Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Consid
Încărcat de
Shobhit Garg0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
8 vizualizări1 paginăd
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentd
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
8 vizualizări1 paginăConsid
Încărcat de
Shobhit Gargd
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
considered the single most important indicator of MOSFET
performance in Switching Mode Power Supplies (SMPS).
Therefore, several new technologies have been developed
to improve the RDS(ON) QG FOM. The super-junction
device utilizing charge balance theory was introduced to the
semiconductor industry ten years back and it set a new
benchmark in the high-voltage power MOSFET market[3].
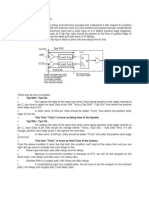
Figure 1 shows the vertical structure and electric field
profile of a planar MOSFET and super-junction MOSFET.
Breakdown voltage of a planar MOSFET is determined by
drift doping and its thickness. The slope of electric field
distribution is proportional to drift doping. Therefore, thick
and lightly-doped EPI is needed to support higher
breakdown voltage. The major contribution to on-resistance
of high-voltage MOSFET comes from the drift region.
Therefore, the on-resistance exponentially increases with
the light doping and thick drift layer for higher breakdown
voltage, as shown in Figure 2.
Super-junction technology has deep P-type pillar-like
structure in the body in contrast to the well-like structure of
conventional planar technology. The effect of the pillars is
to confine the electric field in the lightly doped EPI region.
Thanks to this P-type pillar, the resistance of N-type EPI
can be reduced dramatically compared to the conventional
planar technology, while maintaining same level of
breakdown voltage. Therefore
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Baliga Figure of MeritDocument3 paginiBaliga Figure of MeritKyle BotheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slpa007 PDFDocument3 paginiSlpa007 PDFSreenuj CmÎncă nu există evaluări
- tmpC43E TMPDocument8 paginitmpC43E TMPFrontiersÎncă nu există evaluări
- High Voltage Junctionless FET With Improved DC Performance Compared To LDMOSDocument4 paginiHigh Voltage Junctionless FET With Improved DC Performance Compared To LDMOSIJSTEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science DirectDocument9 paginiScience Directmidhunn08Încă nu există evaluări
- Mems Switches Seminar ReportDocument29 paginiMems Switches Seminar ReportNidhi SaraswatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Application Guide For High Speed MOSFET Gate Drive CircuitsDocument37 paginiDesign and Application Guide For High Speed MOSFET Gate Drive CircuitswewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power MOSFET: Basic StructureDocument10 paginiPower MOSFET: Basic StructureDomagoj ProphectusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optical Tuning of Resistance Switching in Polycrystalline Gallium Phosphide Thin FilmsDocument23 paginiOptical Tuning of Resistance Switching in Polycrystalline Gallium Phosphide Thin FilmsCrainlyÎncă nu există evaluări
- History of Power Mosfets: ApplicationsDocument7 paginiHistory of Power Mosfets: ApplicationsVaishali PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ti - Mosfet Gate DriveDocument40 paginiTi - Mosfet Gate Drivedownload_cruxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit - 3Document8 paginiUnit - 3AgnathavasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LDMOS Technology For RF Power AmplifiersDocument10 paginiLDMOS Technology For RF Power AmplifiersParansaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project 1 FullDocument10 paginiProject 1 FullSaratul AkmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- I - G B T: Nsulated ATE Ipolar RansistorDocument59 paginiI - G B T: Nsulated ATE Ipolar RansistorsushilsemwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S0038110105001073 MainDocument11 pagini1 s2.0 S0038110105001073 MainSanjay G RÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Vertical MOSFETsDocument11 pagini3 - Vertical MOSFETsAbhigyan GangulyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 01Document21 paginiUnit 01mathanstar77Încă nu există evaluări
- NE Multidimension Final v4 CleanDocument27 paginiNE Multidimension Final v4 CleanMario johanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4H-Sic Trench Mosfet With Floating/ Grounded Junction Barrier-Controlled Gate StructureDocument7 pagini4H-Sic Trench Mosfet With Floating/ Grounded Junction Barrier-Controlled Gate Structureshradha shreyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- N PJ Quant Mats 20164Document6 paginiN PJ Quant Mats 20164mojaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soft Switch Phase ShiftDocument4 paginiSoft Switch Phase Shiftjameschall1Încă nu există evaluări
- RF CMOS Power Amplifiers For Mobile Terminals: Ki Yong Son, Bonhoon Koo, Yumi Lee, Hongtak Lee, and Songcheol HongDocument9 paginiRF CMOS Power Amplifiers For Mobile Terminals: Ki Yong Son, Bonhoon Koo, Yumi Lee, Hongtak Lee, and Songcheol HongKhaled AggourÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dual Material Gate Technique For Enhanced Transconductance and Breakdown Voltage of Trench Power MOSFETsDocument17 paginiDual Material Gate Technique For Enhanced Transconductance and Breakdown Voltage of Trench Power MOSFETsMamidala Jagadesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amplificadores Cascode MosfetDocument5 paginiAmplificadores Cascode MosfetlucianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Power MosfetsDocument5 paginiUnderstanding Power MosfetsIskander XandrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conduction Loss, PowerDocument13 paginiConduction Loss, PowerMurtaza RizviÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Novel TFET StructureDocument23 paginiA Novel TFET StructureRohith ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energies: Electric Field Simulations and Analysis For High Voltage High Power Medium Frequency TransformerDocument11 paginiEnergies: Electric Field Simulations and Analysis For High Voltage High Power Medium Frequency Transformer吴川斌Încă nu există evaluări
- tmp1741 TMPDocument5 paginitmp1741 TMPFrontiersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Amplifier 20-100MHzDocument8 paginiPower Amplifier 20-100MHzNikhil GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project On RF Mems SwitchDocument37 paginiProject On RF Mems SwitchAshok Gadhwal100% (3)
- Review of RF MEMS SwitchesDocument37 paginiReview of RF MEMS SwitchesGöksenin BozdağÎncă nu există evaluări
- FinFET Inverter Anlaysis PDFDocument14 paginiFinFET Inverter Anlaysis PDFRakeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOCF Based Control For Optimum Operation of A Grid Tied Solar PV SystemDocument11 paginiTOCF Based Control For Optimum Operation of A Grid Tied Solar PV SystemsrinathÎncă nu există evaluări
- RFmemsDocument9 paginiRFmemsAdrienne JohnstonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Analysis of A Novel Low Actuated Voltage RF MEMS Shunt Capacitive SwitchDocument5 paginiDesign and Analysis of A Novel Low Actuated Voltage RF MEMS Shunt Capacitive SwitchiaetsdiaetsdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaDocument92 paginiChapter 4 - Analog Integrated Circuit Design by John ChomaAriana Ribeiro LameirinhasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mosfet en DetalleDocument66 paginiMosfet en DetallecuervocrowÎncă nu există evaluări
- RF Series Switch PDFDocument6 paginiRF Series Switch PDFAnonymous ybl4y5RIlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Btran White Paper CURRENT 12april2016Document11 paginiBtran White Paper CURRENT 12april2016Wilkins CedanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spatial Power Combiner Technology: I K N K 1 O, K IDocument7 paginiSpatial Power Combiner Technology: I K N K 1 O, K IArun KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyper FETDocument7 paginiHyper FETScurdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Modern Field Effect Transistor Technologie1Document8 paginiReview of Modern Field Effect Transistor Technologie1G ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of A High-Frequency Planar PowerDocument7 paginiDesign of A High-Frequency Planar PowerJorge RestrepoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022-TED-Novel Step Field Plate RF LDMOS Transistor For Improved BV textDS - R textON Tradeoff and RF Performance PDFDocument7 pagini2022-TED-Novel Step Field Plate RF LDMOS Transistor For Improved BV textDS - R textON Tradeoff and RF Performance PDFXiaole JiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultra-Wideband Balun Using A Multiaperture Ferromagnetic CoreDocument4 paginiUltra-Wideband Balun Using A Multiaperture Ferromagnetic Corejax almarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFDocument21 paginiEI2301-IE - Unit 1 - Part A and Part B - With Answers PDFsartpgitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boost Inverter Topology With High-Frequency Link Transformer For PV Grid-Tied ApplicationsDocument8 paginiBoost Inverter Topology With High-Frequency Link Transformer For PV Grid-Tied ApplicationsBandiyah Sri AprilliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fully Integrated Doherty Power Amplifiers For 5 GHZ Wireless-LANsDocument4 paginiFully Integrated Doherty Power Amplifiers For 5 GHZ Wireless-LANsHam Radio HSMMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linearity and Speed Optimization in SOI LDMOS Using Gate EngineeringDocument22 paginiLinearity and Speed Optimization in SOI LDMOS Using Gate EngineeringMamidala Jagadesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Speed (MHZ) Series Resonant Converter (SRC)Document12 paginiHigh-Speed (MHZ) Series Resonant Converter (SRC)teomondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gan Transistors For Efficient Power ConversionDocument3 paginiGan Transistors For Efficient Power ConversionMikhail LavrentyevÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Isolated Series Resonant Converter For PV Application: Manalan108@gmailcomDocument4 paginiAn Isolated Series Resonant Converter For PV Application: Manalan108@gmailcomRaja SajinÎncă nu există evaluări
- A High Efficiency Broadband Class-E Power Amplifier Using A Reactance Compensation TechniqueDocument3 paginiA High Efficiency Broadband Class-E Power Amplifier Using A Reactance Compensation Techniquegagan9385Încă nu există evaluări
- Organic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyDe la EverandOrganic Light-Emitting Transistors: Towards the Next Generation Display TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Value Change Dump (VCD) : Switching Activity Interchange Format SaifDocument1 paginăValue Change Dump (VCD) : Switching Activity Interchange Format SaifShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Planning: Management and I/O Cell Power Management. in Former One VDD and VSS PowerDocument5 paginiPower Planning: Management and I/O Cell Power Management. in Former One VDD and VSS PowerShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- QW123Document7 paginiQW123Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Format of Area of Interest Submit by 14th Sep 2015Document1 paginăFormat of Area of Interest Submit by 14th Sep 2015Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Page 3 of About 8Document2 paginiPage 3 of About 8Shobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yfhb, NMNKNKNKJBJBJMDocument5 paginiYfhb, NMNKNKNKJBJBJMShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Setup and Hold TimeDocument6 paginiSetup and Hold TimeShobhit GargÎncă nu există evaluări