Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
6th Grade Final Exam Study Guide
Încărcat de
api-233736029Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
6th Grade Final Exam Study Guide
Încărcat de
api-233736029Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Name: Date: Period:
6
th
Grade Final Exam Study Guide
Nature of Science
1. DEFINE and GIVE AN EXAMPLE of each of the following terms:
Theory:
Law:
Hypothesis:
Inferences:
Data:
Prior Knowledge:
Plate Tectonics (Chapter 6)
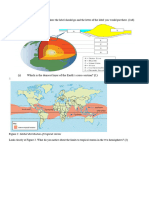
2. Name and describe the three COMPOSITIONAL layers of the Earth. (know what it is made of, its thickness,
and temperature)
a. ______________
i. Composition: ________________.
ii. _______km thick
iii. Temperature:_______
b. _______________
i. Composition:________________.
ii. _______km thick
iii. Temperature:_______
c. _______________
i. Composition:_________________.
ii. _______km thick
iii. Temperature:______
2. What are the five MECHANICAL layers of the Earth, what are their compositions and how thick are they?
a. ______________: composition: ___________________; ____km thick
Name: Date: Period:
b. ______________: composition:____________________; ____km thick
c. ______________: composition:____________________; ____km thick
d. ______________: composition:____________________; ____km thick
e. ______________: composition:____________________; ____km thick
3. What is a tectonic plate? Define it.
4. What type of crust(s) can a tectonic plate be made of?
5. Explain Wegners Theory of Continental Drift. What is some of the evidence for this theory?
6. What is a mid-ocean ridge? Give an example of a well known mid-ocean ridge.
7. Explain sea-floor spreading, and HOW it happens. DRAW A DIAGRAM.
8. What is a magnetic reversal?
9. Explain what the following explanations of how tectonic plates move states:
a. Mantle Convection:
b. Slab pull:
Name: Date: Period:
c. Ridge Push:
Earthquakes
10. DESCRIBE AND EXPLAIN each of the following types of plate boundaries. EXPLAIN WHAT LAND FEATURES
TEND TO FORM AT THESE BOUNDARIES.
a. Convergent boundaries:
b. Divergent boundaries:
c. Transform boundaries:
11. What are the two different types of stress that rocks can experience? Explain what each one is?
12. What is the difference between folding and faulting in a rock layer?
13. What are earthquakes? How do they form?
14. What are the two ways rocks can deform? Define/explain each way.
a. Plastic:
b. Elastic:
Name: Date: Period:
15. What are the different types of seismic waves? Describe their differences including: which ones arrive
first, which ones are the strongest, how they move, and through what they can move.
a. P Waves (Primary waves):
b. S Waves (Secondary waves):
c. L Waves (Surface waves):
16. Define and explain the following terms. Find examples if you need to.
a. Focus:
b. Epicenter:
c. Aftershock:
d. Elastic rebound:
e. Seismic waves:
Name: Date: Period:
17. What are different scales used to measure earthquake magnitudes? What are the benefits and
disadvantages to each?Which one is used now?
a. Mercalli Scale:
b. Richter Scale:
Volcanoes (Chapter 8)
18. What is a volcano?
19. What is the difference between an explosive and a nonexplosive eruption?
20. Describe the characteristics for each of the following types of volcanoes:
a. Composite (stratovolcano):
b. Shield Volcano:
c. Cinder cones:
21. Distinguish (explain) the following classifications of volcanoes:
a. Extinct:
b. Dormant:
c. Active:
22. What is a hot spot?
Name: Date: Period:
Erosion, Rivers and Deposition (Chapter 10 and 11)
23. What is erosion?
24. What are the FIVE agents of erosion?
25. What is run-off?
26. What is deposition?
27. What are conditions are ideal for deposition to occur (speed of river, type of load, etc.) and
EXPLAIN how those conditions make it ideal for deposition to occur?
28. How does weathering/erosion AND deposition change or shape the land/surface of the Earth?
GIVE EXAMPLES!
29. Explain IN DETAIL how rivers form. Explain it in stages (USE THE FLOW CHART WE MADE IN
CLASS!).
30. What is ground water?
Name: Date: Period:
31. Explain why ground water is important?
32. What are the two ZONES of ground water, and explain/describe each?
a. Zone of aeration:
b. Zone of saturation:
33. What is an AQUIFER?
34. What are the TWO qualities which an aquifer has?
35. Explain how the surf can be a powerful agent of erosion and deposition?
36. Define:
a. Shoreline:
b. Beach:
c. Longshore current:
d. Alluvial fan:
e. Delta:
f. Alluvium:
Name: Date: Period:
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 1963 HOUSNER The Dynamic Behaviour of Water TanksDocument7 pagini1963 HOUSNER The Dynamic Behaviour of Water TanksEugenio DurbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCC & PSC Made Easy Class Notes 2019 PDFDocument329 paginiRCC & PSC Made Easy Class Notes 2019 PDFSaud AffanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life Science Module 2 Earth Subsystems, Materials and Processes - Jonivil Vidal PDFDocument23 paginiEarth and Life Science Module 2 Earth Subsystems, Materials and Processes - Jonivil Vidal PDFjosephine100% (2)
- Residential and Low-Rise Steel Framing NZ-Public CommentDocument59 paginiResidential and Low-Rise Steel Framing NZ-Public CommentpengenbangetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Underground Work in Hard Rock Tunnelling and MiningDocument87 paginiUnderground Work in Hard Rock Tunnelling and MiningMiguel CastillejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Quarter Exam in Earth Science (2023-2024)Document2 paginiFirst Quarter Exam in Earth Science (2023-2024)Marvin Earl O. RabinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Space 10 Module First Quarter 1 1Document80 paginiEarth and Space 10 Module First Quarter 1 1Gerwin MilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IGCSE Geography Course Notes: TectonicsDocument42 paginiIGCSE Geography Course Notes: TectonicsxerxesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Folding and FaultingDocument16 paginiFolding and FaultingDeepesh KhandelwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cantilever Scaffolding CalculationDocument2 paginiCantilever Scaffolding CalculationReza FurqonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life Diagnostic TestDocument4 paginiEarth and Life Diagnostic TestAnjhiene CambaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Quarter Questions in ELSDocument3 pagini3rd Quarter Questions in ELSLeizel Mundo100% (1)
- SUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 10 JorsDocument4 paginiSUMMATIVE TEST IN SCIENCE 10 JorsJomarie Asoy Batonghinog90% (10)
- Common Ions Charges ChartDocument2 paginiCommon Ions Charges Chartapi-233736029100% (1)
- Earthandlifescience11 q1 Mod5 Platemovements Its Effects and Dating Techniques v1Document32 paginiEarthandlifescience11 q1 Mod5 Platemovements Its Effects and Dating Techniques v1Arnel UrbinarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Storage Tank Design Calculation - Api 650: Close Cone-RoofDocument14 paginiStorage Tank Design Calculation - Api 650: Close Cone-RoofSalah JallaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Piping 11Document21 paginiPiping 11ashish.mathur1Încă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Geology QuestionsDocument2 paginiEngineering Geology QuestionsDaljeet SidhuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Lifescience DiagnosticDocument11 paginiEarth Lifescience DiagnosticDearest Notes100% (1)
- Bridge Design FhwaDocument58 paginiBridge Design FhwaSyed Muhammad Naeem Ahmed100% (1)
- First Quarter Exam For Grade 10Document3 paginiFirst Quarter Exam For Grade 10Christine De San Jose90% (90)
- Science 10 PretestDocument3 paginiScience 10 PretestMario Uy86% (7)
- Summative Test Science10 1stDocument3 paginiSummative Test Science10 1stDominga SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vol 9 - Operations ManualDocument101 paginiVol 9 - Operations ManualRobert SalasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth & Life First Exam 2018-2019Document6 paginiEarth & Life First Exam 2018-2019Argie Joy Marie AmpolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthquake Test Study GuideDocument3 paginiEarthquake Test Study GuideElbert Alinggom PuasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Sci Quiz 2 Elac Spring 2020 Quiz 2 DRDocument2 paginiEarth Sci Quiz 2 Elac Spring 2020 Quiz 2 DRFavio Enrique PazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Objectives and Review SheetDocument2 paginiUnit 4 Objectives and Review Sheetncl12142Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 Objectives and Review SheetDocument2 paginiUnit 4 Objectives and Review Sheetncl121420% (1)
- Earth Systems Final Exam ReviewDocument2 paginiEarth Systems Final Exam Reviewncl12142Încă nu există evaluări
- PDF - CH 2 Review WorksheetDocument2 paginiPDF - CH 2 Review Worksheetapi-205313794Încă nu există evaluări
- Mackenzie Meyers - ReviewPacketSpringFinalExamCady2023Document15 paginiMackenzie Meyers - ReviewPacketSpringFinalExamCady2023mackenzieomeyersÎncă nu există evaluări
- GazmenDocument1 paginăGazmenAhcel Tejano Cabaña IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Exam Review PacketDocument24 paginiFinal Exam Review Packetnathan casinaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Examview - 8th Grade Earths Structure and Processes 8scDocument8 paginiExamview - 8th Grade Earths Structure and Processes 8scapi-232424041Încă nu există evaluări
- Advance Geo 1 and 2 QuestionsDocument28 paginiAdvance Geo 1 and 2 QuestionsBrowny hustlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gy 100 Testing QuestionsDocument7 paginiGy 100 Testing Questionskatodativa23Încă nu există evaluări
- Plate Tectonics QuestionsDocument8 paginiPlate Tectonics QuestionsGenaro AlberoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 11 PLATE TECTONICSDocument2 paginiUnit 11 PLATE TECTONICSMarian Bernadette Dela PeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Test Review 2013-1Document2 paginiHeat Test Review 2013-1api-208349712Încă nu există evaluări
- Grade 12 - Science Set ADocument4 paginiGrade 12 - Science Set AjonaifahmangiginÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNit 5 Test Review Sheet-Plate Tectonics-Volcanoes-Earthquakes TestDocument3 paginiUNit 5 Test Review Sheet-Plate Tectonics-Volcanoes-Earthquakes TestJosh MolterÎncă nu există evaluări
- HAZARDS Igcse WKBKDocument19 paginiHAZARDS Igcse WKBKkamrunnisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Quarter Exam For Grade 10Document4 paginiFirst Quarter Exam For Grade 10Mary Faviene SalvioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Planet TestDocument8 paginiDynamic Planet TestAnonymous ZZg2Lf0Încă nu există evaluări
- Revision Chapter 8Document6 paginiRevision Chapter 8BenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geo Paper 1 Part1 AnalysisDocument4 paginiGeo Paper 1 Part1 AnalysisrajeshrananoidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review Dynamic Earth CoreScienceDocument3 paginiReview Dynamic Earth CoreScienceVikram BologaneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth and Life Science 2nd Mastery Exam 2019Document2 paginiEarth and Life Science 2nd Mastery Exam 2019Princess Ali Ma-ayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Science 11 Module (Week 1-5)Document38 paginiEarth Science 11 Module (Week 1-5)Hilary Grace Sumbi GargarÎncă nu există evaluări
- FINAL GeoDocument1.260 paginiFINAL Geohana215mohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visualizing Physical Geography 2nd Edition Foresman Test BankDocument28 paginiVisualizing Physical Geography 2nd Edition Foresman Test Bankazuragwencr8ud100% (22)
- Science and Health 6: Reviwer, Dut 3 Grading PeriodDocument3 paginiScience and Health 6: Reviwer, Dut 3 Grading PeriodClaireNavarroÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Quarter Review TestDocument11 paginiFirst Quarter Review TestMariel C. LuceroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1Document2 paginiWeek 1Rufa NarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Sex Am Christian Howard Ls A Gu BayDocument4 paginiTo Sex Am Christian Howard Ls A Gu BayCHRISTIAN HOWARD SAGUBAYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz Seismic WavesDocument2 paginiQuiz Seismic WavesBriannah loiuse P. AdalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toc 2019Document10 paginiToc 2019BODI WAELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth's Origin: 1. The UniverseDocument5 paginiEarth's Origin: 1. The UniverseSamina HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6301 Engineering Geology 2 Marks N 16 Marks PDFDocument114 paginiCE6301 Engineering Geology 2 Marks N 16 Marks PDFveenabalu200% (1)
- Geography WKSHTDocument3 paginiGeography WKSHTjasleenk.marwah13Încă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To Geography Optional 25 Years FinalDocument5 paginiA Guide To Geography Optional 25 Years FinalSingh AdityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: - Sec: Date: ScoreDocument3 paginiName: - Sec: Date: ScoreHONLETH ROMBLONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm Study GuideDocument4 paginiMidterm Study GuideNickÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReviewerDocument7 paginiReviewerJeegj Ecco MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dwnload Full Understanding Weather and Climate 6th Edition Aguado Solutions Manual PDFDocument35 paginiDwnload Full Understanding Weather and Climate 6th Edition Aguado Solutions Manual PDFkotelamalbec6100% (8)
- Geography Plate Tectonics NotesDocument7 paginiGeography Plate Tectonics NotesCaryn LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Our Universe 2Nd Edition Palen Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument31 paginiUnderstanding Our Universe 2Nd Edition Palen Test Bank Full Chapter PDFbrandoncook07011996ogy100% (5)
- Understanding Our Universe 2nd Edition Palen Test BankDocument13 paginiUnderstanding Our Universe 2nd Edition Palen Test Bankkieueugene55ec6100% (26)
- Dynamics of Plate Tectonics and Mantle ConvectionDe la EverandDynamics of Plate Tectonics and Mantle ConvectionJoao C. DuarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccs Ela Reading Assessment 7th GradeDocument6 paginiCcs Ela Reading Assessment 7th Gradeapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Daniel F Life Is Like EssayDocument3 paginiDaniel F Life Is Like Essayapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Bianca R Life Essay Thesis PicDocument2 paginiBianca R Life Essay Thesis Picapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Aidan H Life Is Like EssayDocument2 paginiAidan H Life Is Like Essayapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Kelan M Life Essay Thesis PicDocument2 paginiKelan M Life Essay Thesis Picapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Jessica G Life Is Like EssayDocument2 paginiJessica G Life Is Like Essayapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- 20 Project Presentation GuidelinesDocument4 pagini20 Project Presentation Guidelinesapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Robotics Unit Sneha TharayilDocument8 paginiRobotics Unit Sneha Tharayilapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Ccs Ela Reading Assessment 8th Grade-StudentDocument9 paginiCcs Ela Reading Assessment 8th Grade-Studentapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio-Inspired Robot Cob-EDocument8 paginiBio-Inspired Robot Cob-Eapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio-Inspired Robot-CribotDocument6 paginiBio-Inspired Robot-Cribotapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Youtube Parent Consent FormDocument3 paginiYoutube Parent Consent Formapi-233736029100% (1)
- Classbook Wall Assignment DescriptionDocument2 paginiClassbook Wall Assignment Descriptionapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Robot Prototype Design Project InstructionsDocument7 paginiRobot Prototype Design Project Instructionsapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Coastal Landforms Table Graphic OrganizerDocument2 paginiCoastal Landforms Table Graphic Organizerapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Group Project Partner EvaluationsDocument1 paginăGroup Project Partner Evaluationsapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Data Analysis WorksheetDocument1 paginăData Analysis Worksheetapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- 7th Science Final Exam Study GuideDocument8 pagini7th Science Final Exam Study Guideapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Evidences of Evolution Graphic OrganizerDocument1 paginăEvidences of Evolution Graphic Organizerapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Coastal Landforms Table Graphic OrganizerDocument2 paginiCoastal Landforms Table Graphic Organizerapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Beach Sediment InvestigationDocument1 paginăBeach Sediment Investigationapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Shaping The Land Test Study GuideDocument7 paginiShaping The Land Test Study Guideapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Sle Presentation 6-8 Presentation Rubric CcssDocument2 paginiSle Presentation 6-8 Presentation Rubric Ccssapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Notes - Ionic BondsDocument15 paginiNotes - Ionic Bondsapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Covalent BondsDocument13 paginiCovalent Bondsapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Notes - Chemical EquationsDocument7 paginiNotes - Chemical Equationsapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Catholic Social Teaching and The Un Declaration of Human RightsDocument2 paginiCatholic Social Teaching and The Un Declaration of Human Rightsapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 21 Sec 2-The EyeDocument23 paginiChapter 21 Sec 2-The Eyeapi-233736029Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 1 Sec 1 ReviewDocument7 paginiCH 1 Sec 1 Reviewshermaine genistonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Forms Systems For Tall Building Structures: Er. Nishant Rana, SiddhantranaDocument3 paginiStructural Forms Systems For Tall Building Structures: Er. Nishant Rana, SiddhantranaYamini LokhandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plate Tectonic and Stress-Field Modelling of The North Arm of Sulawesi (Naos), Indonesia, To Better Understand The Distribution of Mineral Deposit StylesDocument2 paginiPlate Tectonic and Stress-Field Modelling of The North Arm of Sulawesi (Naos), Indonesia, To Better Understand The Distribution of Mineral Deposit StylesFriska AyundaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mount KanlaonDocument33 paginiMount KanlaonJenny ForcadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checklist To Evaluate DrawingDocument26 paginiChecklist To Evaluate DrawingMishal LimbuÎncă nu există evaluări
- StructuralDocument45 paginiStructuralBrian PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- AR2015 EngDocument46 paginiAR2015 EngHadrianus Handoko Saputro0% (1)
- High-Rise Buildings Raffles City in Hangzhou ChinaDocument16 paginiHigh-Rise Buildings Raffles City in Hangzhou ChinaIendP 20Încă nu există evaluări
- USGS Volcano Threat AssessmentDocument50 paginiUSGS Volcano Threat AssessmentHNNÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Non-Organic Theory of The Genesis of PetroleumDocument20 paginiThe Non-Organic Theory of The Genesis of Petroleumzaroia100% (8)
- Simplifying Eurocode 8 Ductile Detailing Rules For Reinforced Concrete StructuresDocument12 paginiSimplifying Eurocode 8 Ductile Detailing Rules For Reinforced Concrete StructuressongkkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4icee-Stmf Goel PrenstDocument18 pagini4icee-Stmf Goel PrenstKYINCÎncă nu există evaluări
- HandbookDocument318 paginiHandbookEfrainmanasesRamosAsenciosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of Amplitude Volume Technique Attributes, Their Variations, and ImpactDocument8 paginiApplication of Amplitude Volume Technique Attributes, Their Variations, and ImpactmiragresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daily Lesson Log: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayDocument3 paginiDaily Lesson Log: Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday FridayKaren PolinarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Energy Dissipation of A Building UsingDocument4 paginiSeismic Energy Dissipation of A Building UsingDiegoHenaoLeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Earthquakes On Dams and EmbankmentsDocument22 paginiEffects of Earthquakes On Dams and EmbankmentsssheafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Report) Storage Tanks (Japan)Document179 pagini(Report) Storage Tanks (Japan)RAJENDRA PRASADÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buildings With Earthquake RiskDocument3 paginiBuildings With Earthquake RiskCristina LicăÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synthesis of The Study GuideDocument3 paginiSynthesis of The Study GuideMark Jerome GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări