Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial Infarction
Încărcat de
banyenye25Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial Infarction
Încărcat de
banyenye25Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
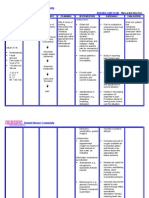
NURSING CARE PLAN Date Assessed August 20, 2012 ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Occlusion of coronary artery
PLANNING Short Term Goal: Subjective: The client reports of chest pain radiating to the left arm, neck and back. P- Upon doing some exertion activities Q- Stabbing pain R- to left arm, neck and back S- 10 out of 10 T- last more than 15 minutes Objective: Restlessness Facial grimacing Easy Fatigability Pallor Cold and clammy skin With Oxygen inhalation at 2-4 Lpm Shortness of Pain Acute chest Pain related to Coronary Artery occlusion secondary to Myocardial Infarction - After 15-30 minutes rendering care and interventions, the patient will be able to verbalized decreased/relieved pain (chest and to radiating areas)felt, AEB: Decreased feeling of fatigue Improve breathing Skin is within the normal color Vital signs within normal range: BP=120/80 PR= 60-100bpm RR= 12-20 cpm Temp= 36.5 Pain rate scale from 10 down to 8 as 10 is the highest Long term Goal: INTERVENTION Independent: 1. Assess characteristics of chest pain (PQRST) 1.) To determine what appropriate interventions will be going to apply for better implementation of care. 2.) It provides information that may help to differentiate current pain from previous problems and complications thus it is a big help to perform such interventions. 3.) An increase in vital signs happens as as the body compensate to pain, which can lead to other serious complications doing if continuous to increase. 4.) To reduce oxygen consumption thus decreased oxygen demand. RATIONALE EVALUATION Short Term Goal: - Goal Met, AEB: Patient will be able to verbalized decreased/relieved pain (chest and to radiating areas)felt, AEB: Decreased feeling of fatigue Improve breathing Skin is within the normal color Vital signs within normal range: BP=120/80 PR= 60-100bpm RR= 12-20 cpm Temp= 36.5 Pain rate scale from 10 down to 8 as 10 is the highest Long term Goal: - Goal Met, AEB: Patient experienced an improved feeling of control and comfort
Decreased blood flow to the myocardium
Decreased blood supply (ischemia)
Anaerobic metabolism
2. Obtain history of previous cardiac pain and familial history of cardiac problems from the S.O.
Lactic Acid formation
3. Assess for respirations, BP and heart rate with each episodes of chest pain.
4. Maintain bed rest during pain, with position of comfort.
breath Vital signs taken as: BP=150/90 PR=109 bpm RR= 26 cpm Temp= 35.0
- After 1 hour of rendering care and interventions, the patient will be able to have an improved feeling of control and comfort AEB: Able to sleep and rest comfortably Improve breathing Vital signs within normal range: BP=120/80 PR= 60-100bpm RR= 12-20 cpm Temp= 36.5 Pain rate scale from 10 down to 2 as 10 is the highest
5. Maintain relaxing 5.) To promote environment conducive calmness, reduce for rest. competing stimuli and reduces anxiety thus it decreases oxygen demand. 6. Instruct patient to avoid/limit activities that causes to increase cardiac workload ( lifting heavy objects, running, stressful task) 6.) To prevent triggering the heart to the need of more oxygen due to exertion, thus, limiting activities decrease myocardial oxygen demand and workload on the heart. 7.) To promote knowledge and compliance with the said therapeutic regimen and for better action.
AEB: Able to sleep and rest comfortably Improve breathing Vital signs within normal range: BP=120/80 PR= 60-100bpm RR= 12-20 cpm Temp= 36.5 Pain rate scale from 10 down to 2 as 10 is the highest
7. Instruct patient/family in medication effects, side-effects, contraindications and symptoms that need to report Collaborative: - Administration of medications and oxygen supplementation: 1.Administer oxygen
1.) To promote adequate oxygen supply
2. Administer analgesics as ordered, such as morphine sulfate
2.) Morphine Sulfate is the drug of choice to control MI pain, it decreases the afterload and preload (workload) of the heart, decrease oxygen demand, Thus, reduces pain 3.) To block sympathetic stimulation, reduce heart rate and lowers myocardial demand. 4.) ECG record changes that can give evidence of further cardiac damage and location of MI, thus ECG monitoring is important for better prevention of damage due to MI.
