Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
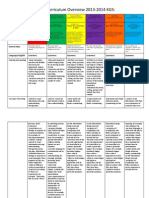
Yearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 Grade 2:: Calendar
Încărcat de
api-236387116Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Yearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 Grade 2:: Calendar
Încărcat de
api-236387116Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Yearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 Grade 2:
Calendar
September/ October Approximately 5/6 weeks November/ December Approximately 5/6 weeks January/ February Approximately 5/6 weeks February/ March Approximately 5/6 weeks April/ May Approximately 5/6 weeks May/ June Approximately 5/6 weeks
Transdisciplinary themes Subjects & Strands
An Inquiry into: Who We Are
An Inquiry into: How We Organize Ourselves An exploration of human systems and communities; of the world of work, its nature and its value; of employment and unemployment and their impact.
An Inquiry into: How The World Works An exploration of the physical and material world; of natural and human-made phenomena; of the world of science and technology.
An Inquiry into: How We Express Ourselves An exploration of the ways in which we discover and express our nature, ideas, feelings, beliefs and values through language and the arts.
An Inquiry into: Sharing The Planet
An Inquiry into: Where We Are In Place & Time An exploration of our orientation in place and time; of our personal histories; of history and geography from local and global perspectives; of our homes and journeys; of the discoveries, explorations and migrations of humankind; of the contributions of individuals and civilizations. Exploring the arts around the world can lead to creative personal journeys.
An exploration of the nature of the self; of our beliefs and values; of personal, physical, mental, social and spiritual health; of our families, friends, communities and cultures; of our rights and responsibilities; of what it means to be human.
An exploration of our rights and responsibilities as we try to share finite resources with other people, with other living things; of communities and of the relationships within and between them.
Central Idea
Role models reflect the beliefs and values of individuals and societies.
We use mapping systems to broaden our understanding of the world.
Given the basics needed for survival, everything in life moves in cycles.
People design messages to target certain groups.
When interacting with natural habitats people make choices that have an impact on other living things.
Language-English
Learners:
Learners:
Learners:
Learners:
Learners:
Learners:
Focus: Launchingnonfiction
Focus: Expert projectsinformational writing
Focus: Writing and revising- realistic fiction
Focus: Writing adaptations of familiar fairytales and folktales express thoughts, ideas, and opinions and discuss them, respecting contributions from others -follow multi-step directions
Focus: Opinion Writing- persuasive reviews
Focus: PoetryPowerful thoughts in tiny Packages
Listening and speaking
-listen attentively and speak appropriately in small and large group interactions. Listen to a variety of oral presentations including stories, poems, rhymes and reports and respond with increasing confidence and detail -use a variety of implements to practice and develop handwriting and presentation skills -use a variety of implements to practice and develop presentation skills
-describe personal experiences. -use language to address the eir needs, express feelings and opinions
retell familiar stories in sequence -describe personal experiences. -use oral language to communicate during classroom activities, conversations and imaginative play
-pick out main events and relevant points in oral text -use grammatical rules of the languages of instructions (learners may overgeneralize at this stage)
-ask questions to gain information and respond to inquiries directed to themselves or to the class
Viewing & Presenting
-recognize ICT iconography and follow prompts to access programs or activate devices
-recognize ICT iconography and follow prompts to access programs or activate devices
-recognize ICT iconography and follow prompts to access programs or activate devices
-recognize and name familiar texts, for example, advertising, logos, labels, signs, ICT iconography
-through teacher modeling, become aware of terminology used to tell about visual effects, for example, features, layout, border, frame
Reading
-recognize a range of different text types, for example, letters, poetry, plays, stories, novels, reports, articles -realize that there is a difference between fiction and non-fiction and use books for particular purposes, with teacher guidance -instantly recognize an increasing bank of high - frequency and high interest word, characters or symbols -discuss their own experiences and relate them to fiction and non-fiction texts -wonder about texts and ask questions to try to understand what the author is trying to say to the reader
-recognize a range of different text types, for example, letters, poetry, plays, stories, novels, reports, articles -realize that there is a difference between fiction and non-fiction and use books for particular purposes, with teacher guidance. -instantly recognize an increasing bank of high - frequency and high interest word, characters or symbols -discuss their own experiences and relate them to fiction and non-fiction texts -wonder about texts and ask questions to try to understand what the author is trying to say to the reader
-recognize a range of different text types, for example, letters, poetry, plays, stories, novels, reports, articles -identify and explain the basic structure of a story, beginning, middle and end; and use storyboards or comic strips to communicate elements -make predictions about a story based on their own knowledge and experience, revise or confirm predictions as a story progresses -instantly recognize an increasing bank of high - frequency and high interest word, characters or symbols -discuss their own experiences and relate them to fiction and non fiction texts -wonder about texts and ask questions to try to understand what the author is trying to say to the reader -use graphic organizers to plan writing, for example mind maps and story
-recognize a range of different text types, for example, letters, poetry, plays, stories, novels, reports, articles -identify and explain the basic structure of a story, beginning, middle and end; and use storyboards or comic strips to communicate elements -make predictions about a story based on their own knowledge and experience, revise or confirm predictions as a story progresses. -instantly recognize an increasing bank of high - frequency and high interest word, characters or symbols -discuss their own experiences and relate them to fiction and non fiction texts -wonder about texts and ask questions to try to understand what the author is trying to say to the reader -use graphic organizers to plan writing, for example mind maps and story
-recognize a range of different text types, for example, letters, poetry, plays, stories, novels, reports, articles -realize that there is a difference between fiction and non-fiction and use books for particular purposes, with teacher guidance. -instantly recognize an increasing bank of high - frequency and high interest word, characters or symbols -discuss their own experiences and relate them to fiction and non-fiction texts -wonder about texts and ask questions to try to understand what the author is trying to say to the reader
-recognize a range of different text types, for example, letters, poetry, plays, stories, novels, reports, articles -instantly recognize an increasing bank of high - frequency and high interest word, characters or symbols -discuss their own experiences and relate them to fiction and nonfiction texts -wonder about texts and ask questions to try to understand what the author is trying to say to the reader
Writing
-use graphic organizers to plan writing, for example mind maps and story
-use graphic organizers to plan writing, for example mind maps and story
-use graphic organizers to plan writing, for example mind maps and story
-use graphic organizers to plan writing, for example mind
boards -organize ideas in a logical sequence -use appropriate writing conventions -form letters/characters conventionally and legibly, with an understanding as to why this is important within a language community -Write legibly and in consistent style -proofread their own writing and make some corrections and improvement -With teacher guidance publish written work in handwritten form or in digital format
boards -organize ideas in a logical sequence -use appropriate writing conventions -form letters/characters conventionally and legibly, with an understanding as to why this is important within a language community -Write legibly and in consistent style -proofread their own writing and make some corrections and improvement -With teacher guidance publish written work in handwritten form or in digital format
boards -organize ideas in a logical sequence. -use appropriate writing conventions -form letters/characters conventionally and legibly, with an understanding as to why this is important within a language community -Write legibly and in consistent style -proofread their own writing and make some corrections and improvement -With teacher guidance publish written work in handwritten form or in digital format
boards -organize ideas in a logical sequence -use appropriate writing conventions -form letters/characters conventionally and legibly, with an understanding as to why this is important within a language community. -Write legibly and in consistent style. -proofread their own writing and make some corrections and improvement. -With teacher guidance publish written work in handwritten form or in digital format
boards -organize ideas in a logical sequence. -use appropriate writing conventions -form letters/characters conventionally and legibly, with an understanding as to why this is important within a language community -Write legibly and in consistent style -proofread their own writing and make some corrections and improvement -With teacher guidance publish written work in handwritten form or in digital format
maps and story boards -organize ideas in a logical sequence -use appropriate writing conventions -form letters/characters conventionally and legibly, with an understanding as to why this is important within a language community -write legibly and in consistent style -proofread their own writing and make some corrections and improvement -with teacher guidance publish written work in handwritten form or in digital format
Language-Arabic
Listening and speaking
Learners:
-listen to a variety of oral presentations.
Learners:
-follow multi-step directions.
Learners:
-listen to a variety of oral presentations including stories and reports and respond with increasing confidence and detail.
Learners:
-use language to address their needs, express feelings and opinions.
Learners:
-ask questions to gain information and respond to inquiries directed to themselves or to the class.
Learners:
-express thoughts, ideas, and opinions and discuss them, respecting contributions from others.
Viewing & Presenting
-resent a life of a famous person.
-recognize and name familiar visual texts-
-use moving images to communicate ideas
-use a variety of implements to
-use a variety of implements to
-use a variety of implements to
signs.
and information.
practice and develop presentation skills.
practice and develop presentation skills.
practice and develop presentation skills.
Reading
-recognize a range of different text types about role model.
-instantly recognize an increasing bank of high- frequency and high-interest words, characters or symbols.
-recognize a range of different text types, for example stories.
-discuss their own experiences and relate them to fiction and non-fiction texts.
-instantly recognize an increasing bank of high- frequency and high-interest words, characters or symbols.
-recognize a range of different text types, for example, letters, plays, stories, novels, reports, articles.
Writing
-use appropriate writing conventions to write about their own role models.
-write legibly, and in a consistent style.
-organize ideas in a logical and correct sequence.
-organize ideas in a logical sequence, for example, write simple narratives with a beginning, middle and end.
-write legibly, and in a consistent style.
-use graphic organizers to plan writing, for example, Mind Maps, storyboards.
Mathematics
Data handling Measurement Shape & Space Pattern & Function Number Problem solving
Learners: -review number patterns, number sequences, number grids, and number lines. -review months, weeks, and days, and telling time. -practice addition facts. -give equivalent names for numbers. -compare numbers using the symbols <, >, and =. -make up, represent, and solve addition and subtraction
Learners: -review place value in 2 digit and 3 digit numbers, -review coin values and exchanges among coins -tell time and write time in digital clock notation -gather data by counting and to analyze data. -solve number stories. -read and show temperatures. -develop different
Learners: -develop the concepts of point and line segment -identify, name and classify polygons. -observe similarities and differences among 3D shape. -explore symmetry. -introduce and practice array models. -review strategies for solving addition and subtraction problems. -develop procedures
Learners: -describe patterns that result from skip counting by 2s, 5s and 10s. -build mental arithmetic skills for adding 1-digit and multidigit numbers. -make frequency tables, line plots, and bar graphs from reallife data. -review basic fraction concepts. -use fractions to name parts of a whole and of a collection. -find pairs of
Learners: -review measuring with yards and meters. -measure longer distances. -develop the concepts of perimeter and area. -know units of weight. -review notation and equivalencies for money amounts. -provide experiences with comparing prices, estimating costs, and making change. -develop and extend place-value concepts.
Learners: -review addition and subtraction algorithms using sums of money. -introduce and practice the tradefirst subtraction algorithm. -solve multiplication and division number stories. -to practice multiplication and division facts using a products table and fact families. -review time
number stories. -review and apply alternative strategies for addition and subtraction. -practice addition and subtraction facts for sums and differences up to and including 10.
strategies for adding 2 and 3 digit numbers.
for multiplication and division problems.
equivalent fractions. -solve number stories involving fractions.
equivalencies and calendar facts. -read times in different ways and show time on a clock.. -show events on a timeline. -review and extend shortcuts and strategies for learning multiplication facts. Investigate the relationship between multiplication and division. -collect and analyze data related to measurement, using line plots, frequency tables, and bar graphs. Identify range, median, and mode.
Science
Living Things Earth & Space Materials & Matter Forces, Motion & Energy Investigations
Learners:
Investigations make observations and predictions and questions are formed -differentiate observations from personal interpretation
Learners:
Earth & Space -study the planet Earth and its position in the universe, particularly its relationship with the sun; the natural phenomena and systems that shape the planet and the
Learners:
Living Things -discover the characteristics, systems and behaviors of humans and other animals, and of plants; the interactions and
Learners:
Forces, Motion & Energy -inquire about energy, its origins, storage and transfer, and the work it can do; the study of forces; the application of scientific understanding through inventions
Learners:
Living Things -investigate the characteristics, systems and behaviors of humans and other animals, and of plants; the interactions and relationships between and among them, and
Learners:
Materials & Matter -examine the properties, behaviors and uses of materials, both natural and human-made; the origins of humanmade materials
distinctive features that identify it; the infinite and finite resources of the planet Focus: Weather Patterns
relationships between and among them, and with their environment Focus: Life Cycles
and machines Focus: Magnets
with their environment Focus: Habitats
and how they are manipulated to suit a purpose Focus: Materials and Matter
Social studies
Hu e - human systems & economic activities -social organization & culture -continuity & change through time -human & natural environments -resources & environment
Learners:
-explore social organisations and culture through role models in our societies
Learners:
-discover that in a community people share responsibility toward a common purpose. -understand that communities provide interconnected services designed to meet peoples needs.
Learners:
-find that human survival is connected to understanding the continual changing nature of the earth.
Learners:
-demonstrate that a variety of signs and symbols facilitate local and global communication.
Learners:
-realize that the design of buildings and structures is dependant upon the environment and available materials.
Learners:
-recognize that the development of global perspectives is supported through understanding our place in the world in relation to others. -discover that family histories provide an insight into cultural and personal identity.
UAE social studies
Learners:
-inquire into people around the world in different cultures and different aspects
Learners:
-use mapping systems to understand the world . Use the mapping symbols to read the map
Learners:
-identify the evidence that the Earth has changed (for example, land formations in local environment)
Learners:
-explore a variety of signs and symbols and interpret their messages
Learners:
-explain the different roles of people in the recycling process
Learners:
-describe how artifacts, heirlooms and rituals are evidence of cultural identity
Islamic studies
Learner profile
Learners:
Caring; -show empathy,
Learners:
Knowledgeable; develop and use
Learners:
Thinkers; -explain some of the
Learners:
Inquirer; -developing skills for
Learners:
Balanced; - create awareness
Learners:
Communicator; -find the ways on
compassion and respect to our beloved prophet and other famous personalities in Islam.
conceptual understanding about maintaining and managing ourselves according to Islam.
verses of Quran about the world and its systems.
inquiry and research, about how Muslims celebrate their Islamic festivals around the world.
towards environment, as Islam defines our roles clearly to maintain and save a peaceful, healthy environment.
maps of different countries, how to go Makkah (Saudi Arabia) -use compass rose to find the direction of Makkah.
PE
Identity; Responsibility
Learners:
-interact within a larger group.
Learners:
-map their bodies to help them understand themselves better.
Learners:
-realize that survival and success come from understanding and applying skills and strategies of movement. -understand that movement is necessary for survival.
Learners:
-develop concept Integration
Learners:
-understand that their choices impact other things and people.
Learners:
-develop concept integration
Active living; Fitness
-discover that exercise can be accomplished in large groups
-understand that keeping all parts of their bodies healthy comes from knowing and improving all parts of our body. -study themselves and how their bodies move and function. -helps students to know more about others and the world. -develop concept Integration
-develop concept integration
-explore decision making and its effects on health and environment.
-develop concept Integration
Interactions; Concepts & Principles
-model positive personal and social habits
-learn that working with others can affect their needs and survival.
-develop concept integration
-inquire how my habitat (i.e. body) impacts others.
-develop concept Integration
Motor skill development
-develop concept integration
-build on knowledge that survival comes from repetitively and continually improving necessary skills.
-develop concept integration
-develop concept integration
-develop concept Integration
The Arts Visual Arts Learners: Learners: Learners: Learners: Learners: Learners:
Creating
-combine a variety of formal elements to communicate ideas, feelings and/or experiences
-sharpen their powers of observation -pattern, Shapes and grids
-identify, plan and make specific choices of materials, tools and processes.
-identify the stages of their own and others creative processes. -demonstrate control of tools, materials and processes -investigate the purposes of the artwork from different times, places and a range of cultures including their own
-consider their audience when creating artwork
-make predictions, experiment and anticipate possible outcomes
Responding
-use appropriate terminology to discuss artwork
-identify the formal elements of an artwork
-investigate the purposes of artwork from different times, places and a range of cultures including their own -students will also use appropriate terminology to discuss artwork
-identify the stages of their own and others creative processes -become an engaged and responsive audience for a variety of art forms
-describe similarities and differences between artworks
Music
Creating
Learners:
-explore sound as a means of expressing imaginative ideas, -participate in creating music both individually and collectively
Learners:
-steady beat Notate whole half quarter -recognize whole half quarter eighth Rests quarter half whole -perform notated rhythm
Learners:
-solfege-Do Mi So La Do (high), Re, Fa with hand signs -sing and match pitch with good vocal quality -broadening vocal repertoire (ethnomusicology)
Learners:
collaboratively create a musical sequence using known musical elements (rhythm, melody, contrast), -create music and movement for different purposes
Learners:
-students will recognize and verbalize p/f, high/low, allegro/largo, staccato/legato
Learners:
-improvise upon basic patterns to reinforce the importance of the individual within the group, -read, write, and perform simple musical patterns and phrases -create and perform a movement sequence to studied music, -reflect upon how their music expresses their personal voice and the impact it has
Responding
-use voice to learn songs in unison -explore a musical response to a story
-improvisation using Pentatone Verbal Composition
-free Composition using Instruments Lyric Composition
-compare aspects of music from different times and places, -share performances with each other and give constructive criticism
-students will sing, listen and respond to a culturally diverse repertoire -students will sing and verbalize expressive markings
upon others
Drama and Dance
Creating
Learners:
-work individually or in groups with trust and confidence
Learners:
-explore basic bodily movements and the use of space
Learners:
-value and develop imaginary roles or situations
Learners:
-create a devised or scripted performance for a particular audience or purpose
Learners:
-manipulate a variety of different drama strategies and techniques to create informed scripts, characterizations and contexts -recognize and discuss how the consequences and actions of a performance teach audience members and performers life lessons
Learners:
-work individually or in groups with confidence
Responding
-compare varied styles of performance with their own culture
-recognize that dance plays an innovative role in communicating ideas within cultures and societies
-talk about ideas and feelings in response to dramatic performances
-understand the role and relevance of drama in their own society through exposure to a variety of performers and their perspectives
-investigate a cultural or historical dance form and identify how it communicates artistic, ritual or social issues, beliefs or values
ICT
Learners:
in development
Learners:
Learners:
Learners:
Learners:
Learners:
ELL Phase 2/3 push-in model
Learners phase 1:
Learners phase 1:
Learners phase 1:
Learners phase 1:
Learners phase 1:
Learners phase 1:
-pronounce, identify and use vocabulary in reading, written and oral responses. Also use words from the Grade 2 WORD WALL. -write a paragraph about role models.
-pronounce, identify and use mapping skills vocabulary in reading, written and oral responses. Also use words from the Grade 2 WORD WALL.. -write a paragraph
-pronounce, identify and use ANIMAL and HABITAT vocabulary in reading, written and oral responses. Also use words from the Grade 4 WORD WALL.. -use Past, Present and
-pronounce, identify and use vocabulary to describe feelings, to express emotions in oral and written form -read and analyse a variety of comprehension activities based on
-use question words (What, who, when where, how) -use plural nouns (including some irregular forms, -es, ies, -ves) -talk about a family and describe family
-pronounce, identify and use TRANSPORT, THINGS IN A TOWN and HOUSE vocabulary. -use verb to be questions, short answers, positive
-talk about their role models and how they are influential. -read non-fiction books for telling values and speaking practice. -write Simple descriptions(influentia l/brave, kind/principled, caring/leader) of people and generalized nouns, in relation to people
about any country. -talk about their (continents, country ,and cities) Bus tour Trip recount using a range of adjectives to express the directions and reflect on learning about the mapping skills
Future tense -describe Cause and Effect (ecosystems, life cycles and adaptations) recount using a range of adjectives to express the 5 senses and reflect on learning about the Eastern Mangroves cause and effect
different cultural traditions to express their values and heritage. -speak & Listen through activities videos and songs from other cultures compare and contrast - completing a Venn diagram
relations their own and the chosen context connected to PYP. -analyse clothes and appearances in a chosen context connected to inquiry
and negative sentences -use future tense making predictions I-use imperatives (must, should) -ask for and tell the time -use Can/ Cant (for ability and requests)
Library
Learners:
-distinguish between fiction and nonfiction books -learn how the Dewey Decimal System helps them find resources in the Library
Learners:
-listen to and view books about maps -use what they know to draw a map of the Library.
Learners:
-evaluate books about life cycles to determine the features of nonfiction texts and how they support our work as researchers
Learners:
-view books with different graphic features -determine what messages those features convey to the reader
Learners:
-research different habitats using database resources; -learn how to compile information from a variety of sources
Learners:
-evaluate picture books for different art methods and the effect that they have on the story and the reader
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Barumbi Kids UnitDocument7 paginiBarumbi Kids Unitapi-243600639100% (2)
- David Campany - The Cinematic (Documents of Contemporary Art) - The MIT Press (2007) PDFDocument118 paginiDavid Campany - The Cinematic (Documents of Contemporary Art) - The MIT Press (2007) PDFCarlos Barradas100% (1)
- The Environmental Case Translating Values Into Policy (Judith A. Layzer)Document750 paginiThe Environmental Case Translating Values Into Policy (Judith A. Layzer)HONG HUI RENÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan - The Day The Crayons QuitDocument2 paginiLesson Plan - The Day The Crayons Quitapi-267016142Încă nu există evaluări
- Where The Wild Things Are - Kim MilikenDocument18 paginiWhere The Wild Things Are - Kim MilikenS TANCRED100% (3)
- Grade 4 Learning OutcomesDocument5 paginiGrade 4 Learning Outcomesapi-296775931100% (2)
- Unit 5 Letter How We Express Ourselves kg2Document5 paginiUnit 5 Letter How We Express Ourselves kg2api-24590655975% (4)
- English Planning Term 2 - CarrianneDocument22 paginiEnglish Planning Term 2 - Carrianneapi-315385324Încă nu există evaluări
- Hatchet Unit PlanDocument27 paginiHatchet Unit Planapi-285111538100% (1)
- MPPS 5 - 6 2014 Scope and SequenceDocument6 paginiMPPS 5 - 6 2014 Scope and SequenceleesclassroomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Read Write and Talk Lesson Plan-Adapted For ToolkitDocument3 paginiRead Write and Talk Lesson Plan-Adapted For Toolkitapi-272654945Încă nu există evaluări
- We Survived the Holocaust Teacher's Guide: The Bluma and Felix Goldberg StoryDe la EverandWe Survived the Holocaust Teacher's Guide: The Bluma and Felix Goldberg StoryÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR 4 5 6 Poetry Unit PlanDocument22 paginiGR 4 5 6 Poetry Unit Planapi-265318262Încă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 Grade 2:: CalendarDocument11 paginiYearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 Grade 2:: Calendarapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- How The World Works How We Express Ourselves Who We Are Where We Are in Place & Time Sharing The Planet How We Organize OurselvesDocument9 paginiHow The World Works How We Express Ourselves Who We Are Where We Are in Place & Time Sharing The Planet How We Organize Ourselvesapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 KG5:: CalendarDocument11 paginiYearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 KG5:: Calendarapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Who We Are Sharing The Planet How We Organize Ourselves How The World Works Where We Are in Place & Time How We Express OurselvesDocument9 paginiWho We Are Sharing The Planet How We Organize Ourselves How The World Works Where We Are in Place & Time How We Express Ourselvesapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Yearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 Grade 4:: CalendarDocument8 paginiYearly Curriculum Overview 2013-2014 Grade 4:: Calendarapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- ESF Reading Scope and SequenceDocument6 paginiESF Reading Scope and SequenceStu LoweÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Letter Where We Are in Place and Time kg2Document6 paginiUnit 4 Letter Where We Are in Place and Time kg2api-245906559100% (1)
- Unit 4 Letter Where We Are in Place and Time kg2Document6 paginiUnit 4 Letter Where We Are in Place and Time kg2api-265244171Încă nu există evaluări
- Setting ApplicationDocument4 paginiSetting ApplicationDavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Kinds of Bears: An Integrated Unit for Elementary SchoolDe la EverandAll Kinds of Bears: An Integrated Unit for Elementary SchoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Map U2Document9 paginiCurriculum Map U2Petruta PacuraruÎncă nu există evaluări
- g1 Hweo Curriculum Map 1516Document2 paginig1 Hweo Curriculum Map 1516api-293372263Încă nu există evaluări
- 2013 - Broken Chain by Gary Soto UNIT PLANDocument21 pagini2013 - Broken Chain by Gary Soto UNIT PLANDavid Velez GonzalezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade7 Language Bookclub ArthuradamskiDocument23 paginiGrade7 Language Bookclub Arthuradamskiapi-333861301Încă nu există evaluări
- Texts and Human Experience Lesson 1Document8 paginiTexts and Human Experience Lesson 1KitKatKÎncă nu există evaluări
- How We Express Ourselves Letter To Parents 2014 FinalDocument7 paginiHow We Express Ourselves Letter To Parents 2014 Finalapi-245913711Încă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Secondary Schools Learning CompetenciesDocument5 paginiPhilippine Secondary Schools Learning CompetenciesBonnibel June Vincoy Mann0% (1)
- ELP Sense of Place EssayDocument3 paginiELP Sense of Place EssayRtoesÎncă nu există evaluări
- RMT - Kindergarten Learning OutcomesDocument5 paginiRMT - Kindergarten Learning Outcomesapi-307152920Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan 1-Standard 8Document4 paginiLesson Plan 1-Standard 8api-310100553Încă nu există evaluări
- RMT Grade 4 Learning OutcomesDocument4 paginiRMT Grade 4 Learning Outcomesapi-307152920Încă nu există evaluări
- Term 1 WritingDocument26 paginiTerm 1 Writingapi-279630111Încă nu există evaluări
- Nonfiction Writing Strategies Using Content-Area Mentor TextsDe la EverandNonfiction Writing Strategies Using Content-Area Mentor TextsÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNF4 Writing-AutobiographyDocument31 paginiCNF4 Writing-AutobiographyNah acaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KG Language Learning OutcomesDocument4 paginiKG Language Learning Outcomesapi-293281365Încă nu există evaluări
- English 8 - Q2 Exam ReviewerDocument12 paginiEnglish 8 - Q2 Exam ReviewerzandercompletoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Text Types P-12: Loddon Mallee RegionDocument34 paginiText Types P-12: Loddon Mallee RegionDila ElfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guided Reading RecordsDocument19 paginiGuided Reading Recordsjoy_simpson384Încă nu există evaluări
- Victorian Essential Learning Standards: English - Standards Reading Writing Speaking and ListeningDocument4 paginiVictorian Essential Learning Standards: English - Standards Reading Writing Speaking and ListeningHafida HaffidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tell Me A Story...Document2 paginiTell Me A Story...Pritam BeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 6 2Document22 paginiModule 6 2Loraine Joy RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Let ReviewerDocument15 paginiLet ReviewerSpencer Asuncion ÜÎncă nu există evaluări
