Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Introduction To The World
Încărcat de
api-235617848Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Introduction To The World
Încărcat de
api-235617848Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Yessica Pacheco
Introduction to the Worlds Biomes
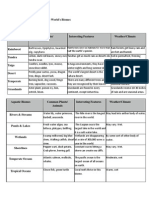
Rainforest 1. What are the two types of rainforests? In the United States, where are our rainforests located? (Be specific). What percentage of out original rainforests does this represent? The two types of rainforests are temperate and tropical. In the U.S, our rainforests are located in the Pacific Northwest. The percentage of original rainforests is 25%. Tundra 2. Where is the Tundra Biome located? What is permafrost? What percentage of the Earth's surface is covered by Tundra? The tundra biome is located in the North Pole. Permafrost is a permanently frozen layer of ground. 20% of the Earth's surface is Tundra. Taiga 3. Where is the Taiga Biome located? What is the soil like in the Taiga-why? Taiga biomes are located in large portions of Canada, Europe and Asia. 50 degrees latitude north of Arctic Circle. The soil in Taiga biomes are thin and lacking nutrients, because of slow decomposition. Desert 4. How much rainfall is characteristic of deserts? Explain where most deserts are located and the RAINSHADOW effect.
Yessica Pacheco Rainfall is steady in the deserts. Deserts are located 30 degrees latitude north and south. Deserts occur in the rainshadow effect, because when wind goes up a mountain it causes cold so it rains/snows. When goes down the other side, it gets warmer causing moisture, so it doesn't rain. This creates a desert. Temperate Deciduous Forest 5. What is special about this biome? Deciduous trees have special leaves that are adapted to the biomeexplain. This biome can go through all four seasons. The leaves in these trees adapt to the season, in the autumn they change color, in the winter the leaves fall off and regrows in the spring. Grasslands 6. Grasslands are found on every continent except for one- which? How much rainfall do grasslands getwhy is this important? What are the 3 types of grasslands that are found in North America? What are grasslands called in other places in the world? Grasslands exist on every continent except for Antarctica. Grasslands get 10-30 inches of rain per year. Too much rain will cause it to become a forest and too little will cause it to become a desert. 3 types of grasslands are the Tall Grass Prairie, Mixed Grass Prairie and Short Grass Prairie. Grasslands are called pampas in South America, steppes in Europe and savannas in Africa. Rivers and Streams 7. how much water on Earth does running water represent? What is watershed? What are the two main processes that happen to surface water? What is the longest river in the world? What is the longest river in the United States? What is a hydroelectric dam? Running water represents .3% of all of water on Earth. Watershed is an area of land that has a common set of streams and rivers that drain into a single body of water. Two main processes that happen to surface water are surface runoff and infiltration. The longest river in the world is the Nile River in Egypt. The longest river in the US is the Mississippi-Missouri River. A hydroelectric dam is a dam that takes water and converts it into hydroelectric power. Ponds and Lakes 8. What is the difference between a pond and lake? Name the four stages of succession of a pond. Explain how an Oxbow Lake is formed. What is the largest lake in the world? What is the largest lake in the United States? What is the deepest lake in the world? What is Lake Effect Snow? Explain. What is the cause of summer kill in some lakes? A pond is shallow and supports rooted plants. A lake is deeper and big enough for waves to be produced. The four stages of succession of a pond is 1) seeds inhabit the ponds.
Yessica Pacheco 2) Debris increases and vegetation appears. 3)Emergents appear. 4) When pond floors are close enough to the bottom, emergents can grow across the floor and the ponds become a marsh. Oxbow Lakes are formed when erosion and deposits of soil change the river's course. The largest lake in the world is the Caspian Sea. The largest lake in the United States is Lake Superior. The deepest lake in the world is Lake Baikal in Siberia. Lake Effect Snow is when cold winds blow and picks up moisture from warm lakes and cools down when it goes uphill. This causes moisture to condense and fall as snow. The causes of summerkill is when algae becomes overabundant and becomes ripe during Summer, which will decrease oxygen levels. Wetlands 9. What are the types of freshwater wetlands- name and define them. Explain why wetlands are so important. what is happening to our wetlands? Types of freshwater wetlands are marsh (inland area inundated with 1-6 feet of water), swamp (Slow moving streams), bog (peat-accumulating wetland), prairie pothole (shallow depressions of water), riparian marsh (Marshes along rivers). Wetlands are important, because they prevent flooding and purifies water. Our wetlands are disappearing anually at 300,000 acres. Shorelines 10. What kind of life forms will you find in the intertidal zone? What is a barrier island? what is an estuary? What is life like in an estuary? What is a salt marsh? What is the Mangrove Forest? How are the trees specially adapted to living in that environment? Why are they important? Lifeforms in the intertidal zones are sea stars, seashells and sea clams. Barrier Islands are islands seperated by main bodies of water that vary in size. An estuary is a partially enclosed body of water where seawater is mixed with fresh water. Life in an estuary has a diverse mix of sea and land creatures. A salt marshes are wetlands that contain saltwater. The Mangrove Forest thrive near mouths of large rivers where the deltas provide a lot of sediment. Trees are specially adapted to living in that environment because they have aerial roots and salt tapping roots. They are important because they protect the coastline and prevent erosion. Temperate Ocean Zones 11. Name and describe the different zones of the ocean and how they are divided. Describe the different photic zones of the ocean. What are kelp forests? Where are they found? The types of zones are benthic (ocean bottom), pelagic zone (water itself), neritic zone (extends from high tide to low tide), oceanic (water deeper than 600 feet). Sunlit zone is the top layer of the ocean. The Twilight zone is a zone where only small amounts of light can penetrate. The midnight zone has no
Yessica Pacheco light 90% of the time. Kelp forests are large amounts of kelp that can grow up to 125 feet. They are found in the Atlantic Coast and Pacific Waters. Tropical Ocean Zones 12. What is coral made of? Explain. Where are most coral reefs located? Where is the largest oral reef? Coral is made of polyp. Polyp is a column shaped animal that attaches to the floor of the reef. Coral reefs are located in tropical oceans near the equator. The largest coral reef is the Great Barrier Reef in Australia.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Compare and Contrast EssayDocument2 paginiCompare and Contrast Essayapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Environmental Science - Desert and Aquatic EcosystemDocument7 paginiEnvironmental Science - Desert and Aquatic EcosystemShruthiDevar100% (1)
- Apes Food For ThoughtDocument5 paginiApes Food For Thoughtapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- MT ST HelensDocument2 paginiMT ST Helensapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Modelling Groundwater Flow in The Plaine Du Nord - Massacre Shallow Aquifer, HaitiDocument17 paginiModelling Groundwater Flow in The Plaine Du Nord - Massacre Shallow Aquifer, HaitiLucia HospinalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apes-Introduction To The Worlds BiomesDocument4 paginiApes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomesapi-235647128Încă nu există evaluări
- Intro To BiomesDocument5 paginiIntro To Biomesapi-235669157Încă nu există evaluări
- Apes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes RepairedDocument7 paginiApes-Introduction To The Worlds Biomes Repairedapi-235658421Încă nu există evaluări
- Apes - Introduction To The Worlds BiomesDocument6 paginiApes - Introduction To The Worlds Biomesapi-236697820Încă nu există evaluări
- Biomes: How Many Biomes Are There?Document12 paginiBiomes: How Many Biomes Are There?Branlie RuetasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomes: Thinking QuestionsDocument21 paginiBiomes: Thinking QuestionsUsman MaukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of BiomeDocument8 paginiTypes of Biomelizzie_mcgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecosystems and Types of EcosystemsDocument42 paginiEcosystems and Types of EcosystemsIbrahim AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 - Lesson 3 ActivityDocument4 paginiModule 1 - Lesson 3 ActivityKirstelle SarabilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Biomes - CompiledDocument7 paginiTypes of Biomes - CompiledToni GutzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinds of Ecosystem and CommunitiesDocument18 paginiKinds of Ecosystem and CommunitiesBelmas CarbonellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biodiversity of Our TimesDocument14 paginiBiodiversity of Our TimesnelsapiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taiga (: Citation NeededDocument4 paginiTaiga (: Citation NeededLyraÎncă nu există evaluări
- GK PDFDocument14 paginiGK PDFManjeet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class-7 Ncert Chapter-5 Water Terrarium: It Is An Artificial Enclosure For Keeping Small House PlantsDocument33 paginiClass-7 Ncert Chapter-5 Water Terrarium: It Is An Artificial Enclosure For Keeping Small House PlantssatyamksspÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rainforests XDocument2 paginiRainforests Xfiralestari128Încă nu există evaluări
- BiomesDocument117 paginiBiomesgeissingert93% (14)
- Review Questions Biosphere (KEY)Document6 paginiReview Questions Biosphere (KEY)owls_1102Încă nu există evaluări
- Tema 11: La EcosferaDocument10 paginiTema 11: La EcosferaAinhoa Pérez GiménezÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Creative Doodle Brainstorming PresentationDocument17 paginiWhite Creative Doodle Brainstorming PresentationZyra AbordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument48 paginiNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentSuperpower KhilafahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco SystemDocument3 paginiEco SystemAnanya GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OceanDocument3 paginiOceanT chÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Aquatic BiomeDocument4 paginiThe Aquatic BiomeAngelie LapeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Module EnviSciDocument55 paginiFinal Module EnviSciJeff Ray BarreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- G 4 PPT Wala Pang Ano YanDocument21 paginiG 4 PPT Wala Pang Ano YanPyrrhus John BagamaspadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desert Eco SystemDocument6 paginiDesert Eco SystemSiva PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terrestrial EcosystemDocument26 paginiTerrestrial EcosystemFrancis PopoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Title /course Code Introduction To Environment (1421)Document7 paginiTitle /course Code Introduction To Environment (1421)M Noaman AkbarÎncă nu există evaluări
- HandOut (World Biomes)Document7 paginiHandOut (World Biomes)Jonel BarrugaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco System 1Document50 paginiEco System 1PORAKH MONE GOHAIN100% (1)
- Desert Eco SystemDocument5 paginiDesert Eco SystemSiva PrasadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vegetation Zones in Nigeria: Azolla Caroliniana (Mosquito Fern), SaururusDocument8 paginiVegetation Zones in Nigeria: Azolla Caroliniana (Mosquito Fern), SaururusIdris MurainaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecology and EcosystemDocument6 paginiEcology and EcosystemYunzcho GhaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomas de La Tierra en InglesDocument2 paginiBiomas de La Tierra en InglesSAAM_BLDÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENGG 413 Environmental Science and Engineering Major Ecosystem of The WorldDocument20 paginiENGG 413 Environmental Science and Engineering Major Ecosystem of The WorldFatima Therese ManaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomes and BioGeoChemical CycleDocument4 paginiBiomes and BioGeoChemical CycleMel Angelo Ayala OrigÎncă nu există evaluări
- Honors Biology 5 8 14 PresentationDocument18 paginiHonors Biology 5 8 14 Presentationapi-239943146Încă nu există evaluări
- People in Earth EcosystemDocument29 paginiPeople in Earth EcosystemAmina SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rosalie Brillantes AsignmentDocument6 paginiRosalie Brillantes AsignmentTata Duero LachicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science PDFDocument152 paginiScience PDFAster Joy MabaquiaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit V BiomesDocument14 paginiUnit V BiomesHyramae CuacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo-Studies chp-1 (Water)Document9 paginiGeo-Studies chp-1 (Water)habiba buttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomes 110821050021 Phpapp02Document26 paginiBiomes 110821050021 Phpapp02Sendaydiego Rainne GzavinÎncă nu există evaluări
- About RainforestDocument4 paginiAbout RainforestAli AusatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Fun Facts About Florida's Everglades: A 15-Minute BookDe la Everand14 Fun Facts About Florida's Everglades: A 15-Minute BookEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- 14 Fun Facts About Florida's Everglades: A 15-Minute Book: Educational VersionDe la Everand14 Fun Facts About Florida's Everglades: A 15-Minute Book: Educational VersionÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.TRF Case StudyDocument33 pagini2.TRF Case StudySidhant BendreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomes Reading1Document2 paginiBiomes Reading1Nathaniel WesterÎncă nu există evaluări
- P5 Reading Exercise 39Document3 paginiP5 Reading Exercise 39中文軍事基地Încă nu există evaluări
- GRADE 8 Pasa Rose PDFDocument75 paginiGRADE 8 Pasa Rose PDFKaparaz, Ronald Allan B. Sec-CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apresentação Educacional Geografia Física Desenhado À Mão AzulDocument13 paginiApresentação Educacional Geografia Física Desenhado À Mão AzulliviamarinadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tropical Rain ForestsDocument2 paginiTropical Rain ForestsStanev DanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environmental ScienceDocument5 paginiEnvironmental ScienceJhupoor GargolesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freshwater BiomesDocument8 paginiFreshwater BiomesMichael clyde LepasanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Eco SystemDocument3 paginiTypes of Eco SystemGagandeep SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unlocking the Secrets of Rivers, Lakes, Oceans and TreesDe la EverandUnlocking the Secrets of Rivers, Lakes, Oceans and TreesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Fresh and Saltwater Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksDe la EverandEcosystem Facts That You Should Know - The Fresh and Saltwater Edition - Nature Picture Books | Children's Nature BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Natural SelectionDocument2 paginiNatural Selectionapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Life in The OceanDocument3 paginiLife in The Oceanapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Life After PeopleDocument1 paginăLife After Peopleapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Aquatic Ecosystems Study GuideDocument5 paginiAquatic Ecosystems Study Guideapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- PhytoplantonDocument3 paginiPhytoplantonapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Happyfishinglab PyessicaDocument2 paginiHappyfishinglab Pyessicaapi-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Dissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1Document7 paginiDissolved Oxygen Primary Prod Activity1api-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6Document2 paginiChapter 6api-235617848Încă nu există evaluări
- Hydrology.21 30Document10 paginiHydrology.21 30CgpscAspirantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is 4410 9 1982 PDFDocument25 paginiIs 4410 9 1982 PDFSameer Singh PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Potentiometric Surfaces QuestiDocument4 paginiPotentiometric Surfaces QuestiWelsinsin Kevin Sin0% (1)
- Module - 1 IntroductionDocument33 paginiModule - 1 IntroductionIffat SiddiqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution of Water On EarthDocument16 paginiDistribution of Water On EarthKaizen ShoriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis AdvisingDocument11 paginiThesis Advisingtamenea DemissieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recorded Sagamore Pond Plat Pickerington OhioDocument5 paginiRecorded Sagamore Pond Plat Pickerington OhioTheBuckeyeRealtyTeamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023 Capstone Project Report Template - Engineering Services ReportDocument14 pagini2023 Capstone Project Report Template - Engineering Services ReportNokwanda PoliteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk Assessment On Water Quality of Calinog CreekDocument9 paginiRisk Assessment On Water Quality of Calinog CreekHoney Grace Lumahang PalasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acp 10 - PPT - Q3 - M3Document86 paginiAcp 10 - PPT - Q3 - M3CherryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irrigation Engineering: Course Instructor: Engr. Arif Asghar GopangDocument22 paginiIrrigation Engineering: Course Instructor: Engr. Arif Asghar GopangArif AsgharÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Most Polluted River in The World, Citarum River, IndonesiaDocument2 paginiThe Most Polluted River in The World, Citarum River, IndonesiaAnggi Dwi PratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 Flood Control Purpose and Flood Control Master PlanningDocument45 pagini02 Flood Control Purpose and Flood Control Master PlanningJapoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Logging (2) FIDocument32 paginiWater Logging (2) FIVaish NaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- KENNETH C. GUTIERREZ (Narrative Report in Hydrology)Document4 paginiKENNETH C. GUTIERREZ (Narrative Report in Hydrology)Kent Arrol GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Landslide Mitigation Strategies: Prepared ForDocument35 paginiLandslide Mitigation Strategies: Prepared ForGabÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCVN 6772-2000 Domestic Waste Water Standards-Permssible Pollution (En)Document2 paginiTCVN 6772-2000 Domestic Waste Water Standards-Permssible Pollution (En)Pn ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- VVVV Imp Projct Evs.... Mithi River Pollution...Document3 paginiVVVV Imp Projct Evs.... Mithi River Pollution...aalimhudda50% (2)
- Nature-Based Solutions For Water in The Peri-Urban: Case Study Brief - Udaipur, IndiaDocument8 paginiNature-Based Solutions For Water in The Peri-Urban: Case Study Brief - Udaipur, IndiaNandita SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Darcy 3Document66 paginiDarcy 3Muh. Farid wajedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Executive Summary of KJA Recommendation On Karnataka State Water Policy 2019Document55 paginiExecutive Summary of KJA Recommendation On Karnataka State Water Policy 2019junkchanduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alker - 2008 - The Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System (NSAS)Document43 paginiAlker - 2008 - The Nubian Sandstone Aquifer System (NSAS)Mcn calmendÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mind Map OutlineDocument1 paginăMind Map OutlineZafirah NabilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kristal Eng PDFDocument32 paginiKristal Eng PDFDũng Phạm AnhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewer and Water Line Layout: P 7 7 Froilan S. Florendo, JRDocument1 paginăSewer and Water Line Layout: P 7 7 Froilan S. Florendo, JRRA CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- EASEMENT-OF-AQUEDUCTS Notes PDFDocument16 paginiEASEMENT-OF-AQUEDUCTS Notes PDFJustineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rainwater HarvestingDocument3 paginiRainwater HarvestingShekh Muhsen Uddin AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sewage Treatment Plant: Q. State The Procedure For Discharging Sewage Into The SeaDocument5 paginiSewage Treatment Plant: Q. State The Procedure For Discharging Sewage Into The SeaMohammad Jahid AlamÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.04-Suardi N-Edi R-Dede R-Yakub S PDFDocument15 pagini2.04-Suardi N-Edi R-Dede R-Yakub S PDFkamalÎncă nu există evaluări