Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Final Project - Term Paper
Încărcat de
api-233082038Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Final Project - Term Paper
Încărcat de
api-233082038Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Liebroder 1 Toni Liebroder FHS 2450 Final Project December 5, 2013
STD or STI? Most of us have heard about STDs or sexually transmitted diseases and more recently are hearing about STIs or sexually transmitted infections. These two terms tend to be used interchangeably, but dont in fact mean the same thing. An STI will always proceed before an STD. You may be sick with an infection, but it doesnt always progress into a disease. For instance, about 90% of women who are infected with human papillomavirus (HPV) clear their infections within two years. Only women with persistent infections are at risk for developing the disease- cervical cancer (Marie). Just because the infection hasnt yet progressed into a disease for some people doesnt mean that they arent still contagious. STIs can still be spread to a sexual partner via vaginal, anal, or oral sex without the use of a condom or other form of physical protection. For some people, having an STI can remain symptomless; they wont always show signs of having an infection. This can be a serious cause for concern, however. In women with chlamydia, if the infection isnt treated in time the results can lead to infertility, meaning that she cannot conceive children. Syphilis is another infection that during its latent stage shows no symptoms, but during a tertiary stage can cause blindness, heart failure, mental disturbance, and even death (Crooks and Baur, 435).
Liebroder 2 There are two different types of STIs, bacterial and viral. Bacterial STIs are infections that can be cured and most viral STIs have no cure and a person with these will have it for the rest of their life despite treatment. Bacterial STIs are chlamydia, gonorrhea, nongonococcal urethritis (NGU), syphilis, vaginosis, yeast infections, trichomoniasis, pubic lice, and scabies. Viral STIs are herpes simplex 1 (oral) and 2 (genital), genital warts, hepatitis A, B, and C, and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome AIDS (Crooks and Baur, 434). Out of the many different STIs, a few are definitely more common than others; chlamydia is one that we have all heard of. Chlamydia is the most frequent infection to be reported in the U.S. Any gender can contract chlamydia, but women and especially young women, are more susceptible because of their immature cervixes. This infection can be spread via vaginal, anal, and oral sex, but can also be spread by the fingers from body to body and to the eyes (Crooks and Baur, 438). There are two types of genital chlamydia that affect females only. The first is inflammation in the lower reproductive tract and urethral tube or in the cervix. Many women with this type of chlamydia can remain without symptoms, but some experience burning during urination and itching of the genital tissue. The second type is invasion in the upper reproductive tract. Symptoms for this infection include pelvic inflammatory disease (PID). PID has its own set of symptoms that range from unusual menstrual cycles, pelvic pain, lower back pain, fever, nausea, vomiting, headache, and in severe cases can cause infertility (Crooks and Baur, 438). Treatment for chlamydia is very simple, usually a 7-day cycle of doxycycline or a single dose of azithromycin, both by mouth. All partners exposed to the infected person will need to be treated or the infection will continue to spread even with treatment (Crooks and Baur, 439).
Liebroder 3 The second most reported infection is gonorrhea, or sometimes referred to on the streets as the clap. Gonorrhea is transmitted through vaginal, anal, oral, and body-finger contact. Primary stages of gonorrhea are more noticeable in men than in women, but still some may not experience any symptoms at all. For men, symptoms can appear in about 2-5 days after exposure and may consist of foul-smelling, cloudy discharge, burning during urination, and swollen lymph glands in the groin. If left untreated, symptoms can progress and spread to the genitourinary tract, infecting the prostate, bladder, kidneys, and testes. In severe cases, where the infection has gone months without treatment the bacteria may spread down the vas deferens causing scar tissue to develop and can result in sterility (Crooks and Baur, 440). For women with gonorrhea, they may not know they have the infection at all. Usually the cervix will become inflamed and there may be mild burning with urination. Other types of bacteria produce the same symptoms and can mask the presence of gonorrhea, making it go unnoticed. After prolonged exposure to this infection, women will start to develop more serious symptoms. The infection will spread to the upper reproductive tract causing PID. PID in women with gonorrhea is more serious than in women with chlamydia. Ectopic pregnancies and sterility are more prevalent with gonorrhea infections (Crooks and Baur, 440). As I mentioned earlier, gonorrhea can sometimes be mistaken for another bacteria so it is very important to be checked specifically for gonorrhea so that it can be treated promptly. In prior years, treatment for gonorrhea consisted of both a single dose of fluoroquinolone and azithromycin, but recently there have been reports that have shown people to be resistant to fluoroquinolone antibiotics. A substitute of cephalosporin is now in place. New research shows some strains of gonorrhea to be untreatable by either medication and so far have no cure (Crooks and Baur, 441).
Liebroder 4 Throughout the years, rates of syphilis have declined, but recently they have risen to a new high. Bacteria from syphilis thrive in warm, moist areas of the body and are spread from open lesions via vaginal, anal, and oral contact. There are four stages of syphilis if the infection progresses without treatment. These stages are: primary, secondary, latent, and tertiary (Crooks and Baur, 442). In the primary stage a painless chancre starts to develop where the infection entered the body, usually the vagina or labia for women and the glans or shaft of the penis for men. The chancre will usually heal on its own in about 3 to 6 weeks and there may be no other symptoms that present themselves. Because the symptoms in the primary stage are minimal, the infection will go unnoticed and untreated. This will then progress to the secondary stage. In this stage, a rash will start to spread throughout the exterior of the body, showing up in places like the feet and hands. The rash can range anywhere from mild to severe, but generally wont bother the person affected by it. Other symptoms in this stage include fever, swollen glands, fatigue, weight loss, and joint and bone pain. These symptoms typically go away in a few weeks and the infection continues to spread. In the latent stage of syphilis, there are usually no symptoms at all and this can last for several years. After one year of untreated syphilis the infection continues to multiply, but is no longer contagious to potential sexual partners. The last and final stage of syphilis is the tertiary stage. In this stage the results are very serious and can often lead to death. This can happen anywhere from 10 to 20 years of untreated infection. Symptoms in this stage are heart failure, blindness, ruptured blood vessels, paralysis, skin ulcers, liver damage, and mental disturbance, but luckily treatment even at this stage can help (Crooks and Baur, 442-444). In the primary, secondary, and latent stages of syphilis, an effective injection of benzathine penicillin G will treat the infection. People in the tertiary stage of syphilis who have
Liebroder 5 had the infection for over a year will need to be treated with the same injection, but once a week for a consecutive 3 weeks (Crooks and Baur, 444). Herpes is another STI, but this one is viral and there is no known cure. There are eight different types of herpes viruses that can affect people, but the most common are herpes simplex viruses 1 and 2. These are the two that are contracted through sexual contact. Herpes simplex 1 is more known for cold sores. These will appear on the mouth and someone doesnt need to have sexual relations with another to get it, usually just kissing someone will do the trick. However, herpes simplex 1 can be spread to the genitals and herpes simplex 2 can be spread orally. Herpes simplex 2 is genital herpes where lesions will form around the genital area. These usually present themselves as red, painful bumps that can develop into blisters. More women than men will develop this infection because it is easier for them to contract. Transmission of this infection is contracted through vaginal, anal, and oral contact. With herpes, a person can go through outbreaks, meaning that the lesions are not always present, but the infection is still highly contagious (Crooks and Baur, 445-446). Although I mentioned only a very small number of actual STIs, these are some of the most common and most severe. Believe me when I say that sex is a major bonus in life and we all know that if we could do it all day we would, but there is responsibility that comes with that pleasure. We owe it to ourselves and our intimate partners to make sure that we are aware of the consequences that can occur when were not careful. Spreading of these infections only takes a few minutes, but can last a lifetime. For some people, contracting these infections is the last mistake they will ever get to make. Enjoy your sex life, but make sure you take preventative measures to continue to enjoy your sex life.
Liebroder 6 Works Cited Crooks, Robert, Karla Baur. Our Sexuality. 12th ed. Canada: Jon-David Hague, 2011. Print. Marie, Jenelle. STD vs STI- Whats the Difference. The STD Project. Nov. 15, 2013 http://www.thestdproject.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Causes, Types and Evaluation of HematuriaDocument34 paginiCauses, Types and Evaluation of HematuriaSai RakshikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Important Clues in Diagnosis of CRFDocument3 paginiImportant Clues in Diagnosis of CRFDiwakesh C BÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexually Transmitted InfectionsDocument97 paginiSexually Transmitted Infectionstummalapalli venkateswara raoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HematuriaDocument42 paginiHematuriaWasim R. IssaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syndromic Management of STDsDocument13 paginiSyndromic Management of STDsMeenachi SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrotic Syndrome Definition and CausesDocument23 paginiNephrotic Syndrome Definition and CausesamlymarsÎncă nu există evaluări
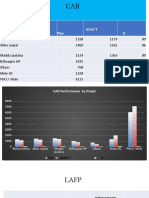
- Name of HP Plan Achv'T %Document41 paginiName of HP Plan Achv'T %habtamu WegayehuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific SessionDocument3 paginiScientific SessionAshpavi ArunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbial Diseases of The Urinary and Reproductive SystemsDocument139 paginiMicrobial Diseases of The Urinary and Reproductive Systemsone_nd_onlyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 (Prostatitis)Document43 paginiLecture 2 (Prostatitis)Rian Permana PÎncă nu există evaluări
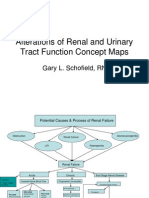
- Renal Concept MapDocument8 paginiRenal Concept MapDavis KallanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Treatment Sti What'S The Story With These Stis?: Protect Yourself!Document2 paginiTreatment Sti What'S The Story With These Stis?: Protect Yourself!fuck youÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal DiseaseDocument4 paginiRenal DiseaseApril Lady Faith P. PaundogÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAKUTDocument50 paginiCAKUTsantosh subediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexually Transmitted Infections - Hatem Sadek PresentationDocument36 paginiSexually Transmitted Infections - Hatem Sadek PresentationHatem SadekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Urinary AssessmentDocument3 paginiRenal Urinary AssessmentJosephine NavarroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic of the Philippines Department of Health EPIDEMIOLOGY BUREAU LABORATORY AND BLOOD BANK SURVEILLANCE (LaBS) Form 1Document1 paginăRepublic of the Philippines Department of Health EPIDEMIOLOGY BUREAU LABORATORY AND BLOOD BANK SURVEILLANCE (LaBS) Form 1Evo SingsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Invitation LetterDocument1 paginăInvitation LetterAngelo SinfuegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preceptor: Dr. Arief Effendi, SP - KK: OlehDocument13 paginiPreceptor: Dr. Arief Effendi, SP - KK: OlehriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kelompok 2 - Tugas TT PT 6 - KODEFIKASI.Document3 paginiKelompok 2 - Tugas TT PT 6 - KODEFIKASI.Nalisa JasrinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. YeshwiniDocument34 paginiDr. YeshwiniSai RakshikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HEMATURIADocument9 paginiHEMATURIAAndreina AcevedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Session #42 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)Document4 paginiSession #42 SAS - AnaPhy (Lab)G IÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrotic Nephritic SyndromeDocument15 paginiNephrotic Nephritic Syndromeshefalika mandremÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrotic vs Nephritic SyndromesDocument3 paginiNephrotic vs Nephritic Syndromeskvs gouthamÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNAIDS Core Epidemiology Slides enDocument11 paginiUNAIDS Core Epidemiology Slides enTabarcea VitaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Providing Urology Care in Maret 2021Document25 paginiProviding Urology Care in Maret 2021Little DevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar PustakaDocument3 paginiDaftar PustakaMiranda NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uti PBL 2Document1 paginăUti PBL 2Aliah ZuhairahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3HIV AIDSWordSearchDocument1 pagină3HIV AIDSWordSearchTimothy William C. LaurenceÎncă nu există evaluări