Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Igcse Physics Forces Movement
Încărcat de
api-255623302Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Igcse Physics Forces Movement
Încărcat de
api-255623302Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Describe an experiment
to investigate forces
acting upon falling
objects.
Give some examples of
vector quantities.
Describe elastic
behaviour.
How do you calculate
force using momentum
statistics?
Explain why force is a
vector quantity.
How do you calculate
force?
Forces can change...
How do you calculate
moment?
Give some examples of
scalar quantities.
How do you calculate
momentum?
1a
-Velocity
-Momentum
Drop a parachute from a
certain height record the
results and repeat with
different sized parachutes.
force (N) = change in
momentum (kg m/s) /
time taken (s)
Elastic objects will be able to
recover to it's initial
formation/shape. However when
the force has over come this limit it
cannot return to it's original shape.
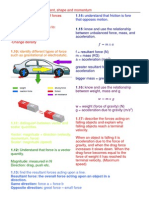
F = m x a
Magnitude: Measured in
N
Direction: Drag, push,
pull etc.
moment (Nm) = force
(N) x perpendicular
distance from the pivot.
-Change direction
-Change velocity
-Change Shape
-Change density
momentum (kg m/s) =
mass (kg) x velocity
(m/s)
-Speed
1b
How do you calculate the
resultant force when the
bodies are in opposite
directions ( -> <- )
Outline Newton's third
law.
How do you calculate
the resultant force when
the bodies are in the
same direction.( -> -> )
Outline the centre of
mass.
How do you calculate
the stopping distance?
What affect the
vehicle's stopping
distance?
How do you calculate
weight?
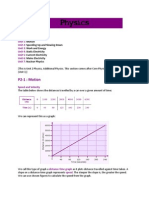
What does a force-
extension graph show?
How is the force-
extension graph
related to hook's law?
What does that law of
conservation state?
2a
That when two objects
interact they are both
exerting equal forces on
each other.
Greater force - smaller
force.
Every object has a centre
of mass at which when it
is suspended will be
balanced from this point.
force a + force b
-Speed of the car
-Mass of the car
-Weather conditions
-Condition of the car
-Condition of the roads
stopping distance =
thinking distance +
braking distance
How mucha a material
stretches in a certain
amount of time.
w = m x g
w = weight (force of gravity)
(N)
g = acceleration due to gravity
(m/s^2)
Whenever object interact,
the total momentum
before is equal to the total
momentum after.
The initial linear region is a
straight diagonal line which
shows the relationship
between force and extension.
2b
What is a scalar
quantity?
Why does an object
reach terminal velocity
when it is falling?
What is a vector
quantity?
What is the principle
of moments?
What is the resultant
force?
When we say an object
is in equilibrium, we
mean it is...
3a
When an object is falling it is
accelerating due to gravity,
When the drag force becomes
equal to the force it has
reached terminal velocity.
Only has magnitude
Has magnitude and
direction
If the object is balanced
then the clock-wise and
anti-clockwise moment
will be equal.
The resultant force is
the overall force acting
upon an object in a
direction
It has come to rest at its
centre of mass when
suspended.
