review on adding mixed forms and similar fractions. 3. Game: Cooperative work B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 99-101 2. A. Find the sum. Simplify if possible. a. 1 4/9 + 3 1/3 + 4 b. 6 + 4 + 3 B. Draw diagrams to illustrate the following. a. 2 + 1 + 2 2/3 b. 4 1/3 + 3 + 2 2/3 3. What kind of numbers did we add today ? How do we add mixed forms and whole numbers? C. Application 1. Mang Lando catches 5-kg tuna fish. Mang Andres catches a 8 3/5 yellow-fin fish. Mang Mario catchesa 6 2/5 kg blue-fin fish. What is the total weight of the catches? 2. A mixtures contains 10 cups of egg yolks, 4 cups of milk, 2 2/4 cups of water, and 1 cups of sugar. How many cups will be filled by the mixtures/ IV. A. What addition sentence is shown by the diagram? 1. + _________ B. Add the following: 1. 4 + 2 7/8 = 2. 7 + 5 = V. Illustrate then find the sum. 1. 6 + 3 2/6 = 2. 5 5/9 + 6 + 4 = 3. 18 + 2 7/10 = 4. 3 + 7 2/10 = 5. 12 + 3 5/9 = + ________
32
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add whole numbers and mixed forms. Psychomotor: Illustrate addition of whole numbers and mixed forms through a diagram. Affective : Budget ones time wisely. II. Adding Whole Numbers and Mixed Forms Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.5, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 99-103 Materials : , regions, cut-outs, cartolina , pair of scissors Values: Spending time wisely III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on changing fractions to simplest form. 2. Review on adding mixed forms and similar fractions. 3. Game: Cooperative work B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 99-101 2. A. Find the sum. Simplify if possible. a. 1 4/9 + 3 1/3 + 4 b. 6 + 4 + 3 B. Draw diagrams to illustrate the following. a. 2 + 1 + 2 2/3 b. 4 1/3 + 3 + 2 2/3 3. What kind of numbers did we add today ? How do we add mixed forms and whole numbers? C. Application 1. Mang Lando catches 5-kg tuna fish. Mang Andres catches a 8 3/5 yellow-fin fish. Mang Mario catchesa 6 2/5 kg blue-fin fish. What is the total weight of the catches? 2. A mixtures contains 10 cups of egg yolks, 4 cups of milk, 2 2/4 cups of water, and 1 cups of sugar. How many cups will be filled by the mixtures/ IV. A. What addition sentence is shown by the diagram? 1. + _________ B. Add the following: 1. 4 + 2 7/8 = 2. 7 + 5 = V. Illustrate then find the sum. 1. 6 + 3 2/6 = 2. 5 5/9 + 6 + 4 = 3. 18 + 2 7/10 = 4. 3 + 7 2/10 = 5. 12 + 3 5/9 = + ________
33
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add a mixed form and a dissimilar fraction. Psychomotor: Illustrate the number sentence using models. Affective : Demonstrate love and concern for love ones.. II. Adding Dissimilar fractions and Mixed Forms Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.6, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 104-107 Materials : frcation cards, regions, number line model Values: Thoughtfulness III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on adding dissimilar fractions 2. Review on giving the LCD of 2 or more fractions 3. Cooperative work B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 105-106 2. Find the sum. a. 9 + 1/3 = b. 5 2/10 + = 3. How do we add a mixed form and dissimilar fraction? C. Application 1. Lito harvested 50 2/3 sacks of palay, 25 sacks of corn, and 18 sacks of mango. How many sacks did he harvest in all? 2. Myrna wraps her four gifts. One gift used 3/5 meter of wrapper, another used 1 2/3 m, and the remaining two gifts used 2 m each. How much wrapper was used in all? IV. Add the following. Reduce answers to lowest term. 1. 2 + 3/8 = 2. 1 2/10 + 3/5 = V. Illustrate then find the sum. 1. 3 2/7 + 1/3 = 2. 5 5/9 + = 3. 4 9/16 + = 4. 7 1/12 + 3/8 = 5. 17 3/6 + 3/8 =
34
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add a mixed form and a dissimilar fraction. Psychomotor: Illustrate the number sentence using models. Affective : Demonstrate love and concern for love ones.. II. Adding Dissimilar fractions and Mixed Forms Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.6, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 104-107 Materials : fraction cards, regions, number line model Values: Thoughtfulness III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on adding dissimilar fractions 2. Review on giving the LCD of 2 or more fractions 3. Cooperative work B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 105-106 2. Find the sum. a. 9 + 1/3 = b. 5 2/10 + = 3. How do we add a mixed form and dissimilar fraction? C. Application 1. Lito harvested 50 2/3 sacks of palay, 25 sacks of corn, and 18 sacks of mango. How many sacks did he harvest in all? 2. Myrna wraps her four gifts. One gift used 3/5 meter of wrapper, another used 1 2/3 m, and the remaining two gifts used 2 m each. How much wrapper was used in all? IV. Add the following. Reduce answers to lowest term. 1. 2 + 3/8 = 2. 1 2/10 + 3/5 = V. Illustrate then find the sum. 1. 3 2/7 + 1/3 = 2. 5 5/9 + = 3. 4 9/16 + = 4. 7 1/12 + 3/8 = 5. 17 3/6 + 3/8 =
35
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add mixed forms. Psychomotor: Illustrate how to find the sum of mixed forms using actual objects such as sheets of paper, etc. Affective : Use things wisely and economically. II. Adding Mixed Forms Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.7, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 107-111 Materials : flashcards, show me cards, pieces of art paper, fraction chart Values: Cooperation III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on converting fractions to lowest terms 2. Review on giving the LCD of 2 or more fractions 3. Present the lesson through a Math song B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 108-110 2. Find the sum. Reduce to lowest term if necessary a. 5 + 3 2/6 = b. 3 4/10 +5 = 3. How do we add a mixed forms? C. Application : Answer the following. 1. The base of the sculpture is 1 m. and 2 2/3 m. in height. How tall is the sculpture with the base? 2. Harold dug a hole in the ground 4 3/7 dm. deep. martin continued and made it 8 dm. deeper. How deep was the hole they made? IV. Add the following. Reduce answers to lowest term. 1. 6 3/8 + 3 1/5 = 2. 2 1/7 + 8 = V. Illustrate then find the sum. 1. 16 2/7 + 27 1/3 = 2. 27 5/9 + 18 = 3. 18 9/16 + 25 = 4. 12 1/12 + 16 3/8 = 5. 25 3/6 + 10 3/8 = _________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add mixed forms. Psychomotor: Illustrate how to find the sum of mixed forms using actual objects such as sheets of paper, etc. Affective : Use things wisely and economically. II. Adding Mixed Forms Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.7, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 107-111 Materials : flashcards, show me cards, pieces of art paper, fraction chart Values: Cooperation III. Procedures A. 1. Drill on converting fractions to lowest terms 2. Review on giving the LCD of 2 or more fractions 3. Present the lesson through a Math song B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 108-110 2. Find the sum. Reduce to lowest term if necessary
36
a. 5 + 3 2/6 = b. 3 4/10 +5 = 3. How do we add a mixed forms? C. Application : Answer the following. 1. The base of the sculpture is 1 m. and 2 2/3 m. in height. How tall is the sculpture with the base? 2. Harold dug a hole in the ground 4 3/7 dm. deep. martin continued and made it 8 dm. deeper. How deep was the hole they made? IV. Add the following. Reduce answers to lowest term. 1. 6 3/8 + 3 1/5 = 2. 2 1/7 + 8 = V. Illustrate then find the sum. 1. 16 2/7 + 27 1/3 = 2. 27 5/9 + 18 = 3. 18 9/16 + 25 = 4. 12 1/12 + 16 3/8 = 5. 25 3/6 + 10 3/8 = _________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Estimate sums of fractions. Psychomotor: Make use of wise guesses in estimating sums of fractions. Affective : Estimate properly when a situation demands it. II. Estimating the Sum of Fractions Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.8, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 111- 115 Materials : fraction strips, fraction model and cards Values: Cooperation, health-wise III. Procedures A. 1. Drill: Tell whether each fraction is closer to 0, to or to 1 2. Review addition of fractions 3. Are you fond of eating fruits? Do you frequently buy fruits from the market? What do you observe about the way the vendors weigh fruits? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 112-114 2. Estimate the sum. a. 7/8 + 4/5 = b. 1/5 + 7/8 = 3. How do you estimate the sum of two or more fractions? C. Application : Answer the following. 1. You have 5 5/8 cups of flour. Your sister has 1 1/3 cups of flour to make a cake. Estimate how many cups of flour are there in all? 2. Harold dug a hole in the ground 4 3/7 dm. deep. martin continued and made it 8 dm. deeper. How deep was the hole they made? IV. Estimate the sum 1. 2 3/6 + 5 7/10 = 2. 9 2/4 + 2 7/8 = V. Estimate the sum. 1. 3 2/6 + 4 3/5 = 4. 2 1/12 + 6 3/8 = 2. 15 2/8 + 9 = 5. 5 3/6 + 1 3/8 = 3. 7 2/6 + 5 3/10 = _________________ _________________
37
I. Cognitive: Estimate sums of fractions. Psychomotor: Make use of wise guesses in estimating sums of fractions. Affective : Estimate properly when a situation demands it. II. Estimating the Sum of Fractions Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.8, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 111- 115 Materials : fraction strips, fraction model and cards Values: Cooperation, health-wise III. Procedures A. 1. Drill: Tell whether each fraction is closer to 0, to or to 1 2. Review addition of fractions 3. Are you fond of eating fruits? Do you frequently buy fruits from the market? What do you observe about the way the vendors weigh fruits? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 112-114 2. Estimate the sum. a. 7/8 + 4/5 = b. 1/5 + 7/8 = 3. How do you estimate the sum of two or more fractions? C. Application : Answer the following. 1. You have 5 5/8 cups of flour. Your sister has 1 1/3 cups of flour to make a cake. Estimate how many cups of flour are there in all? 2. Harold dug a hole in the ground 4 3/7 dm. deep. martin continued and made it 8 dm. deeper. How deep was the hole they made? IV. Estimate the sum 1. 2 3/6 + 5 7/10 = 2. 9 2/4 + 2 7/8 = V. Estimate the sum. 1. 3 2/6 + 4 3/5 = 4. 2 1/12 + 6 3/8 = 2. 15 2/8 + 9 = 5. 5 3/6 + 1 3/8 = 3. 7 2/6 + 5 3/10 = _________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Add mentally. Psychomotor: Make use of wise guesses in estimating sums of fractions. Affective : Estimate properly when a situation demands it. II. Estimating the Sum of Fractions Reference: BEC PELC II.B.1.8, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 111- 115 Materials : fraction strips, fraction model and cards Values: Cooperation, health-wise III. Procedures A. 1. Drill: Tell whether each fraction is closer to 0, to or to 1 2. Review addition of fractions 3. Are you fond of eating fruits? Do you frequently buy fruits from the market? What do you observe about the way the vendors weigh fruits? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 112-114 2. Estimate the sum. a. 7/8 + 4/5 = b. 1/5 + 7/8 = 3. How do you estimate the sum of two or more fractions? C. Application : Answer the following. 1. You have 5 5/8 cups of flour. Your sister has 1 1/3 cups of flour to make a cake. Estimate how many cups of flour are there in all?
