Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Ap - Cellular Energetics - Cell Respiration
Încărcat de
api-251015600Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Ap - Cellular Energetics - Cell Respiration
Încărcat de
api-251015600Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Chapters 9-10: Cellular
Energetics
I. Free Energy
FREE ENERGY (G) = the portion of an
organisms energy that can perform work when/if
homeostasis is maintained.
Homeostasis = the maintenance of steady internal
conditions of an organisms e.g., regulating body
temperature (humans = 98.6
o
F).
Organisms regulate body temperature and
metabolism one of two ways:
1. Endothermy = the use of internal thermal
energy generated by metabolism to maintain
homeostatic temperature (eating a meal will
warm your core temperature) inaccurately
known as warm-blooded.
2. Ectothermy = the use of external energy to
maintain homeostatic temperature (a snake
bathing in the morning sun to warm up)
inaccurately known as cold-blooded.
EXERGONIC reactions release free energy G
is negative and the reaction occurs spontaneously:
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O + 36 ATP
36 ATP = G of ~ -686 kcal/mol.
ENDERGONIC reactions absorbs free energy
G is positive and the reaction is NOT
spontaneous.
Life requires organisms to be HIGHLY ordered.
Order is maintained by constantly adding free energy to
an organism.
Increased DISORDER = entropy (what nature wants
to do).
Entropy or loss of free energy leads to DEATH.
Entropy is offset by biological processes
metabolism that maintain or increase order.
Increasing entropy = -G exergonic.
Decreasing entropy = +G endergonic.
Exergonic reactions MUST therefore, be coupled with
endergonic reactions in order to maintain or increase order
in an organism.
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O (exergonic)
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
(endergonic)
C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O
II. Energy Flow
Organisms capture and store free energy for use in
biological processes CELLULAR
RESPIRATION and PHOTOSYNTHESIS.
AUTOTROPHS capture free energy independently
(make their own food):
1. Photosynthetic organisms capture free energy
from sunlight.
2. Chemosynthetic organisms capture free energy
from inorganic compounds in the environment
in the presence OR ABSENCE of O
2
=
fermentation products include alcohol and lactic
acid.
HETEROTROPHS capture free energy present in
the carbon compounds produced by other
organisms (DO NOT make their own food)
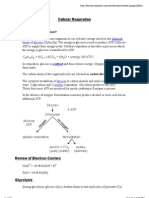
III. Cellular Respiration
The process of extracting stored energy from glucose.
ATP is made from ADP and P
i
.
Equation = C
6
H
12
O
6
+ 6O
2
6CO
2
+ 6H
2
O +36ATP.
Aerobic respiration = in the presence of O
2
.
Anaerobic respiration = without O
2
fermentation.
Occurs in the cytoplasm and MITOCHONDRIA.
Process is divided into three phases:
1. Glycolysis in cytoplasm.
2. Krebs Cycle in mitochondrial matrix.
3. Oxidative Phosphorylation (Electron
Transport Chain/E.T.C.) in mitochondrial
cristae membranes.
1. Glycolysis
Occurs in the CYTOPLASM not the mitochondria.
Converts glucose to PYRUVATE (pyruvic acid)
transported INTO the mitochondria.
In the process of making pyruvate:
2ATP are made from 2ADP and 2P
i
.
2NADH are made from NAD
+
and H acts as an
electron carrier taking the 2e
-
to the E.T.C. in order to
fuel the formation of additional ATP.
2. Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
Occurs in the MATRIX of the mitochondria.
Converts pyruvate into ACETYL CoA (in mitochondria)
transported into the matrix.
In the process of making acetyl CoA:
2CO
2
are made.
2NADH are made.
Converts acetyl CoA into CITRATE (citric acid).
In the process of making citrate:
4CO
2
are made.
6NADH are made.
2ATP are made.
2FADH
2
from FAD
+
and H acts as an electron carrier
taking the 2e
-
to the E.T.C. in order to fuel the
formation of additional ATP.
6 CO
2
The CO
2
produced by
the Krebs
Cycle is the
CO
2
that
animals
EXHALE
when they
breathe.
)
3. Oxidative Phosphorylation
Process of making ATP from ADP and P
i
=
phosphorylation fueled by the electrons carried in
NADH and FADH
2
.
Occurs in the CRISTAE membrane of the mitochondria.
e
-
are passed from NADH and FADH
2
down an electron
transport chain across the cristae membrane from carrier
protein to carrier protein, losing energy at each step in the
chain.
THE LAST e
-
ACCEPTOR IS O
2
H
2
O is made.
34ATP are made:
1NADH = 3ATP 10NADH enter = 30ATP.
1FADH
2
= 2ATP 2FADH
2
enter = 4ATP.
FADH
2
FAD
+
+ 2H
+
+ 2e
-
ADP + P
i
ADP + P
i
ADP + P
i
ADP + P
i
ADP + P
i
ATP
ATP
ATP
ATP
ATP
O
2
+ 2H
+
H
2
O
NADH NAD
+
+ H
+
+ 2e
-
4. Chemiosmotic Theory
Describes phosphorylation of ATP from ADP and P
i
as
NADH and FADH
2
pass electrons along the E.T.C.
1. Protons (H
+
) accumulate in the INTERMEMBRANE
SPACE: as the donated e
-
s from NADH and FADH
2
move
through the E.T.C., H
+
is pumped from the matrix into the
intermembrane space.
2. The accumulation of H
+
creates a PROTON/pH
GRADIENT ACROSS THE CRISTAE: [H+] in
intermembrane space > [H+] in matrix = a proton gradient
POTENTIAL ENERGY reserves.
3. H
+
flow back into the matrix via ATP SYNTHASE
generating atp from adp and p
i
: ATP synthase = a
channel protein in the cristae that allows H
+
in the
intermembrane space to flow back into the matrix
turbine creating energy to produce ATP from ADP and P
i
.
Total ATP produced during respiration = 38 ATP:
Glycolysis = 2ATP
Krebs Cycle = 2ATP
Oxidative Phosphorylation = 34 ATP
NET ATP produced = 36 ATP:
Glycolysis occurs in the CYTOPLASM
2NADH made in glycolysis MUST BE ACTIVELY
PUMPED into the mitochondria to get to the E.T.C.
Pumping the 2NADH into the mitochondria
requires 2ATP
38 ATP 2 ATP = 36 ATP (NET)
5. NET ATP Production from 1Glucose
IV. Anaerobic Respiration
Occurs when there is NO O
2
available.
No O
2
= no e- acceptor at the end of the E.T.C.
NADH accumulates NOT being recycled back into
NAD
+
.
Once all the NAD+ has been used, glycolysis and the Krebs
Cycle shut down no more ATP is produced the cell
dies.
Two similar processes are used to combat this problem,
both with the same objective replenish NAD
+
so at the
very least, glycolysis can proceed and SOME ATP (2) can
be made:
1. Alcohol Fermentation plants, fungi, and bacteria
products formed (ethanol and CO
2
) responsible for
alcoholic beverages and the carbonation in such drinks.
2. Lactic Acid Fermentation animals product formed
(lactic acid) responsible for muscle aches after working
out.