- HE Mportance of Eading: Making TheDocument4 paginiHE Mportance of Eading: Making TheSiti QomariahÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Does Nature Teach UsDocument26 paginiWhat Does Nature Teach Usapi-430097640Încă nu există evaluări
- 4MS - New Yearly Planning 2019Document6 pagini4MS - New Yearly Planning 2019Larbi NadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literacy and Math Targets Uoi Where We Are in Place and TimeDocument4 paginiLiteracy and Math Targets Uoi Where We Are in Place and Timeapi-239483488Încă nu există evaluări
- LiteratureDocument9 paginiLiteratureAnonymous U2xGEwMgPÎncă nu există evaluări
- RMT Grade 2 Learning OutcomesDocument5 paginiRMT Grade 2 Learning Outcomesapi-307152920Încă nu există evaluări
- English Language Arts Travel Learning TasksDocument5 paginiEnglish Language Arts Travel Learning Tasksapi-181927398Încă nu există evaluări
- English 3RD QuarterDocument4 paginiEnglish 3RD QuarterG03 Bonavente, Mickaela Vhey M.Încă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Writing in Grades 10-12Document2 paginiTeaching Writing in Grades 10-12api-265626147Încă nu există evaluări
- Long Range Plan FinalDocument10 paginiLong Range Plan Finalapi-177378486Încă nu există evaluări
- Propósitos Quinto AñoDocument6 paginiPropósitos Quinto AñoMauroGermanRojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semester Plan Backward DesignDocument15 paginiSemester Plan Backward DesignRuthann RustÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literacy Activities for Circle Time: Alphabet, Ages 3 - 6De la EverandLiteracy Activities for Circle Time: Alphabet, Ages 3 - 6Încă nu există evaluări
- Junior Writer and OratorDe la EverandJunior Writer and OratorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Order FormDocument1 paginăOrder Formapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Newsletter Submission Endof April 2014Document1 paginăNewsletter Submission Endof April 2014api-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Newsletter VictoriaDocument1 paginăNewsletter Victoriaapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Canterbury Tales PosterDocument1 paginăCanterbury Tales Posterapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Spring Camp Gaa Sign UpDocument1 paginăSpring Camp Gaa Sign Upapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Gaa FlyerDocument1 paginăGaa Flyerapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Edr Summer Programme 2014Document1 paginăEdr Summer Programme 2014api-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Spring Camp Gaa Sign UpDocument1 paginăSpring Camp Gaa Sign Upapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Newsletter 30 January 2014Document3 paginiNewsletter 30 January 2014api-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Newsletter 13 March 2014Document1 paginăNewsletter 13 March 2014api-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Spring Camp Gaa Sign UpDocument1 paginăSpring Camp Gaa Sign Upapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Gaapa Logo SignDocument1 paginăGaapa Logo Signapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Yearbook ScreensDocument1 paginăYearbook Screensapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Yearbook ScreensDocument1 paginăYearbook Screensapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Spring BreakDocument1 paginăSpring Breakapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Yearbook ScreensDocument1 paginăYearbook Screensapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Spring BreakDocument1 paginăSpring Breakapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Newsletter 20 February 2014Document1 paginăNewsletter 20 February 2014api-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursery Rhyme InviteDocument1 paginăNursery Rhyme Inviteapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Community Sharing Dates and Parental Engagement January - June 2014Document1 paginăCommunity Sharing Dates and Parental Engagement January - June 2014api-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Newsletter 6 February 2014Document1 paginăNewsletter 6 February 2014api-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Newsletter 6 MarchDocument1 paginăNewsletter 6 Marchapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- MarietteDocument2 paginiMarietteapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- kg5 Community ShareDocument1 paginăkg5 Community Shareapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- kg5 Community ShareDocument1 paginăkg5 Community Shareapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Thank You For VolunteersDocument1 paginăThank You For Volunteersapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Vision and Mission at Gems American AcademyDocument2 paginiVision and Mission at Gems American Academyapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Thank You For VolunteersDocument1 paginăThank You For Volunteersapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- Order FormDocument1 paginăOrder Formapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- MarietteDocument2 paginiMarietteapi-236387116Încă nu există evaluări
