Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
3 Diesel Engine Fundamentals (I) (Solved Example 2 and 3) PT
Încărcat de
Than HtetDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
3 Diesel Engine Fundamentals (I) (Solved Example 2 and 3) PT
Încărcat de
Than HtetDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
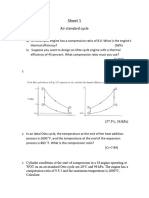
Solved example for Diesel Cycle
Question 2: An air standard cycle consists of the following processes: isentropic compression from 15 C, 1.013 bar through a compression ratio of 18; heat addition at constant pressure of 2500 kJ/kg; isentropic expansion to the initial volume and heat rejection at constant volume. Solution: Step1: list known parameters: P1 = 1.013 bar T1 = 15 C Compression ratio: rv = 18 Heat addition at constant pressure: Q23 = 2500 kJ/kg; this is a Diesel cycle. Isentropic compression Isentropic expansion Heat rejection at constant volume Cp = 1.005 kJ/kg Cv = 0.718 kJ/kg
Find: Sketch the p-v diagram calculate its ideal efficiency (diesel ) and peak pressure (Pmax = P2 = P3) Solution: a) Sketch the p-v diagram:
b) Calculation :
c) Answer: The ideal efficiency of the cycle is 56.24%; the peak pressure is 57.90 bar.
Solved example for Otto Cycle
Question 3: An air standard cycle consists of the following processes: isentropic compression from 15 C, 1.013 bar through a compression ratio of 18; heat addition at constant volume of 2500 kJ/kg; isentropic expansion to the initial volume and heat rejection at constant volume. Solution:
Step1: list known parameters: P1 = 1.013 bar T1 = 15 C Compression ratio: rv = 18 Heat addition at constant volume: Q23 = 2500 kJ/kg; this is a Otto cycle. Isentropic compression Isentropic expansion Heat rejection at constant volume Cp = 1.005 kJ/kg Cv = 0.718 kJ/kg
Find: Sketch the p-v diagram calculate its ideal efficiency (Otto) and peak pressure (Pmax = P3 ) Solution: a) Sketch the p-v diagram:
b) Calculation :
c) Answer: The ideal efficiency of the cycle is 68.53%; the peak pressure is 278.34 bar.
Note:
From the above results, it can be seen that with the same compression ratio and the same heat addition, the ideal efficiency of Otto cycle is higher than that of Diesel cycle.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Solved - Problems in ThermodynamicsDocument29 paginiSolved - Problems in ThermodynamicsAngelica Joyce Benito100% (6)
- PDMS:PLOT User GuideDocument61 paginiPDMS:PLOT User GuidePRAMUKHRAWAL100% (1)
- CH 7 PowerCyclesDocument12 paginiCH 7 PowerCyclescarleston thurgoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW3 SolutionsDocument19 paginiHW3 SolutionsmhishamnaeemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas TurbineDocument7 paginiGas TurbineVishal ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICE Assign#2 May 18Document2 paginiICE Assign#2 May 18Isyraf FitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cat C280-12 Spec SheetsDocument16 paginiCat C280-12 Spec SheetsThan Htet100% (1)
- 4 Air Standared Cycles PDFDocument75 pagini4 Air Standared Cycles PDFAli ZameerÎncă nu există evaluări
- LT4 GRP5Document17 paginiLT4 GRP5AegeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add File: Brayton Cycle With Neat SketchDocument1 paginăAdd File: Brayton Cycle With Neat SketchWater VapourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Combustion Engines Solution - v1Document13 paginiInternal Combustion Engines Solution - v1xLibelle100% (4)
- Module 5 Activity No. 2Document1 paginăModule 5 Activity No. 2Sharmaine MauricioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics QuestionsDocument3 paginiFluid Mechanics QuestionsWaleed UsmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 - Gas Power Cycles - Updated - 2023Document2 paginiChapter 6 - Gas Power Cycles - Updated - 2023Yonas BelaynehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Power Cycles - Mech Engineering: Thermodynamics Carnot CycleDocument22 paginiGas Power Cycles - Mech Engineering: Thermodynamics Carnot CycleShihab RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9,10,11Document50 paginiChapter 9,10,11myra091100% (1)
- Assignment 4Document2 paginiAssignment 4Siddharth JajoriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 ProblemsDocument6 paginiChapter 9 ProblemsKartikKhatriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cuestionario Cap18 RefrigeracionDocument5 paginiCuestionario Cap18 RefrigeracionchechobgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 1Document3 paginiHomework 1meeshoe90% (1)
- Chapter 3 - ExercisesDocument2 paginiChapter 3 - ExercisesMc AxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No: 2: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (110006) 28/10/2011Document3 paginiAssignment No: 2: Elements of Mechanical Engineering (110006) 28/10/2011SaumilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermo Cycle Problems OnlyDocument11 paginiThermo Cycle Problems OnlyMaridil Joy IsidroÎncă nu există evaluări
- 125452033-Thermodynamics D.J.Dunn PDFDocument185 pagini125452033-Thermodynamics D.J.Dunn PDFkalite123Încă nu există evaluări