38
2. Harold dug a hole in the ground 4 3/7 dm. deep. martin continued and made it 8 dm. deeper. How deep was the hole they made? IV. Estimate the sum 1. 2 3/6 + 5 7/10 = 2. 9 2/4 + 2 7/8 = V. Estimate the sum. 1. 3 2/6 + 4 3/5 = 4. 2 1/12 + 6 3/8 = 2. 15 2/8 + 9 = 5. 5 3/6 + 1 3/8 = 3. 7 2/6 + 5 3/10 = _________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Solve word problems involving addition of similar and dissimilar fraction without and with regrouping. Psychomotor: Write the correct number sentence for a problem. Affective : Participate willingly in the school activities. II. Solving word problems involving addition of similar and dissimilar fraction without and with regrouping. Reference: BEC PELC II.B.2.1, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 119-124 Materials : fraction strips, fraction model and cards Values: Cooperation III. Procedures A. 1. Drill: Adding similar fractions using show me board. 2. Review addition of dissimilar fractions 3. Do you join in the school activities and celebrations? What occasions and events do we celebrate in school? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 120-122 2. Analyze then solve. a. May had 2 2/5 of lace. She bought 3 1/5 m of the same kind of lace. How many meters of lace did she have? b. Mother bought three dressed chicken. One weighed 1 1/6 kg, another weighed 1 2/5 kg., and the third weighed 1 3/10 kg. How many kg of chicken did mother buy? 3. Elicit answers for the following questions? 1) How do we solve problems? 2) What are the steps in problem solving? 3) If the fractions involved are dissimilar, what do we do? C. Application : Analyze then solve. 1. You have 5 5/8 cups of flour. Your sister has 1 1/3 cups of flour to make a cake. Estimate how many cups of flour are there in all? 2. Harold dug a hole in the ground 4 3/7 dm. deep. Martin continued and made it 8 dm. deeper. How deep was the hole they made? IV. Read the problem carefully. Write the number sentence then solve.
Sally uses 2 meters of ribbon to decorate one package and 1 meters to decorate another. How much ribbon does she use altogether?
1) Number sentence __________________________ 2) Solution and answer _______________________
Sam painted of the wall while jim painted 1/6 of it. Together , what part of the wall did they paint? 39
1) Number sentence __________________________ 2) Solution and answer _______________________ V. Analyze the problems by answering the given questions.
Grace buys 5 meters of fabric, while Margie buys 3 meters. How many meters of fabric do the two girls buy?
1) 2) 3) 4) What is asked? ___________ What are given? ___________ What is the number sentence? ___________ What is the solution and the answer? ___________
Josh bought 1 kg of peanuts. Jill bought 2 for their retail merchandising project in class. How many kilograms of peanut did they buy in all?
1) 2) 3) 4) What is asked? ___________ What are given? ___________ What is the number sentence? ___________ What is the solution and the answer? ___________
Miss Hernandez bought cloth for her three nieces. If she gave them 1 2/5 m, 2 m, and 1 each, how many meters of cloth did she buy in all?
1) 2) 3) 4) What is asked? ___________ What are given? ___________ What is the number sentence? ___________ What is the solution and the answer? ___________
English takes hour, mathematics 2/3 hour, and Science 1/3 hour. How much time is spent for the three subjects?
1) 2) 3) 4) What is asked? ___________ What are given? ___________ What is the number sentence? ___________ What is the solution and the answer? ___________
Margie bought 10 m of printed cloth and 2 2/5 m of plain white cloth. How many meters of cloth did she buy in all?
1) 2) 3) 4) What is asked? ___________ What are given? ___________ What is the number sentence? ___________ What is the solution and the answer? ___________
_________________ _________________ I. Cognitive: Solve word problems involving addition of similar and dissimilar fraction without and with regrouping. Psychomotor: Write the correct number sentence for a problem. Affective : Participate willingly in the school activities. II. Solving word problems involving addition of similar and dissimilar
40
fraction without and with regrouping. Reference: BEC PELC II.B.2.1, Lesson Guide in Mathematics pp. 119-124 Materials : fraction strips, fraction model and cards Values: Cooperation III. Procedures A. 1. Drill: Adding similar fractions using show me board. 2. Review addition of dissimilar fractions 3. Do you join in the school activities and celebrations? What occasions and events do we celebrate in school? B. 1. Refer to lesson guide p. 120-122 2. Analyze then solve. a. May had 2 2/5 of lace. She bought 3 1/5 m of the same kind of lace. How many meters of lace did she have? b. Mother bought three dressed chicken. One weighed 1 1/6 kg, another weighed 1 2/5 kg., and the third weighed 1 3/10 kg. How many kg of chicken did mother buy? 3. Elicit answers for the following questions? 1) How do we solve problems? 2) What are the steps in problem solving? 3) If the fractions involved are dissimilar, what do we do? C. Application : Analyze then solve. 1. You have 5 5/8 cups of flour. Your sister has 1 1/3 cups of flour to make a cake. Estimate how many cups of flour are there in all? 2. Harold dug a hole in the ground 4 3/7 dm. deep. Martin continued and made it 8 dm. deeper. How deep was the hole they made? IV. Read the problem carefully. Write the number sentence then solve.
Sally uses 2 meters of ribbon to decorate one package and 1 meters to decorate another. How much ribbon does she use altogether?
1) Number sentence __________________________ 2) Solution and answer _______________________
Sam painted of the wall while jim painted 1/6 of it. Together , what part of the wall did they paint?
1) Number sentence __________________________ 2) Solution and answer _______________________ V. Analyze the problems then solve. 1) Grace buys 5 meters of fabric, while Margie buys 3 meters. How many meters of fabric do the two girls buy? 2) Josh bought 1 kg of peanuts. Jill bought 2 for their retail merchandising project in class. How many kilograms of peanut did they buy in all? 3) Miss Hernandez bought cloth for her three nieces. If she gave them 1 2/5 m, 2 m, and 1 each, how many meters of cloth did she buy in all? 4) English takes hour, mathematics 2/3 hour, and Science 1/3 hour. How much time is spent for the three subjects? 5) Margie bought 10 m of printed cloth and 2 2/5 m of plain white cloth. How many meters of cloth did she buy in all? _________________ _________________ I. Visualize subtraction of fraction.
41
Values: Perseverance in ones work II. Visualizing Subtraction of Fraction Reference: BEC PELC II.C.1.1 Materials : Flashcards, concrete objects, fraction cards III. 1. Drill: on identifying fractional parts. 2. Checking of assignment 3. Refer to LP pp. 88-90 4. Show the following sentence on a number line. 1. 8/15 - 3/15 2. 9/11 - 5/11 IV. Draw regions or number line to illustrate the following. Then find the difference. 1. 5/6 2/6 = ________ 2. 7/9 4/9 = ________ V. Illustrate the following equations by drawing fractional regions. 1. 8/7 3/7 = N 2. 5/7 - 1/7 = N _________________ _________________ I. Subtract whole numbers from mixed forms.. Values: Helping parents / elders II. Subtracting whole numbers from Mixed Forms Reference: BEC PELC II.C.1.2 Materials : Flashcards, concrete objects, fraction cards III. 1. Drill: on subtracting whole numbers in patterns. 2. Checking of assignment 3. Refer to LP pp. 91 - 93 4. Subtract the following. Reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 15 2. 26 5/7 - 2___ - 20____ IV. Find the difference then reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 5 2/7 - 1 = ________ 2. 35 - 20 = ________ V. Solve Mila has 13 tomatoes for the vegetable salad. She used 8 tomatoes, how many tomatoes were left? _________________ _________________ I. Subtract mixed numbers from mixed numbers with similar fraction. Values: Thrifty /Economy II. Subtracting mixed numbers from mixed numbers with similar fraction. Reference: BEC PELC II.C.1.3 Materials : Flashcards, concrete objects, fraction cards III. 1. Drill: on subtracting similar fractions. 2. Checking of assignment 3. Refer to LP pp. 93 - 95 4. Perform as indicated. Reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 10 5/6 2. 26 8/11 - 2_1/6_ - 5 3/11
42
