Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 3 Parallel and Pipelined Processing: 1 ECE734 VLSI Arrays For Digital Signal Processing
Încărcat de
Anup00080 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
13 vizualizări13 paginiy6ihg
Titlu original
Para Pipe
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documenty6ihg
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
13 vizualizări13 paginiChapter 3 Parallel and Pipelined Processing: 1 ECE734 VLSI Arrays For Digital Signal Processing
Încărcat de
Anup0008y6ihg
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PPT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 13
1 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
Chapter 3 Parallel and
Pipelined Processing
2 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
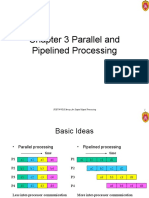
Basic Ideas
Parallel processing Pipelined processing
a1 a2 a3 a4
b1 b2 b3 b4
c1 c2 c3 c4
d1 d2 d3 d4
a1 b1 c1 d1
a2 b2 c2 d2
a3 b3 c3 d3
a4 b4 c4 d4
P1
P2
P3
P4
P1
P2
P3
P4
time
Colors: different types of operations performed
a, b, c, d: different data streams processed
Less inter-processor communication
Complicated processor hardware
time
More inter-processor communication
Simpler processor hardware
3 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Data Dependence
Parallel processing requires
NO data dependence
between processors
Pipelined processing will
involve inter-processor
communication
P1
P2
P3
P4
P1
P2
P3
P4
time time
4 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Usage of Pipelined Processing
By inserting latches or
registers between
combinational logic circuits,
the critical path can be
shortened.
Consequence:
reduce clock cycle time,
increase clock frequency.
Suitable for DSP
applications that have
(infinity) long data stream.
Method to incorporate
pipelining: Cut-set retiming
Cut set:
A cut set is a set of edges of
a graph. If these edges are
removed from the original
graph, the remaining graph
will become two separate
graphs.
Retiming:
The timing of an algorithm is
re-adjusted while keeping
the partial ordering of
execution unchanged so
that the results correct
5 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Graphic Transpose Theorem
The transfer function of a signal flow graph remain
unchanged if
The directions of each arc is reversed
The input and output labels are switched.
z
1
z
1
x[n]
y[n] h[2]
h[1] h[0]
z
1
z
1
y[n]
x[n]
h[2] h[1] h[0]
u[n]
=
?
6 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Data broadcast structure
Algorithm transform may
lead to pipelined structure
without adding additional
delays.
Given a FIR filter SFG
Critical path T
M
+2T
A
Use graph transposition
theorem:
Reverse all arcs
Reverse input/output
We obtain
Critical path T
M
+ T
A
No additional delay added!
7 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Fine-grain pipelining
To further reduce T
M.
Critical Path = Max {T
M1
, T
M2
, T
A
}
8 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Block Processing
One form of vectorized
parallel processing of DSP
algorithms. (Not the parallel
processing in most general
sense)
Block vector: [x(3k) x(3k+1)
x(3k+2)]
Clock cycle: can be 3 times
longer
Original (FIR filter):
Rewrite 3 equations at a
time:
Define block vector
Block formulation:
(3 ) (3 ) (3 1) (3 2)
(3 1) (3 1) (3 ) (3 1)
(3 2) (3 2) (3 1) (3 )
y k x k x k x k
y k a x k b x k c x k
y k x k x k x k
( ( ( (
( ( ( (
+ = + + +
( ( ( (
( ( ( ( + + +
( ) ( ) ( 1)
( 2)
y n a x n b x n
c x n
= +
+
(3 )
( ) (3 1)
(3 2)
x k
k x k
x k
(
(
= +
(
( +
x
0 0 0
( ) 0 ( ) 0 0 ( 1)
0 0 0
a c b
k b a k c k
c b a
( (
( (
= +
( (
( (
y x x
9 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Block Processing
10 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
General approach for block processing
11 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Original formulation:
Rewrite
Define block vectors
Then
Block Processing for IIR Digital Filter
Time indices
n: sampling period
k: clock period (processor)
k = 2n
Note:
Pipelining: clock period =
sampling period.
Block (parallel): clock period
not equal to sampling period.
( ) ( 2) ( ) y n a y n x n = +
(2 ) (2 )
( ) , ( )
(2 1) (2 1)
x n y n
k k
x n y n
( (
= =
( (
+ +
x y
(2 ) (2 2) (2 )
(2 1) (2 1) (2 1)
y n a y n x n
y n a y n x n
= +
+ = + +
( ) ( 1) ( ) k a k k = + y y x
12 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Block IIR Filter
D
D
S/P P/S
+
+
x(2k)
x(2k+1)
y(2k+1)
y(2k)
x(n) y(n)
y(2(k1))
y(2(k1)+1)
13 ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing
(C) 1997-2006 by Yu Hen Hu
Timing Comparison
Pipelining
Block processing
1 2 3 4
x(1) x(2) x(3) x(4)
y(1) y(2) y(3) y(4)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
x(1) x(2) x(3) x(4) x(5) x(6) x(7) x(7)
MAC
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
y(1) y(2) y(3) y(4) y(5) y(6) y(7) y(7)
Add
a y(1)
Mul
1 1 3 3 5 5 7 7
2 2 4 4 6 6 8 8
x(2) x(4) x(6) x(8)
x(1) x(3) x(5) x(7)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- ECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing Chapter 4 RetimingDocument24 paginiECE734 VLSI Arrays for Digital Signal Processing Chapter 4 RetimingaravinthcpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Parallel and Pipelined Processing in VLSI Arrays for DSPDocument13 paginiChapter 3 Parallel and Pipelined Processing in VLSI Arrays for DSPM Madan GopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- SOLDSPX06Document16 paginiSOLDSPX06Shafayet UddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP Exam Solutions from University of ManchesterDocument16 paginiDSP Exam Solutions from University of ManchesterEmmanuel Aron JoshuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Retiming for Digital Signal ProcessingDocument24 paginiChapter 4 Retiming for Digital Signal ProcessinggalaxystarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument7 paginiDigital Signal ProcessingJagadeesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSS Exp5Document11 paginiDSS Exp5Nayan MaheshwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Convolutional Codes ExplainedDocument25 paginiConvolutional Codes Explainedtrungthanhbk01Încă nu există evaluări
- Vlsi Signal ProcessingDocument455 paginiVlsi Signal ProcessingPavan TejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RK4 MethodDocument6 paginiRK4 MethodfurqanhamidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cordic: (Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer)Document25 paginiCordic: (Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer)santhiyadevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cordic: (Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer)Document25 paginiCordic: (Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer)Magdalene MilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DE - KOE 039 - Question BankDocument6 paginiDE - KOE 039 - Question Bankyash vatsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture7 Ee689 Eq Intro TxeqDocument27 paginiLecture7 Ee689 Eq Intro TxeqdogudoguÎncă nu există evaluări
- 766 10nDocument19 pagini766 10nSenthil Murugan SÎncă nu există evaluări
- UnfoldingDocument11 paginiUnfoldinghshheÎncă nu există evaluări
- VIGNAN ECE QUESTION BANKDocument15 paginiVIGNAN ECE QUESTION BANKAdnan Zahid67% (3)
- Course Notes Advanced DSPDocument122 paginiCourse Notes Advanced DSPAnonymous hDKqasfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vlsidsp Chap4 PDFDocument33 paginiVlsidsp Chap4 PDFgaru1991Încă nu există evaluări
- EEE6209 Advanced Digital Signal Processing (ADSP) : DR Charith Abhayaratne (CA)Document24 paginiEEE6209 Advanced Digital Signal Processing (ADSP) : DR Charith Abhayaratne (CA)dialauchennaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Implementation of A High-Speed, Low-Power VLSI Chip For The DCT TransformDocument34 paginiDesign and Implementation of A High-Speed, Low-Power VLSI Chip For The DCT TransformEric DharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument2 paginiDigital Signal ProcessingSreedeviRajithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Electrical Engineering National Institute of Technology Srinagar Tutorial IIIDocument3 paginiDepartment of Electrical Engineering National Institute of Technology Srinagar Tutorial IIIAkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advance Communication System Lectures Part 3Document23 paginiAdvance Communication System Lectures Part 3Shahzad Khalid ChÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fpgas in DSP Applications: Haibo Wang Ece Department Southern Illinois University Carbondale, Il 62901Document34 paginiFpgas in DSP Applications: Haibo Wang Ece Department Southern Illinois University Carbondale, Il 62901Huzur AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cockrum Fall 2008 Final PaperDocument15 paginiCockrum Fall 2008 Final Papernayeem4444Încă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal Processing Exam QuestionsDocument8 paginiDigital Signal Processing Exam QuestionsBharath LudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parallel Implementation of The DSPParallel Implementation of The DSPFunctions of The PAM-5 10Gb/sFunctions of The PAM-5 10Gb/sTransceiverDocument12 paginiParallel Implementation of The DSPParallel Implementation of The DSPFunctions of The PAM-5 10Gb/sFunctions of The PAM-5 10Gb/sTransceiverxaskÎncă nu există evaluări
- B1 Data ParallelDocument52 paginiB1 Data ParallelTg WallasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Set No: 1: Code No: V3218/R07Document6 paginiSet No: 1: Code No: V3218/R07Viswa ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE223 Signals & Systems - Spring 2021 Assignment 5Document11 paginiEE223 Signals & Systems - Spring 2021 Assignment 5Muhammad AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct Digital Frequency Synthesizer With CORDIC AlgorithmDocument12 paginiDirect Digital Frequency Synthesizer With CORDIC AlgorithmYermakov Vadim IvanovichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipelining and Parallel ProcessingDocument16 paginiPipelining and Parallel ProcessingBilgaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Wavelet Transform and Image CompressionDocument47 paginiIntroduction To Wavelet Transform and Image CompressionShivappa SiddannavarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP Paper Questions on Sampling, DFT, FIR Filters & DSP ProcessorsDocument3 paginiDSP Paper Questions on Sampling, DFT, FIR Filters & DSP ProcessorsDhariniJeevanandamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Signal Processing For Deep Space TransponderDocument6 paginiDigital Signal Processing For Deep Space TransponderSatish KapalavayiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital control system designDocument31 paginiDigital control system designdini bestÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSI & ASIC Digital Design Interview QuestionsDocument6 paginiVLSI & ASIC Digital Design Interview QuestionsRupesh Kumar DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hwang SolDocument29 paginiHwang Solamit_iitdÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP Question Paper Code 53123Document3 paginiDSP Question Paper Code 53123DhariniJeevanandamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euree 701Document2 paginiEuree 701swaroop0309Încă nu există evaluări
- Z Cryptogrphic AlgorithmsDocument71 paginiZ Cryptogrphic AlgorithmsSurangma ParasharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robust online particle size estimationDocument13 paginiRobust online particle size estimationrichard gutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- VSP Lec02 UnfoldingDocument47 paginiVSP Lec02 UnfoldingS RAVIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Implementation of Control Systems: Karl-Erik Årzen, Anton CervinDocument58 paginiComputer Implementation of Control Systems: Karl-Erik Årzen, Anton CervinAnonymous cW0QeMÎncă nu există evaluări
- GATE 2015 COMPUTER SCIENCE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERSDocument12 paginiGATE 2015 COMPUTER SCIENCE QUESTIONS AND ANSWERSPooja SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- X (N) (F U (N)Document2 paginiX (N) (F U (N)049 Narendran KÎncă nu există evaluări
- KL University, Vaddeswaram, Dept. of Ece B. Tech (All Branches), Iind Year, Sem-1 Test-1 Solutions, Signal Processing-13-Es205 Max Marks 30Document6 paginiKL University, Vaddeswaram, Dept. of Ece B. Tech (All Branches), Iind Year, Sem-1 Test-1 Solutions, Signal Processing-13-Es205 Max Marks 30Sai RanadheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discrete Time SignalDocument11 paginiDiscrete Time Signaldheerajdb99Încă nu există evaluări
- Discrete-Time Signals and SystemsDocument11 paginiDiscrete-Time Signals and SystemsCharan Priya MangipudyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cordic (Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer) : For VLSI Signal Processing CourseDocument25 paginiCordic (Coordinate Rotation Digital Computer) : For VLSI Signal Processing CourseAnandiacrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spreading Codes in Cdma Detection: Eastern Mediterranean University July 2003Document24 paginiSpreading Codes in Cdma Detection: Eastern Mediterranean University July 2003Alex BadeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A L D I S HW/SW C - D: Shun-Wen ChengDocument6 paginiA L D I S HW/SW C - D: Shun-Wen Chengmorvarid7980Încă nu există evaluări
- Convolution LectureDocument11 paginiConvolution Lecturespong1ertzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsDe la EverandMathematical and Computational Modeling: With Applications in Natural and Social Sciences, Engineering, and the ArtsRoderick MelnikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemDe la EverandDigital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Envsc Specs Samp WDocument35 paginiEnvsc Specs Samp WAnup0008Încă nu există evaluări
- Copy Right FormDocument1 paginăCopy Right FormAnup0008Încă nu există evaluări
- Copy Right FormDocument1 paginăCopy Right FormAnup0008Încă nu există evaluări
- Copy Right FormDocument1 paginăCopy Right FormAnup0008Încă nu există evaluări
- Active Filter NotesDocument19 paginiActive Filter NotesSrinivasu RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Static OptimizationDocument15 paginiStatic Optimizationsastry1234Încă nu există evaluări
- CT006!3!3 ADPLC 02 FunctionalProgramming Part 1Document42 paginiCT006!3!3 ADPLC 02 FunctionalProgramming Part 1suraj chimchimÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACO Ant Colony Optimization for the Quadratic Assignment ProblemDocument13 paginiACO Ant Colony Optimization for the Quadratic Assignment Problemjaved765Încă nu există evaluări
- W EE 418 - Lecture 3 Block Diagram and Signal Flow GraphDocument32 paginiW EE 418 - Lecture 3 Block Diagram and Signal Flow GraphGGAP LASTÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS331 Exam 2002 SolutionDocument11 paginiCS331 Exam 2002 SolutionKISHORE uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rich Automata SolnsDocument196 paginiRich Automata SolnsAshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 2 UpdatedDocument6 paginiAssignment 2 UpdatedB FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dip Ete 2020Document2 paginiDip Ete 2020MyDude IsHungryÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEDI Slides-Intro1-Chapter11-Inheritance, Polymorphism, InterfacesDocument37 paginiJEDI Slides-Intro1-Chapter11-Inheritance, Polymorphism, InterfacesSBC BSITÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 02 UninformedSearchDocument42 paginiChapter 02 UninformedSearchAd ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daa Lab ManualDocument37 paginiDaa Lab ManualsridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical MethodsDocument2 paginiNumerical MethodsJeoff Libo-on0% (1)
- P1 Create A Design Specification For Data Structures Explaining The Valid Operations That Can Be CDocument7 paginiP1 Create A Design Specification For Data Structures Explaining The Valid Operations That Can Be CRaishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systems: NeurolabDocument17 paginiNeural Networks and Fuzzy Systems: NeurolabmesferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 8A Unit Commitment Part 1Document25 paginiLecture 8A Unit Commitment Part 1malini72Încă nu există evaluări
- DSA Unit - I NotesDocument18 paginiDSA Unit - I Notesneha yarrapothu100% (1)
- Class 12 Informatic Practices Investigatory Project On Paralympic Data AnalysisDocument28 paginiClass 12 Informatic Practices Investigatory Project On Paralympic Data AnalysisNITIN MATTUÎncă nu există evaluări
- SummaryDocument59 paginiSummaryEmi IonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daa Ue18cs280 PDFDocument2 paginiDaa Ue18cs280 PDFPruthvi PutuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constraint SatisfactionDocument52 paginiConstraint SatisfactionNguyễn Thị Mỹ HânÎncă nu există evaluări
- C++ Programming: Chapter 1: Revision On Problem Solving TechniquesDocument21 paginiC++ Programming: Chapter 1: Revision On Problem Solving TechniquesShumet WoldieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Godel's incompleteness theorem ends in meaninglessnessDocument68 paginiGodel's incompleteness theorem ends in meaninglessnessgamahucherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variable Assignment: Rules For Variable NamesDocument5 paginiVariable Assignment: Rules For Variable Namesmahanth gowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CP2 Module 2 - Algorithm and PseudocodeDocument21 paginiCP2 Module 2 - Algorithm and PseudocodeJhaun Paul EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- All INT Quizzes 3Document25 paginiAll INT Quizzes 3Tiberiu UngurianuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADA Viva Questions Unit 1 and 2Document5 paginiADA Viva Questions Unit 1 and 2Yash PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical 2Document46 paginiTechnical 2PRANAV KUMAR 17BEC0473Încă nu există evaluări
- AITKEN INTERPOLATION - Metodos NumericosDocument13 paginiAITKEN INTERPOLATION - Metodos NumericosDiego Rangel RangelÎncă nu există evaluări
- OsDocument9 paginiOsanon_48973018Încă nu există evaluări
- Business Mathematics - Bus 202: Systems of Linear Equations and MatricesDocument3 paginiBusiness Mathematics - Bus 202: Systems of Linear Equations and MatricesIstiak bin mannanÎncă nu există evaluări