Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapters 14-15 Guided Reading
Încărcat de
api-237899555Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapters 14-15 Guided Reading
Încărcat de
api-237899555Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Botkin & Keller: Environmental Science: Earth as a Living Planet 8th Edition Guided Reading Assignment: Energy Unit-
Chapters 14-15 Name: _________________________________________________________ Chapter #14- Energy: Some Basics 1: How does the energy crisis in Ancient Greece and Rome compare to the oil crisis today? Explain. The local resources of wood were running out and had to bring some from other places, now the local oil is being used and we are having to buy oil from other countries
Energy Basics 2: What is work? Definition and mathematical equation. It is the amount of force used over a distance, The product of a force times a distance
Define the following: * Chemical Energy: Energy in form of chemicals
* Kinetic Energy: Energy of motion
* Heat Energy: Energy created by heat
* Potential Energy: Highest point of energy
3: What is the first law of thermodynamics? Total energy must be conserved
4: What does it mean to have a higher quality of energy? It means that it is more easily converted into work
5: What is the second law of thermodynamics? energy always goes from usable to less-usable
Energy Efficiency 6: Define: First-Law Efficiency Deals with the amount of energy without any consideration of the quality or availability of the energy
7: Define: Second-Law Efficiency How matched the energy end use is with the quality of the energy source
Energy Units 8: What is the fundamental energy unit in the Metric System? How is it defined? joules
9: What is POWER? How is it expressed? Power is the amount force to make energy
10: What is thermal efficiency? Energy that is efficient in heat
11: What is electrical resistivity? What does it cause? How strongly a certain material opposes the flow of electricity
Energy Sources and Consumption 12: What percentage of the energy in the United States is derived from fossil fuels? 90%
13: What percentage of the energy use in the United States is used efficiently? A little bit
Energy Conservation, Increased Efficiency and Cogeneration Define the following: 14: Conservation: Conserving to have more for later
15: Cogeneration (define and give an example): increasing efficiency of our energy by using wasted heat energy Example (hot water that is created by condensing the steam) 16: In the United States, space heating and cooling of homes and offices, water heating, industrial processes and automobiles account for nearly ___30___% of the total energy use Building Design 17: What is a passive solar energy system? Give examples. building designs for better energy conservation, passive solar designs
18: What are some ways that older homes can be modified to be more energy efficient? Putting solar panels in the roof
Industrial Energy 19: U.S. Industry consumes about ____1/3___ of the energy produced. Values, Choices and Energy Conservation 20: Name 3 ways that people could modify their behavior to help save energy using micropower, turning of stuff we dont use, using other energy resources like wind turbines
21: What is the concept of Integrated, Sustainable Energy Management? Using many energy resources instead of a single one
Micropower 22: What is the concept of micropower? Using small systems to produce electricity
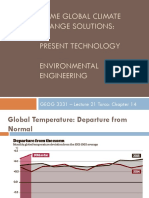
Critical Thinking Issue: Use of Energy Today and in 2030 23: How much energy in exajoules, did the world use in 2010 and what would you project global energy use to be in 2030? 2.1X10-16, in 2030 it will increase by 20%
24: The average person emits as heat 100 watts of power. If we assume that 25% of it is emitted by the brain, how much energy does your brain emit as heat in a year? 25 watts
25: Can the world supply one-third more energy by 2030 without unacceptable environmental damage? How? Yes by using other form of energy
26: In what specific ways could energy be used more efficiently in the United States? Using more solar power and wind turbines
Chapter #15: Fossil Fuels and the Environment 1: What is Peak Oil? What is predicted to happen when we reach peak oil? When the global production of oil reaches its highest point, it is predicted to happen in 2020
Fossil Fuels 2: How were fossil fuels created? through pressure and heat of decayed organisms
3: The major fossil fuels- crude oil, natural gas and coal- are our primary energy sources; they provide approximately ___90%__ of the energy consumed worldwide. Crude Oil and Natural Gas 4: Where were crude oil and natural gas deposits created? in plate boundaries in depositional basins
5: Why do we not find oil and gas in geologically old rocks? they are light and mitigate to the surface
6: What the favorable rock structure to trap oil and gas deposits? cap rock are the favorable rock structure
Petroleum Production 7: How much oil can be recovered from wells by primary production? 25% 8: What are enhanced recovery techniques of oil and gas deposits? using steam, water and compressed gas
9: Where are 60% of the total known reserves found? In the Middle East
10: When will world oil production likely to peak? In a couple of decades
Natural Gas 11: How is natural gas primarily transported? It is transported through pipelines
12: Why is natural gas considered to be a clean fuel? because it doesnt pollute as much as coal
Coal-Bed Methane 13: What is coal-bed methane and how much is estimated to exist? (How many years does this represent?) It is a form of natural gas from coal beds, 20 cubic trillion meters is estimated to exist for about 5yrs
14: What are the PROS and CONS of drilling for and using coal-bed methane? the pros are that it is a clean burning and produces low amounts of CO2 the Cons are the disposal, it can pollute the water
Black Shale Natural Gas 15: What are some of the concerns of hydrologic fracturing for black shale natural gas? The gas that is released can pollute the groundwater
Methane Hydrates 16: What are methane hydrates composed of? How were they formed? made of white ice like compounds, formed of microbial decomposition in the seafloor
17: Where do methane hydrates form? in the seafloor
The Environmental Effects of Oil and Natural Gas 18: What are some of the environmental effects of recovery of oil and gas? The release of CO2 and other greenhouse gases
19: What are some of the environmental effects of refining of oil and gas? spills of the oil and gas
20: What are some of the environmental effects of delivery and use of oil and gas? spills, destruction of pipelines
21: What are some arguments FOR and AGAINST drilling in the ANWR (Alaskan National Wildlife Refuge)? For: we wont rely on other countries and we can get lots of oil out of it Against: Its a refuge and it will destroy the habitat of animals
Coal 22: What is COAL? How is it created? its a rock and the largest source of fossil fuel, it is created through years of pressure and heat
23: Which type of coal has the greatest energy content? Which type has the lowest? anthracite is the highest and lignite is the lowest energy content
Coal Mining and the Environment 24: What is strip mining? it is destroying the top soil to reach the coal
25: What are some of the environmental impacts of strip mining? destruction of the top soil
Mountaintop Removal 26: What are some of the environmental impacts of mountaintop removal? pollution of the atmosphere which can cause lung problems
27: What does the Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of 1977 require? requires all the land that is mined to be restored Underground Mining 28: Underground Mining accounts for approximately _40__% of the coal mined in the United States 29: What are the dangers to miners in underground mining? they can get lung cancer by breathing all the chemicals that are used
30: What are the environmental impacts of underground mining? contamination of the groundwater
Transporting Coal 31: How is most of the coal transported in the United States? by tucks and trains
The Future of Coal 32: The burning of coal produces nearly _50_% of the electricity used and about 25_% of the total energy consumed in the United States today
33: How much air emissions are created using coal to create electricity in the U.S.? 35% of the air emission is CO2 and 70% is sulfur dioxide
34: What did the Clean Air Amendment of 1990 mandate? It mandated the cut of sulfur released
35: What is allowance trading? reducing pollution
Oil Shale and Tar Sands 36: What is oil shale? How is it created and where is it found? its a sedimentary rock containing kerogen, created by heating shale yield to 500C , found in Colorado, Utah, and Wyoming 37: What are the environmental impacts of developing oil shale? It can lead to earthquakes in the surface affecting the people living there
Tar Sands 38: Why cant petroleum be recovered from tar sands from conventional methods? the oil is to thick
39: How are tar sands processed? they mine it and then mix it with water to separate the oil from it
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Geochemistry, Earths System Processes (D. Panagiotaras, 2012) - (Geo Pedia Geo-Library)Document512 paginiGeochemistry, Earths System Processes (D. Panagiotaras, 2012) - (Geo Pedia Geo-Library)Omar RodriguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Primer: A Handbook of Energy Market BasicsDocument128 paginiEnergy Primer: A Handbook of Energy Market BasicsLJ's infoDOCKETÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crude Oil Properties-Handling Fire SafetyDocument96 paginiCrude Oil Properties-Handling Fire SafetyMichael J. BaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrogen Production: Stanko Ho Cevar and William SummersDocument65 paginiHydrogen Production: Stanko Ho Cevar and William SummersFatih AtatugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cook and Sherwood (1991) Classification of Oil Shales, Coals and Other Organic Rich R 2.17.gxyfDocument12 paginiCook and Sherwood (1991) Classification of Oil Shales, Coals and Other Organic Rich R 2.17.gxyfIsra KhoiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Project On Solar Battery ChargerDocument27 paginiA Project On Solar Battery ChargerVaibhav Charanti89% (53)
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of Renewable EnergyDocument15 paginiThe Advantages and Disadvantages of Renewable EnergySakura KeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pipeline Coatings Nov 2013Document46 paginiPipeline Coatings Nov 2013vincent.w.stone6724100% (3)
- 2014 PTQ q1Document156 pagini2014 PTQ q1coolvishal2003100% (1)
- Section A Strategy Project Group 7 Exxon MobilDocument34 paginiSection A Strategy Project Group 7 Exxon MobilAkhilAgrawal67% (3)
- Natural Gas StudyDocument104 paginiNatural Gas StudyaakashtrivediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slurry Phase Hydrocracking Bottoms UpgradingDocument6 paginiSlurry Phase Hydrocracking Bottoms UpgradingAndrei100% (1)
- Chapter 14 15Document4 paginiChapter 14 15api-236051971Încă nu există evaluări
- GR 14-15Document10 paginiGR 14-15api-238016123Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16-17 Guided ReadingDocument10 paginiChapter 16-17 Guided Readingapi-239466415Încă nu există evaluări
- 11 Global WarmingDocument44 pagini11 Global WarmingKiran RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16-17Document12 paginiChapter 16-17api-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- AP Enviormental Science Review For Chapter 12 in The Book by FriedlandDocument1 paginăAP Enviormental Science Review For Chapter 12 in The Book by FriedlandHenry HeinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2Document2 paginiModule 2Vaishnavi KamathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switch Doc. QuestionsDocument5 paginiSwitch Doc. QuestionsAurora PeughÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Renewable SourcesDocument95 paginiNon Renewable SourcesS.m. FerdousÎncă nu există evaluări
- The End of Oil - Explained QuestionsDocument5 paginiThe End of Oil - Explained QuestionsWIIIIIIIIIIIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chevron 05Document13 paginiChevron 05anon-915338Încă nu există evaluări
- A Sustainable Energy FutureDocument8 paginiA Sustainable Energy FutureJohn DambarefuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Benefits of Nuclear EnergyDocument5 paginiThe Benefits of Nuclear EnergyAiman FarhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Argumentation Dave Wimert Student HandoutDocument8 paginiEnergy Argumentation Dave Wimert Student HandoutScottÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENGR250Document2 paginiENGR250davidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benefits of NuclearDocument7 paginiBenefits of Nuclearapi-320457297Încă nu există evaluări
- Chris Rhodes - What Happens When The Oil Runs OutDocument44 paginiChris Rhodes - What Happens When The Oil Runs OutOnTheWightNewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Year ProjectDocument56 paginiFinal Year ProjectBiniam SolomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- RussiaDocument5 paginiRussia54 Pe AravindswamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renewable Energy ResourcesDocument12 paginiRenewable Energy Resourcesashish kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Carbon Buildings Week 1bDocument42 paginiLow Carbon Buildings Week 1bLeify KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sun, Wind and Desert: MENA, the upcoming Clean Energy World ChampionDe la EverandSun, Wind and Desert: MENA, the upcoming Clean Energy World ChampionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slide 7: Travel & TransportationDocument4 paginiSlide 7: Travel & TransportationReza ZillullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big Ass ReportDocument6 paginiBig Ass ReportKudzai SaunyamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EVS Study GuideDocument8 paginiEVS Study Guidebmur37Încă nu există evaluări
- Finalreport FinalDocument9 paginiFinalreport Finalshailaja.dubey.seÎncă nu există evaluări
- Res MCQDocument18 paginiRes MCQMelvinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renewable Energy - Solar Cells F3 - CTDocument40 paginiRenewable Energy - Solar Cells F3 - CTMortuzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Green Building MODULE 3Document13 paginiGreen Building MODULE 3impanac147Încă nu există evaluări
- HandbookDocument99 paginiHandbookutsavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Think Global,: Act LocalDocument4 paginiThink Global,: Act LocaltonybattistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-2 Global EnergyDocument10 paginiUnit-2 Global Energyhacker7899Încă nu există evaluări
- The Burning of Coal 1Document11 paginiThe Burning of Coal 1api-255463653Încă nu există evaluări
- P.SC CH 1 EngDocument2 paginiP.SC CH 1 EngShatadru ChaudhuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fossil Fuel - WikipediaDocument15 paginiFossil Fuel - Wikipediapowew28978Încă nu există evaluări
- Energetic Limits To GrowthDocument7 paginiEnergetic Limits To Growth::nyxÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnglaisDocument3 paginiAnglaisSyrine BoukhrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Towards The Hydrogen EconomyDocument13 paginiTowards The Hydrogen EconomyAntonio MontoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 - Sources of EnergyDocument31 paginiChapter 3 - Sources of EnergyPremshankar RajbharÎncă nu există evaluări
- OGCF QuizDocument95 paginiOGCF Quizpandeyamritesh100% (1)
- Energy Test SG AnsweredDocument3 paginiEnergy Test SG AnsweredbmurtaghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Original 1489663394 Chapter 1-Global Energy Landscape-Non-RenewablesDocument23 paginiOriginal 1489663394 Chapter 1-Global Energy Landscape-Non-RenewablesNaavaneethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuelcells 1Document15 paginiFuelcells 1Fatih ÖztürkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Semester PaperDocument12 paginiSemester Paperapi-317138514Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 8 - 2 - World Energy SourcesDocument16 paginiTopic 8 - 2 - World Energy SourcesEdisonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy ChallengeDocument30 paginiEnergy Challengemlkz_01Încă nu există evaluări
- MaincerdocumentDocument14 paginiMaincerdocumentapi-307043468Încă nu există evaluări
- Fossil FuelsDocument3 paginiFossil FuelsKhawaja Ammar HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3331 Lecture21 CC Solutions W16Document32 pagini3331 Lecture21 CC Solutions W16Ijaz Fazil Syed Ahmed KabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Debunking The Green Myth: Perma CreteDocument5 paginiDebunking The Green Myth: Perma CreteZeb'sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 5-CHAN Cheuk SangDocument6 paginiAssignment 5-CHAN Cheuk SangJackson ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem 111 - Week 4Document16 paginiChem 111 - Week 4Reyy ArbolerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 6 Cmerlang Global Warming 2010Document27 paginiGroup 6 Cmerlang Global Warming 2010arveanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Warming and Civil EngineeringDocument20 paginiGlobal Warming and Civil EngineeringMathumai100% (1)
- Popular Science Magazine FinalDocument9 paginiPopular Science Magazine Finalapi-606883375Încă nu există evaluări
- OzoneDocument4 paginiOzoneapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- Coyote Lab Case StudyDocument2 paginiCoyote Lab Case Studyapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- HamburgerDocument2 paginiHamburgerapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- CN - Chapter 20Document5 paginiCN - Chapter 20api-2378995550% (2)
- WeatherDocument2 paginiWeatherapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- DammDocument2 paginiDammapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- 2Document2 pagini2api-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- GGGGGDocument2 paginiGGGGGapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- PhosphateDocument2 paginiPhosphateapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- 1Document4 pagini1api-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- ArticleDocument2 paginiArticleapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- GmoDocument5 paginiGmoapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 18Document4 paginiChapter 18api-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- Fast FoodDocument2 paginiFast Foodapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- MountainDocument1 paginăMountainapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- Salton SeaDocument5 paginiSalton Seaapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- NotesDocument3 paginiNotesapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 19Document5 paginiChapter 19api-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- WaterpollutionDocument3 paginiWaterpollutionapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- Recycle CityDocument3 paginiRecycle Cityapi-2378995550% (1)
- Chapter 23Document6 paginiChapter 23api-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- DecimelDocument2 paginiDecimelapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- GeothermalDocument2 paginiGeothermalapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- PersonDocument1 paginăPersonapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- Lung Toxicology Worksheet WordDocument4 paginiLung Toxicology Worksheet Wordapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- ToxicologyDocument5 paginiToxicologyapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- PopulationpovertyandthelocalenvironmentDocument1 paginăPopulationpovertyandthelocalenvironmentapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- GlobalbazaarDocument2 paginiGlobalbazaarapi-237899555Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Cybercrime - Group 2Document12 paginiChapter 6 Cybercrime - Group 2Billy Joe G. BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Get TRDocDocument239 paginiGet TRDocMohammad ElhedabyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IS230 3rdedition PDFDocument60 paginiIS230 3rdedition PDFFabian Andres Blanco GÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1Document96 pagini1Ninh Quoc TrungÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Oil Council's 'Drillers and Dealers' Magazine - March 2010 IssueDocument28 paginiThe Oil Council's 'Drillers and Dealers' Magazine - March 2010 IssuerossstewartcampbellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy Conversion AssessmentDocument10 paginiEnergy Conversion AssessmentTruong CaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shale OilDocument3 paginiShale OilArpan BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drilling Deeper: A Reality Check On U.S. Government Forecasts For A Lasting Tight Oil & Shale Gas BoomDocument315 paginiDrilling Deeper: A Reality Check On U.S. Government Forecasts For A Lasting Tight Oil & Shale Gas BoomPost Carbon Institute100% (1)
- More Unanswered QuestionsDocument8 paginiMore Unanswered QuestionspermaculturistÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geir Sjurseth 2014Document24 paginiGeir Sjurseth 2014agarwal.rmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Petroleum Microbiology Lecture 4 Oil ShaleDocument43 paginiPetroleum Microbiology Lecture 4 Oil ShaleBarnabasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gab Preliminar 822 Petrobras 23 CB1 01 PDFDocument1 paginăGab Preliminar 822 Petrobras 23 CB1 01 PDFNailson BritoÎncă nu există evaluări
- WorldEnergyBalancesHighlights FinalDocument597 paginiWorldEnergyBalancesHighlights FinalDavid Rosenstand0% (1)
- Situ CombustionDocument30 paginiSitu CombustionSuleiman BaruniÎncă nu există evaluări
- SGIGDocument115 paginiSGIGndlr81Încă nu există evaluări
- United States Patent: (45) Date of Patent: Sep - 8, 2020Document14 paginiUnited States Patent: (45) Date of Patent: Sep - 8, 2020M FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spe-9988899-Ms NewDocument10 paginiSpe-9988899-Ms NewNicholas GawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1. Innovations WorkbookDocument2 paginiUnit 1. Innovations WorkbookDmytro ShulzhenkoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marcellus Gas Well EconomicsDocument109 paginiMarcellus Gas Well EconomicsJames "Chip" NorthrupÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChE Thoughts - Vol-03, No-1 PDFDocument52 paginiChE Thoughts - Vol-03, No-1 PDFshahed IasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Heavy Crude-Prod. & TechnologyDocument4 paginiFuture Heavy Crude-Prod. & TechnologyHARISHKOTHARU48Încă nu există evaluări