Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Part I: Introduction
Încărcat de
rajap102Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Part I: Introduction
Încărcat de
rajap102Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Part I: Introduction
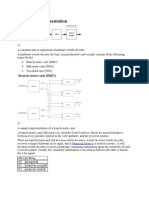
A typical point-to-point digital communication link can be functionally diagramed as
Figure 1: Source encoder aims to reduce the redundancy (without losing any information) or reduce the transmission rate (within a pre-determined distortion level), in the representation of input data sequence. (Topics of Information Theory) Channel encoder is intended to reduce the transmission error rate by inserting redundancy into the input data sequence, or reformatting its input to conform with the constraints of the coding channel. (Topics of Information Theory and Error Correcting Codes) Modulator is a mapping from discrete data sequence to waveform stream. The purpose of modulator/demodulator pair is to eectively transmit (coded or uncoded) discrete data sequences through the noisy transmission channel. - Major functions of demodulator: (a) Symbol waveform synchronization (timing, frequency, phase) (b) Data detection (Soft decision or hard decision) 1
(c) Channel equalization, channel estimation - Notes: (a) If the carrier phase has to be known (or accurately estimated) for data detection, the demodulator is called coherent. If the less accurate estimate of carrier phase is used for data detection, the demodulator is called partially coherent. (b) If the carrier phase is not needed for data detection, the demodulator is called noncoherent. If the previously received symbols are used for phase reference in data detection, the demodulator is called dierentially coherent. - Symbol waveform synchronization and channel estimation are applications of parameter estimation theory, while data detection is a subject of decision theory or sometimes a subject of joint decision and estimation theory. The objectives of this course: (i) Establishing theoretical frameworks for digital demodulation (decision and estimation theories) (ii) Providing fundamentals for data detection. (iii) Understanding digital modulations.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Error-Correction on Non-Standard Communication ChannelsDe la EverandError-Correction on Non-Standard Communication ChannelsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview coding theory and techniques for reliable data transmissionDocument2 paginiOverview coding theory and techniques for reliable data transmissionManal SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Digital Modulation - Jun2019 NewDocument70 paginiChapter 2 Digital Modulation - Jun2019 NewElveronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ref: Data and Computer Communications, William StallingDocument14 paginiRef: Data and Computer Communications, William StallingSwet SheershÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation and Bit Error Rate Analysis of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using MatlabDocument5 paginiImplementation and Bit Error Rate Analysis of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using MatlabHayatun NufusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commsim 2001 Tutorial Simulation of Communication Systems: TransmitterDocument21 paginiCommsim 2001 Tutorial Simulation of Communication Systems: TransmitterDonatas Pelenis100% (1)
- Implementation and Bit Error Rate Analysis of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using MATLABDocument5 paginiImplementation and Bit Error Rate Analysis of BPSK Modulation and Demodulation Technique Using MATLABseventhsensegroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 3 1 Digital Mod Tech v7Document80 paginiSection 3 1 Digital Mod Tech v7dragon20665Încă nu există evaluări
- Digital Communications PDFDocument113 paginiDigital Communications PDFZoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Data EncodingDocument90 paginiChapter 4 - Data EncodingTehillah IncÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Communications Lecture NotesDocument135 paginiDigital Communications Lecture Notescheku rakeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Digital Modulation TechniquesDocument67 paginiSimulation of Digital Modulation TechniquesEkta KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter4 OKDocument39 paginiChapter4 OKliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital CommunicationDocument148 paginiDigital CommunicationValÎncă nu există evaluări
- ImpDocument214 paginiImpAniket SankpalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th - Data-Signal Encoding Techniques-Version2Document90 pagini4th - Data-Signal Encoding Techniques-Version2Turyahebwa AlexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Theory, Shannon Limit and Error Correction Codes For Terrestrial DTV BroadcastingDocument37 paginiInformation Theory, Shannon Limit and Error Correction Codes For Terrestrial DTV BroadcastingSarun NellooliÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC FarraDocument22 paginiDC FarrargegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viterbi Science DirectDocument13 paginiViterbi Science Directapi-19790923Încă nu există evaluări
- Line CodingDocument19 paginiLine CodingRajesh Nandalike0% (1)
- TSN QN BankDocument14 paginiTSN QN BankbeslinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answers To CT303 Part 1Document3 paginiAnswers To CT303 Part 1RAMOLIYA HARSH MADHUKANTBHAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure: Chapter 1: Error Control CodingDocument66 paginiStructure: Chapter 1: Error Control Codingabhilash gowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method For Converter Synchronization With RF InjectionDocument8 paginiMethod For Converter Synchronization With RF InjectionAI Coordinator - CSC JournalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Error Coding Reed SolomonDocument28 paginiError Coding Reed SolomonAnumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hardware Implementation: Branch Metric Unit (BMU)Document6 paginiHardware Implementation: Branch Metric Unit (BMU)api-19790923Încă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Iterative Decoding For Turbo Codes Using Maximum A Posteriori AlgorithmDocument100 paginiAnalysis of Iterative Decoding For Turbo Codes Using Maximum A Posteriori AlgorithmWilliam Paul MacherlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communications 2: Modulation and Coding TechniquesDocument9 paginiCommunications 2: Modulation and Coding Techniquesbecy welbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NotesDocument19 paginiNotesvenkiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Coding: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 paginiDifferential Coding: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediafiraszekiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNT UNIT 2204 ASSESSMENTDocument3 paginiCCNT UNIT 2204 ASSESSMENTKimani MikeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of PSAC For Rayleigh Fading ChannelsDocument6 paginiImplementation of PSAC For Rayleigh Fading ChannelsAmrutha EzhilarasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DWC-USRP - LectureNotes PDFDocument84 paginiDWC-USRP - LectureNotes PDFJesús Mendoza PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Comparison of Adaptive Modulation and Coding in OFDM Systems Using Signalling and Automatic Modulation ClassificationDocument8 paginiPerformance Comparison of Adaptive Modulation and Coding in OFDM Systems Using Signalling and Automatic Modulation ClassificationYasser NaguibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital CommunicationDocument94 paginiDigital Communicationkartikeya kannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ece Vi Digital Communication (10ec61) NotesDocument203 paginiEce Vi Digital Communication (10ec61) NotesRaghu N Gowda100% (1)
- Data Directed Estimation Techniques For Single-Tone HF ModemsDocument10 paginiData Directed Estimation Techniques For Single-Tone HF Modemsradga1977Încă nu există evaluări
- The Novel Broadcast Encryption Method For Large Dynamically Changing User GroupsDocument8 paginiThe Novel Broadcast Encryption Method For Large Dynamically Changing User GroupsRavindra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important QuestionsDocument14 paginiImportant QuestionsUmer EhsanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Error CDDocument6 paginiError CDproblemslo420Încă nu există evaluări
- Gulu University Faculty of Science Computer Networks & Data Communications Marking GuideDocument15 paginiGulu University Faculty of Science Computer Networks & Data Communications Marking Guidereagan oloya100% (1)
- Electronics AssignmentDocument7 paginiElectronics AssignmentMookie RichardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3: Physical-Layer Transmission Techniques: Section 3.1: Digital ModulationsDocument81 paginiChapter 3: Physical-Layer Transmission Techniques: Section 3.1: Digital Modulationsvanlinh leÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Wireless Communication/Tti403: Bab 4: Digital Baseband TechniquesDocument54 paginiOptical Wireless Communication/Tti403: Bab 4: Digital Baseband TechniquesSyachivani Riski AbdilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of Adaptive Viterbi DecoderDocument7 paginiImplementation of Adaptive Viterbi DecoderseventhsensegroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Modulation I August09Document14 paginiDigital Modulation I August09gzb012Încă nu există evaluări
- BER Coding SchemesDocument3 paginiBER Coding SchemesAnonymous Th1S33Încă nu există evaluări
- Digital Communication Micro Lesson Plan for Sardar Raja CollegeDocument19 paginiDigital Communication Micro Lesson Plan for Sardar Raja Collegejeevitha86Încă nu există evaluări
- R&S Zvl-ManualDocument515 paginiR&S Zvl-ManualGuadalajara JaliscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adcl-01 EXP V1.1Document12 paginiAdcl-01 EXP V1.1tom_116Încă nu există evaluări
- Aug 94 A 3Document9 paginiAug 94 A 3Norazimah Mat ZainÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC 2301 Digital Communication Unit I and II Question BankDocument63 paginiEC 2301 Digital Communication Unit I and II Question Bankgayathri nathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use FEC to Improve Data over Noisy ChannelsDocument3 paginiUse FEC to Improve Data over Noisy ChannelsVaibhav MisraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communication System CH#3Document27 paginiCommunication System CH#3Haylemaryam G.Încă nu există evaluări
- Data EncodingDocument7 paginiData EncodingAmit ChauhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dac Interface To 8051 PDFDocument4 paginiDac Interface To 8051 PDFRAVI100% (1)
- Of Of: February 4987-Vol. 25, No. 2 IEEE Communications MagazineDocument7 paginiOf Of: February 4987-Vol. 25, No. 2 IEEE Communications MagazinethangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Audio Broadcasting: Principles and Applications of Digital RadioDe la EverandDigital Audio Broadcasting: Principles and Applications of Digital RadioWolfgang HoegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Software Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationDe la EverandSoftware Radio: Sampling Rate Selection, Design and SynchronizationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atmospheric Thermodynamics 1 v2Document53 paginiAtmospheric Thermodynamics 1 v2rajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Time Table (Even Semester 2012-2013)Document2 paginiDepartment of Electronics and Communication Engineering Time Table (Even Semester 2012-2013)rajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Even Sem TPR PlanDocument26 paginiEven Sem TPR Planrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- AntennasDocument29 paginiAntennasUdayan Sarma100% (2)
- C 02Document46 paginiC 02prabhumalu0% (1)
- 351 Ways To Conserve EnergyDocument28 pagini351 Ways To Conserve Energyrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Part IIDocument28 paginiPart IIrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- AntennaDocument58 paginiAntennarajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Antenna FundamentalDocument54 paginiAntenna FundamentalMardan KadivarÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Speed Calculations A Guide For GRE GMAT SAT CandidatesDocument114 paginiHigh Speed Calculations A Guide For GRE GMAT SAT CandidatesOsama PervaizÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Speed Calculations A Guide For GRE GMAT SAT CandidatesDocument114 paginiHigh Speed Calculations A Guide For GRE GMAT SAT CandidatesOsama PervaizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ec2151 Electric Circuits and Electron Devices SyllabusDocument1 paginăEc2151 Electric Circuits and Electron Devices SyllabusArun Kumar100% (1)
- Verilog HDL Testbench PrimerDocument14 paginiVerilog HDL Testbench Primernirmal_jate1Încă nu există evaluări
- 351 Ways To Conserve EnergyDocument28 pagini351 Ways To Conserve Energyrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- C 02Document46 paginiC 02prabhumalu0% (1)
- Acedemic Plan For CS2202Document8 paginiAcedemic Plan For CS2202rajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- LinearDocument2 paginiLinearrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- PSR College PDFDocument3 paginiPSR College PDFrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Ug Broucher eDocument44 paginiUg Broucher erajap102100% (1)
- Sampling With The Effect of AliasingDocument3 paginiSampling With The Effect of Aliasingrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Digital Electronics Lab ManualDocument108 paginiDigital Electronics Lab Manualkunaraj88% (17)
- Cadence CompareDocument1 paginăCadence Comparerajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Sampling With The Effect of Aliasing (Reconstructed)Document3 paginiSampling With The Effect of Aliasing (Reconstructed)rajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Inverse Discrete Fourier TransformDocument2 paginiInverse Discrete Fourier Transformrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- DFT Magnitude and Phase PlotsDocument2 paginiDFT Magnitude and Phase Plotsrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Circular Convolution ExplainedDocument2 paginiCircular Convolution Explainedrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Module TLCDocument3 paginiModule TLCrajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- Atmospheric Thermodynamics 1 v2Document53 paginiAtmospheric Thermodynamics 1 v2rajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- 4-Bit Array Multiplier (Unsigned)Document7 pagini4-Bit Array Multiplier (Unsigned)rajap102Încă nu există evaluări
- MSIT 116A Advanced Management Information SystemDocument182 paginiMSIT 116A Advanced Management Information SystemErr3350% (2)
- Data Collection Methods Course OutlineDocument7 paginiData Collection Methods Course OutlinelordÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory LogDocument262 paginiMemory LogKevin BernellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Marketing-AIDocument61 paginiJournal of Marketing-AIRaghavendra Vishwas KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Computer OrganizationDocument207 paginiIntroduction To Computer Organizationhemanth ramireddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between Market Research Vs Marketing ResearchDocument41 paginiDifference Between Market Research Vs Marketing Researchhaniausmani0% (1)
- FBackup User ManualDocument93 paginiFBackup User Manualolecosas4273100% (1)
- Tagore's Vision of EducationDocument80 paginiTagore's Vision of EducationManwinder Singh Gill75% (16)
- LIB101 Chapter 1Document19 paginiLIB101 Chapter 1Nurza RoslanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluating Strategies For Cost Reduction in SCM Relating To Exports and Imports.Document53 paginiEvaluating Strategies For Cost Reduction in SCM Relating To Exports and Imports.Makp112Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 4 Fundamental of Data BaseDocument10 paginiAssignment 4 Fundamental of Data BasekkkkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q&A - What Is SAE J1939?: (Source For The Following Answers: SAE HS-1939)Document3 paginiQ&A - What Is SAE J1939?: (Source For The Following Answers: SAE HS-1939)Ponraj Govindarajan100% (1)
- Course Contents: Subject Name: Session Plan BI (Business Intelligence) With ExcelDocument3 paginiCourse Contents: Subject Name: Session Plan BI (Business Intelligence) With ExcelChangani Jagdish GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Java RC6 Encryption AlgorithmDocument6 paginiJava RC6 Encryption AlgorithmSeptiyonoAdiPutroÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAP HANA Data Tiering With SAP NSEDocument21 paginiSAP HANA Data Tiering With SAP NSELiguo LiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gathering and Analyzing Quantitative Data - Practical Research - A Basic Guide To Planning, Doing, and WritingDocument22 paginiGathering and Analyzing Quantitative Data - Practical Research - A Basic Guide To Planning, Doing, and Writingharoon shahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Data Vault Guru - A Pragmati - Patrick CubaDocument709 paginiThe Data Vault Guru - A Pragmati - Patrick Cubatracdiadk52Încă nu există evaluări
- 030-Mandat (1) Nov2004Document30 pagini030-Mandat (1) Nov2004MoEe RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datanest - Data Science InterviewDocument19 paginiDatanest - Data Science InterviewJuan Guillermo Ferrer VelandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 06Document2 paginiLab 06vannylla100% (1)
- AZ 304 QuestionsDocument6 paginiAZ 304 QuestionsUdit DharniÎncă nu există evaluări
- SDG Implementers GuideDocument311 paginiSDG Implementers GuideKali Raj50% (2)
- Chapter 2 NotesDocument5 paginiChapter 2 NotesEmily ClevelandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Index Structures For Files: StructureDocument16 paginiUnit 4 Index Structures For Files: StructuregaardiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Transaction Processing Concepts and Concurrency ControlDocument65 paginiIntroduction to Transaction Processing Concepts and Concurrency ControlDeepak JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CommVault SnapProtect Field Guide For HP 3PAR StorageDocument52 paginiCommVault SnapProtect Field Guide For HP 3PAR Storagew3bl33tÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constructability Owners, Designers, and ContractorsDocument12 paginiConstructability Owners, Designers, and ContractorsFrancisco DondaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Fractured BlocksDocument13 paginiWhat Are Fractured BlocksKranthi Kumar100% (1)
- AWS Certified Solutions Architect - AssociateDocument128 paginiAWS Certified Solutions Architect - AssociateMoe Kaungkin80% (5)
- Encoder DecoderDocument6 paginiEncoder Decodermarkcelis1Încă nu există evaluări