Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
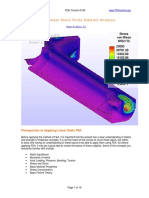
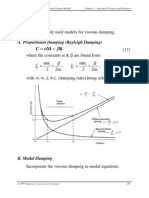
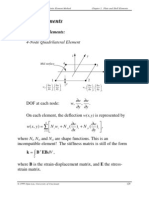
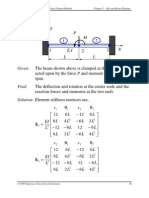
Chapter 4. Finite Element Modeling and Solution Techniques
Încărcat de
Mohit KulkarniTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapter 4. Finite Element Modeling and Solution Techniques
Încărcat de
Mohit KulkarniDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method
Chapter 4. FE Modeling and Solution Techniques
Chapter 4. Finite Element Modeling and Solution Techniques
I. Symmetry
A structure possesses symmetry if its components are arranged in a periodic or reflective manner.
Types of Symmetry: Reflective (mirror, bilateral) symmetry Rotational (cyclic) symmetry Axisymmetry Translational symmetry ...
Examples:
1998 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati
105
Lecture Notes: Introduction to Finite Element Method
Chapter 4. FE Modeling and Solution Techniques
Applications of the symmetry properties: Reducing the size of the problems (save CPU time, disk space, postprocessing effort, etc.) Simplifying the modeling task Checking the FEA results ...
Symmetry of a structure should be fully exploited and retained in the FE model to ensure the efficiency and quality of FE solutions.
Examples:
Cautions: In vibration and buckling analyses, symmetry concepts, in general, should not be used in FE solutions (works fine in modeling), since symmetric structures often have antisymmetric vibration or buckling modes.
1998 Yijun Liu, University of Cincinnati
106
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Practical Considerations in Finite Element ModelingDocument44 paginiPractical Considerations in Finite Element ModelingRabia ZulqarnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling Enterprise Architecture with TOGAF: A Practical Guide Using UML and BPMNDe la EverandModeling Enterprise Architecture with TOGAF: A Practical Guide Using UML and BPMNEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Intro To FemDocument28 paginiIntro To FemcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Models Approach in Automation: Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy SystemsDe la EverandMultiple Models Approach in Automation: Takagi-Sugeno Fuzzy SystemsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelling and Simulation (ME 620)Document34 paginiModelling and Simulation (ME 620)Sachin verma T20081Încă nu există evaluări
- 01 Chapter 1Document12 pagini01 Chapter 1Bibek MohatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student's Guide to Fundamentals of Chemistry: Brescia, Arents, Meislich, TurkDe la EverandStudent's Guide to Fundamentals of Chemistry: Brescia, Arents, Meislich, TurkEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- Basic Linear Static Finite Element AnalysisDocument19 paginiBasic Linear Static Finite Element AnalysisRuben Bartolome GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMF062 VehicleDynamics MemorandumDocument8 paginiMMF062 VehicleDynamics MemorandumAkshay GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 - PPT 1Document28 paginiUnit 1 - PPT 1Hari priyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document69 paginiLecture 1litrakhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1Document53 paginiLecture 1Kedir ShiferawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro1 M05 Gen ProcedureDocument20 paginiIntro1 M05 Gen ProceduresmartebuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSG Brep Solid ModelingDocument64 paginiCSG Brep Solid ModelingHariÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEA 2014-Course NotesDocument164 paginiFEA 2014-Course NotesVitor Folador GonçalvesÎncă nu există evaluări
- W1 - Introduction To SimulationDocument40 paginiW1 - Introduction To SimulationUswatun MaulidiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Process SynthesisDocument5 paginiIntroduction To Process SynthesisHansraj RahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- L.7. Analisis Model MatematisDocument28 paginiL.7. Analisis Model MatematisNasikhuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- F E MethodDocument11 paginiF E MethodJudy TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction Finite Element MethodDocument31 paginiIntroduction Finite Element MethodAgus SaefudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theoretical and Experimental Modal AnalysisDocument25 paginiTheoretical and Experimental Modal Analysislonkar.dinesh@gmail.com0% (1)
- FEM Lecture Notes Liu UCDocument188 paginiFEM Lecture Notes Liu UCsujan_duttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Analysis ProcedureDocument20 paginiGeneral Analysis ProcedureAyush ChoudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element Methods of Structural AnalysisDocument98 paginiFinite Element Methods of Structural Analysiswaqasahmed1983100% (1)
- Finite Element Method (FEMDocument95 paginiFinite Element Method (FEMthink groupyÎncă nu există evaluări
- L.6. Pemodelan MatematisDocument23 paginiL.6. Pemodelan MatematisNasikhuddin100% (1)
- Michael Okereke, Simeon Keates - Finite Element Applications. A Practical Guide To The FEM Process-Springer (2018) PDFDocument482 paginiMichael Okereke, Simeon Keates - Finite Element Applications. A Practical Guide To The FEM Process-Springer (2018) PDFAníbal Antonio Rojas JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech 324 - Prelim - Module No 5Document14 paginiMech 324 - Prelim - Module No 5Aomine DaikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- M1 Learning ObjectivesDocument2 paginiM1 Learning ObjectivesnnernÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cutting Forces Evaluation in Milling Using An Anal PDFDocument10 paginiCutting Forces Evaluation in Milling Using An Anal PDFBillel LouniciÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 1 Verifikasi Validasi Mathematical Model L06Document27 pagini6 1 Verifikasi Validasi Mathematical Model L06David MichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element Method (FEM) Module Code:: Lecture On Introduction To FEM, 15 September 2019Document17 paginiFinite Element Method (FEM) Module Code:: Lecture On Introduction To FEM, 15 September 2019Mesay Alemu TolchaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Module 1 FeaDocument53 paginiUnit 1 Module 1 FeaBharathi KannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class1 Intorduction FemDocument40 paginiClass1 Intorduction FemGuru MaheshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Creo Simulate - WBT 3911 0 WBTDocument3 paginiIntro To Creo Simulate - WBT 3911 0 WBTAndXDDÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.introduction To OptimizationDocument16 pagini1.introduction To OptimizationEsra TanyıldızÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 Book EngineeringComputationOfStruct PDFDocument325 pagini2015 Book EngineeringComputationOfStruct PDFSiyavash QahremaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- L1 Numerical Methods-AnalysisDocument16 paginiL1 Numerical Methods-AnalysisEdenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 6Document13 paginiClass 6One PieceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Design MorphologyDocument15 paginiProduct Design Morphologybalaganesh50% (2)
- Optimization, Modelling and SimulationDocument20 paginiOptimization, Modelling and Simulationrakesh yadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson-1 Modeling and SimulationDocument24 paginiLesson-1 Modeling and SimulationSundaramali Govindaswamy GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triangulation in Six SigmaDocument203 paginiTriangulation in Six SigmaClerenda McgradyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimization For Engineers by Kalyanmoy DebDocument45 paginiOptimization For Engineers by Kalyanmoy Deblankyrck69% (16)
- Sessional On Solid Mechanics and Machine Design Course No. - ME 2222 (Machine Shop & Mechanics Lab)Document24 paginiSessional On Solid Mechanics and Machine Design Course No. - ME 2222 (Machine Shop & Mechanics Lab)Somnath SomadderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Design For Manual Assembly: DFA Tool: To Reduce Manufacturing and Assembly CostsDocument62 paginiProduct Design For Manual Assembly: DFA Tool: To Reduce Manufacturing and Assembly CostsgetchmenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- RBE CAE10 (Structural Elements)Document58 paginiRBE CAE10 (Structural Elements)veeresh180802Încă nu există evaluări
- Computational Engineering ENG435 - FEM Part (Weeks 1-3)Document51 paginiComputational Engineering ENG435 - FEM Part (Weeks 1-3)Trevor LingÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEMDocument26 paginiFEMHossam M ALrohilyÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction to the Finite Element Method in 40 StepsDocument18 paginiAn Introduction to the Finite Element Method in 40 StepsIVAN DARIO JURADOÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEM IntroductionDocument26 paginiFEM IntroductionAlfia BanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 3 One 2 One N Inverse FunctionsDocument23 pagini2 3 One 2 One N Inverse Functionstarek mahmoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- 98 - Understanding Cyclic Symmetry Constraints PDFDocument5 pagini98 - Understanding Cyclic Symmetry Constraints PDFSameOldHatÎncă nu există evaluări
- A First Course in Finite Elements: CIVL 8/7117 Chapter 1 - Introduction To FEM 1/53Document53 paginiA First Course in Finite Elements: CIVL 8/7117 Chapter 1 - Introduction To FEM 1/53Fábio1 GamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AttachmentDocument58 paginiAttachmentAman Sharma0% (1)
- Unit - 1Document10 paginiUnit - 1Prashant SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 07 Lect02Document4 paginiChapt 07 Lect02Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 07 Lect03Document5 paginiChapt 07 Lect03Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV. Nature of Finite Element Solutions: Stiffening EffectDocument7 paginiIV. Nature of Finite Element Solutions: Stiffening EffectShanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 06 Lect03Document6 paginiChapt 06 Lect03Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 05 Lect02Document9 paginiChapt 05 Lect02Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 02 Lect07Document3 paginiChapt 02 Lect07Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6. Solid Elements For 3-D Problems I. 3-D Elasticity TheoryDocument6 paginiChapter 6. Solid Elements For 3-D Problems I. 3-D Elasticity TheoryShanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindlin Plate TheoryDocument10 paginiMindlin Plate TheoryKunal RanjaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 02 Lect03Document6 paginiChapt 02 Lect03Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 02 Lect06Document7 paginiChapt 02 Lect06Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Finite Element Method - Chapt - 02 - Lect04Document9 paginiIntroduction To Finite Element Method - Chapt - 02 - Lect04Eng_2014Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 02 Lect02Document6 paginiChapt 02 Lect02Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 02 Lect05Document5 paginiChapt 02 Lect05Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 02 Lect01Document7 paginiChapt 02 Lect01Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 01 Lect04Document5 paginiChapt 01 Lect04Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapt 01 Lect02Document6 paginiChapt 01 Lect02Shanmukha SundaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-I Circulation and VorticityDocument23 paginiChapter-I Circulation and VorticitydrsomenathduttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat ExchangerDocument155 paginiHeat ExchangerSajilal JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsDe la EverandCoating and Drying Defects: Troubleshooting Operating ProblemsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Is That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandIs That a Fact?: Frauds, Quacks, and the Real Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Science Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeDe la EverandScience Goes Viral: Captivating Accounts of Science in Everyday LifeEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (14)
- The Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionDe la EverandThe Periodic Table: A Very Short IntroductionEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- The Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsDe la EverandThe Disappearing Spoon: And Other True Tales of Madness, Love, and the History of the World from the Periodic Table of the ElementsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (146)
- The Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableDe la EverandThe Elements We Live By: How Iron Helps Us Breathe, Potassium Lets Us See, and Other Surprising Superpowers of the Periodic TableEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (22)
- Essential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilDe la EverandEssential Oil Chemistry Formulating Essential Oil Blends that Heal - Aldehyde - Ketone - Lactone: Healing with Essential OilEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction in the Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (9)
- An Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksDe la EverandAn Introduction to the Periodic Table of Elements : Chemistry Textbook Grade 8 | Children's Chemistry BooksEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- It's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingDe la EverandIt's Elemental: The Hidden Chemistry in EverythingEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (10)
- Organic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolDe la EverandOrganic Chemistry for Schools: Advanced Level and Senior High SchoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsDe la EverandThe Regenerative Grower's Guide to Garden Amendments: Using Locally Sourced Materials to Make Mineral and Biological Extracts and FermentsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- Introduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisDe la EverandIntroduction to Strategies for Organic SynthesisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandChemistry for Breakfast: The Amazing Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (90)
- Napoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryDe la EverandNapoleon's Buttons: 17 Molecules That Changed HistoryEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (25)
- Guidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementDe la EverandGuidelines for Asset Integrity ManagementEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Chemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableDe la EverandChemical Elements Pocket Guide: Detailed Summary of the Periodic TableÎncă nu există evaluări
- Monkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeDe la EverandMonkeys, Myths, and Molecules: Separating Fact from Fiction, and the Science of Everyday LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- The History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionDe la EverandThe History of Chemistry (Vol.1&2): Complete EditionEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)