3. Administer betablockers such as metropolol as ordered.
4. Perform a 12-lead ECG and monitor for cardiac changes
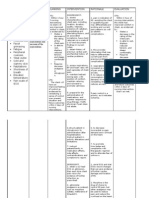
Date Assessed August 22, 2012 ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Deficient oxygen in the coronary arteries Use of anaerobic pathway to for ATP production Oxygen to the myocardium Inadequate amounts of oxygen to the tissues Imbalance between oxygen Supply and Demand Activity Intolerance PLANNING Short Term Goal: Subjective: - Mabilis akong mapagod at manghina, simpleng Gawain lng nakakramdam na ako ng hirap sa paghinga as verbalized by the patient Objective: Weak in appearance Pallor Experience shortness of breathing Needs assistance in doing minimal activities Easy fatigability With Oxygen inhalation at 2-4 Lpm Activity Intolerance related to Imbalance between oxygen Supply and Demand secondary to Myocardial Infarction - After 5-8 hours shift duty of rendering care and interventions, the patient will be able to verbalized understanding about her condition, AEB: Reduced feeling of fatigue and weakness Able to mention and apply ways on how managed her condition Participate to interventions Vital signs within normal limits upon performing limited activities: BP=120/80 PR= 60-100bpm RR= 12-20 cpm Temp= 36.5 Long term Goal: INTERVENTION Independent: 1. Establish rapport both to patient and S.O. 1.) To gain their trust and for better intervention participation. 2.) For baseline data and to determine the of other complication in relation to increase vital signs if possible. 3.) Informing her about her condition and limitations prevents her to develop further complication and it will be a help to manage properly her condition. 4.) Reduces physical stress and tension, it decreases the demand of oxygen thus decreases also the workload of the heart. RATIONALE EVALUATION Short Term Goal: Goal Met: Patient was able to verbalized understanding about her condition, AEB: Reduced feeling of fatigue and weakness Able to mentioned and apply ways on how managed her condition Vital signs within normal limits upon performing limited activities: BP=120/80 PR= 60-100bpm RR= 12-20 cpm Temp= 36.5 Long term Goal: Goal Met, Patient showed measurable increase in activity tolerance, AEB: Reduced feeling
2. Monitor vital signs, before and after doing such activities.
3. Encourage patient to verbalize her feelings and concerns regarding her present condition and limitations.
4. Maintain stressful activity restrictions and assist patient with self care activities as needed.
Vital signs taken as: BP=130/90 PR=90 bpm RR= 20 cpm Temp= 37.8 Functional Level Classification: Level III means, walk no more than 50 ft on level without stopping; unable to climb one flight of stairs without stopping.
- After 1 to 2 weeks of intervention, the patient will report measurable increase in activity tolerance, AEB: Reduced feeling of fatigue and weakness Demonstrate a decrease in physiological signs of intolerance Vital signs within normal limits upon performing limited activities: BP=120/80 PR= 60-100bpm RR= 12-20 cpm Temp= 36.5 Perform ADLs without the need of assistance and able to do it comfortably
5. Provide frequent rest periods, especially after meals.
5.) Resting decreases the oxygen demand of the heart. Large meals may increase myocardial workload and causes vagal stimulation thus increases the demand of oxygen. 6.) Postural hypotension/ cerebral hypoxia may cause dizziness, fainting, and increased risk of injury
6. Encourage rest periods between care activities.
Collaborative: 1. Administer betablockers such as metoprolol, as ordered. 1.) It blocks sympathetic stimulation, thus, reduces heart rate and lowers myocardial demand.
of fatigue and weakness Demonstrate a decrease in physiological signs of intolerance Vital signs within normal limits upon performing limited activities: BP=120/80 PR= 60-100bpm RR= 12-20 cpm Temp= 36.5 Perform ADLs without the need of assistance and able to do it comfortably.