- Application To Flow ProcessesDocument27 paginiApplication To Flow Processessam_kamali85Încă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Otto and Diesel CycleDocument8 paginiModule 1 - Otto and Diesel CycleRoi Vincent Anit100% (1)
- GT Powerplants Additional ExamplesDocument8 paginiGT Powerplants Additional ExamplesKarina Nur Rakhmawaty25% (4)
- GT ThermodynamicsDocument22 paginiGT Thermodynamicsforzama100% (1)
- Problem Set #2 - ChE 124 - Summer 2018Document3 paginiProblem Set #2 - ChE 124 - Summer 2018SkambalahardarÎncă nu există evaluări
- WK 4 TR2019 - ICE TheoryDocument72 paginiWK 4 TR2019 - ICE TheoryHoàng LongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set G 10.213 Solution Spring 2002 23) A Schematic of The Rankine Cycle and Representation On A T-S Diagram: Q 2 TDocument10 paginiProblem Set G 10.213 Solution Spring 2002 23) A Schematic of The Rankine Cycle and Representation On A T-S Diagram: Q 2 TRalph Segundo SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanical Engineering Thermodynamics II - Lecture 03 - 27 SepDocument25 paginiMechanical Engineering Thermodynamics II - Lecture 03 - 27 SepThineshraaj Naidu Jaya RamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Cycles Otto, Diesel, Dual CyclesDocument43 paginiGas Cycles Otto, Diesel, Dual Cyclesprasad5034100% (1)
- ThermodynamicsDocument79 paginiThermodynamicstixy2013Încă nu există evaluări
- Intermediate Thermodynamics Cycles: Heat-Engine CycleDocument7 paginiIntermediate Thermodynamics Cycles: Heat-Engine Cycleabdul_rehman_124Încă nu există evaluări
- Srinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur-621212: Question Bank Unit I Gas Power CyclesDocument18 paginiSrinivasan Engineering College, Perambalur-621212: Question Bank Unit I Gas Power CyclesagrikarthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICE Assignment 8AMDocument5 paginiICE Assignment 8AMRushabh PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENGR251 F 2011 X M F ProbDocument4 paginiENGR251 F 2011 X M F ProbDawood AljumayahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorials 1-4Document6 paginiTutorials 1-4KrishnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ic Assignment 2Document1 paginăIc Assignment 2Nilven GastardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Standard CycleDocument6 paginiAir Standard CycleBishOy NasrÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMPRESSORSDocument12 paginiCOMPRESSORSonigirialphaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample ExamDocument1 paginăSample ExamPierce HardinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial Thermal1Document2 paginiTutorial Thermal1vivekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ae8301 Aetd QBDocument22 paginiAe8301 Aetd QBMoses DevaprasannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turbin Gas: Siklus Terbuka Turbine GasDocument34 paginiTurbin Gas: Siklus Terbuka Turbine GasRezky RinaldyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Power Cycle - Part 2 v2Document35 paginiGas Power Cycle - Part 2 v2Shahran IezzatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Thermodynamics (LECTURE)Document117 paginiEngineering Thermodynamics (LECTURE)Arvind ArvindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Class Notes (1) - 7873c957 95fe 46cb b8b3 A02ca18d80fcDocument81 paginiThermodynamics Class Notes (1) - 7873c957 95fe 46cb b8b3 A02ca18d80fcmayanksarda36Încă nu există evaluări
- Ex The Air Standard Cycle ExercisesDocument1 paginăEx The Air Standard Cycle ExercisesSyira ShahimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- By: Carlo Manuel A. BanquerigoDocument10 paginiBy: Carlo Manuel A. BanquerigoChristy Joy RetanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITK-233-6 - Power Production & RefrigerationDocument30 paginiITK-233-6 - Power Production & RefrigerationAndy Noven KrisdiantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - I - Gas Power Cycles: Cap BL PP CosDocument4 paginiUnit - I - Gas Power Cycles: Cap BL PP CosdineshvaricomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 21: Isentropic Efficiencies, Air: Standard Cycle, Carnot Cycle, Otto CycleDocument45 paginiLec 21: Isentropic Efficiencies, Air: Standard Cycle, Carnot Cycle, Otto CycleAshok PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1 Soln PDFDocument13 paginiAssignment 1 Soln PDFJawahar Khetan100% (1)
- HW 13Document5 paginiHW 13Maria Mikaela PelagioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Across Kick at 10000'Document1 paginăPressure Across Kick at 10000'Than HtetÎncă nu există evaluări
- AutoDRAFT User GuideDocument68 paginiAutoDRAFT User GuidesimplekelechiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey Report East of EnglandDocument55 paginiSurvey Report East of EnglandThan Htet100% (1)
- Printable Collection of Bode Plot Web PagesDocument48 paginiPrintable Collection of Bode Plot Web PagesThan HtetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caesar II TrainingDocument61 paginiCaesar II TrainingReaderRRGHT86% (7)
- HX F N H XF H XFH XFH XF: 10 Where ! ......... !2Document5 paginiHX F N H XF H XFH XFH XF: 10 Where ! ......... !2Than HtetÎncă nu există evaluări