- QAU TTS Form Annual AssessmentDocument6 paginiQAU TTS Form Annual AssessmentsohaibtarikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edgar Schein Organizational CultureDocument3 paginiEdgar Schein Organizational CultureAutolocal PieseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inglés Nivel San Marcos - Sem01Document16 paginiInglés Nivel San Marcos - Sem01nk jjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1 1 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Edited PDFDocument61 paginiModule 1 1 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Edited PDFVille MharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To StatisticsDocument21 paginiIntroduction To StatisticsREKKI100% (1)
- No Field of Study Can Advance Significantly Unless Outsiders Bring Knowledge and Experience To That of Field of StudyDocument5 paginiNo Field of Study Can Advance Significantly Unless Outsiders Bring Knowledge and Experience To That of Field of StudyMehul PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dual Nature of Electrons: Written Work Activity 1.1Document9 paginiDual Nature of Electrons: Written Work Activity 1.1Mark Chester CuetoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Webquest Sense of Smell and TasteDocument3 paginiWebquest Sense of Smell and Tastekhudson108Încă nu există evaluări
- Terence Tao Interview TranscriptDocument9 paginiTerence Tao Interview TranscriptscribrrrrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self-Directed Learning Activity Sheet Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsDocument5 paginiSelf-Directed Learning Activity Sheet Understanding Culture, Society and PoliticsRobert Brin SevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Durkheim On Crime and PunishmentDocument25 paginiDurkheim On Crime and PunishmentIon SanduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qualitative ResearchDocument8 paginiQualitative ResearchSchahyda ArleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Effectiveness of A Work-Text in Logic For College StudentsDocument18 paginiThe Effectiveness of A Work-Text in Logic For College StudentsAmadeus Fernando M. PagenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- MPS-004 ENG Papers PDFDocument32 paginiMPS-004 ENG Papers PDFManishKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07.02.2022 - Examination Schedule - UG (V) & PG (III) Semester - TCDocument6 pagini07.02.2022 - Examination Schedule - UG (V) & PG (III) Semester - TCLucifer royÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPSC Pms Subjects SyllabusDocument2 paginiPPSC Pms Subjects SyllabusShahzaib Domki100% (1)
- Sources of Power of Lower Participants in Complex OrganizationsDocument17 paginiSources of Power of Lower Participants in Complex OrganizationsFrancisco MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HEC Recognized Journals: BackgroundDocument11 paginiHEC Recognized Journals: Backgrounds_m_u_yousaf100% (1)
- Remigio Agpalo (Report For PS201 17-18 2nd Semester)Document16 paginiRemigio Agpalo (Report For PS201 17-18 2nd Semester)Michael Anjielo TabuyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR Chapter 3Document3 paginiPR Chapter 3Ellayjahh NicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survival AnalysisDocument29 paginiSurvival AnalysisNaolShamsuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photo BlogDocument6 paginiPhoto BlogFrancis Joseph Del Espiritu SantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Written Report in UTSDocument5 paginiWritten Report in UTSClaire Awa-aoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure PuzzleDocument2 paginiPressure PuzzleasdafafafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample EssayDocument13 paginiSample EssayVincent Wen Feng HeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disentangling Classical and Bayesian Approaches To Uncertainty AnalysisDocument19 paginiDisentangling Classical and Bayesian Approaches To Uncertainty Analysiszilangamba_s4535Încă nu există evaluări
- Sobrang Pahirap Na Sa BuhayDocument31 paginiSobrang Pahirap Na Sa BuhayB17 Santos, Israel C.Încă nu există evaluări
- Apologia General Science Study Guide For Homeschool Co-OpDocument211 paginiApologia General Science Study Guide For Homeschool Co-OpBeccaMondayBeard94% (17)