3b
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsDe la EverandA-level Physics Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (10)
- Parachute Research - SRTDocument28 paginiParachute Research - SRTapi-367217803Încă nu există evaluări
- Momentum: A Conserved QuantityDocument93 paginiMomentum: A Conserved QuantitySteve100% (1)
- D3755-14 Standard Test Method For Dielectric BreakdowDocument6 paginiD3755-14 Standard Test Method For Dielectric Breakdowjose flores100% (1)
- Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDocument8 paginiMost Essential Learning CompetenciesKaterina TagleÎncă nu există evaluări
- HL Physics Revision NotesDocument58 paginiHL Physics Revision NotesZohebCurrimbhoy100% (1)
- Physics Unit 1 MechanicsDocument49 paginiPhysics Unit 1 Mechanicsamir hamza100% (1)
- Physics 11Document11 paginiPhysics 11moorchehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics CompilationsDocument117 paginiPhysics CompilationsRenard Vince MalunesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksDe la EverandPower, Momentum and Collisions - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- NASA ERAST Program Develops High-Altitude UAVsDocument17 paginiNASA ERAST Program Develops High-Altitude UAVsEgz AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The History of PumpsDocument8 paginiThe History of Pumpsdhanu_aquaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Momentum Student NotesDocument17 paginiMomentum Student NotesabdulfcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology Cell StructureDocument2 paginiIgcse Biology Cell Structureapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDocument9 paginiGce o Level Physics MatterirmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Mechanics Revision NotesDocument5 pagini1 - Mechanics Revision NotesHuaxiang HuangÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM PhysicsDocument21 paginiSPM PhysicsWoody Cys100% (2)
- Software Test ReportDocument4 paginiSoftware Test ReportSabahat HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- 大连学校物理动量知识Document33 pagini大连学校物理动量知识leoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quick Union Reference Tables: Pressure Control EquipmentDocument1 paginăQuick Union Reference Tables: Pressure Control EquipmentMiguel FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Companies in IndiaDocument11 paginiConstruction Companies in Indiashobhit.goel33% (3)
- Uniformly Accelerated Motion in Vertical DimentaionDocument11 paginiUniformly Accelerated Motion in Vertical DimentaionEricka Pallon CamayudoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Physics Short NotesDocument56 paginiIgcse Physics Short NotesakashÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB Physics Topic 2Document18 paginiIB Physics Topic 2wee100% (1)
- Husky Air Assignment 5 and 6Document15 paginiHusky Air Assignment 5 and 6varunkalra6Încă nu există evaluări
- IAL Physics MechanicsDocument6 paginiIAL Physics Mechanicsvekariaraj99Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics Guide to Motion, Forces, Energy & ElectricityDocument12 paginiPhysics Guide to Motion, Forces, Energy & ElectricityMehmet ImamzadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics As NotesDocument28 paginiPhysics As NotesShyam SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout Momentum:: The Momentum Equation As A Guide To ThinkingDocument3 paginiHandout Momentum:: The Momentum Equation As A Guide To Thinkingmarium khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Center of Mass, Momentum, Impulse & CollisionsDocument8 paginiCenter of Mass, Momentum, Impulse & CollisionsRolando Jerome MagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newtonian Mechanics ExplainedDocument15 paginiNewtonian Mechanics ExplainedKrish Madhav ShethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Unit - C Forces Movement Shapeand MomentumDocument3 paginiIgcse Unit - C Forces Movement Shapeand Momentumapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Physics Dynamics NotesDocument9 paginiIntroduction To Physics Dynamics NotesNKHICQ1mEbIwÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics - Unit 1 (Mechanics)Document49 paginiPhysics - Unit 1 (Mechanics)hippohorse100% (1)
- Introduction to Physics ConceptsDocument84 paginiIntroduction to Physics ConceptsMhelveneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Momentum and ForcesDocument32 paginiCalculating Momentum and ForcesC-Jay Nash TsigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Science: ForcesDocument17 paginiPhysical Science: ForcesAubrey Marie VillamorÎncă nu există evaluări
- MechanixDocument39 paginiMechanixShikta TopsheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Momentum FundamentalsDocument14 paginiMomentum FundamentalsPreetesh SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHM1 Organic2Document18 paginiCHM1 Organic2Hakim AbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHYSICSDocument35 paginiPHYSICSPrincess Mae AlejandrinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gce o Level Physics MatterDocument8 paginiGce o Level Physics MatterJonas Tianyou KhooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Momentum Grade 9 and 10Document19 paginiMomentum Grade 9 and 10Shams ZubairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scalar and vector quantities, equations of motion, and Newton's lawsDocument7 paginiScalar and vector quantities, equations of motion, and Newton's lawsApollo Wong100% (1)
- HSC Physics Circular Motion SummaryDocument5 paginiHSC Physics Circular Motion SummaryShekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conservation of Momentum CalculationsDocument14 paginiConservation of Momentum CalculationsDaniel BerryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Force, Mass and MomentumDocument16 paginiForce, Mass and MomentumAlberto BenitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion Forces and EnergyDocument13 paginiMotion Forces and EnergyAbid KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ForcesDocument41 paginiForcesGhazi DallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forces and Motion ExplainedDocument25 paginiForces and Motion ExplainedEbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPH3U1 Exam Review NotesDocument26 paginiSPH3U1 Exam Review Notesrahihot100% (1)
- A2 Unit 4 Sample PageDocument20 paginiA2 Unit 4 Sample PageSyEd Mohammed IfrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes - Momentum - WsDocument3 paginiNotes - Momentum - WsNot IsmdanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics - Unit 1Document7 paginiPhysics - Unit 1michaela menzelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics Chapter 13Document9 paginiDynamics Chapter 13ABDFERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 2010Document15 paginiChapter 2 2010Agnes YaoYaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 2 Forces and MotionDocument14 paginiSPM PHYSICS SHORT NOTES CHAPTER 2 Forces and MotionJay BeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics: 2.1 - Motion Distance and DisplacementDocument17 paginiMechanics: 2.1 - Motion Distance and DisplacementMido YoussefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics: Mechanics Definitions: Small Distance Travelled/ Small Interval of TimeDocument5 paginiPhysics: Mechanics Definitions: Small Distance Travelled/ Small Interval of TimeAman SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics Equations and FormulasDocument12 paginiMechanics Equations and FormulasLiang LuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edrolo ch3Document42 paginiEdrolo ch3YvonneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Chapter VIIDocument15 paginiPhysics Chapter VIIHime AoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2: Mechanics: 2.1 - Motion Distance and DisplacementDocument18 paginiTopic 2: Mechanics: 2.1 - Motion Distance and DisplacementMona Mohamed SafwatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balanced and Unbalanced ForcesDocument19 paginiBalanced and Unbalanced ForcessreekanthkataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Exam ReviewDocument23 paginiPhysics Exam ReviewYashoda SubrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shell History Exam Revsison GuideDocument2 paginiShell History Exam Revsison Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology Digestion Revision GuideDocument3 paginiIgcse Biology Digestion Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Shell Revision Guide Summer Exam 2014Document1 paginăShell Revision Guide Summer Exam 2014api-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology Respiration, Lungs & Smoking Revision GuideDocument2 paginiIgcse Biology Respiration, Lungs & Smoking Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Revision Guide Summer AxamsDocument2 paginiRevision Guide Summer Axamsapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- English Persuade Argue and To Advice Revision GuideDocument1 paginăEnglish Persuade Argue and To Advice Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Areas of Plane ShapesDocument1 paginăAreas of Plane Shapesapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Volumes of Solids and Surface AreasDocument1 paginăVolumes of Solids and Surface Areasapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Revision Guide AstronomyDocument1 paginăIgcse Revision Guide Astronomyapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Shell Revision Guide Problem of Evil and SufferingDocument2 paginiShell Revision Guide Problem of Evil and Sufferingapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Bonding Revision GuidesDocument1 paginăBonding Revision Guidesapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Math Number Revision GuideDocument9 paginiMath Number Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Revision Guide AstronomyDocument1 paginăIgcse Revision Guide Astronomyapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Mindnode Velocity - Time GraphDocument1 paginăMindnode Velocity - Time Graphapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Unit - C Forces Movement Shapeand MomentumDocument3 paginiIgcse Unit - C Forces Movement Shapeand Momentumapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Physics Forces MovementDocument6 paginiIgcse Physics Forces Movementapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse C Biological Molecules Revision GuideDocument1 paginăIgcse C Biological Molecules Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Units B Movement and Posistion Revision GuideDocument1 paginăIgcse Units B Movement and Posistion Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology PhotosynthesisDocument6 paginiIgcse Biology Photosynthesisapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology Gas ExchangeDocument2 paginiIgcse Biology Gas Exchangeapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology DigestionDocument6 paginiIgcse Biology Digestionapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology Biological MolecDocument4 paginiIgcse Biology Biological Molecapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Movement of Substances in and Out of CellsDocument1 paginăIgcse Movement of Substances in and Out of Cellsapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Life Processes Revision GuideDocument2 paginiLife Processes Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Photosynthesis Igcse Revision GuideDocument2 paginiPhotosynthesis Igcse Revision Guideapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Biology Movement of SubsDocument4 paginiIgcse Biology Movement of Subsapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Variety of Living OrganismsDocument4 paginiVariety of Living Organismsapi-255623302Încă nu există evaluări
- Vernier, Dial, and Electronic Digital Calipers: Session 3Document40 paginiVernier, Dial, and Electronic Digital Calipers: Session 3Emman Bosito100% (1)
- Structural Analysis of Beams Using Moment Distribution MethodDocument15 paginiStructural Analysis of Beams Using Moment Distribution MethodneetuÎncă nu există evaluări
- c600 17lookinsideDocument6 paginic600 17lookinsideИван МинчевÎncă nu există evaluări
- American English File Starter Ichecker - File 3Document3 paginiAmerican English File Starter Ichecker - File 3Daniel AugustoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HP w2007 w2007v SMDocument75 paginiHP w2007 w2007v SMfeliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pco2Document55 paginiPco2camdentownÎncă nu există evaluări
- EML 4507 Spring 2017 HW11 SolutionDocument7 paginiEML 4507 Spring 2017 HW11 SolutionUnmil PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation FileDocument10 paginiPresentation FileInnoVentureCommunityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Float Trap PennantDocument2 paginiFloat Trap PennantJinalkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral and Practical Tests: MechanicDocument19 paginiOral and Practical Tests: MechanicHugo AlmeidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fall Protection Marking GuidelinesDocument2 paginiFall Protection Marking GuidelinescuervohijoguachoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maximum Power Tracking System for Solar Panels Using Automatic ControlDocument79 paginiMaximum Power Tracking System for Solar Panels Using Automatic ControlHarish VarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DTH Equipment - Product - Catalogue - tcm45-3560033 PDFDocument48 paginiDTH Equipment - Product - Catalogue - tcm45-3560033 PDFJALFAROROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zw3d2022 Lite Vs Cadbro 2022Document4 paginiZw3d2022 Lite Vs Cadbro 2022Carlos LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonox101 PdsDocument3 paginiTrigonox101 PdsPaula RiveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- QlassicDocument31 paginiQlassicQila HusinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructions For Installation, Operating and Maintenance InstructionDocument30 paginiInstructions For Installation, Operating and Maintenance InstructionmilacronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extrusion-Spheronization Process Variables and CharacterizationDocument57 paginiExtrusion-Spheronization Process Variables and CharacterizationKhanh Le0% (1)
- Modified 0-30V - 0-3A Variable Power Supply - Rev.2Document2 paginiModified 0-30V - 0-3A Variable Power Supply - Rev.2Manuel Cereijo NeiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narayana 10 01 24 SR Star Co Scmodel A, B&C Jee Main GTM 12n Key&sDocument10 paginiNarayana 10 01 24 SR Star Co Scmodel A, B&C Jee Main GTM 12n Key&sReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standardization of Welding ElectrodesDocument8 paginiStandardization of Welding ElectrodesAqsa BanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explorador Ww90j6410cwec Version 02Document13 paginiExplorador Ww90j6410cwec Version 02Cristi PopescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridge Operational ClassificationDocument1 paginăBridge Operational ClassificationFrancis DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări