Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
GSM Cell
Încărcat de
Sameer SulemanDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
GSM Cell
Încărcat de
Sameer SulemanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
8/2/13
GSM Cell
GSM Network Basics
An Introduction to GSM Networks
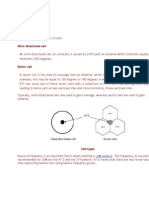
GSM CELLS
There are two main types of cells: Omni directional cell An omni-directional cell (or omnicell) is served by a BTS with an antenna which transmits equally in all directions (360 degrees). Sector cell A sector cell is the area of coverage from an antenna, which transmits, in a given direction only. For example, this may be equal to 120 degrees or 180 degrees of an equivalent omni- directional cell. One BTS can serve one of these sector cells with a collection of BTSs at a site serving more than one, leading to terms such as twosectored sites and more commonly, three-sectored sites. Typically, omni-directional cells are used to gain coverage, whereas sector cells are used to gain capacity.
Cell types Reuse of frequency is an important factor when planning a GSM network. The frequency re-use patterns recommended for GSM are the 4/12 and the 3/9 pattern. 4/12 means that there are four three-sector sites supporting twelve cells using twelve frequency groups.
Frequency reuse patterns
gsmbasics.awardspace.info/cell.htm
1/2
8/2/13
GSM Cell
Home | BSS | NSS | GSM Cell | Transmission Planning | Tower & Antenna | Power System | WCDMA | SS7
Chathuranga Perera, Electrical Engineer Ceylon Electricity Board
gsmbasics.awardspace.info/cell.htm
2/2
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Wave Concept in Electromagnetism and Circuits: Theory and ApplicationsDe la EverandThe Wave Concept in Electromagnetism and Circuits: Theory and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GDe la EverandIndoor Radio Planning: A Practical Guide for 2G, 3G and 4GEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- GSM Cells: Omni Directional CellDocument2 paginiGSM Cells: Omni Directional CellNicky NiranjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Sample ProblemsDocument20 paginiReview Sample ProblemsmmgcelesteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument139 paginiGlobal System For Mobile CommunicationMarian Joseph Ramzy100% (1)
- Unit-Iii Cell Site and Mobile Antennas: Ece/Liet C410 CMC Notes Sudheer Asst Prof ECE DeptDocument10 paginiUnit-Iii Cell Site and Mobile Antennas: Ece/Liet C410 CMC Notes Sudheer Asst Prof ECE DeptJeevan Sai MaddiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 6Document20 paginiLec 6Dhruv WaliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Directional Antennas: Cellular Telephone Frequency Reuse Pattern. SeeDocument1 paginăDirectional Antennas: Cellular Telephone Frequency Reuse Pattern. SeeTry LangÎncă nu există evaluări
- II Cellular4Document23 paginiII Cellular4Muhammad AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- MANET Cellular Network ArchitectureDocument7 paginiMANET Cellular Network ArchitectureGtecEceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular NetworkDocument8 paginiCellular NetworkElvin Fabulare EscalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Network: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 paginiCellular Network: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediabinsaad20Încă nu există evaluări
- ITT575 - Chapter 5Document54 paginiITT575 - Chapter 5Narahiko FujiwaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Transceiver StationDocument4 paginiBase Transceiver StationMandriz MordecaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Site Antennas and Mobile AntennasDocument8 paginiCell Site Antennas and Mobile AntennasS Bharadwaj ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP02 Course - Motorola - GSM All in One: Features, Components, Interfaces, Call Flow.Document124 paginiCP02 Course - Motorola - GSM All in One: Features, Components, Interfaces, Call Flow.Xuan Hong MaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 The Cellular ConceptDocument6 pagini2 The Cellular ConceptGopinathan MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radio Transceiver Cell Site Base Station Mobile Phones PagersDocument11 paginiRadio Transceiver Cell Site Base Station Mobile Phones PagersWilly Octopasz MuiruÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18-Antennas For Terrestrial Mobile Communication Mobile Handsets and Base Station. Antennas For Satcom-30-Oct-2020Material - I PDFDocument34 pagini18-Antennas For Terrestrial Mobile Communication Mobile Handsets and Base Station. Antennas For Satcom-30-Oct-2020Material - I PDFBarry AllenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency Reuse Patterns in GSMDocument2 paginiFrequency Reuse Patterns in GSMnshefeekÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Fundamentals & RFDocument111 paginiGSM Fundamentals & RFKwame Otchere-TawiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Evolution of Base Station Antennas For Mobile CommunicationsDocument8 paginiThe Evolution of Base Station Antennas For Mobile CommunicationsAnup KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Topics With Material: UNIT-1Document69 paginiAssignment Topics With Material: UNIT-1Prabhakara RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Cellular NetworkDocument7 paginiA Cellular NetworkvvrusffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study: Cellular NetworkDocument6 paginiCase Study: Cellular Networkrohank87Încă nu există evaluări
- 1-Cell Sectorization: AdvantagesDocument5 pagini1-Cell Sectorization: AdvantagesAbdiraxman SecidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Smart Antenna SystemsDocument17 paginiTypes of Smart Antenna SystemsanashabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Network: Cellular System Navigation Search Talk Page Guide To Writing Better ArticlesDocument9 paginiCellular Network: Cellular System Navigation Search Talk Page Guide To Writing Better ArticlesSamridhi GulatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- WLL (NSS) 1) History of Mobile Communication 2) Cellular Network Concepts 3) CDMA PrinciplesDocument73 paginiWLL (NSS) 1) History of Mobile Communication 2) Cellular Network Concepts 3) CDMA Principlesharoon karimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angle and Space Diversity Comparisons in Different Mobile Radio EnvironmentsDocument12 paginiAngle and Space Diversity Comparisons in Different Mobile Radio EnvironmentsAlejandro Barraza HenriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Nineteen-Beam Steering Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Based On Quarter-Mode Substrate Integrated WaveguideDocument6 paginiA Nineteen-Beam Steering Pattern Reconfigurable Antenna Based On Quarter-Mode Substrate Integrated WaveguideAMARNATH KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antennas at Cell SiteDocument14 paginiAntennas at Cell SiteMark Abadies100% (1)
- Microcell Zone ConceptDocument2 paginiMicrocell Zone ConceptKavyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular CommunicationDocument49 paginiCellular CommunicationMansoor KasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architecture of BtsDocument7 paginiArchitecture of BtsLuther NkapnangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co Channel Interference ReductionDocument32 paginiCo Channel Interference ReductionWorth Elog100% (1)
- Frequency ReuseDocument8 paginiFrequency ReuseiamhannielynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacity Increase Techniques OnlyDocument6 paginiCapacity Increase Techniques OnlyvivekdharmaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture3 Last Cellular Concept UMS 2021Document101 paginiLecture3 Last Cellular Concept UMS 2021بليغ عبدالله صبريÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Communication 2Document77 paginiWireless Communication 2Ganesha H S HaraveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dimensioning Cellular Wimax Part Ii: Multihop NetworksDocument7 paginiDimensioning Cellular Wimax Part Ii: Multihop NetworksAmineBenSalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Network ArchitectureDocument52 paginiWireless Network Architecturekkpandyaji2013Încă nu există evaluări
- Wireless Communication: Cellular ConceptDocument25 paginiWireless Communication: Cellular ConceptHashir AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cellular Concept - System Design FundamentalsDocument43 paginiThe Cellular Concept - System Design FundamentalsRutuja VartaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Wireless Networks: by Dr. Malik AbdulrazzaqDocument44 paginiCellular Wireless Networks: by Dr. Malik AbdulrazzaqMOHAMMADÎncă nu există evaluări
- CC541-Lecture 1Document54 paginiCC541-Lecture 1mohamedmohab34Încă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Network Planning and Optimization Part4Document44 paginiCellular Network Planning and Optimization Part4puljkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Mobile Phone Service - An OverviewDocument5 paginiAdvanced Mobile Phone Service - An OverviewmailmeasddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Triple-Frequency Microstrip-Fed Monopole Antenna Using Defected Ground StructureDocument7 paginiDesign of Triple-Frequency Microstrip-Fed Monopole Antenna Using Defected Ground StructurenripinthampanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test1 Marking Scheme FDocument3 paginiTest1 Marking Scheme FFahad IsmailÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document88 paginiChapter 3anon_494993240Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.2 Literature Survey 1. Compact Triple-Band Antenna For Wimaxand Wlan ApplicationsDocument49 pagini1.2 Literature Survey 1. Compact Triple-Band Antenna For Wimaxand Wlan ApplicationsRampratheep vÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Transceiver Station - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 paginiBase Transceiver Station - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaR.s. FélixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antenna Terms GlossaryDocument7 paginiAntenna Terms GlossaryMishelle RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect2Document15 paginiLect2annapoorna c kÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Dipole AntennaDocument3 paginiApplications of Dipole AntennaAhsan IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Networks Concepts and Fundamentals By: Waheed Ur RehmanDocument41 paginiCellular Networks Concepts and Fundamentals By: Waheed Ur RehmanWaheed RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Site Master S325D: Cable and Antenna Analyzer, 250 MHZ To 2500 MHZDocument12 paginiSite Master S325D: Cable and Antenna Analyzer, 250 MHZ To 2500 MHZSameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Network Basics: Wcdma TechnologyDocument2 paginiGSM Network Basics: Wcdma TechnologySameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tower & AntennaDocument3 paginiTower & AntennaSameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts SiteDocument1 paginăGSM Network Basics: Power System of A Typical Bts SiteSameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningDocument4 paginiGSM Network Basics: Transmission PlanningSameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Network BasicsDocument2 paginiGSM Network BasicsSameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM IdentitiesDocument3 paginiGSM IdentitiesSameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Network Basics: Authentication Process of A SubscriberDocument2 paginiGSM Network Basics: Authentication Process of A SubscriberSameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Network Basics: Mobile Originating CallDocument2 paginiGSM Network Basics: Mobile Originating CallSameer SulemanÎncă nu există evaluări