IV. Find the difference then reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 27 2/7 - 12 1/7 = ________ 2. 35 12/19 - 20 7/19 = ________ V. Solve Amor weighs 50 1/8 kilos. Marife weighs 36 3/8 kilos. How many kilos heavier is Amor than Marife? _________________ _________________ I. Subtract mixed numbers from mixed numbers with similar fraction. Values: Thrifty /Economy II. Subtracting mixed numbers from mixed numbers with similar fraction. Reference: BEC PELC II.C.1.3 Materials : Flashcards, concrete objects, fraction cards III. 1. Drill: on subtracting similar fractions. 2. Checking of assignment 3. Refer to LP pp. 93 - 95 4. Perform as indicated. Reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 10 5/6 2. 26 8/11 - 2_1/6_ - 5 3/11 IV. Find the difference then reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 27 2/7 - 12 1/7 = ________ 2. 35 12/19 - 20 7/19 = ________ V. Solve Amor weighs 50 1/8 kilos. Marife weighs 36 3/8 kilos. How many kilos heavier is Amor than Marife? _________________ _________________ I. Subtract fractions from whole numbers. Values: Thrifty /Economy II. Subtracting Fractions from Whole Numbers . Reference: BEC PELC II.C.1.4 Materials : Flashcards, concrete objects, fraction cards III. 1. Drill: on subtracting mixed numbers from mixed numbers 2. Checking of assignment 3. Refer to LP pp. 96 - 98 4. Perform as indicated. Reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 10 2. 26 - _1/6_ 3/11 IV. Find the difference then reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 56 5/25 = ________ 2. 28 3/12 = ________ V. Solve Ms. Sison bought 4 gallons of paint. She asked a painter to paint their wall. The painter used gallons. How much paint was left? _________________ _________________ I. Subtract fractions from mixed numbers. Values: Love and concern
43
II. Subtracting Fractions from Mixed Numbers . Reference: BEC PELC II.C.1.5 Materials : Flashcards, concrete objects, fraction cards III. 1. Drill: on subtracting similar fractions 2. Checking of assignment 3. Refer to LP pp. 99 - 102 4. Use the drill boards in subtracting the following 1. 15 3/9 8/9 2. 25 2/8 5/8 IV. Find the difference then reduce answers to lowest terms. 1. 10 4/12 1/12 = ________ 2. 16 - = ________ V. Find the difference. Change to lowest term if possible. 1. 10 1/8 3/8 2. 19 11/12 2/12 _________________ _________________ I. Subtract mixed number from whole numbers. Values: Dignity of labor II. Subtracting Mixed numbers from Whole Numbers . Reference: BEC PELC II.C.1.6 Materials : Flashcards, coins, drawing of soap bars III. 1. Drill: on expressing a whole number as mixed form. 2. Checking of assignment 3. Refer to LP pp. 103 - 105 4. Subtract the following 1. 15 3 8/9 2. 25 20 5/8 IV. Subtract 5 3/7 from the input. Input Output 10 7 13 V. Find the difference. Change to lowest term if possible. 1. 10 7 3/8 _________________ _________________ I. Visualize multiplication of fractions. Values: Neatness, Cooperation II. Visualizing Multiplication of Fraction Ref: BEC-PELC II.D.1.1 Materials: Flashcards, strips of paper III. 1. Drill on multiplying mentally. 2. What is of a whole? 3. Refer to LP pp125-127. 4. Illustrate and find the product. 1. 4/8 x IV. Illustrate and then give the product. 1. 1/3 x = 2. 2/5 x =
44
V. Use paper folding to illustrate the following equations 1. 2/3 x _________________ _________________ I. Find the fractional part of a number. Values: Alertness, active participation II. Find a Fractional Part of a Number Ref: BEC-PELC II.D.1.2 Materials: bottles, strips of paper, pictures III. 1. Drill on naming fraction. 2. Checking of assignment. 3. Refer to LP pp128-129. 4. Find the answer. 1. 5/6 x 20 = N IV. Multiply. Write each answer in lowest term 1. 7/8 x 5 = 2. 3/7 x 21 = V. Find the product. Express your answers to simplest form. 1. 25 x 3/4 = _________________ _________________ I. Find the fractional part of a number. Values: Alertness, active participation II. Find a Fractional Part of a Number Ref: BEC-PELC II.D.1.2 Materials: bottles, strips of paper, pictures III. 1. Drill on naming fraction. 2. Checking of assignment. 3. Refer to LP pp128-129. 4. Find the answer. 1. 5/6 x 20 = N IV. Multiply. Write each answer in lowest term 1. 7/8 x 5 = 2. 3/7 x 21 = V. Find the product. Express your answers to simplest form. 1. 25 x 3/4 = _________________ _________________ I. Translate expressions such as of, 2/3 of, of 1/6 into equation. Values: Cooperation, active participation II. Translating expressions such as of, 2/3 of, of 1/6 into equation. Ref: BEC-PELC II.D.1.2 Materials: flashcards, show me cards III. 1. Drill on visualizing multiplication of fractions. 2. Checking of assignment. 3. Refer to LP pp130-133. 4. Find the answer. 1. of of 1/5 = N 2. of 4/5 of 5/6 = N
45
IV. Multiply. Write each answer in lowest term 1. 1/3 of 2/3 of 3/5 = 2. 2/5 of 5/6 of 3/7 = V. Find the product. Express your answers to simplest form. 1. of 5/8 of 5/9 = 2. of 2/3 of 5/8 = _________________ _________________ I. A. Compare the two quantities using ratio. B. Write ratios in 2 ways C. Appreciate use of ratio in real-life situation. II. Naming and Writing Ratio in Two ways Ref: BEC-PELC II.E. 1.1 1.2 Materials: flashcards, cut-outs, real objects Value : Appreciation for use of ratio III. A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill on reducing fraction to lowest terms as review of previous lesson. Use flashcards (pen-and-paper drill) B. Lesson proper 1. Refer to Strategy 1: Using actual pupils in naming ratio, Lesson Guide pp218-219 2. Fixing Skills: Write a ratio for the following. First as fraction in lowest term and then with the colon (:) a) 12 chairs to 3 tables _________ , ___________ b) 2 pencils for 5 pesos _________ , ___________ 3. Generalization: What is a ratio? What are the two ways of writing ratio? C. Application: Write the ratio in two ways . a. 2 , 8 1. ratio of circles to triangles _____ , _____ 2. ratio of triangles to circles _____ , _____ IV. Write the ratio of the following in 2 ways. 1) 3 books, 5 bags ratio of books to bags 2) 10 candies, 2 chocolate bars ratio of chocolate bars to candies V. Write the following ratios in 2 ways. 1. number of days in a week to the number of months in a year 2. number of hours in a day to the number of hours in a week _________________ _________________ I. A. Compare the two quantities using ratio. D. Write ratios in 2 ways E. Appreciate use of ratio in real-life situation. II. Naming and Writing Ratio in Two ways Ref: BEC-PELC II.E. 1.1 1.2 Materials: flashcards, cut-outs, real objects Value : Appreciation for use of ratio III. A. Preparatory Activities 1. Drill on reducing fraction to lowest terms as review of previous lesson.
46
Use flashcards (pen-and-paper drill) B. Lesson proper 1. Refer to Strategy 1: Using actual pupils in naming ratio, Lesson Guide pp218-219 2. Fixing Skills: Write a ratio for the following. First as fraction in lowest term and then with the colon (:) a) 12 chairs to 3 tables _________ , ___________ b) 2 pencils for 5 pesos _________ , ___________ 3. Generalization: What is a ratio? What are the two ways of writing ratio? C. Application: Write the ratio in two ways . a. 2 , 8 1. ratio of circles to triangles _____ , _____ 2. ratio of triangles to circles _____ , _____ IV. Write the ratio of the following in 2 ways. 1) 3 books, 5 bags ratio of books to bags 2) 10 candies, 2 chocolate bars ratio of chocolate bars to candies V. Write the following ratios in 2 ways. 1. number of days in a week to the number of months in a year 2. number of hours in a day to the number of hours in a week _________________ _________________ I. A. Reduce ratios to lowest terms. B. Write ratios in lowest term. C. Demonstrate love for Mother Earth by recycling. II. Writing ratios in lowest terms, Solving word problems Ref: BEC-PELC II.E. 1.2 and 1.3 , Lesson Guide in Mathematics 5, pp222 - 226 Materials: flashcards, cut-outs, real object Values: Love for Mother Earth by recycling III. A. 1. Drill on reducing fraction to lowest terms. a) 3/9 b) 6/30 2. Review in the definition of ratio and the two ways of writing a ratio (Colon and fraction form. 3. Use patterns to help you complete the table below. Recycling Campaign Number of Bottle 1 2 7 10 15 s (kg) points 5 10 15 60 B. 1. See Activity 1, Lesson Guide pp223-224 2. Express the ratio of the first quantity to the second quantity in simplest form. 1) 12 flowers to 4 vases 2) 21 garbage cans to 14 classrooms 3. How do we reduce ratios to lowest term? (We divide the numerator and denominator by a common factor until the two numbers have the number 1 as the only common factor.
47
C. Express the ratio of the first quantity too the second quantity and reduce to simplest form. 1) 2 teachers to 46 pupils 2) 4 books to 10 students 3) 36 glasses of juice to 30 sandwiches IV. Reduce the ratios to lowest term 1. 10:5 3) 3:12 V. Write the ratios in lowest term. 1. 100 dm 2. 120 min 10 dm 2 hr _________________ _________________ I. A. Reduce ratios to lowest terms. B. Write ratios in lowest term. C. Demonstrate love for Mother Earth by recycling. II. Writing ratios in lowest terms, Solving word problems Ref: BEC-PELC II.E. 1.2 and 1.3 , Lesson Guide in Mathematics 5, pp222 - 226 Materials: flashcards, cut-outs, real object Values: Love for Mother Earth by recycling III. A. 1. Drill on reducing fraction to lowest terms. a) 3/9 b) 6/30 2. Review in the definition of ratio and the two ways of writing a ratio (Colon and fraction form. 3. Use patterns to help you complete the table below. Recycling Campaign Number of Bottle 1 2 7 10 15 s (kg) points 5 10 15 60 B. 1. See Activity 1, Lesson Guide pp223-224 2. Express the ratio of the first quantity to the second quantity in simplest form. 1) 12 flowers to 4 vases 2) 21 garbage cans to 14 classrooms 3. How do we reduce ratios to lowest term? (We divide the numerator and denominator by a common factor until the two numbers have the number 1 as the only common factor. C. Express the ratio of the first quantity too the second quantity and reduce to simplest form. 1) 2 teachers to 46 pupils 2) 4 books to 10 students 3) 36 glasses of juice to 30 sandwiches IV. Reduce the ratios to lowest term 1) 10:5 2) 3:12 V. Write the ratios in lowest term. 1. 100 dm 2. 120 min 10 dm 2 hr
48
_________________ _________________ I. A. Identifying equal ratios. Find the missing term in equal ratios. B. Write equal ratios in two ways C. Appreciate the value of good nutrition to ones health II. Identifying Equal Ratio Ref: BEC-PELC II.E. 1.4, Lesson Guide in Mathematics 5 , pp227-231 Materials: pictures Values: Appreciating the value of proper nutrition III. A. 1. Drill on naming ratios. a) 5 red cars, 6 white cars b) 3 handbags , 4 hats 2. Review on reducing ratios to lowest terms. a) 4: 12 b) 10:16 3. Do you know how to cook? What recipes can you cook? B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide pp228 2. Solve for the missing term in each pair of ratios. a) 8/n = 14/45 b) 5/7 = n/35 3. When are the ratios equal? How can we build sets of equal ratios? C. Complete the table to build set of equal ratios. Petals 5 20 Leaves 12 IV. Identify equal ratio. Write yes or no on the blank. 1. 3:4 = 12:16 _______ 2. 3:2 = 6:4 _______ V. Give three or more equal ratios for each. 1. 2:5 2. 2:14 _________________ _________________ I. A. Rename in decimal form fractions whose denominators are powers of ten and vice versa. B. Write in decimal form fractions whose denominators are powers of 10. C. Rename the fractions to decimals accurately. II. Renaming in Decimal form Fractions whose denominators are Powers of 10 Ref: BEC-PELC II.F. 1.1 Materials: charts, grid Values: Accuracy, Alertness, speed III. A. 1. Drill : Mental computation In a group of 10 members , 3 are boys. What is the ratio of the boys to the number of members? If you write this ratio as a fraction, which is the numerator? which is the denominator? 2. Review on writing word fractions into fraction symbols. Fraction Word Fraction Symbols four tenths ____________ six tenths ____________ B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide in Mathematics 5, pp232 - 233 2. Matching type. Match column A with column B _____ 1. eighty-nine thousandths a. 0.890
49
_____2. eight and nine-thousandths b. 0.089 3. How do we determine the number of decimal places when changing fractions to decimals? C. Rename these decimals as fractions. 1) 0.38 2) 0.6 Rename as decimals. 1) 3/10 2) 5/100 IV. A. Express each fraction in decimal form. 1. 3/10 2. 12/100 B. Rename as fractions. 1. 0.25 2. 0.7 V. Express as a fraction with a power of 10 as denominators. 1. 0.0275 2. 0.0002 _________________ _________________ I. A. Identify the place value of each digit of a given decimal. B. Write the place value of each digit in a decimal number. C. Manifest accuracy in giving the place value of the given decimal. II. Giving the Place Value of each digit of a Given Decimal Ref: BEC-PELC II.F. 1.2 , Lesson Guide pp. 237-241 Materials: Place value Chart Values: Accuracy and orderliness III. A. 1. Drill on renaming fractions in decimal form and vice versa a) 2/10 a) 0.35 b) 9/100 b) 0.007 2. Review on place value of whole numbers. a) 345 b) 1,096 3. Matching Game. Refer to p. 238 B. 1. Refer to Strategy 3 , lesson Guide p. 239 2. Give the place value of the underlined digit. 1. 0.146 ____________ 2. 0.614 ____________ 3. How do we determine the place value of digit in a decimal? If you have a number with whole number and decimal part, how will you read it? How will you write it? C. Give the answer. 1) I am a decimal number. My thousandths digit is less than my hundredths digit and 2 less than my tenths digit. What decimal number am I? 2) How many decimal places does two and four hundred seventeen thousandths have? IV. Write the place value of the underlined digit. 1. 0.1867 2. 19.567 V. Write the digit in each place
50
1. 0.34607 a) _________ Hundredths b) _________ Tenths c) _________ Thousandths _________________ _________________ I. A. Identify the place value of each digit of a given decimal. B. Write the place value of each digit in a decimal number. C. Manifest accuracy in giving the place value of the given decimal. II. Giving the Place Value of each digit of a Given Decimal Ref: BEC-PELC II.F. 1.2 , Lesson Guide pp. 237-241 Materials: Place value Chart Values: Accuracy and orderliness III. A. 1. Drill on renaming fractions in decimal form and vice versa a) 2/10 a) 0.35 b) 9/100 b) 0.007 2. Review on place value of whole numbers. a) 345 b) 1,096 3. Matching Game. Refer to p. 238 B. 1. Refer to Strategy 3 , lesson Guide p. 239 2. Give the place value of the underlined digit. 1. 0.146 ____________ 2. 0.614 ____________ 3. How do we determine the place value of digit in a decimal? If you have a number with whole number and decimal part, how will you read it? How will you write it? C. Give the answer. 1) I am a decimal number. My thousandths digit is less than my hundredths digit and 2 less than my tenths digit. What decimal number am I? 2) How many decimal places does two and four hundred seventeen thousandths have? IV. Write the place value of the underlined digit. 1. 0.1867 2. 19.567 V. Write the digit in each place 1. 0.34607 a) _________ Hundredths b) _________ Tenths c) _________ Thousandths _________________ _________________ I. A. Read and write decimals through thousandths. B. Draw models of given decimals C. Be aware of current issues or events that affect our country. II. Reading and Writing Decimals through Thousandths Ref: BEC-PELC II.F. 2 , Lesson Guide pp241-247 Materials: Place value Chart, grid Values: Vigilance to current issues
51
III. A . 1. Drill on expressing fractions as decimals 2/5 2. Review on place value of decimals Write the digit in each place 0.34912 __________ hundredths __________ tenths __________ thousandths 3. Are you all aware of what is happening in our country? Are you aware of the economic situation in the Philippines. B. 1. Refer to Strategy 2, Lesson Guide pp 243-244 2. Write decimals that the teacher will dictate. 1. 267.249 2. 1383.561 3. What are the rules in reading and writing decimals? C. Write the following in words. a) 267.249 b) 1383.561 IV. Based on the given clues, write the correct decimal number for each. 1. 7 in the thousandths 5 in the ones place 8 in the tenths 4 in the tens 2. 9 in the tenths 7 in the thousandths 6 in the hundredths 1 in the ones V. Write the following as fraction and as decimal. 1. One hundred twenty five and one hundredths. 2. Sixty-four and thirty three hundredths. _________________ _________________ I. A. Read and write decimals through thousandths. B. Draw models of given decimals C. Be aware of current issues or events that affect our country. II. Reading and Writing Decimals through Thousandths Ref: BEC-PELC II.F. 2 , Lesson Guide pp241-247 Materials: Place value Chart, grid Values: Vigilance to current issues III. A . 1. Drill on expressing fractions as decimals 2/5 2. Review on place value of decimals Write the digit in each place 0.34912 __________ hundredths __________ tenths __________ thousandths 3. Are you all aware of what is happening in our country? Are you aware of the economic situation in the Philippines. B. 1. Refer to Strategy 2, Lesson Guide pp 243-244 2. Write decimals that the teacher will dictate. 1. 267.249 2. 1383.561
52
3. What are the rules in reading and writing decimals? C. Write the following in words. c) 267.249 d) 1383.561 IV. Based on the given clues, write the correct decimal number for each. 1. 7 in the thousandths 5 in the ones place 8 in the tenths 4 in the tens 2. 9 in the tenths 7 in the thousandths 6 in the hundredths 1 in the ones V. Write the following as fraction and as decimal. 1. One hundred twenty five and one hundredths. 2. Sixty-four and thirty three hundredths. _________________ _________________ I. A. Round decimals to the nearest tenths/ hundredths/ thousandths. B. Round decimals to the nearest tenths/ hundredths/ thousandths. C. Round decimals to the nearest tenths/ hundredths/ thousandths with speed and accuracy. II. Rounding decimals to the nearest tenths/ hundredths/ thousandths. Ref: BEC-PELC II.F. 2.2, Lesson Guide pp 247-251 Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards Values: Speed and Accuracy III. A. 1. Drill on reading decimal numbers. 0.25 0.7483 0.46 0.3912 2. Review on reading and writing decimals. One hundred twenty three thousandths - _________ Four and five ten thousandths - __________ B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1 , Lesson Guide pp.218-219 2. Round off to the underlined digit. 1. 267.249 2. 1383.561 3. What is the rule in rounding off decimal numbers. C. Round off to the underlined digit. 1) 6.450 2) 7.35 3) 0.3892 IV. Round off the following decimals to the nearest place indicated. Tenths Hundredths Thousandths 1. 6.5864 2. 35.0453 V. Round 85.81267 to the nearest place indicated. Tenths ___________ Hundredths ___________ Thousandths ___________ _________________
53
_________________ I. A. Add decimals through thousandths without and with regrouping. B. Write the sum of decimals. C. Add accurately with speed. II. Adding Decimals through Thousandths without or With Regrouping Ref: BEC-PELC II.G. 1.a Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards Values: Speed and Accuracy III. A. 1. Drill on basic addition facts (using flashcards). 2. Review on adding whole numbers (Refer to Strategy 2, pp251) B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide pp. 252 2. Write the following in column then add. 1) 25.17 + 8.23 2) 6.14 + 14.3 1. How do we add decimal numbers? How do we write the addends? Where do we put the decimal point in the sum? C. Write the following in column then add. a) 23.34 + 0.334 b) 4.175 + 52.1 IV. Add 1. 7.32 + 5.21 = n 2. 73.236 + 24.5 = n V. Find the sum. 1. 23.34 + 0.3 2. 0.76 + 0.23 _________________ _________________ I. A. Add decimals through thousandths without and with regrouping. B. Write the sum of decimals. C. Add accurately with speed. II. Adding Decimals through Thousandths without or With Regrouping Ref: BEC-PELC II.G. 1.a Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards Values: Speed and Accuracy III. A. 1. Drill on basic addition facts (using flashcards). 2. Review on adding whole numbers (Refer to Strategy 2, pp251) B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide pp. 252 2. Write the following in column then add. 1) 25.17 + 8.23 2) 6.14 + 14.3 3. How do we add decimal numbers? How do we write the addends? Where do we put the decimal point in the sum? C. Write the following in column then add. a) 23.34 + 0.334 b) 4.175 + 52.1 IV. Add 1. 7.32 + 5.21 = n 2. 73.236 + 24.5 = n V. Find the sum. 1. 23.34 + 0.3 2. 0.76 + 0.23
54
_________________ _________________ I. A. Add decimals through thousandths without and with regrouping. B. Write the sum of decimals. C. Add accurately with speed. II. Adding Decimals through Thousandths without or With Regrouping Ref: BEC-PELC II.G. 1.a Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards Values: Speed and Accuracy III. A. 1. Drill on basic addition facts (using flashcards). 2. Review on adding whole numbers (Refer to Strategy 2, pp251) B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide pp. 252 2. Write the following in column then add. 3) 25.17 + 8.23 4) 6.14 + 14.3 3. How do we add decimal numbers? How do we write the addends? Where do we put the decimal point in the sum? C. Write the following in column then add. c) 23.34 + 0.334 d) 4.175 + 52.1 IV. Add 1. 7.32 + 5.21 = n 2. 73.236 + 24.5 = n V. Find the sum. 1. 23.34 + 0.3 2. 0.76 + 0.23 _________________ _________________ I. A. Subtract decimals through thousandths without and with regrouping. B. Write the difference of decimal numbers. C. Manifest accuracy and speed in subtracting decimals. II. Subtracting Decimals through Thousandths without or With Regrouping Ref: BEC-PELC II.G. 1.b, Lesson Guide pp254 - 257 Values: Speed and Accuracy Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards III. A. 1. Drill on subtracting whole number. 45 - 19= ___ 70 21 = ___ 2. Review on addition of decimals. a) 0.5 + 0.33 + 0.451 = b) 1.85 + 3.056 + 5.03 = B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide pp. 255 2. Find each difference a) 0.4 0.27 = n b) 0.8 0.3 = n 3. What important points did you learn? What should you remember when the minuend has less decimal places than the subtrahend? C. Application :Find the difference a) 0.762 0.36 = b) 0.93 0.642 =
55
IV. Write the following in column then find the difference 1. 0.753 0.54 2. 2.4 - 0.963 = V. Read and solve. 1. Mr. Cruz has a 0.56 hectare land. He allotted 0.198 hectare to build a fishpond. What part of his land is not allotted to his fishpond? 2. What is the difference between 0.83 and 0.622 ? _________________ _________________ I. A. Subtract decimals through thousandths without and with regrouping. B. Write the difference of decimal numbers. C. Manifest accuracy and speed in subtracting decimals. II. Subtracting Decimals through Thousandths without or With Regrouping Ref: BEC-PELC II.G. 1.b, Lesson Guide pp254 - 257 Values: Speed and Accuracy Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards III. A. 1. Drill on subtracting whole number. 45 - 19= ___ 70 21 = ___ 2. Review on addition of decimals. a) 0.5 + 0.33 + 0.451 = b) 1.85 + 3.056 + 5.03 = B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide pp. 255 2. Find each difference a) 0.4 0.27 = n b) 0.8 0.3 = n 3. What important points did you learn? What should you remember when the minuend has less decimal places than the subtrahend? C. Application :Find the difference a) 0.762 0.36 = b) 0.93 0.642 = IV. Write the following in column then find the difference 1. 0.753 0.54 2. 2.4 - 0.963 = V. Read and solve. 1. Mr. Cruz has a 0.56 hectare land. He allotted 0.198 hectare to build a fishpond. What part of his land is not allotted to his fishpond? 2. What is the difference between 0.83 and 0.622 ? _________________ _________________ I. A. Add mixed decimals with regrouping. B. Write mixed decimal addends properly in column. C. Value/ Importance of lining up of decimals points accurately. II. Adding mixed decimals with regrouping Ref: BEC-PELC II.G. 2, Lesson Guide pp257 - 263 Values: Speed and Accuracy Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards III. A. 1. Drill on addition of whole number. 23 + 8= ___ 41 + 26 = ___ 2. Review on adding decimals without or with regrouping. a) 0.5 + 0.33 + 0.451 =
56
b) 1.85 + 3.056 + 5.03 = 3. Game See Lesson Guide p 258 B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide pp. 258-259 2. Find each sum. a) 3.9 + 6.27 = n b) 40.59 + 1.2 = n 3. How do we add mixed decimals with regrouping? C. Application :Add the following. a) 4.38 + 4.79 = b) 2.485 + 4.25= IV. Write the following in column and add. 1. 8.6 + 7.4 + 9.35 = n 2. 4.521 + 1.46 + 2.8 = n V. Find the missing addend or sum. 1. 33.45 + 14.25 = ___ 2. ____ + 174.6 = 211 _________________ _________________ I. A. Subtract decimals through thousandths without and with regrouping. B. Write the difference of the given mixed decimals. C. Subtract mixed decimals with and without regrouping with accuracy. II. Subtracting Decimals through Thousandths without or With Regrouping Ref: BEC-PELC II.G. 2.b Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards Values: Speed and Accuracy III. A. 1. Drill on subtraction from multiples of 10 (Drill cards) 50 27 = 30 16 = 2. Review on subtracting whole numbers without and with regrouping. 2345 763 = 897 189 = B. 1 . Refer to Strategy 1 and 2, LG pp265 266. 2. Find each difference. a) 5.3 1.8 b) 3.28 1.59 3. What should be done when the last two digits from the right of the subtrahend are greater than the minuend? (Regrouping is done) C. Write in column and subtract. 1) Subtract 25.963 from 114.04 2) Take away P 83.12 from P 200. IV. Write the following in column then find the difference 1. 9.99 4.56 = n 2. 41.2 25.731 = n V. Read and solve. 1. If 18.0039 is taken away from 32.2746, what is left? 2. A barangay has a total road length of 184.53 km. If 109.97 km of this had been paved, how much more remains to be paved? _________________ _________________
57
I. Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of decimals including money. Values: Speed and Accuracy II. Solving Word Problems Involving Addition and Subtraction of Decimals Including Money Ref: BEC-PELC II.G. 3.1 Materials: Place value Chart, flashcards, charts III. 1. Drill on addition and subtraction of decimals. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 268-269 4. Solve the following problems 1. A meter measures about 39.37 inches. How much longer is a meter than a yard? IV. Solve the following problems. 1. Ellen has P7.35 while her brother has P4.95 a. How much money do they have? b. How much more money does Ellen have than her brother? V. Read and solve. 1. Mrs. Flores bought 3 chickens, which weighed 2.7 kilos, 1.8 kg and 2.7 kg. What was the total weight? _________________ _________________ I. A. Visualize multiplication of decimals using models. B. Draw and color neatly the decimal models. C. Appreciate the value of clean work. II. Visualizing Multiplication of Decimals Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.1 Materials: flashcards, colored chalk, drawings Values: Keep ones work and work area neat and clean III. A. 1. Drill on addition and subtraction of decimals. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide p 275 2. Use number line to show the product of the following. a) 3 x 0.4 b) 0.5 x 0.8 3. How do we visualize multiplication of decimals? C. Shade the figures to represent each number sentence. 1. 0.8 0.3
IV. Illustrate the following number sentence. 1. 2 x 0.5 = N 2. 0.6 x 0.7 = N V. Show the following multiplication equations by using number lines. 1. 0.3 x 0.6 2. 0.5 x 0.8 _________________ _________________ I. A. Visualize multiplication of decimals using models. B. Draw and color neatly the decimal models. C. Appreciate the value of clean work.
58
II. Visualizing Multiplication of Decimals Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.1 Materials: flashcards, colored chalk, drawings Values: Keep ones work and work area neat and clean III. A. 1. Drill on addition and subtraction of decimals. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, Lesson Guide p 275 2. Use number line to show the product of the following. c) 3 x 0.4 d) 0.5 x 0.8 3. How do we visualize multiplication of decimals? C. Shade the figures to represent each number sentence. 2. 0.8 0.3
IV. Illustrate the following number sentence. 1. 2 x 0.5 = N 2. 0.6 x 0.7 = N V. Show the following multiplication equations by using number lines. 1. 0.3 x 0.6 2. 0.5 x 0.8 _________________ _________________ I. A.Multiply tenths by another tenths. B. Write decimal point in the product correctly. C. Appreciate the beauty of nature. II. Multiplying tenths by another tenths Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.2 Materials: multiplication wheel, 10 by 10 grid Values: Appreciation of the beauty of nature III. A. 1. Drill on basic multiplication facts using the multiplication wheel. 2. Illustrate the number sentence below 1. 3 x 0.5 2. 0.6 x 0.3 3. How many of you have gone to Luneta? Fort Santiago? What do you usually see in these places? B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, p280 2. Give the product . a) 0.5 x 0.2 = n b) 0.9 x 0.4 = n 3. How do we multiply tenths by another tenths? C. Multiply the following decimals 1. 0.8 x 0.3 = n 2. 0.7 x 0.8 = n IV. Copy and place the decimal point in the product 1. 0.7 x 0.5 = N 3. 0.6 x 0.3 = N V. Copy and complete the table. x 0.3 0.4 0.5
59
1 2 3
0.6 0.7 0.8
_________________ _________________ I. A. Multiply hundredths by tenths and vice versa. B. Apply the rule in multiplying decimals. C. Appreciate the value of helping one another. II. Multiplying tenths by another tenths Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.3 Materials: multiplication wheel, 10 by 10 grid Values: Appreciation of the beauty of nature III. A. 1. Drill on basic multiplication facts using the multiplication wheel. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. What can you say about the family in the picture Why do you think the family looks happy? B. 1. See Strategy 1, p283 2. Tell how many decimal places each product will have without actually computing. a) 0.6 x 0.05 _________ b) 0.11 x 0.7 _________ 3. How do we multiply hundredths by tenths? C. Multiply the following decimals 1. 0.48 x 0.3 = n 2. 0.71 x 0.8 = n IV. Multiply and place the decimal point in the product 1. 0.93 x 0.8 = N 2. 0.7 x 0.95 = N V. Write in column then multiply. 1. 0.28 x 0.3 = 2. 0.6 x 0.36 = 3. 2.4 x 0.04 = _________________ _________________ I. Multiply mixed decimals with tenths and hundredths by whole numbers. Values: Working well with others II. Multiplying mixed decimals with tenths and Hundredths by Whole number Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.4 Materials: multiplication wheel, 10 by 10 grid III. 1. Drill on basic multiplication facts using the multiplication wheel. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 185-187 4. Multiply the following decimals 1. 50.04 x 93 = n 2. 10.49 x 6 = n IV. Multiply and place the decimal point in the product 1. 16.57 x 6 = N 2. 38.2 x 7 = N
60
V. Tell whether the decimal point I written on the proper place. Put a check mark to indicate the correct answers, if not, write the correct answer. 1. 2.3 x 2 = 0.46 2. 3.6 x 4 = 14.4 _________________ _________________ I. Multiply mixed decimals by mixed decimals with tenths and hundredths. Values: Health consciousness, accuracy II. Multiplying mixed decimals by Mixed Decimals with Tenths and Hundredths Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.5 Materials: pictures, flashcards, number cards III. 1. Drill on basic multiplication facts using the multiplication wheel. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 187 - 190 4. Copy and place the decimal point in the product. 1. 2.3 x 4.09 = 9407 2. 3.6 x 5.28 = 19008 IV. Multiply and place the decimal point in the product 1. 74.12 x 6.3 = N 2. 5.49 x 4.6 = N V. Find the products. 1. 6.3 x 10.25 = N 2. 18.4 x 35.15 = N _________________ _________________ I. Multiply decimals by 10 and 100. Values: Awareness II. Multiplying Decimals by 10 and 100 Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.5 Materials: pictures, flashcards, number cards III. 1. Drill on basic multiplication of whole numbers by 10, 100, 100 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 190 - 192 4. Give the product orally. 1. 2.147 x 10 = ______ 2. 35.86 x 100 = _______ IV. Multiply. A. 10 x 0.9 _______ B. 100 x 75.46 = ________ 0.6 _______ 4.08 = ________ 0.75 ______ 56.79 = ________ 0.8317 = _______ V. Find the products. 1. 6.3 x 102 = N 2. 18.4 x 103 = N _________________ _________________ I. Multiply decimals by 0.1 , 0.01 and 0.001 Values: Awareness
61
II. Multiplying Decimals by 0.1 , 0.01 and 0.001 Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.7 Materials: pictures, flashcards, number cards III. 1. Drill on multiplying decimals by 10 100 and 1000 mentally 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 192-194 4. Give the product orally using flashcards 0.12 x 0.01 = ______ 0.8 x 0.001 = _______ IV. Multiply the following mentally. 1. 2.8 x 0.1 2. 197.64 x 0.001 3. 35.678 x 0.01 V. Make flashcards showing multiplication of decimals by 0.1 , 0.01 and 0.001 Practice multiplying at home. _________________ _________________ I. Solve word problems involving multiplication of decimals. Values: Accuracy / Spending money wisely II. Solving Word Problems involving Multiplication of Decimals Ref: BEC-PELC II.H.1.8 Materials: pictures, flashcards, number cards III. 1. Drill on multiplying decimals. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 194-196 4. Solve the problem a. Arnel plays volleyball with his friends for 1.9 hours every practice day. How many hours does he play in 5 days? IV. Write the mathematical sentence then solve. 1. Ms. Sison bought 5 bags of refine sugar each weighing 2.5 kilograms. What is the total weight of 5 bags of sugar? V. Solve the following. 1. Ana went to the market. She bought the following: kg of onions at P34.45 a kg kg of tomatoes at P25.25 a kg 1.5 kg of potatoes at P28.30 a kg a. Find the cost of onions b. Find the cost of tomatoes c. Find the cost of potatoes _________________ _________________ I. Divide decimals by whole number. Values: Health consciousness II. Dividing Decimals bu whole Numbers Ref: BEC-PELC II.I. 1.2 Materials: pictures, flashcards, number cards III. 1. Drill on basic division facts. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 199-201
62
4. Find the quotient 1. 3.5 7 = 2. 7.44 18 = IV. Find the quotient 1. 0.207 9 = _____ 1. 2.35 5 = _____ V. Solve the n 1. Solve for N in the equation 0.805 9 = N _________________ _________________ I. Divide the decimals by decimals through hundredths. Values: Punctuality II. Dividing Decimals bu Decimals through Hundredths Ref: BEC-PELC II.I. 1.3 Materials: pictures, flashcards, number cards III. 1. Drill on easy division 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 201 - 204 4. Find the quotient 1. 0.81 0.9 = 2. 0.56 0.7 = IV. Find the quotient 1. 0.207 0.4 = _____ 2. 0.35 0.8 = _____ V. Answer the questions. 1. How many 0.31 meters are there in 96.1 meters? 2. How many 0.12 cm are there in 6.48 cm? _________________ _________________ I. Solve word problems involving division of decimals or whole numbers by decimals Values: Wise spending II. Solving Word problems Involving Division of Decimals and Whole Numbers Ref: BEC-PELC II.I. 2 Materials: pictures, flashcards, number cards III. 1. Drill on dividing decimals by whole numbers in flashcards 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 204-206 4. Solve A group of 31 pupils signed up for a weekend computer course. They paid a total of P315.50. How much did each pupil pay? IV. Read and solve. 1. A 0.60 kg sack of fertilizer was used equally at 0.12 sack per field. How many fields were covered? 2. Mrs. Aldaba bought 5 mangoes for P45.50 . How much did each mango cost? V. Solve 1. Harry used 0.72 of silver were to repair 8 bracelets. How much did he use for each bracelet? _________________ _________________
63
I. Solve word problems involving division of decimals or whole numbers by decimals Values: Wise spending II. Solving Word problems Involving Division of Decimals and Whole Numbers Ref: BEC-PELC II.I. 2 Materials: pictures, flashcards, number cards III. 1. Drill on dividing decimals by whole numbers in flashcards 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 204-206 4. Solve A group of 31 pupils signed up for a weekend computer course. They paid a total of P315.50. How much did each pupil pay? IV. Read and solve. 1. A 0.60 kg sack of fertilizer was used equally at 0.12 sack per field. How many fields were covered? 2. Mrs. Aldaba bought 5 mangoes for P45.50 . How much did each mango cost? V. Solve 1. Harry used 0.72 of silver were to repair 8 bracelets. How much did he use for each bracelet? _________________ _________________ I. Visualize 3-4 sided polygons Draw 3-4 sided polygons. Values: Patience and cooperation II. Visualizing, Identifying, Describing and Drawing 3-4 sided Polygons Ref: BEC-PELC III.I. Materials: cut-outs of 3-4 sided polygons III. 1. Drill on naming angles 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 223-225 4. Identify the following 3-4 sided polygons a. d. b. e. c. IV. Match column A with column B. A _______ 1. It has 4 equal sides and 4 right angles. _______ 2. Three sides are congruent _______ 3. A three sides polygon with two sides equal _______ 4. A four sided polygon with one pair of parallel side. _______ 5. A four sided polygon with 2 pairs of parallel side. a. b. c. d. e. f. B trapezoid parallelogram equilateral triangle isosceles triangle rectangle square B
64
V. Draw the following 1. Equilateral triangle 2. Trapezoid 3. Rhombus _________________ _________________ I. Visualize 3-4 sided polygons Draw 3-4 sided polygons. Values: Patience and cooperation II. Visualizing, Identifying, Describing and Drawing 3-4 sided Polygons Ref: BEC-PELC III.I. Materials: cut-outs of 3-4 sided polygons III. 1. Drill on naming angles 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 223-225 4. Identify the following 3-4 sided polygons a. d. b. e. c. IV. Match column A with column B. A _______ 1. It has 4 equal sides and 4 right angles. _______ 2. Three sides are congruent parallelogram _______ 3. A three sides polygon with two sides equal _______ 4. A four sided polygon with one pair of parallel side. _______ 5. A four sided polygon with 2 pairs of parallel side. V. Draw the following 1. Equilateral triangle 2. Trapezoid 3. Rhombus _________________ _________________ I. Draw 5 or more sided polygons. Values: Cooperation II. Visualizing, Identifying, Describing and Drawing 5 or more sided Polygons Ref: BEC-PELC III.2. Materials: cut-outs of 3-4 sided polygons III. 1. Drill : Identifying geometrical figures. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 226-227 4. Encircle the polygons. Explain why the others are not polygons. a. d. b. e. B a. trapezoid b. c. equilateral d. isosceles e. rectangle f. square
65
c. IV. Name the polygon described. _______ 1. Polygons with 5 sides. _______ 2. Polygon with 8 sides _______ 3. Polygon with 10 sides _______ 4. Polygon with 9 sides _______ 5. Polygon with 7 sides V. Draw the following 1. nonagon 2. dodecagon 3. heptagon _________________ _________________ I. Visualize congruence or similarity of polygons Values: Willingness to do assigned tasks II. Visualizing Congruent or Similarity of Polygons Ref: BEC-PELC III.3. Materials: cut-outs of 3-4 sided polygons III. 1. Drill : Identifying geometrical figures. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review 3. Refer to LP pp. 228-230 4. A. Draw congruent polygons. 1. 2. B. Draw similar polygons 1. 2. IV. Identify if congruent or similar. 1. _______________ 2. V. Draw the following 1. congruent polygons 2. similar octagon _________________ _________________ I. A. 1. Derive a formula for finding the distance around a circle. 2. Find the circumference of a circle in meter and cm. B. Write formula for the circumference of a circle. C. Work cooperatively with the other members of the group II. Deriving a Formula for finding the distance around a circle Ref: BEC-PELC IV.A.1 _______________
66
Materials: circular objects Values: Cooperation III. A. 1. Drill on identifying different kinds of plane figures. Flash models of plane figures.
2. Checking of assignment. / Review Identify the parts of a circle.
3. Let the pupils sing the song about circles. Small Circle, Big Circle B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, lesson guide pp364-365 2. Using 3.14 for , find the circumference of a circle. a) d= 12 cm b) d= 5 cm c) r = 2 m 3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? C.. Application. 1. About how many times as great is the diameter with the circumference? Using 22/7 for , find the circumference of a) r = 2.5 cm b) d = 42 cm c) r = 5 cm IV. Find the circumference of these circles using 3.14 1. 2.
6 cm 7m
2.
V. Draw a diagram to help you solve the problem A. Barry , a puppy , made a path by wailing at the end of his chain, which is 6 meters long. What is the distance around Barrys path. _________________ _________________ I. A. 1. Derive a formula for finding the distance around a circle. 2. Find the circumference of a circle in meter and cm. B. Write formula for the circumference of a circle. C. Work cooperatively with the other members of the group II. Deriving a Formula for finding the distance around a circle Ref: BEC-PELC IV.A.1 Materials: circular objects Values: Cooperation III. A. 1. Drill on identifying different kinds of plane figures. Flash models of plane figures. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review
67
Identify the parts of a circle.
3. Let the pupils sing the song about circles. Small Circle, Big Circle B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, lesson guide pp364-365 2. Using 3.14 for , find the circumference of a circle. a) d= 12 cm b) d= 5 cm c) r = 2 m 3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? C.. Application. 1. About how many times as great is the diameter with the circumference? Using 22/7 for , find the circumference of a) r = 2.5 cm b) d = 42 cm c) r = 5 cm IV. Find the circumference of these circles using 3.14 1. 2.
6 cm 7m
2.
V. Draw a diagram to help you solve the problem Barry , a puppy , made a path by wailing at the end of his chain, which is 6 meters long. What is the distance around Barrys path. _________________ _________________ I. A. 1. Derive a formula for finding the distance around a circle. 2. Find the circumference of a circle in meter and cm. B. Write formula for the circumference of a circle. C. Work cooperatively with the other members of the group II. Deriving a Formula for finding the distance around a circle Ref: BEC-PELC IV.A.1 Materials: circular objects Values: Cooperation III. A. 1. Drill on identifying different kinds of plane figures. Flash models of plane figures. 2. Checking of assignment. / Review Identify the parts of a circle. 3. Let the pupils sing the song about circles. Small Circle, Big Circle B. 1. Refer to Strategy 1, lesson guide pp364-365 2. Using 3.14 for , find the circumference of a circle. a) d= 12 cm b) d= 5 cm c) r = 2 m 3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? C.. Application.
68
1. 2.
About how many times as great is the diameter with the circumference?
Using 22/7 for , find the circumference of a) r = 2.5 cm b) d = 42 cm c) r = 5 cm IV. Find the circumference of these circles using 3.14 1. 2.
10 cm 9m
V. Draw a diagram to help you solve the problem A circular lagoon is 15 meter in radius. If you walk twice around it, How many meters will that be? _________________ _________________ I. A. Find the circumference of a circle in meter and cm. B. Write the formula for the circumference of a circle. C. Observe accuracy in ones work. II. Finding the Circumference a circle Ref: BEC-PELC IV.A.2 Materials: cut outs of different sizes of object Values: Accuracy III. A. 1. Drill on identifying different kinds of polygons. 2. Review on finding the perimeter. a) A rectangle with a length of 12.5 cm. and width of 9.5 cm b) A square whose side is 12.75 m. Review and Identify the parts of a circle. 3. Let the pupils sing the song about circles. Small Circle, Big Circle B. 1. Refer to Strategy 3, lesson guide pp367-368 2. Using 3.14 for , find the circumference of each circle below. 7m 9.5 cm 4.5 cm 15 m
3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? To find the circumference of the circle , use the formula : C = 2r or C = d C.. Application. 1. Find the error. Your friend is finding for the circumference of a circle with a radius of 3 millimeters. Describe and correct the error.
C = d = (314) (3)
2. Find the circumference of the circle described. Tell what the value you used for IV. Find the circumference of these circle using 3.14 with the following radius or diameter. 1. r = 11 m C=?
69
2. d = 2 cm C=? 3. r = 9.5 m C=? V. Complete the table below. Circle Radius A 24 cm B C D 34.5 m
Diameter 40 m 35 cm
Circumference
_________________ _________________ I. A. Find the circumference of a circle in meter and cm. B. Write the formula for the circumference of a circle. C. Observe accuracy in ones work. II. Finding the Circumference a circle Ref: BEC-PELC IV.A.2 Materials: cut outs of different sizes of object Values: Accuracy III. A. 1. Drill on identifying different kinds of polygons. 2. Review on finding the perimeter. a) A rectangle with a length of 12.5 cm. and width of 9.5 cm b) A square whose side is 12.75 m. Review and Identify the parts of a circle. 3. Let the pupils sing the song about circles. Small Circle, Big Circle B. 1. Refer to Strategy 3, lesson guide pp367-368 2. Using 3.14 for , find the circumference of each circle below. 7m 9.5 cm 4.5 cm 15 m
3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? To find the circumference of the circle , use the formula : C = 2r or C = d C.. Application. 1. Find the error. Your friend is finding for the circumference of a circle with a radius of 3 millimeters. Describe and correct the error.
C = d = (314) (3)
2. Find the circumference of the circle described. Tell what the value you used for IV. Find the circumference of these circle using 3.14 with the following radius or diameter. 1. r = 11 m C=? 2. d = 2 cm C=? 3. r = 9.5 m
70
C=? V. Find the circumference of each circle (use = 3.14) 1. r = 16 cm C=? 2. d = 21 cm C=? 3. d = 26 m C=? _________________ _________________ I. A. Solve word problems involving circumference measure. B. Write solutions of word problems C. Participate actively in class activities. II. Solving Word problems involving circumference measure Ref: BEC-PELC IV.A.3 Materials: cut outs of different sizes of object, problem chart Values: Creativity in doing things III. A. 1. Drill on basic multiplication facts using flashcards. 2. Review: Fill in the blanks with the correct answer. a) The distance around a circle is _____________ b) A line that passes through the center of the circle is _____________ 3. Let the pupils sing the song about circles. Small Circle, Big Circle B. 1. Refer to Activity 1, Lesson Guide pp 370-371 2. Solve the following problems. a) What is the circumference of a cylindrical jar 40 cm in diameter? b) A circular table top has a diameter of 35.5 cm. How many lace is needed to decorate the lace? 3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? How do you solve problems on circumference? To find the circumference of the circle , use the formula : C = 2r or C = d C.. Application. 1. Your friend is finding for the circumference of a circle with a radius of 16 cm . What is the circumference? 2. A bicycle tire has a radius of 30 cm. Find the circumference of the tire. IV. Find the circumference of these circle using 3.14 with the following radius or diameter. 1. A circular garden has a radius of 5.5 m. What is the circumference? 2. A manmade lagoon has a radius of 25 m. If you walk thrice around it how many meters will that be? V. Copy and solve the problem. 1. Fredericks bicycle wheel has a diameter of 70 cm. What is the circumference of the wheel? 2. A circle is half the radius of the larger circle. If the radius of the larger circle is 100 meters, what is the : a) radius of the smaller circle b) circumference of the smaller circle _________________ _________________ I. A. Solve word problems involving circumference measure.
71
B. Write solutions of word problems C. Participate actively in class activities. II. Solving Word problems involving circumference measure Ref: BEC-PELC IV.A.3 Materials: cut outs of different sizes of object, problem chart Values: Creativity in doing things III. A. 1. Drill on basic multiplication facts using flashcards. 2. Review: Fill in the blanks with the correct answer. a) The distance around a circle is _____________ b) A line that passes through the center of the circle is _____________ 3. Let the pupils sing the song about circles. Small Circle, Big Circle B. 1. Refer to Activity 1, Lesson Guide pp 370-371 2. Solve the following problems. a) What is the circumference of a cylindrical jar 40 cm in diameter? b) A circular table top has a diameter of 35.5 cm. How many lace is needed to decorate the lace? 3. What is the formula for the circumference of a circle? How do you solve problems on circumference? To find the circumference of the circle , use the formula : C = 2r or C = d C.. Application. 1. Your friend is finding for the circumference of a circle with a radius of 16 cm . What is the circumference? 2. A bicycle tire has a radius of 30 cm. Find the circumference of the tire. IV. Find the circumference of these circle using 3.14 with the following radius or diameter. 1. A circular garden has a radius of 5.5 m. What is the circumference? 2. A manmade lagoon has a radius of 25 m. If you walk thrice around it how many meters will that be? V. Copy and solve the problem. 1. Fredericks bicycle wheel has a diameter of 70 cm. What is the circumference of the wheel? 2. A circle is half the radius of the larger circle. If the radius of the larger circle is 100 meters, what is the : a) radius of the smaller circle b) circumference of the smaller circle
72
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 5 Math Lesson PlanDocument245 pagini5 Math Lesson PlanMaximino Eduardo SibayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 5Document4 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 5Francis Maluntag73% (41)
- Lesson Plan in Grade 4 MathDocument4 paginiLesson Plan in Grade 4 MathJulio Mestidio100% (4)
- A Lesson Plan in Mathematics VDocument3 paginiA Lesson Plan in Mathematics Vdamunchi100% (5)
- Adding Similar Fractions Lesson PLanDocument6 paginiAdding Similar Fractions Lesson PLanWize Dee86% (14)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math v. 2Document11 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math v. 2Alma Reynaldo Tucay54% (13)
- Marjorie Ann Deramas - DLP in Math 4Document2 paginiMarjorie Ann Deramas - DLP in Math 4Marjorie Ann100% (2)
- DLP Demonstration Lesson in Math Iv Q1Document3 paginiDLP Demonstration Lesson in Math Iv Q1EvelynMartinez100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math (Grade 6)Document5 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math (Grade 6)Princess Guia PoyogaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LESSON GUIDE - Gr. 6 Chapter IV - Meter Reading v1.0 PDFDocument21 paginiLESSON GUIDE - Gr. 6 Chapter IV - Meter Reading v1.0 PDFnoronisa talusob100% (4)
- Cot in Math 5Document35 paginiCot in Math 5Yhple Directo100% (1)
- 2013 Grade 4 Math Challenge - Division Level With Answer KeyDocument2 pagini2013 Grade 4 Math Challenge - Division Level With Answer KeyArmi Bernardino50% (2)
- Maths Grade 5 Lesson Plans Term 2Document57 paginiMaths Grade 5 Lesson Plans Term 2Thabo MaforaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 5Document5 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 5MARJUN BARTOLOÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 6Document3 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 6derick0% (1)
- Reflective Lesson Plan 2 Adding and Subtracting DecimalsDocument11 paginiReflective Lesson Plan 2 Adding and Subtracting DecimalsAlfred Cedrix BornelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson PlanDocument5 paginiLesson PlanJam Casan0% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IvDocument5 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Ivcherkarlo100% (1)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics GCF FASTDocument9 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics GCF FASTMarlynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 5 - Uses Divisibility Rules For 2, 5 and 10 To Find Coomon FactorsDocument8 paginiLesson 5 - Uses Divisibility Rules For 2, 5 and 10 To Find Coomon FactorsChris Val86% (7)
- FS Detailed Lesson PlanDocument18 paginiFS Detailed Lesson PlanMeryll83% (6)
- Math K-12 GRADE 5Document12 paginiMath K-12 GRADE 5Mhaye Cendana67% (3)
- Demo For Grade 6Document6 paginiDemo For Grade 6Arwel CaisioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 35 - Adding and Subtracting Similar FractionsDocument15 paginiLesson 35 - Adding and Subtracting Similar FractionsGenevieve MorilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 6 Spatial FiguresDocument5 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Math 6 Spatial FiguresJohnny S. Corrales100% (2)
- Adding Similar Fractions Lesson PLanDocument6 paginiAdding Similar Fractions Lesson PLanWize DeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MDocument4 paginiMMark Jashon Masayon0% (1)
- A Sample Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade FourDocument12 paginiA Sample Lesson Plan in Mathematics Grade FourGuia Marie Diaz Brigino75% (4)
- Lesson Plan On Adding Dissimilar Fractions Without RegroupingDocument3 paginiLesson Plan On Adding Dissimilar Fractions Without RegroupingChristopher Reyes Viernes91% (11)
- Math 6 DLP - Q1Document152 paginiMath 6 DLP - Q1Julius Madayag71% (7)
- Math 4 PDFDocument20 paginiMath 4 PDFalodiamae100% (2)
- DLL Math 6 Q2 Week 4-1Document7 paginiDLL Math 6 Q2 Week 4-1Astro0% (1)
- COT Math Grade 4Document10 paginiCOT Math Grade 4Jasselle Quiapo100% (1)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 6Document5 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics 6Jun Rey Parreño100% (4)
- Daily Lesson Plan in Mathematics 6 Day 1Document2 paginiDaily Lesson Plan in Mathematics 6 Day 1Saniata Yanuaria Gumaru100% (1)
- A Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Math VIDocument4 paginiA Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Math VIAnalyn GirayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plans (Repaired) (Repaired) (Repaired)Document125 paginiLesson Plans (Repaired) (Repaired) (Repaired)Jin BicomongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Greatest Common FactorDocument4 paginiGreatest Common FactorMadel Panes Carlem LptÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics V - WindzDocument6 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics V - WindzWindrell Bagalanon Mongcupa82% (17)
- Lesson Plan Grade 1 Addition of Two Digit NumbersDocument10 paginiLesson Plan Grade 1 Addition of Two Digit NumbersOdie Oronico100% (1)
- Demo For Grade 6Document7 paginiDemo For Grade 6Arwel CaisioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Exemplar: (If Available, Write The Attached Enabling Competencies)Document5 paginiLesson Exemplar: (If Available, Write The Attached Enabling Competencies)Jhem Goronal0% (1)
- Math-5-Greatest Common Factor Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiMath-5-Greatest Common Factor Lesson Planapi-31363677571% (7)
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 5 DemoDocument3 paginiSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Math 5 DemoMark Rafael Pascual100% (1)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IDocument6 paginiSemi-Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics Ijane50% (8)
- Prime and Composite Numbers-EditedDocument5 paginiPrime and Composite Numbers-EditedKim Sumalag100% (1)
- LP GCF SlowDocument8 paginiLP GCF SlowMarlyn100% (1)
- MATH 6 Q2 WEEK 9 Day 1-4 Performs Basic Operations On IntegersDocument81 paginiMATH 6 Q2 WEEK 9 Day 1-4 Performs Basic Operations On IntegersAstro50% (4)
- Math Quarter 1 Week 4-Day 1-5Document86 paginiMath Quarter 1 Week 4-Day 1-5Nelson Valenton100% (1)
- DLP Area of A Circle Math 5 Q4Document4 paginiDLP Area of A Circle Math 5 Q4Emz Mzz100% (2)
- Mathematics Lesson Plan For Grade 6Document8 paginiMathematics Lesson Plan For Grade 6Jupiter BacuadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in Math 6Document5 paginiLesson Plan in Math 6Katie Leigh100% (2)
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics VDocument12 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics VCharina P. BrunoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semi Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics VDocument5 paginiSemi Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics VAldrin Bustarga Alfaro100% (1)
- Demo Lesson Plan MathDocument6 paginiDemo Lesson Plan MathElleiram Arellano100% (1)
- DETAILED LESSON PLAN in MATHDocument17 paginiDETAILED LESSON PLAN in MATHChristy100% (2)
- Solves Routine and Non-Routine Problems Using Data Presented in A Pie Graph - Math 6Document6 paginiSolves Routine and Non-Routine Problems Using Data Presented in A Pie Graph - Math 6THESSA MAE ETINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan MathDocument12 paginiLesson Plan MathAlex BerlinÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR 4 Mathematics 1st 4thDocument230 paginiGR 4 Mathematics 1st 4thGolden SunriseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics VDocument175 paginiMathematics VGodfrey Loth Sales Alcansare Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- 05 Req For QuotationDocument18 pagini05 Req For QuotationRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL Mathematics 6 q4 w4Document9 paginiDLL Mathematics 6 q4 w4Ronan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 RIS MarchDocument9 pagini10 RIS MarchRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tinang ES - Teaching and Non-Teaching TemplateDocument1 paginăTinang ES - Teaching and Non-Teaching TemplateRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 Purchase Req 2017Document20 pagini04 Purchase Req 2017Ronan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Demo ICT Semi Detailed Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiFinal Demo ICT Semi Detailed Lesson PlanRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitoring & EvalDocument8 paginiMonitoring & EvalJudy Panguito AralarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Loyalty Card Application Form (HQP-PFF-108) PDFDocument2 paginiRevised Loyalty Card Application Form (HQP-PFF-108) PDFJason Sylar100% (4)
- BFP RequestDocument3 paginiBFP RequestRonan Sibbaluca100% (2)
- Seminar On Gender and Development GadDocument2 paginiSeminar On Gender and Development GadRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brigada Eskwela 2017: Number of VolunteersDocument4 paginiBrigada Eskwela 2017: Number of VolunteersRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Updated List of Teachers TrainingDocument2 paginiUpdated List of Teachers TrainingRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GAD Accomplishment ReportDocument1 paginăGAD Accomplishment ReportRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monitoring & EvalDocument8 paginiMonitoring & EvalJudy Panguito AralarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rowel Application LetterDocument1 paginăRowel Application LetterRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mati City GADDocument5 paginiMati City GADRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gad DocumentsDocument13 paginiGad DocumentsRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pinpinas Recog ProgDocument3 paginiPinpinas Recog ProgRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Results (2015-2016)Document30 paginiTest Results (2015-2016)Ronan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pinpinas Recog ProgDocument3 paginiPinpinas Recog ProgRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rowel Application LetterDocument1 paginăRowel Application LetterRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cover LetterDocument1 paginăCover LetterRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 4 TG - pp.1-63Document65 paginiEnglish 4 TG - pp.1-63Agni Rudra100% (1)
- Elln ScriptDocument1 paginăElln ScriptRonan Sibbaluca100% (1)
- CulinaryDocument28 paginiCulinaryRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OKRAPIDocument6 paginiOKRAPIRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gad TrainingDocument4 paginiGad TrainingRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cameras VsDocument10 paginiCameras VsRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sip Vargas Es 2015-2018Document9 paginiSip Vargas Es 2015-2018Ronan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home ValuesDocument9 paginiHome ValuesRonan SibbalucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Stage 3 MathsDocument295 paginiKey Stage 3 MathslawrencewoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Project Lesson Plan Template: Name DateDocument4 paginiFinal Project Lesson Plan Template: Name DateAshlee ShiverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reconceptualizing Mathematics 3rd Edition Ebook PDFDocument61 paginiReconceptualizing Mathematics 3rd Edition Ebook PDFsummer.yates61198% (42)
- Translate Phrases To Mathematical Expressions: Answer KeyDocument3 paginiTranslate Phrases To Mathematical Expressions: Answer KeyMarivic EndayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Koerner T.W.-Calculus For The Ambitious-CUP (2014) PDFDocument180 paginiKoerner T.W.-Calculus For The Ambitious-CUP (2014) PDFtitan100100% (16)
- Bethel University Lesson Plan Template: MinutesDocument2 paginiBethel University Lesson Plan Template: Minutesapi-510122073Încă nu există evaluări
- Math ReflectionDocument4 paginiMath Reflectionssooshi85% (27)
- EnVision G4!03!01 AP 2Document2 paginiEnVision G4!03!01 AP 2Rashed NadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- G7 Mathematics-DLL-Q1-W3Document3 paginiG7 Mathematics-DLL-Q1-W3Gim SadolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - ExerciesDocument5 paginiChapter 3 - ExerciesJorge Franco IbañezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge IGCSE Mathematics Core and Extend Coursebook Examination Practice - Written by Nick MacharashviliDocument3 paginiCambridge IGCSE Mathematics Core and Extend Coursebook Examination Practice - Written by Nick MacharashviliNickTheTurtleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6A - Ôn luyện toán T.A - 8.5.2022Document3 pagini6A - Ôn luyện toán T.A - 8.5.2022Đặng Hoàng LâmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co-Teaching Lesson Plan (Inquiry)Document3 paginiCo-Teaching Lesson Plan (Inquiry)api-211261167Încă nu există evaluări
- Math6 q1 Mod7 MultiplicationofDecimals VADocument38 paginiMath6 q1 Mod7 MultiplicationofDecimals VAClyde Ryeanne Revelo100% (3)
- Rocket MathDocument453 paginiRocket MathJunior MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aitchison College Syllabus 2022-23Document18 paginiAitchison College Syllabus 2022-23Salman Jawaid33% (3)
- UIMO OPP Class 02Document45 paginiUIMO OPP Class 02yedidi67% (3)
- MathsStop - Y7Algebra - Teaching SlidesDocument17 paginiMathsStop - Y7Algebra - Teaching Slidesadvick.duaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module1 Ge4 Mmws.y.2022 2023Document19 paginiModule1 Ge4 Mmws.y.2022 2023Jucel May MaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Ks2 Mathematics Mark SchemesDocument36 pagini2018 Ks2 Mathematics Mark SchemesAAÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLC Meeting Minutes-10-31-18Document2 paginiPLC Meeting Minutes-10-31-18api-316781445Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Whole Numbers 2: Mathematics 7Document4 paginiChapter 1 Whole Numbers 2: Mathematics 7RaoJazibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Math Curriculum 2021Document44 paginiRevised Math Curriculum 2021Keith AugustineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Math 7 (2019)Document3 paginiLesson Plan Math 7 (2019)Dhen Velez LargoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 4d: Multiplying 1-To 2-Digit Numbers by 1 000Document19 paginiMathematics: Quarter 2 - Module 4d: Multiplying 1-To 2-Digit Numbers by 1 000Lourdes EjocÎncă nu există evaluări
- ) Mathematics 7: Illustrate The Different Properties of Operations On The Set of IntegersDocument4 pagini) Mathematics 7: Illustrate The Different Properties of Operations On The Set of IntegersClaudette Nicole GardoceÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Properties of Real Numbers ChartDocument1 pagină3 Properties of Real Numbers ChartwlochÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Abacus Japanese Theory and Practice PDFDocument75 paginiAdvanced Abacus Japanese Theory and Practice PDFalrighting619100% (1)
- Intro Solving Graph InequalDocument32 paginiIntro Solving Graph InequalOvidiu Bagdasar DimitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Y6A Practice Book Answers White Rose Maths EditionDocument23 paginiY6A Practice Book Answers White Rose Maths EditionmadajjuanÎncă nu există evaluări