Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Trig Cheat Sheet
Încărcat de
DinoDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Trig Cheat Sheet
Încărcat de
DinoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
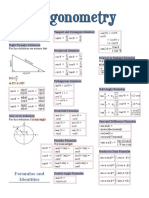
Trig Cheat Sheet Formulas and Identities
Tangent and Cotangent Identities Half Angle Formulas
sin θ cos θ
sin 2 θ = (1 − cos ( 2θ ) )
1
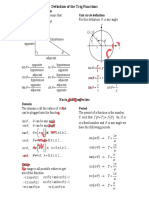
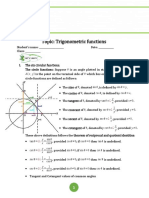
Definition of the Trig Functions tan θ = cot θ =
Right triangle definition cos θ sin θ 2
Reciprocal Identities
cos 2 θ = (1 + cos ( 2θ ) )
For this definition we assume that Unit circle definition 1
π For this definition θ is any angle. csc θ =
1
sin θ =
1 2
0 <θ < or 0° < θ < 90° .
2 y sin θ csc θ 1 − cos ( 2θ )
tan θ =
2
sec θ =
1
cos θ =
1 1 + cos ( 2θ )
( x, y ) cos θ sec θ Sum and Difference Formulas
sin (α ± β ) = sin α cos β ± cos α sin β
hypotenuse 1 1 1
y θ cot θ = tan θ =
opposite tan θ cot θ
x
x
Pythagorean Identities cos (α ± β ) = cos α cos β ∓ sin α sin β
θ sin 2 θ + cos 2 θ = 1 tan α ± tan β
tan (α ± β ) =
adjacent tan θ + 1 = sec θ
2 2 1 ∓ tan α tan β
Product to Sum Formulas
opposite hypotenuse y 1 1 + cot 2 θ = csc 2 θ
sin θ = csc θ = sin θ = =y csc θ = 1
hypotenuse opposite 1 y Even/Odd Formulas sin α sin β = ⎡⎣cos (α − β ) − cos (α + β ) ⎤⎦
2
cos θ =
adjacent
sec θ =
hypotenuse x 1 sin ( −θ ) = − sin θ csc ( −θ ) = − cscθ
cos θ = = x sec θ = 1
cos α cos β = ⎡⎣cos (α − β ) + cos (α + β ) ⎤⎦
hypotenuse adjacent 1 x cos ( −θ ) = cos θ sec ( −θ ) = sec θ 2
opposite adjacent y x
tan θ = cot θ = tan θ = cot θ = tan ( −θ ) = − tan θ cot ( −θ ) = − cot θ 1
sin α cos β = ⎣⎡sin (α + β ) + sin (α − β ) ⎦⎤
adjacent opposite x y 2
Periodic Formulas 1
Facts and Properties If n is an integer. cos α sin β = ⎡⎣sin (α + β ) − sin (α − β ) ⎤⎦
2
Domain sin (θ + 2π n ) = sin θ csc (θ + 2π n ) = csc θ Sum to Product Formulas
The domain is all the values of θ that Period
cos (θ + 2π n ) = cos θ sec (θ + 2π n ) = sec θ ⎛α + β ⎞ ⎛α −β ⎞
can be plugged into the function. The period of a function is the number, sin α + sin β = 2sin ⎜ ⎟ cos ⎜ ⎟
T, such that f (θ + T ) = f (θ ) . So, if ω tan (θ + π n ) = tan θ cot (θ + π n ) = cot θ ⎝ 2 ⎠ ⎝ 2 ⎠
sin θ , θ can be any angle is a fixed number and θ is any angle we ⎛α + β ⎞ ⎛α − β ⎞
Double Angle Formulas sin α − sin β = 2 cos ⎜ ⎟ sin ⎜ ⎟
cos θ , θ can be any angle ⎝ 2 ⎠ ⎝ 2 ⎠
⎛ 1⎞
have the following periods. sin ( 2θ ) = 2sin θ cos θ
tan θ , θ ≠ ⎜ n + ⎟ π , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,… ⎛α + β ⎞ ⎛α −β ⎞
⎝ 2⎠ 2π cos ( 2θ ) = cos 2 θ − sin 2 θ cos α + cos β = 2 cos ⎜ ⎟ cos ⎜ ⎟
sin (ωθ ) → T= ⎝ 2 ⎠ ⎝ 2 ⎠
csc θ , θ ≠ n π , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,… ω = 2 cos 2 θ − 1 ⎛α + β ⎞ ⎛α − β ⎞
⎛ 1⎞ 2π cos α − cos β = −2sin ⎜ ⎟ sin ⎜ ⎟
sec θ , θ ≠ ⎜ n + ⎟ π , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,… cos (ω θ ) → T = = 1 − 2sin 2 θ ⎝ 2 ⎠ ⎝ 2 ⎠
⎝ 2⎠ ω
π 2 tan θ Cofunction Formulas
cot θ , θ ≠ n π , n = 0, ± 1, ± 2,… tan ( ωθ ) → = tan ( 2θ ) =
T
ω 1 − tan 2 θ ⎛π ⎞ ⎛π ⎞
sin ⎜ − θ ⎟ = cos θ cos ⎜ − θ ⎟ = sin θ
2π ⎝2 ⎠ ⎝2 ⎠
Range csc (ωθ ) → T =
Degrees to Radians Formulas
The range is all possible values to get ω If x is an angle in degrees and t is an ⎛π ⎞ ⎛π ⎞
csc ⎜ − θ ⎟ = sec θ sec ⎜ − θ ⎟ = csc θ
out of the function. 2π angle in radians then ⎝2 ⎠ ⎝2 ⎠
−1 ≤ sin θ ≤ 1 csc θ ≥ 1 and csc θ ≤ −1 sec (ω θ ) → T = π πx
ω =
t
⇒ t= and x =
180t ⎛π ⎞ ⎛π ⎞
tan ⎜ − θ ⎟ = cot θ cot ⎜ − θ ⎟ = tan θ
−1 ≤ cos θ ≤ 1 sec θ ≥ 1 and sec θ ≤ −1 π 180 x 180 π ⎝ 2 ⎠ ⎝ 2 ⎠
−∞ ≤ tan θ ≤ ∞ −∞ ≤ cot θ ≤ ∞ cot (ωθ ) → T =
ω
© 2005 Paul Dawkins © 2005 Paul Dawkins
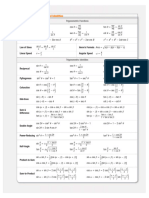
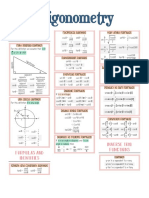
Unit Circle
Inverse Trig Functions
Definition Inverse Properties
cos ( cos −1 ( x ) ) = x
y
( 0,1) y = sin −1 x is equivalent to x = sin y cos−1 ( cos (θ ) ) = θ
π ⎛1 3⎞
⎜⎜ , ⎟⎟
y = cos −1 x is equivalent to x = cos y sin ( sin −1 ( x ) ) = x sin −1 ( sin (θ ) ) = θ
⎛ 1 3⎞
⎜− , ⎟ ⎝2 2 ⎠ −1
2 y = tan x is equivalent to x = tan y
⎝ 2 2 ⎠ π ⎛ 2 2⎞ tan ( tan −1 ( x ) ) = x tan −1 ( tan (θ ) ) = θ
2π 90° ⎜⎜ , ⎟⎟
⎛ 2 2⎞ 3 ⎝ 2 2 ⎠
⎜− , ⎟
⎝ 2 2 ⎠ 3
120° 60°
π Domain and Range
3π ⎛ 3 1⎞ Function Domain Range Alternate Notation
4 ⎜⎜ 2 , 2 ⎟⎟ sin −1 x = arcsin x
⎛ 3 1⎞ ⎝ ⎠ π π
⎜− , ⎟
4
135° 45° π y = sin −1 x −1 ≤ x ≤ 1 − ≤ y≤
⎝ 2 2⎠ 5π 2 2 cos −1 x = arccos x
6 −1
0≤ y ≤π
6 30° y = cos x −1 ≤ x ≤ 1 tan −1 x = arctan x
150° π π
y = tan −1 x −∞ < x < ∞ − < y<
2 2
( −1,0 ) π 180° 0° 0 (1,0 )
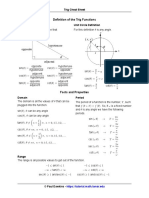
Law of Sines, Cosines and Tangents
360° 2π x
c β a
210°
7π 330°
11π
6 225°
⎛ 3 1⎞ 6 ⎛ 3 1⎞ α γ
⎜− ,− ⎟ 5π 315° ⎜ ,− ⎟
⎝ 2 2⎠ ⎝ 2 2⎠
4 240° 300° 7π
⎛ 2⎞ 4π 270° b
5π
2 4
⎜− ,− ⎟ ⎛ 2 2⎞
⎝ 2 2 ⎠ 3 3π ⎜
⎝ 2
,− ⎟
2 ⎠
3 Law of Sines Law of Tangents
⎛ 1 3⎞ 2
⎜ − ,− ⎟
⎛ 1
⎜ ,−
3⎞
⎟ sin α sin β sin γ
= = a − b tan 12 (α − β )
⎝ 2 2 ⎠ ⎝2 2 ⎠ =
( 0,−1) a b c a + b tan 12 (α + β )
Law of Cosines b − c tan 12 ( β − γ )
=
a 2 = b 2 + c 2 − 2bc cos α b + c tan 12 ( β + γ )
For any ordered pair on the unit circle ( x, y ) : cos θ = x and sin θ = y b 2 = a 2 + c 2 − 2ac cos β a − c tan 12 (α − γ )
=
c = a + b − 2ab cos γ
2 2 2
a + c tan 12 (α + γ )
Example
Mollweide’s Formula
⎛ 5π ⎞ 1 ⎛ 5π ⎞ 3
cos ⎜ ⎟ = sin ⎜ ⎟ = − a + b cos 12 (α − β )
⎝ 3 ⎠ 2 ⎝ 3 ⎠ 2 =
c sin 12 γ
© 2005 Paul Dawkins © 2005 Paul Dawkins
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Part 1Document4 paginiCalculus Cheat Sheet Part 1Dave Cloud100% (27)
- Physics EquationsDocument5 paginiPhysics Equationsanon-992211100% (64)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Limit at InfinityDocument11 paginiCalculus Cheat Sheet Limits Definitions Limit at Infinityapi-1192241886% (7)
- The Ultimate Calculus Cheat SheetDocument11 paginiThe Ultimate Calculus Cheat SheetRhine Osser-Rich Ramblespin100% (4)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet Part 3Document4 paginiCalculus Cheat Sheet Part 3Dave Cloud100% (12)
- Calculus Cheat Sheet IntegralsDocument5 paginiCalculus Cheat Sheet Integralshyd arnes100% (5)
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiAlgebra Cheat SheetDino97% (72)
- Definite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsDe la EverandDefinite Integral (Calculus) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument2 paginiDefinition of The Trig FunctionsJulie OcolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument4 paginiTrigonometry: Definition of The Trig FunctionsJulie OcolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition of The Trig Functions: Right Triangle Definition Unit Circle DefinitionDocument4 paginiDefinition of The Trig Functions: Right Triangle Definition Unit Circle DefinitionjonahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument11 paginiTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionscharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Class 12 Formulas - RemovedDocument18 paginiAll Class 12 Formulas - Removedhakirel928Încă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionsDocument4 paginiTrigonometric Formula Sheet: Definition of The Trig FunctionscristianÎncă nu există evaluări
- All Class 12 FormulasDocument26 paginiAll Class 12 Formulashakirel928Încă nu există evaluări
- _Math_Resources_Trigonometric_FormulasDocument10 pagini_Math_Resources_Trigonometric_Formulasnobodynothing052Încă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry: θ in degrees θ in radians sinθ cosθ tanθDocument3 paginiTrigonometry: θ in degrees θ in radians sinθ cosθ tanθAna CvetkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry Formulas and IdentitiesDocument3 paginiTrigonometry Formulas and IdentitiesAna CvetkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math FormulasDocument3 paginiMath FormulasSubscribe right nowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig formula sheetDocument6 paginiTrig formula sheetHarrison BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig Identities ExplainedDocument10 paginiTrig Identities ExplainedVictoria BratinellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tablas Diferenciales Con FuncionesDocument2 paginiTablas Diferenciales Con FuncionesHector AlejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAPE Unit 1 Trig NotesDocument19 paginiCAPE Unit 1 Trig NotesAndre MaxwellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig Cheat SheetDocument4 paginiTrig Cheat SheetJASPER LEGASPIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument1 paginăTrig Cheat Sheet: by ViaNeia De JesusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry SheetDocument4 paginiTrigonometry SheetKelah AligÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plane Trigonometry & Plane GeometryDocument16 paginiPlane Trigonometry & Plane GeometryStephen Megs Booh MantizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pure Math: Topic: Trigonometric FunctionsDocument8 paginiPure Math: Topic: Trigonometric FunctionsKienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiTrigonometry Cheat SheetJulie OcolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigo 2Document2 paginiTrigo 2Julie OcolÎncă nu există evaluări
- l-22_introduction_to_trigonometryDocument3 paginil-22_introduction_to_trigonometrysoorya_taÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRIGONOMY IDENTITIES AND EQUATIONSDocument6 paginiTRIGONOMY IDENTITIES AND EQUATIONSAmmar RizwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Trigonom Etria: 1.1 DefinicionesDocument7 pagini1 Trigonom Etria: 1.1 DefinicionesJulissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary Trigident PDFDocument1 paginăSummary Trigident PDFgebran sarkisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 111: Summary of Trig IdentitiesDocument1 paginăMath 111: Summary of Trig IdentitiesJhan Ray Gomez BarrilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 paginăMath 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesYunz IvensÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 paginăMath 111: Summary of Trigonometric IdentitiesalyssaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 36 Trig Identities You Need To KnowDocument16 paginiThe 36 Trig Identities You Need To Knowjohn hodgsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry Angles and Functions Conversion TableDocument10 paginiTrigonometry Angles and Functions Conversion TableLeviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument2 paginiFundamental Trigonometric IdentitiesqaisarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fund Trig IdentitiesDocument4 paginiFund Trig IdentitiesCamden J. LienÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alevelsb p1 Ex10cDocument5 paginiAlevelsb p1 Ex10ceduguideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Identities (Study Sheet)Document1 paginăTrigonometric Identities (Study Sheet)Arfred VillaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry PDFDocument2 paginiTrigonometry PDFadamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig IdentitiesDocument1 paginăTrig IdentitiesYishan HaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formula SheetDocument6 paginiFormula SheetpaulineannedimapilisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Functions LessonsDocument122 paginiAdvanced Functions Lessonskristenstephens87Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Trigonometric Relationships and IdentitiesDocument1 paginăBasic Trigonometric Relationships and Identitieshadukenryu9761Încă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric IdentitiesDocument1 paginăTrigonometric IdentitiesCarlos Manuel Rodríguez MartínezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 1.4Document4 paginiSection 1.4Terra DrakeÎncă nu există evaluări
- TrigonometryDocument1 paginăTrigonometryteachopensourceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometric Formulas R3Document3 paginiTrigonometric Formulas R3weird factsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Productivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionDe la EverandProductivity Now: Social Administration, Training, Economics and Production DivisionÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (8)
- On the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)De la EverandOn the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)Încă nu există evaluări
- Mac OS X Terminal Commands ListDocument5 paginiMac OS X Terminal Commands ListDino100% (29)
- Client Questionnaire For Web DevelopersDocument1 paginăClient Questionnaire For Web DevelopersDino89% (9)
- Bioshock ArtbookDocument78 paginiBioshock ArtbookDino92% (24)
- 10 Lessons of An MIT EducationDocument7 pagini10 Lessons of An MIT EducationDino100% (13)
- Complete Hip-Hop Radio Station Listing (USA)Document4 paginiComplete Hip-Hop Radio Station Listing (USA)Dino99% (192)
- Byte SizeDocument1 paginăByte SizeDino100% (5)
- Calculus Cheat SheetDocument6 paginiCalculus Cheat SheetDino99% (75)
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pagini6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Algebra Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiAlgebra Cheat SheetDino97% (72)
- Asian Games Exhibit (Pics)Document7 paginiAsian Games Exhibit (Pics)Dino100% (7)
- Multimedia Development Contract TemplateDocument4 paginiMultimedia Development Contract TemplateDino97% (38)
- Actual Vs Budget Income Statement TemplateDocument1 paginăActual Vs Budget Income Statement TemplateDino100% (9)
- Employee Referral TemplateDocument2 paginiEmployee Referral TemplateDino100% (9)
- Fat Burning FoodDocument3 paginiFat Burning FoodDino100% (73)
- Production Efficiency Worksheet TemplateDocument2 paginiProduction Efficiency Worksheet TemplateDino100% (10)
- Business Plan TemplateDocument9 paginiBusiness Plan TemplateDino98% (469)
- Action by Written Consent of Shareholder(s)Document1 paginăAction by Written Consent of Shareholder(s)Dino100% (3)
- Performance and Behavioral InterviewingDocument40 paginiPerformance and Behavioral InterviewingDino100% (7)
- Modulus-Argument Form of A Complex Number LESSONDocument3 paginiModulus-Argument Form of A Complex Number LESSONangusliang41Încă nu există evaluări
- Bcse204l Design-And-Analysis-Of-Algorithms TH 1.0 70 Bcse204lDocument2 paginiBcse204l Design-And-Analysis-Of-Algorithms TH 1.0 70 Bcse204lMohammed MohsinÎncă nu există evaluări
- EulerDocument4 paginiEulerIshmael Hossain SheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- P3 Edexcel Mock QPDocument3 paginiP3 Edexcel Mock QPJonMortÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diophantine Equations ProblemsDocument3 paginiDiophantine Equations ProblemsAditya MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 Uniform Convergence and IntegrationDocument27 paginiChapter 9 Uniform Convergence and Integrationnormal@backup100% (1)
- Non Rigid Registration MethodsDocument113 paginiNon Rigid Registration MethodsZahid Hasan AnsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circle geometry concepts and termsDocument4 paginiCircle geometry concepts and termsmamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- VTAMPS 5.0 Primary 3 Set 5Document9 paginiVTAMPS 5.0 Primary 3 Set 5Lance AlfantaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genmath q1 Mod2 Evaluatingfunctions v2Document27 paginiGenmath q1 Mod2 Evaluatingfunctions v2Jomark RebolledoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig Cheat SheetDocument4 paginiTrig Cheat SheetJEJUNGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kruskal's Algorithm Explained: Find Minimum Spanning Trees in GraphsDocument25 paginiKruskal's Algorithm Explained: Find Minimum Spanning Trees in GraphsGAUTAM JHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Algebra 2 Course GuideDocument4 paginiAlgebra 2 Course Guideapi-526889056Încă nu există evaluări
- Combinatorics 1 Solutions UHSMCDocument7 paginiCombinatorics 1 Solutions UHSMCWalker KroubalkianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Various System Identification Methods For A MISO SystemDocument16 paginiComparison of Various System Identification Methods For A MISO SystemSashank Varma JampanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogue: MathematicsDocument76 paginiCatalogue: MathematicsGaurav GagwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMW Module 1 Nature of MathematicsDocument6 paginiMMW Module 1 Nature of MathematicsJhess GaliciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTH101 Math SolvedDocument5 paginiMTH101 Math SolvedSyedsAreKingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 7 MathDocument8 paginiGrade 7 MathSirLhitz B. UmaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Apcalcprobbook Mccaffrey RevisedDocument216 paginiApcalcprobbook Mccaffrey Reviseddivyanshu33Încă nu există evaluări
- Simultaneous Linear Equations in Three VariablesDocument2 paginiSimultaneous Linear Equations in Three VariablesizumiÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Non-Equivalent (Self-Dual) MDS Codes From Elliptic Curves (Hao Chen)Document24 paginiNew Non-Equivalent (Self-Dual) MDS Codes From Elliptic Curves (Hao Chen)Marvin OlavidesÎncă nu există evaluări
- C1498117505umathematics 10th SolutionDocument148 paginiC1498117505umathematics 10th SolutionVimal sabariÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAT 111 - ElemantryDocument92 paginiMAT 111 - ElemantryDinesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uem Sol To Exerc ContentsDocument5 paginiUem Sol To Exerc Contents9Ak CHANNELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2Document4 paginiAssignment 2umieÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Analytic Solved ProblemDocument7 pagini2 Analytic Solved ProblemAshutosh Singh100% (7)
- 15 Programs On PythonDocument6 pagini15 Programs On PythonREDDY SARAGADAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Component Transformation MatrixDocument11 paginiComponent Transformation MatrixSurya BhartiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of the Balance of Interaction Between Coral Reef, Drupella Snail and Predator Populations Through Phase PortraitDocument12 paginiAnalysis of the Balance of Interaction Between Coral Reef, Drupella Snail and Predator Populations Through Phase PortraitFarida RhamadhaniÎncă nu există evaluări