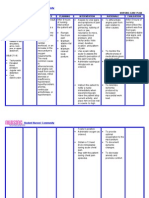
ASSESSMENT
DIAGNOSIS
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Experienced chest pain Myocardial ischemia reported Diagnosed as myocardial infarction Frequent monitoring needed Conscious, irritable, poor eye contact, restless Confusion Anxiety
PLANNING Short Term Goal:
INTERVENTION Independent: 1. Establish rapport
RATIONALE
EVALUATION Short Term Goal:
Subjective: Hindi ko maipaliwanag nararamdaman ko,malala ba kondisyon ko?hindi pa ako handa as vervalized by the patient. Objective: Usually staring at the wall or ceiling. Unexplained facial expression Poor eye contact Confusion irritability Restlessness Ask questions Decreased interaction to the family/S.O
Anxiety (moderate) related to Actual Threats to present condition Secondary to Myocardial Infarction
- After the 8 hrs shift of duty of rendering care and interventions, the patient will be able to understand the complications about his condition and able to control his anxiety through proper explanation in her present situation, AEB: Verbalized awareness of feelings of anxiety Actively interacts to family Open to his conditions and ask questions for security and reassurance With eye contact Decreased irritability, restlessness and confusion. Long term Goal: - After 3-5 days of rendering care and
1.) To have a trusted nurse to patient relationship and to have a therapeutic communication. 2.) Continuity of care promotes security and development of rapport. 3.) Accurate information about his condition reduces fear , strengthens the nurse-patient relationship and assist the patient and familt to face the situation realistically. 4.) Sharing information elicits support and comfort and can relieve tension and unexpressed worries. 5.) To reassure the patient that frequent monitoring may prevent him to
2. Provide continuity of care
3. Encourage the patient and family to ask questions and bring up common concerns.
4. Encourage patient and S.O to verbalize concerns and fears.
Goal Met: Patient already understand the complications about his condition and able to control his anxiety through proper explanation in her present situation, AEB: Verbalized awareness of feelings of anxiety Actively interacts to family Open to his conditions and ask questions for security and reassurance With eye contact Decreased irritability, restlessness and confusion. Long Term Goal : Goal Met: Patient was able to accept the reality about his condition and readily
5. Inform them that frequent assessment are routinely done to monitor her condition
interventions, the patient will be able to accept the reality about his condition and readily participates in activities, AEB: Appeared relax and report anxiety is reduced to manageable level Open to his conditions and ask questions for security and reassurance With eye contact Decreased irritability, restlessness and confusion.
and dont necessarily imply a deteriorating condition. 6. Repeat the information as necessary because patient and family may reduce their attention span.
develop of more serious complications.
6.) Anxiety decreases learning and attention.
7. Provide a 7.) A comfortable comfortable And quiet environment enhances environment. coping mechanisms and reduces myocardial workload and oxygen consumption.
participates in activities, AEB: Appeared relax and report anxiety is reduced to manageable level Open to his conditions and ask questions for security and reassurance With eye contact Decreased irritability, restlessness and confusion.
Date Assessed August 20, 2012
ASSESSMENT
DIAGNOSIS
SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Deposits from a large atherosclerotic plaque cause in increase in size and bulge into the artery
PLANNING Short Term Goal:
INTERVENTION Independent: 1. Establish rapport both to patient and to the S.O
RATIONALE
EVALUATION Short Term Goal:
Subjective: Mabuti naman na pakiramdam ko, hindi na sumasakit ang dibdib ko,minsan minsan na lang pero hindi na kagaya noon as verbalized by the patient. Objective: Experience easy fatigability Experience dizziness and shortness of breath upon doing minimal activities ( Standing) Experiences chest pain, nausea and vomiting, and epigastric pain. Restlessness With an Oxygen
Risk for Decrease cardiac output related to increase vascular resistance as evidenced by narrowing of coronary arteries secondary to Myocardial Infarction
Endothelial lining of coronary activation of coagulation cascade arteries will rupture Plaque protrudes in lumen of the vessels Thrombus may dislodge from a broken plaque Narrowed blood vessels/impedes blood flow Decreased cardiac output
- After 8 hours shift of duty and rendering patient care and nursing interventions, the patient will verbalized understanding about his risk for decrease cardiac output and promote appropriate actions to promote patients condition AEB: Able to participate in medication regimen and in restrictions regarding to her condition. Identify signs and symptoms of cardiac decompression and able to seek attention if occur Report of continuous
Goal Met: Patient verbalized understanding about his risk for decrease 2.) Tachycardia may cardiac output and 2. Monitor patients able to promote vital signs, noting be present because of pain and anxiety and appropriate actions to blood pressure reduced cardiac promote patients changes. output. Changes may condition AEB: also occur in BP Participates in (hypertension or medication hypotension) because regimen and in of cardiac response. restrictions regarding to her condition. 3. Provide a calm and 3.) It promotes comfort and Identify signs and restful relaxation. symptoms of surroundings cardiac 4.) Reduces physical decompression 4. Maintain activity stress and tension. and able to seek restrictions and Conserves attention if occur assisted patient energy, reduces Reported with self care cardiac workload. continuous activities as disappearance of needed. minimal 5.) Decreases occurrence of 5. Provided comfort discomfort and chest pain being measures (ex. may reduce intermittently Back massage and
1.) In order to have a trusting relationship on them.
inhalation at 2-4 Lpm Vital signs taken as: BP=150/90 PR=109 bpm RR= 26 cpm Temp= 35.0
disappearance of elevation of head) minimal occurrence of 6. Encouraged to do chest pain being relaxation intermittently felt. techniques such as Vital signs are distraction within normal limits. Long term Goal: 7. Maintain head elevated - After 3-5 days of approximately 30 rendering patient care degrees. and interventions, the patient will report 8. Instruct patient to feeling of comfort and avoid activities that lessen the possible create a Valsalva signs and symptoms of response (e.g. being in risk for straining to have a decrease cardiac bowel movement, output through the holding breath while proper management moving up in bed) and participation to intervention and medication regimens AEB: Display a hemodynamic Stability 9. Maintain on bed Shows proper rest or semi fowlers breathing pattern position. and no need to use an oxygen therapy for support. Collaborative: can perform basic
sympathetic stimulation. 6.) Can reduce stressful stimuli and produce a calming effect. 7.) To promote optimal cerebral perfusion.
felt. Vital signs are within normal limits. Long term Goal: Goal partially Met: Patient reported feeling of comfort and lessen signs and symptoms being felt and observed through the proper management and participation to intervention and medication regimens AEB: -Display an improvement in hemodynamic Stability Shows proper breathing pattern but still have the need to use an oxygen therapy for support. Able to perform basic activities without experiencing dizziness and minimally
8.) Valsalva maneuver causes vagal stimulation, reducing heart rate (bradycardia), which may be followed by rebound tachycardia, which causes to impair cardiac output. 9.) Decreases oxygen consumption/dem and, reducing myocardial workload
activities without experiencing dizziness and easy fatigability will improved into an active body tolerance. Adequate cardiac output AEB: stable/improving ECG result after performing PTCA done on the same day.
1. Administer Administer betablockers such as metoprolol, as ordered.
1.) It blocks sympathetic stimulation, thus, reduces heart rate and lowers myocardial demand. 2.) Increases oxygen available for myocardial uptake to improve contractility, reduce ischemia, and reduce lactic acid levels. 3) It helps to improve the condition of the patient and it contributes patients wellness and danger.
2. Administer supplemental oxygen as needed.
experience fatigability. Adequate cardiac output, AEB: stable/improving ECG result after performing PTCA done on the same day.
3. Perform surgical intervention such as PTCA as needed.
Date Assessed August 21, 2012 ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS SCIENTIFIC EXPLANATION Deposits from a large atherosclerotic plaque cause in increase in size and bulge into the artery Endothelial lining of coronary activation of coagulation cascade arteries will rupture Plaque protrudes in lumen of the vessels Thrombus may dislodge from a broken plaque Narrowed blood vessels/impedes blood flow Decreased cardiac output Ineffective Tissue Perfusion PLANNING Short Term Goal: Subjective: The patient reports of difficulty of breathing and chest discomfort. Objective: restlessness irritability easy fatigability Diaphoresis Dizziness Cold clammy skin Pale in appearance With an Oxygen inhalation at 24 Lpm Vital signs taken as: BP=150/90 PR=109 bpm RR= 26 cpm Temp= 35.0 Ineffective Cardiac Tissue Perfusion related to Reduced Coronary Blood Flow Secondary to Myocardial Infarction - After 8 hours of rendering nursing intervention the patient will show adequate coronary perfusion and reported feeling of relieved from discomforts, AEB: decrease restlessness decrease irritability decrease feeling of fatigability Skin warm and dry and in normal color Vital signs within normal range Relieved chest discomfort Improve breathing discomfort Long Term Goal: - After 3 Days of nursing intervention the patient will be free from the signs and symptoms of ineffective cardiac tissue perfusion AEB: Reported a comfortable 3. Provides period of undisturbed rest and calming environment 4. Instruct patient in a complete bed rest. 3.) To reduce myocardial oxygen demand and work load 4.) It promotes decreases oxygen demand, INTERVENTION Independent: 1. Monitor vital signs especially blood pressure. 1.) For baseline data and to monitor or determine for further myocardial ischemia, thus preventing the occurrence of other potential complications 2.) It is the signs and symptoms of inadequate systemic perfusion which can affect cardiac function RATIONALE EVALUATION Short Term Goal: Goal Met, Patient will showed adequate coronary perfusion and reported feeling of relieved from discomforts, AEB: decrease restlessness decrease irritability decrease feeling of fatigability Skin warm and dry and in normal color Vital signs within normal range Relieved chest discomfort Improve breathing discomfort Long Term Goal: Goal Met, Patient was observed as free from the signs and
2. Asses for restlessness fatigue, changes of level of consciousness appearance of skin color.
feeling Free of pain and other signs and symptoms ineffective tissue perfusion Collaborative: VS within normal limits Adequate cardiac output 1. Administer AEB:stable/improving medication ECG result regimens as ordered such as: Morphine sulfate
thus promoting symptoms of adequate oxygen ineffective cardiac circulation. tissue perfusion and showed feeling of wellness AEB: Reported a comfortable feeling Free of pain and other signs and symptoms ineffective tissue perfusion VS within normal limits Adequate cardiac output AEB: stable/improving ECG result after performing PTCA done on the same day.
Administer beta- blockers as ordered.
Morphine Sulfate is the drug of choice to control MI pain, it decreases the afterload and preload (workload) of the heart, decrease oxygen demand, Thus, reduces pain To block sympathetic stimulation, reduce heart rate and lowers myocardial demand.
