Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
The Main Diff
Încărcat de
Shobhit GargDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
The Main Diff
Încărcat de
Shobhit GargDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
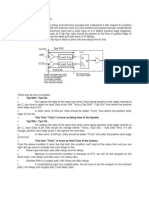
The main difference between GPS and GLONASS is that in GLONASS each satelilite
has its own frequencies but the same code whereas in GPS als satellites use the same
frequencies but have different codes. GLONASS uses what is called a frequency
devision multiple access method (FDMA) whereas GPS and Galileo uses a code
devision multiple access technique (CDMA)
All signals transmitted by the satellite are derived from the fundamental frequency
(f0) of the satellite oscillator. Each satellite transmits on a different frequency using
originally a 25-channel frequency division multiple access (FDMA) technique
spanning from 1602.5625 MHz to 1615.5 MHz, known as the L1 band. The equation
to calculate the exact center frequency is 1602 MHz + n 0.5625 MHz, where n is a
satellite's frequency channel number (n=0,1,2,...24). On the L2 band, between 1240
MHz and 1260 MHz, the center frequency is determined by the equation 1246 MHz +
n 0.4375 MHz.
The GLONASS transmissions in the band 1610.6 - 1613.8 MHz degraded radio
astronomical observations dramatically in the years since the launch of the first
GLONASS satellites. With the full GLONASS constellation the band 1610.6 - 1613.8
MHz would be closed for any radio astronomical research. In the fall of 1992 the
Radio Astronomy Service made dedicated observations in full collaboration of the
GLONASS administration in a world-wide campaign to test this interference.
Negotiations between IUCAF and the GLONASS administration led in November
1993 to an agreed step-by-step plan to clear the band 1610.6-1613.8 MHz of
interference by GLONASS. This agreement became model for agreements between
the administration of the Russian Federation and those of other countries. According
to this agreement GLONASS satellites launched after 2005 will use channels n=-7 to
+6, with channels +5 and +6 used only for orbital insertion, or during periods of
exceptional circumstances. Satellites will incorporate filters, protecting both the 1660-
1670 MHz and the 1610.6-1613.8 MHz band from out of band emissions to the
required ITU-R RA769.1 limit (as above, -238 dB(Wm-2Hz-1)).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- QW123Document7 paginiQW123Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Change Dump (VCD) : Switching Activity Interchange Format SaifDocument1 paginăValue Change Dump (VCD) : Switching Activity Interchange Format SaifShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExtractionDocument2 paginiExtractionShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sta 9 1Document125 paginiSta 9 1Jayaprakash Polimetla100% (1)
- PDDocument66 paginiPDShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Planning: Management and I/O Cell Power Management. in Former One VDD and VSS PowerDocument5 paginiPower Planning: Management and I/O Cell Power Management. in Former One VDD and VSS PowerShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- GHDocument5 paginiGHShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vacancy For Senior Research Fellow To Work in DST Sponsored Project in IIT RoparDocument3 paginiVacancy For Senior Research Fellow To Work in DST Sponsored Project in IIT RoparShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frank MLPD 03Document8 paginiFrank MLPD 03Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- EdatoolsDocument44 paginiEdatoolsThomas JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eula Microsoft Visual StudioDocument3 paginiEula Microsoft Visual StudioqwwerttyyÎncă nu există evaluări
- QDocument12 paginiQShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format of Area of Interest Submit by 14th Sep 2015Document1 paginăFormat of Area of Interest Submit by 14th Sep 2015Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtmDocument32 paginiAtmSebastian HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ConsidDocument1 paginăConsidShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ps 2Document3 paginiPs 2Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yfhb, NMNKNKNKJBJBJMDocument5 paginiYfhb, NMNKNKNKJBJBJMShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- I DayDocument1 paginăI DayShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Library1.Opj LognmDocument1 paginăLibrary1.Opj LognmShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- MemoryDocument24 paginiMemoryShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 3 of About 8Document2 paginiPage 3 of About 8Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Setup and Hold TimeDocument6 paginiSetup and Hold TimeShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties and Directive Principles of State Policy Fundamental RightsDocument14 paginiFundamental Rights, Fundamental Duties and Directive Principles of State Policy Fundamental RightsgrsrikÎncă nu există evaluări
- BelDocument1 paginăBelShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZigBee Is A Technological StandardDocument9 paginiZigBee Is A Technological StandardShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atmega 16Document8 paginiAtmega 16Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- ZigBee Is A Technological StandardDocument9 paginiZigBee Is A Technological StandardShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Landmarks in The Constitutional Development of IndiaDocument13 paginiLandmarks in The Constitutional Development of IndiagrsrikÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)