Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions - Jacob Schwegman
Încărcat de
berniemonkeyzorDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions - Jacob Schwegman
Încărcat de
berniemonkeyzorDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public.
Page 1 of 3
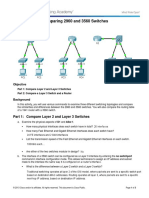
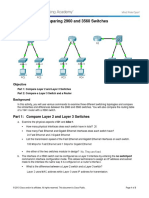
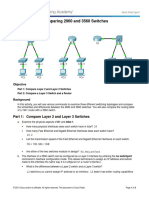
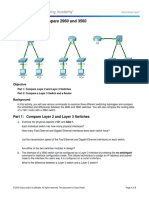
Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches
Topology
Objective
Part 1: Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches
Part 2: Compare a Layer 3 Switch and a Router
Background
In this activity, you will use various commands to examine three different switching topologies and compare
the similarities and differences between the 2960 and 3560 switches. You will also compare the routing table
of a 1941 router with a 3560 switch.
Part 1: Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches
a. Examine the physical aspects of D1 and ASw-1.
How many physical interfaces does each switch have in total?
How many Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces does each switch have?
List the transmission speed of the Fast Ethernet and Gigabit Ethernet interfaces on each switch.
Are either of the two switches modular in design?
b. The interface of a 3560 switch can be configured as a Layer 3 interface by entering the no switchport
command in interface configuration mode. This allows technicians to assign an IP address and subnet
mask to the interface the same way it is configured on a routers interface.
What is the difference between a Layer 2 switch and a Layer 3 switch?
22, 2
FE = 100, GB = 1GB
24
No, they are fixed.
L2 switches you cannot assign IP address to an interface. L3 switch has better routing capabilities.
Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 2 of 3
What is the difference between a switchs physical interface and the VLAN interface?
On which layer does a 2960 and 3560 operate?
Which command allows a technician to assign an IP address and subnet mask to the Fast Ethernet
interface on a 2960?
Issue the show run command to examine the configurations of the D1 and ASw-1 switches. Do you
notice any differences between them?
Display the routing table on both switches using the show ip route command. Why do you think the
command does not work on ASW-1, but works on the D1?
Part 2: Compare a Layer 3 Switch and a Router
a. Up until recently, switches and routers have been separate and distinct devices. The term switch was set
aside for hardware based devices that function at Layer 2. Routers, on the other hand, are devices that
make forwarding decisions based on Layer 3 information and use routing protocols to share routing
information and to communicate with other routers. Layer 3 switches, such as the 3560, can be
configured to forward Layer 3 packets. Entering the ip routing command in global configuration mode
allows Layer 3 switches to be configured with routing protocols, thereby possessing some of the same
capabilities as a router. However, although similar in some forms, they are different in many other
aspects.
Open the Physical tab on D1 and R1. Do you notice any similarities and differences between the two?
Issue the show run command and examine the configurations of R1 and D1. What differences do
you see between the two?
Vlan interfaces are created virtually and do not have a physical ports on the switch.
2960 = Layer 2 only, 3560 = Layer 2 and 3
You can't
The differences is that the 3560 switch can assign an ip address to a physical address.
They have some of the same types of ports, but the router has more types of interfaces.
D1 does not have serial interface and R1 does. They both have FE and GB interfaces.
D1 has a lot more FE interfaces than R1. R1 has two serial ports as D1 does not. GB interfaces are both
configured with addressing.
Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches
2013 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public. Page 3 of 3
Which command allows D1 to configure an IP address on one of its physical interfaces?
Use the show ip route command on both devices. Do you see any similarities or differences
between the two tables?
Now, analyze the routing table of R2 and D2. What is evident now that was not in the configuration of
R1 and D1?
b. Verify that each topology has full connectivity be completing the following tests:
Ping from PC1 to PC2
Ping from PC3 to PC4
Ping from PC5 to PC6
In all three examples, each PC is on a different network. Which device is used to provide communication
between networks?
Why were we able to ping across networks without there being a router?
Suggested Scoring Rubric
Activity Section
Question
Location
Possible
Points
Earned
Points
Part 1: Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3
Switches
a 20
b 40
Part 1 Total 60
Part 2: Compare a Layer 3 Switch and a
Router
a 30
b 10
Part 2 Total 40
Total Score 100
Type interface. example interface FE 1
R1 has locally connected networks, while D1 does not. They both have directly connected networks.
R2 and D2 are both configured with EIGRP.
The router and Layer 3 switch
Because a layer 3 switch has that capability.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- 1217 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument3 pagini1217 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument3 pagini1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsJozeph Abod67% (3)
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument3 pagini1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsEdisonJoshuaValistoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches: TopologyDocument3 paginiPacket Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches: TopologyMiguel DragoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsDocument3 pagini1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches InstructionsRoy Janssen100% (3)
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesDocument4 pagini1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesKurt John MiñozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 2 1 7Document2 pagini1 2 1 7Francis janeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.5.1 Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Devices - ILMDocument4 pagini11.5.1 Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Devices - ILMLizardo Hilario Hinostroza GuillermoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesDocument3 pagini1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesAnonymous sYXo4KÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACTIVITY 9 - Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 (B) : CISC003 - Cisco Networking 3Document2 paginiACTIVITY 9 - Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 (B) : CISC003 - Cisco Networking 3Klienze Ashtrid MelencioÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER1 Quiz - NET202Document3 paginiCHAPTER1 Quiz - NET202Analiza NatividadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Docslide - Us 1217 Packet Tracer Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions 56847ae83fed6Document3 paginiDocslide - Us 1217 Packet Tracer Comparing 2960 and 3560 Switches Instructions 56847ae83fed6Christian EspinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.5.1 Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Devices AnswerDocument4 pagini11.5.1 Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Devices AnswerVinicio MartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesDocument7 pagini1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesJulio Cesar MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches and RoutersDocument3 paginiCompare Layer 2 and Layer 3 Switches and RouterscoleparksÎncă nu există evaluări
- 11.5.1 - Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 DevicesDocument3 pagini11.5.1 - Packet Tracer - Compare Layer 2 and Layer 3 DevicesMaría ArmijosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesDocument3 pagini1.2.1.7 Packet Tracer - Compare 2960 and 3560 SwitchesAnonymous GHHtATVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packet Tracer 13Document3 paginiPacket Tracer 13cristhoper espinozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asd Asd ADocument12 paginiAsd Asd ADarrylJanMontemayorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packet Tracer ScriptsDocument53 paginiPacket Tracer ScriptsLammetje Lives33% (3)
- 5.3.1.10 Lab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address TablesDocument5 pagini5.3.1.10 Lab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address TablesLaura HampÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inter VLANDocument26 paginiInter VLANAmro GoneimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address Tables: Sergio David Valdes Torres A01365520Document10 paginiLab - Using IOS CLI With Switch MAC Address Tables: Sergio David Valdes Torres A01365520a01365520Încă nu există evaluări
- 5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument5 pagini5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingShaun50% (2)
- Inter VLANDocument5 paginiInter VLANRamon Eduardo Lopez HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.4.3.3 - ZachDocument5 pagini6.4.3.3 - ZachZack ShoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFDocument8 pagini9 3 2 13 Lab Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs PDFEl Amrani MoutiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN - InstructionsDocument5 pagini6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN - InstructionsLaura HampÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableDocument12 paginiPacket Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN: Addressing TableMENDOZA GASPAR PAOLA Ingeniería en Sistemas ComputacionalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced IP Services-Assignment QuestionsDocument11 paginiAdvanced IP Services-Assignment QuestionsYuvaraj V, Assistant Professor, BCAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 4Document8 paginiLab 4pzydf6wjxvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 10 CCNDocument15 paginiLab 10 CCNMalik WaqarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocument7 pagini6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesultracsokiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 2 1 4 Configuring - EtherChannelDocument7 pagini3 2 1 4 Configuring - EtherChannelETRI100% (1)
- Presentation ON Ccna: TRAINED BY - Kundan Singh (Aptron Solutions PVT LTD)Document36 paginiPresentation ON Ccna: TRAINED BY - Kundan Singh (Aptron Solutions PVT LTD)Akshay Mishra BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA 4 Chapter 7 V4.0Document8 paginiCCNA 4 Chapter 7 V4.0ccnatrainingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMDocument16 pagini4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMCte eduÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument10 pagini5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN Routingcamilo veraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccna TestDocument24 paginiCcna TestArt CamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN Instructions IGDocument5 pagini6.4.3.3 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LAN Instructions IGopiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAN Redundancy Protocols and ConceptsDocument72 paginiLAN Redundancy Protocols and ConceptsXa MauÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMDocument9 pagini4.2.2.13 Lab - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLs - ILMGuri DhillonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccna 3 Final Exam NotesDocument67 paginiCcna 3 Final Exam NotesaoryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 7 - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLsDocument6 paginiLab 7 - Configuring and Verifying Extended ACLsmeerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingDocument5 pagini5.1.2.4 Lab - Configuring Per-Interface Inter-VLAN RoutingNery Cifuentes0% (1)
- Dynamic Routing (RIP) : 1. ObjectiveDocument11 paginiDynamic Routing (RIP) : 1. ObjectiveNouman SaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- JARKOM11 DaviAdrian - 1803007Document10 paginiJARKOM11 DaviAdrian - 1803007Davi AdrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- CCNA Practice Certification Exam 2Document11 paginiCCNA Practice Certification Exam 2Gabriel GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCP/IP Abc's Layer 3 Layer 2 Switch Web Switch Virtual LANDocument6 paginiTCP/IP Abc's Layer 3 Layer 2 Switch Web Switch Virtual LANapi-26278159Încă nu există evaluări
- Navdeep Singh Parewa (2030075 - 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANDocument4 paginiNavdeep Singh Parewa (2030075 - 10.3.4 Packet Tracer - Connect A Router To A LANNavdeep ParewaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPANNING TREE PROTOCOL: Most important topic in switchingDe la EverandSPANNING TREE PROTOCOL: Most important topic in switchingÎncă nu există evaluări
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONDe la EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONÎncă nu există evaluări
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksDe la EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolDe la EverandFirst Hop Redundancy Protocol: Network Redundancy ProtocolÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingDe la EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingDe la EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-A: A Beginner's Guide to Next Level of NetworkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- IPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1De la EverandIPv4 Subnetting for Beginners: Your Complete Guide to Master IP Subnetting in 4 Simple Steps: Computer Networking, #1Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxDe la EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1De la EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationDe la EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9.1.2.5 Packet Tracer - Using A TFTP Server To Upgrade A Cisco IOS Image Instructions CompleteDocument2 pagini9.1.2.5 Packet Tracer - Using A TFTP Server To Upgrade A Cisco IOS Image Instructions Completeberniemonkeyzor50% (2)
- 6.2.3.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 InstructionsDocument2 pagini6.2.3.7 Packet Tracer - Configuring Multiarea OSPFv3 Instructionsbubblybubbles19000% (1)
- Greenfoot ReadmeDocument1 paginăGreenfoot ReadmeberniemonkeyzorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab1 1Document7 paginiLab1 1shellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EX 1 Chapter02 Communicating NetworkDocument40 paginiEX 1 Chapter02 Communicating NetworkberniemonkeyzorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 ExamDocument8 paginiChapter 1 ExamberniemonkeyzorÎncă nu există evaluări
- ModemLog - HDAUDIO Soft Data Fax Modem With SmartCPDocument5 paginiModemLog - HDAUDIO Soft Data Fax Modem With SmartCPAji WibowoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLI Management User GuideDocument25 paginiCLI Management User GuideerickgugoÎncă nu există evaluări
- STRATELLITES: HIGH-ALTITUDE TELECOMMUNICATIONS AIRSHIPSDocument20 paginiSTRATELLITES: HIGH-ALTITUDE TELECOMMUNICATIONS AIRSHIPSsanskar jhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- C1000Z 802.11n VDSL2 Wireless Gateway: BenefitsDocument2 paginiC1000Z 802.11n VDSL2 Wireless Gateway: BenefitsTorrey PinesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fortinac: Fortigate Endpoint Management IntegrationDocument41 paginiFortinac: Fortigate Endpoint Management IntegrationAlan Becerra Arrieta100% (1)
- Antena 7750Document3 paginiAntena 7750cordoba_bÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.) Pasolink Neo Standard (Lecture)Document41 pagini1.) Pasolink Neo Standard (Lecture)Nguyễn ThiênÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Communications With VoipDocument206 paginiData Communications With Voipapi-3860591Încă nu există evaluări
- TL Wa801nd PDFDocument81 paginiTL Wa801nd PDFgeorgedragosÎncă nu există evaluări
- TR 101 - Issue 2Document101 paginiTR 101 - Issue 2ergismiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prezentare-Mateinfo de Deded Dededed FrfrfwfwefDocument3 paginiPrezentare-Mateinfo de Deded Dededed FrfrfwfwefVLADÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRVCC Feature Parameter Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDDocument35 paginiSRVCC Feature Parameter Description: Huawei Technologies Co., LTDvikash984Încă nu există evaluări
- Manual - 5240 - DatasheetDocument2 paginiManual - 5240 - DatasheetCosme RodolfoÎncă nu există evaluări
- PTP 49600 Bridge: 4.9 GHZ Point-To-Point Solutions For Public SafetyDocument2 paginiPTP 49600 Bridge: 4.9 GHZ Point-To-Point Solutions For Public SafetyFernando PereiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The UnOfficial VCIX NV Study Guide v1.0Document245 paginiThe UnOfficial VCIX NV Study Guide v1.0Andrei MateiÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To Computer Networks PDFDocument617 paginiAn Introduction To Computer Networks PDFJuan ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS 302 Question PaperDocument3 paginiCS 302 Question PaperNandita HansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cve 172Document4 paginiCve 172Jesimie OriasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Growth of Lan TechnologyDocument5 paginiGrowth of Lan TechnologyMuhammad hamzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CR50-100 Ing QSGDocument12 paginiCR50-100 Ing QSGPaul Anim AmpaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Block Websites Using Pfsense Firewall FeatureDocument12 paginiHow To Block Websites Using Pfsense Firewall FeatureVcastiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11: Wide-Area Networks and The InternetDocument11 paginiChapter 11: Wide-Area Networks and The InternetDavid van TeeselingÎncă nu există evaluări
- ProCurve Switch 2610 SeriesDocument10 paginiProCurve Switch 2610 SeriesedgemangahasÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEEE 802.11n MAC Frame Aggregation Mechanisms For Next-Generation High-Throughput WLANs (Medium Access Control Protocols For Wireless LANs)Document8 paginiIEEE 802.11n MAC Frame Aggregation Mechanisms For Next-Generation High-Throughput WLANs (Medium Access Control Protocols For Wireless LANs)Paul Downey100% (1)
- Cardax FT Controller 6000Document12 paginiCardax FT Controller 6000weso9Încă nu există evaluări
- DatacommunicationDocument4 paginiDatacommunicationSumit S SutraveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anisur Rehman's 15-Year IT Project Management ExperienceDocument6 paginiAnisur Rehman's 15-Year IT Project Management Experienceanis rehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ADX Overview and Applications GuideDocument37 paginiADX Overview and Applications Guidekhuecamau100% (1)
- Part - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No. Questions Bloom's Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeDocument11 paginiPart - A (Short Answer Questions) : S. No. Questions Bloom's Taxonomy Level Course OutcomeDevendra BhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- IP Security: Henric Johnson Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden Henric - Johnson@bth - SeDocument31 paginiIP Security: Henric Johnson Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden Henric - Johnson@bth - Seahmadamminudin89Încă nu există evaluări