Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lookup Vector
Încărcat de
arunasagar_2011Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lookup Vector
Încărcat de
arunasagar_2011Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
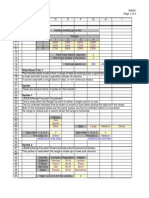
Excel Function Dictionary 1998 - 2000 Peter Noneley A 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 B C D E F G H
LOOKUP (Vector) Page 1 of 1 I J
LOOKUP (Vector)
Name Alan Bob Carol David Eric Francis Gail Jan 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Feb 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 Eric 120 =LOOKUP(F12,D4:G10,F4:F10) Mar 97 69 45 51 77 28 73
Type a Name in this cell : The Feb value for this person is :
What Does It Do ? This function looks for a piece of information in a list, and then picks an item from a second range of cells. Syntax =LOOKUP(WhatToLookFor,RangeToLookIn,RangeToPickFrom) The WhatToLookFor should be a single item. The RangeToLook in can be either horizontal or vertical. The RangeToPickFrom must have the same number of cells in it as the RangeToLookin. Be careful not to include unnecessary heading in the ranges as these will cause errors. Formatting No special formatting is needed. Example The following example shows how the =LOOKUP() function was used to match a name typed in cell G41 against the list of names in C38:C43. When a match is found the =LOOKUP() then picks from the second range E38:J38. If the name Carol is used, the match is made in the third cell of the list of names, and then the function picks the third cell from the list of values. RangeToLookIn Alan Bob Carol David Eric Fred RangeToPickFrom 15 20
10
25
30
Type a name : Value :
Carol 15 =LOOKUP(G41,C38:C43,E38:J38)
Problems The list of information to be looked through must be sorted in ascending order, otherwise errors will occur, either as #N/A or incorrect results.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- LookupDocument2 paginiLookuparunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Vlook Up FormulaDocument31 paginiVlook Up FormulaAnonymous 3hPIuGABÎncă nu există evaluări
- HLOOKUPDocument3 paginiHLOOKUParunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Index: 250 INDEX (D7:G9, G11, G12)Document3 paginiIndex: 250 INDEX (D7:G9, G11, G12)arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- LargeDocument1 paginăLargearunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- MS Excel FormulasDocument223 paginiMS Excel FormulasJakir ShajeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Excel FormulasDocument234 paginiMS Excel FormulasJkjiwani Acca100% (1)
- Excel FormulaDocument223 paginiExcel FormulavenkatchittiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self Learning Excel FormulasDocument223 paginiSelf Learning Excel Formulaspragadish_n100% (2)
- EXCEL FormulaeDocument223 paginiEXCEL FormulaeAbraham KramonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 47 Excel FormulasDocument139 pagini47 Excel FormulasSeeta Ram PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- AreasDocument1 paginăAreasarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- CS301 Midterm Exam ReviewDocument8 paginiCS301 Midterm Exam ReviewNetwork BullÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE368 O1 Assignment2 Dr-MohammedHalloushDocument6 paginiCE368 O1 Assignment2 Dr-MohammedHalloushAvinash KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FREQUENCYDocument2 paginiFREQUENCYarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Excel VlookupDocument3 paginiExcel VlookupSanjay L. RathodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Break EvenDocument49 paginiBreak EvenChristian Romeroso BaldonanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Highline Excel 2013 Class Videos 2-8Document208 paginiHighline Excel 2013 Class Videos 2-8خواكين زامبرانوÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexfield in ReportDocument4 paginiFlexfield in ReportSuneelTejÎncă nu există evaluări
- ContinueDocument2 paginiContinueZweli shabanguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final ExamDocument14 paginiFinal Examabegaz100% (1)
- Ehadocs Mod05 Vba Active Filter and EhdroplistsDocument10 paginiEhadocs Mod05 Vba Active Filter and Ehdroplistsamine bcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1 SolutionsDocument4 paginiWeek 1 SolutionsRahul MoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- IT111Document6 paginiIT111Thinesh RavechandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Structures and Algo FINALS 2Document23 paginiData Structures and Algo FINALS 2RiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cs301 02 Mid Spring 20101 My Comp Let FileDocument59 paginiCs301 02 Mid Spring 20101 My Comp Let FileSobia_Zaheer_22520% (1)
- Zoho Placement PaperDocument16 paginiZoho Placement PaperKrishna AbhishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Texas Instruments Activity #10 Title: Exploring Taylor's Integrals Author: Charles P. Kost II Estimated Time: 40-50 Minutes NCTM StandardsDocument4 paginiTexas Instruments Activity #10 Title: Exploring Taylor's Integrals Author: Charles P. Kost II Estimated Time: 40-50 Minutes NCTM StandardsIrtizahussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bahan Kursus Ms Excel 2007 Dipkg AmpangDocument8 paginiBahan Kursus Ms Excel 2007 Dipkg AmpangDequeNo Mohd NoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- List Manipulation QBDocument23 paginiList Manipulation QBVK CREATIONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3Document5 paginiAssignment 3FawadNaseerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Busn214 Week04Document150 paginiBusn214 Week04Nepomuseno WiliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zoho2 PDFDocument16 paginiZoho2 PDFPrincyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dsa521s Stack 2Document8 paginiDsa521s Stack 2g4zbjcw8jpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheetname Startdate Enddate Hours TotalcostDocument45 paginiSheetname Startdate Enddate Hours TotalcostAnupam DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generate Data in ExcelDocument28 paginiGenerate Data in ExcelTanya GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview of Excel VLOOKUP FunctionDocument9 paginiOverview of Excel VLOOKUP FunctionNorth PawÎncă nu există evaluări
- About Feature Construction +Document7 paginiAbout Feature Construction +anhanh81Încă nu există evaluări
- COUNTBLANKDocument1 paginăCOUNTBLANKarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Relation and FunctionDocument7 paginiRelation and Functionpatriciariza.torratoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brief Introduction of Data StructureDocument36 paginiBrief Introduction of Data Structureiwc2008007Încă nu există evaluări
- JAC2Document16 paginiJAC2Yash GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excel TipsDocument2 paginiExcel Tipsjtibrewala6250Încă nu există evaluări
- CS301 Finalterm Subjective 2013 Solved - 2Document16 paginiCS301 Finalterm Subjective 2013 Solved - 2Network Bull100% (2)
- Highline Excel 2013 Class Videos 2-8Document176 paginiHighline Excel 2013 Class Videos 2-8Nepomuseno WiliamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- EXCEL FormulaeDocument223 paginiEXCEL FormulaeMazter HukomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch-15 Spreadsheet Analysis Using MS Excel-Final Version 2018Document83 paginiCh-15 Spreadsheet Analysis Using MS Excel-Final Version 2018Syed Mir Talha ZobaedÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTA3O1 - Productivity Software - Unit 2Document10 paginiBTA3O1 - Productivity Software - Unit 2api-26077977Încă nu există evaluări
- Quiz PboDocument25 paginiQuiz Pboangganurwanto100% (3)
- Abdulrhman Aljifri, Lab5 With ExtraDocument5 paginiAbdulrhman Aljifri, Lab5 With Extraspecial gamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mid Term 2 PLSQLDocument4 paginiMid Term 2 PLSQLDa DadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Structures Lab Tasks - Linked Lists and Binary SequencesDocument3 paginiData Structures Lab Tasks - Linked Lists and Binary SequencesFaizan Butt0% (1)
- Lesson 1 - VlookupDocument9 paginiLesson 1 - VlookupAbdallah HashamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Csd201 Pe Instructions Students Are ONLY Allowed To Use:: Not Submit The Un-Edited Given ProjectDocument2 paginiCsd201 Pe Instructions Students Are ONLY Allowed To Use:: Not Submit The Un-Edited Given ProjectLong NguyễnÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGN 251Document18 paginiMGN 251Prableen KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visualizing Data in R 4: Graphics Using the base, graphics, stats, and ggplot2 PackagesDe la EverandVisualizing Data in R 4: Graphics Using the base, graphics, stats, and ggplot2 PackagesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionDe la EverandAdvanced C Concepts and Programming: First EditionEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Data Clean-Up and Management: A Practical Guide for LibrariansDe la EverandData Clean-Up and Management: A Practical Guide for LibrariansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Cabin Qty Details 2274/DSN/TW/D/012 R:R1 Dtd:16.12.2013Document4 paginiSecurity Cabin Qty Details 2274/DSN/TW/D/012 R:R1 Dtd:16.12.2013arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Civil DesignDocument2 paginiCivil Designarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Abcdedf 1 3 Abcdedf 2 3 Abcdedf 5 2 ABC-100-DEF ABC-200-DEF ABC-300-DEF Item Size: Large Item Size: Medium Item Size: SmallDocument2 paginiAbcdedf 1 3 Abcdedf 2 3 Abcdedf 5 2 ABC-100-DEF ABC-200-DEF ABC-300-DEF Item Size: Large Item Size: Medium Item Size: Smallarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Match: Bob 250 Alan 600 David 1000 Carol 4000 Alan 1000Document3 paginiMatch: Bob 250 Alan 600 David 1000 Carol 4000 Alan 1000arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Excel MOD Function GuideDocument1 paginăExcel MOD Function Guidearunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Lower: Alan Jones Bob Smith Carol Williams Cardiff ABC123Document1 paginăLower: Alan Jones Bob Smith Carol Williams Cardiff ABC123arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Minute: What Does It Do?Document2 paginiMinute: What Does It Do?arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Alan 1000 5000 Bob 6000 5000 Carol 2000 4000: What Does It Do?Document2 paginiAlan 1000 5000 Bob 6000 5000 Carol 2000 4000: What Does It Do?arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- MmultDocument2 paginiMmultarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- 100 MIN (C4:G4) : What Does It Do ?Document1 pagină100 MIN (C4:G4) : What Does It Do ?arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- 800 MAX (C4:G4) : What Does It Do ?Document1 pagină800 MAX (C4:G4) : What Does It Do ?arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- MeadianDocument1 paginăMeadianarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- LenDocument1 paginăLenarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- What Does It Do ?: 60 LCM (C4, D4) 36 LCM (C5, D5) 1632 LCM (C6, D6)Document1 paginăWhat Does It Do ?: 60 LCM (C4, D4) 36 LCM (C5, D5) 1632 LCM (C6, D6)arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Istext: True ISTEXT (D4) False ISTEXT (D5) False ISTEXT (D6) False ISTEXT (D7)Document1 paginăIstext: True ISTEXT (D4) False ISTEXT (D5) False ISTEXT (D6) False ISTEXT (D7)arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- LeftDocument1 paginăLeftarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Istext: True ISTEXT (D4) False ISTEXT (D5) False ISTEXT (D6) False ISTEXT (D7)Document1 paginăIstext: True ISTEXT (D4) False ISTEXT (D5) False ISTEXT (D6) False ISTEXT (D7)arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- IsrefDocument1 paginăIsrefarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- ISNONTEXTDocument1 paginăISNONTEXTarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Isodd: 1 2 2.5 2.6 3.5 3.6 Hello 1-Feb-98 1-Feb-96Document1 paginăIsodd: 1 2 2.5 2.6 3.5 3.6 Hello 1-Feb-98 1-Feb-96arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Islogical: False True 20 1-Jan-98 Hello #DIV/0!Document1 paginăIslogical: False True 20 1-Jan-98 Hello #DIV/0!arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Isodd: 1 2 2.5 2.6 3.5 3.6 Hello 1-Feb-98 1-Feb-96Document1 paginăIsodd: 1 2 2.5 2.6 3.5 3.6 Hello 1-Feb-98 1-Feb-96arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Hello 1-Jan-98 #N/A: What Does It Do?Document1 pagină1 Hello 1-Jan-98 #N/A: What Does It Do?arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- IserrDocument1 paginăIserrarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Isnumber: True Isnumber (D4) True Isnumber (D5) False Isnumber (D6) False Isnumber (D7) False Isnumber (D8)Document1 paginăIsnumber: True Isnumber (D4) True Isnumber (D5) False Isnumber (D6) False Isnumber (D7) False Isnumber (D8)arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Iseven: 1 2 2.5 2.6 3.5 3.6 Hello 1-Feb-98 1-Feb-96Document1 paginăIseven: 1 2 2.5 2.6 3.5 3.6 Hello 1-Feb-98 1-Feb-96arunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări
- IserrorDocument1 paginăIserrorarunasagar_2011Încă nu există evaluări