2. Perform a 12-lead ECG and monitor for cardiac changes
2.) It helps in determining cardiac insufficiency
and it helps to monitor the cardiac electrical activity. 3. Administer Oxygen as ordered 3.) In order to improve or maintain cardiac and systemic tissue perfusion
4. Administer 4.) To maintain intravenous systemic fluids as circulation and routinely ordered optimal cardiac function. 5. Perform surgical intervention such as PTCA as needed. 5.) It helps to improve the condition of the patient and it contributes patients wellness and danger.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument8 paginiNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarction NCPderic86% (14)
- NURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionDocument16 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN For Myocardial InfarctionFreisanChenMandumotan100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionDocument7 paginiNursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionjamieboyRN88% (8)
- Nursing Care Plan - Myocardial InfarctionDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan - Myocardial Infarctionderic80% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan For Myocardial InfarctionDocument7 paginiNursing Care Plan For Myocardial Infarctionmariejo95% (125)
- NURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument4 paginiNURSING CARE PLAN - Myocardial Infarction Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationsweethoney220% (1)
- SAMPLE NCP For Angina PectorisDocument3 paginiSAMPLE NCP For Angina Pectorisseanne_may100% (4)
- Nursing Assessment and Interventions for Acute Chest PainDocument3 paginiNursing Assessment and Interventions for Acute Chest PainAjay SupanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Myocardial InfarctionDocument1 paginăNCP Myocardial InfarctionjamieboyRN88% (8)
- MI Chest Pain AssessmentDocument5 paginiMI Chest Pain AssessmentDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument35 paginiAcute Myocardial Infarctionvirnzrobz80% (10)
- Care Plan Unstable AnginaDocument4 paginiCare Plan Unstable Anginaالغزال الذهبي50% (6)
- NCP 2 and Soapie 1Document5 paginiNCP 2 and Soapie 1narsD100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for Mrs. Kanchan Rajput with Subarachnoid HemorrhageDocument21 paginiNursing Care Plan for Mrs. Kanchan Rajput with Subarachnoid HemorrhageDr-Sanjay SinghaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial Infarction NCPDocument3 paginiMyocardial Infarction NCPlapistolero33% (3)
- NCPDocument4 paginiNCPElbert Vierneza100% (2)
- Acute Myocardial Infarction - CSDocument49 paginiAcute Myocardial Infarction - CSMASII94% (17)
- Nursing Care Plan for Altered Level of ConsciousnessDocument8 paginiNursing Care Plan for Altered Level of ConsciousnessJeffrey Dela Cruz50% (4)
- Nursing Care Plan (Septick Shock)Document6 paginiNursing Care Plan (Septick Shock)REMILYN ROSE ASUNCION67% (9)
- NCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome AssessmentDocument3 paginiNCP for Acute Coronary Syndrome Assessmentsarahtot67% (3)
- NCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleDocument5 paginiNCP For RS-HF (Cor PulmonaleMika Saldaña100% (1)
- Cva NCP AnxietyDocument1 paginăCva NCP AnxietyQueenElsaDeVeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Knowledge DeficitDocument3 paginiKnowledge DeficitInigo Miguel DulayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument21 paginiMyocardial InfarctionasdnofalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP AnginaDocument3 paginiNCP AnginaShie LA100% (1)
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansDocument21 pagini"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Nursing Care PlansCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Angina Pectoris NCPDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Angina Pectoris NCPderic73% (15)
- Decreased Cardiac Output NCPDocument2 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output NCPmicah1318100% (2)
- Final Case Study - CADDocument109 paginiFinal Case Study - CADPatricia Marie Buenafe100% (1)
- NCP On Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument4 paginiNCP On Electrolyte Imbalancefreyah_bc67% (3)
- NCP Head InjuryDocument3 paginiNCP Head InjuryEdelou Alegria Jumawan67% (3)
- Decreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiDecreased Cardiac Output Nursing Care Planjudssalangsang86% (7)
- NCP For CTTDocument1 paginăNCP For CTTJen Rhae LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiNursing Care Planmanu_gutierrez0891% (11)
- Nursing Care Plan TBIDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan TBIChester Manalo87% (15)
- NCP Heart BlockDocument3 paginiNCP Heart BlockEköw Santiago Javier33% (3)
- Case study-NLMDocument4 paginiCase study-NLMGil Platon Soriano40% (10)
- Nursing Care Plan For Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Coronary Artery DiseaseLorraineAnneSantiagoCandelario91% (22)
- NCP - Acute Pain Related Myocardial IschemiaDocument2 paginiNCP - Acute Pain Related Myocardial IschemiaKian HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument16 paginiMyocardial InfarctionCay Sevilla100% (4)
- NCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 paginiNCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputErienne Lae Manangan - CadalsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Pain NURSING CARE PLANDocument2 paginiAcute Pain NURSING CARE PLANMatthew Emmanuel M. Martinez100% (4)
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivebanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument3 paginiNCP Rheumatic Heart DiseaseAdrian Mallar71% (28)
- NCP For Mi PainDocument2 paginiNCP For Mi PainKahMallariÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument3 paginiNCPKrizelle Abadesco Libo-on50% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan-1Document4 paginiNursing Care Plan-1Sh3meeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 2Document27 paginiCase Study 2Hal00mÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP PTBDocument6 paginiNCP PTBJay Dela VegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fatigue and weakness assessmentDocument18 paginiFatigue and weakness assessmentBob Joyce Dela PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCPDocument5 paginiNCPRose AnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP HCVD (Final)Document8 paginiNCP HCVD (Final)khrizaleeh100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Raynaud's SyndromeDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan For Raynaud's SyndromeAmerah Sangcopan Sultan100% (5)
- Prioritization of Nursing ProblemsDocument7 paginiPrioritization of Nursing ProblemsJoseph Raymund Fabian Huelar50% (4)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentDocument4 paginiAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjective: Short Term Goal: IndependentNinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NUR240 Nursing Care Plan Forms: Suffolk County Community CollegeDocument10 paginiNUR240 Nursing Care Plan Forms: Suffolk County Community CollegeJennifer AltenburgÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP MiDocument8 paginiNCP MiPitaca Madiam Annabehl PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Acute Chest PainDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan for Acute Chest PainNickale PeraltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ami 2Document10 paginiAmi 2sivakhamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ineffective Tissue PerfusionDocument1 paginăIneffective Tissue PerfusionRhae RaynogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Instructor Cover LetterDocument1 paginăClinical Instructor Cover Letterbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Virginia Henderson TheoryDocument6 paginiVirginia Henderson Theorybanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Assessment CHFDocument3 paginiLaboratory Assessment CHFbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Com Epi PaperDocument25 paginiCom Epi Paperbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- A G E - PathoDocument1 paginăA G E - Pathoranee dianeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Interventions CHFDocument3 paginiNursing Interventions CHFbanyenye25100% (1)
- NCP BurnDocument9 paginiNCP Burnbanyenye2533% (3)
- Patho MIDocument2 paginiPatho MIbanyenye25100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Congestive Heart Failure: Cardiovascular Systembanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Patho MIDocument2 paginiPatho MIbanyenye25100% (2)
- Principles of BioethicsDocument5 paginiPrinciples of Bioethicsbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care for Fracture PatientDocument2 paginiNursing Care for Fracture Patientbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Acute Bronchitis PathoDocument3 paginiAcute Bronchitis Pathobanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Electro Cardiograph yDocument14 paginiElectro Cardiograph ybanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Philippines Population Pyramid For 2010Document4 paginiPhilippines Population Pyramid For 2010banyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- EndometriosisDocument7 paginiEndometriosisbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation SubjectiveDocument6 paginiAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Explanation Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Subjectivebanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Philippine healthcare laws overviewDocument5 paginiPhilippine healthcare laws overviewbanyenye25100% (2)
- NCPDocument4 paginiNCPbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument2 paginiPa Tho Physiologybanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument3 paginiNCP Risk For Infectionbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP Risk For InfectionDocument3 paginiNCP Risk For Infectionbanyenye25Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Coaching - Im 2022Document9 paginiFinal Coaching - Im 2022Jhon PauloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sony Hilal Wicaksono, MD Universitas Indonesia HospitalDocument14 paginiSony Hilal Wicaksono, MD Universitas Indonesia HospitalSonyHilalWicaksonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physic An Checklist SampleDocument1 paginăPhysic An Checklist SampleNida AtmimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beta Blockers and Other Sympatholytic AgentsDocument43 paginiBeta Blockers and Other Sympatholytic AgentsAriel OlshevskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NGCM 112 Course OutlineDocument7 paginiNGCM 112 Course OutlineAYTONA, JAMAICA F.Încă nu există evaluări
- Heart Awareness Paula Cervera Joana Villanueva Regina IbarraDocument2 paginiHeart Awareness Paula Cervera Joana Villanueva Regina IbarraPaula CerveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes 11Document23 paginiNotes 11Yash SirowaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PracticeExam 4 QsDocument17 paginiPracticeExam 4 QsBehrouz YariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hi-Yield Notes in Im & PediaDocument20 paginiHi-Yield Notes in Im & PediaJohn Christopher LucesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Ischemic Heart Disease (IHDDocument9 paginiPathophysiology of Ischemic Heart Disease (IHDjohnhenryvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mutt and JeffDocument8 paginiMutt and Jeffyoyo1rn100% (2)
- Project 4.4.2: Heart Disease Interventions - Principles of BiomedicalDocument6 paginiProject 4.4.2: Heart Disease Interventions - Principles of BiomedicalMATTHEW DIAZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seminar On Mobile Coronary Care UnitDocument11 paginiSeminar On Mobile Coronary Care UnitASIR DHAYANI95% (19)
- Heart Failure Nursing Care Plans - 15 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsDocument13 paginiHeart Failure Nursing Care Plans - 15 Nursing Diagnosis - NurseslabsJOSHUA DICHOSOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bringing Down High Blood Pressure-ManteshDocument298 paginiBringing Down High Blood Pressure-Manteshzulmohd1100% (3)
- Horizon DXA System: Technical and Clinical AdvantagesDocument4 paginiHorizon DXA System: Technical and Clinical AdvantagesAhmet Can TezcanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15A ArteryDocument72 pagini15A Arterypavi7muruganathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac Rehabilitation in German Speaking Countries of Europe-Evidence-Based Guidelines From Germany, Austria and Switzerland Llkardreha-Dach-Part 2Document51 paginiCardiac Rehabilitation in German Speaking Countries of Europe-Evidence-Based Guidelines From Germany, Austria and Switzerland Llkardreha-Dach-Part 2NataliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Terms in Lay LanguageDocument7 paginiMedical Terms in Lay LanguageMavra zÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome - A Case StudyDocument11 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome - A Case StudyRocel Devilles100% (2)
- Medicine Lecture 17,18Document51 paginiMedicine Lecture 17,18Nayela AkramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart Rate Variability Today PDFDocument11 paginiHeart Rate Variability Today PDFVictor SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timi Risk Score AhaDocument8 paginiTimi Risk Score AhaNurvia AndrianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- FULL Download Ebook PDF Huszars Ecg and 12 Lead Interpretation 5th Edition PDF EbookDocument41 paginiFULL Download Ebook PDF Huszars Ecg and 12 Lead Interpretation 5th Edition PDF Ebookcody.cherry20097% (30)
- Jamainternal Byrne 2022 Oi 220004 1647010631.26452Document8 paginiJamainternal Byrne 2022 Oi 220004 1647010631.26452Irving Santiago SandovalÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACLS Post Test (Copy) 낱말 카드 - QuizletDocument18 paginiACLS Post Test (Copy) 낱말 카드 - Quizlet김민길Încă nu există evaluări
- Pub Annual Ar07Document46 paginiPub Annual Ar07Nichole Audrey SaavedraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in WomenDocument20 pagini2011 Cardiovascular Disease Prevention in WomenRafi UllahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiovascular System ReviewDocument237 paginiCardiovascular System ReviewsenthilmnurseÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 112 Eval ExamDocument11 paginiNCM 112 Eval ExamMartin T Manuel100% (1)