Alcohol (Ethanol) Fermentation
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ap - Gel Electrophoresis Post Lab QuestionsDocument1 paginăAp - Gel Electrophoresis Post Lab Questionsapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds GlucoseDocument10 paginiCellular Respiration: Chemical Bonds Glucosemegamega11Încă nu există evaluări
- 10 CH26 Nutrition and Metabolism 2 2015Document29 pagini10 CH26 Nutrition and Metabolism 2 2015AbdullionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument41 paginiCellular Respiration and PhotosynthesisCarissa MarchanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bioenergetics and MetabolismDocument30 paginiBioenergetics and MetabolismShimmering MoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2022 Metabolism and EnergyDocument35 pagini2022 Metabolism and EnergyClaire WeerepasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Peroxisome Metabolism 20760414Document56 pagini2nd Peroxisome Metabolism 20760414Rawbeena RamtelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-BioDocument17 paginiMitochondria and Its Pathways: Arvin G. Concha Mst-Biocassidy conchaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Chain & Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument57 paginiRespiratory Chain & Oxidative PhosphorylationHanifa AffianiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 - Introduction To MetabolismDocument37 paginiChapter 8 - Introduction To Metabolismprehealthhelp88% (8)
- Beta-Oxidation of Fatty AcidsDocument6 paginiBeta-Oxidation of Fatty AcidsBinku Dutta100% (1)
- Study Questions Biology 141 Cellular Respiration, Kreb CycleDocument3 paginiStudy Questions Biology 141 Cellular Respiration, Kreb CycleMeï QadriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body System ChecklistDocument6 paginiBody System Checklistapi-422967453Încă nu există evaluări
- 6.1 Types of NutritionDocument11 pagini6.1 Types of NutritionNoor Hidayah SambliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11. Metabolism of CarbohydrateDocument35 paginiChapter 11. Metabolism of CarbohydrateMohd RidzuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Respiration WebQuest 2015Document3 paginiCell Respiration WebQuest 2015Haley HaunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Instructor-RclDocument33 paginiGlycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Instructor-RclPrince Kyle R. DolosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aug 9 Sbi4u Quiz 4Document3 paginiAug 9 Sbi4u Quiz 4api-216300751Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 PDFDocument13 paginiChapter 5 PDFNicholas LeongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Affecting Enzyme ActionDocument18 paginiFactors Affecting Enzyme Actionanon_458882066Încă nu există evaluări
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument43 paginiCarbohydrate MetabolismMarliza CauntaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- U4 PhotosynthesisDocument14 paginiU4 PhotosynthesisjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atp Synthesis by Cellular Respiration AT P: Caroline SueperDocument9 paginiAtp Synthesis by Cellular Respiration AT P: Caroline SueperCaroline SueperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Immune Response DRPath Part 1Document71 paginiImmune Response DRPath Part 1SITI NUR FA'IZULBA'EDAH BINTI MAT RAZIÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOL 307 Biochemistr Y: by Çağdaş D. SonDocument101 paginiBIOL 307 Biochemistr Y: by Çağdaş D. SonMetehan KaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestion and Absorption of LipidsDocument5 paginiDigestion and Absorption of LipidsAngelo Jude Cobacha100% (1)
- Photosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureDocument11 paginiPhotosynthesis: Leaves and Leaf StructureMatthew BetinolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kreb CycleDocument6 paginiKreb Cycle211BT014 Jeev Sheen JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bioenergetics and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument32 paginiBioenergetics and Oxidative PhosphorylationShimmering MoonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amino Acids Metabol Synth of UreaDocument32 paginiAmino Acids Metabol Synth of UreaAnastasiafynn100% (1)
- PROTEINSDocument17 paginiPROTEINSAbhijat Jha100% (1)
- Enzymes and Their Importance in Plants and AnimalsDocument4 paginiEnzymes and Their Importance in Plants and Animalsanili50% (2)
- Isoenzymes Multienzyme ComplexDocument20 paginiIsoenzymes Multienzyme ComplexAnisam Abhi100% (2)
- MYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerDocument4 paginiMYP Exercises. Cell Respiration.: AnswerRishar bokÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Summary NotesDocument42 paginiBiology Summary Notesjessica_choy_4Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 45Document9 paginiCH 45homamunfatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 LipidsDocument44 pagini3 LipidsSuresh ChovatiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GlycolysisDocument21 paginiGlycolysisAli AlqumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cellular RespirationDocument29 paginiCellular RespirationDominic MaderaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 paginiIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB Style Test - Topic 8 HL Metabolism, Respiration and PhotosynthesisDocument8 paginiIB Style Test - Topic 8 HL Metabolism, Respiration and Photosynthesisika100% (1)
- Body Fluids Hbc202-Lecture Notes-1Document9 paginiBody Fluids Hbc202-Lecture Notes-1Shreya AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- High School Science Virtual Learning: Biology Homeostasi SDocument20 paginiHigh School Science Virtual Learning: Biology Homeostasi SEdchel EspeñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Anatomy and Physiology II: Biology 1414 Unit 8 Metabolism and NutritionDocument103 paginiHuman Anatomy and Physiology II: Biology 1414 Unit 8 Metabolism and Nutritionciroj25Încă nu există evaluări
- Lipid Absorption and Transport UptakeDocument218 paginiLipid Absorption and Transport UptakeSimra Zahid100% (1)
- Biology NotesDocument6 paginiBiology NotesElizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PROTEIN METABOLISM Dea Farha Fira Darson FineDocument44 paginiPROTEIN METABOLISM Dea Farha Fira Darson FineFarhati MardhiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Cells Harvest EnergyDocument26 paginiHow Cells Harvest EnergyMarita YaghiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glycogen MetabolismDocument34 paginiGlycogen MetabolismJomi PorinchuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Biology Chapter 8 Reading GuideDocument7 paginiAP Biology Chapter 8 Reading GuideVal HathiramaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Basics of EnzymesDocument40 paginiChapter 2 - Basics of EnzymesSakinah MuhamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Micro Endocrine OrgansDocument8 paginiMicro Endocrine OrgansMonica100% (1)
- SBI4U0: Examination and Course Review: Unit 1: BiochemistryDocument6 paginiSBI4U0: Examination and Course Review: Unit 1: BiochemistrySukhvir AujlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Cells Harvest Chemical Energy - Cellular RespirationDocument25 paginiHow Cells Harvest Chemical Energy - Cellular RespirationMohamad Saadatian SipanÎncă nu există evaluări
- scsc7211's Version of Alan's DAT Biology NotesDocument47 paginiscsc7211's Version of Alan's DAT Biology NotesMusawir YasinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Project: Saturated Solutions: Measuring SolubilityDocument8 paginiChemistry Project: Saturated Solutions: Measuring SolubilityAbhay Kumar NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Citric Acid CycleDocument43 paginiThe Citric Acid CycleMohammed AlMujainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ap - Diffusion Osmosis Lab Report RubricDocument1 paginăAp - Diffusion Osmosis Lab Report Rubricapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap - Blast Lab RevisedDocument1 paginăAp - Blast Lab Revisedapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap - Gel Electrophoresis Virtual Lab ModifiedDocument1 paginăAp - Gel Electrophoresis Virtual Lab Modifiedapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap - Enzyme LabDocument1 paginăAp - Enzyme Labapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap PollutionprojectDocument1 paginăAp Pollutionprojectapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- SPP ExpectationsagreementDocument4 paginiSPP Expectationsagreementapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap ErinbrockovichDocument3 paginiAp Erinbrockovichapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap - Unit 01 Chemistry of Life Study GuideDocument2 paginiAp - Unit 01 Chemistry of Life Study Guideapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap - Cell Division - MeiosisDocument24 paginiAp - Cell Division - Meiosisapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- Ap - Chemistry of LifeDocument58 paginiAp - Chemistry of Lifeapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- SPP - Hotel RwandaDocument1 paginăSPP - Hotel Rwandaapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- SPP FinalexamDocument1 paginăSPP Finalexamapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- SPP - Weebly Term ProjectDocument2 paginiSPP - Weebly Term Projectapi-251015600Încă nu există evaluări
- The Stony Brook Press - Volume 11, Issue 4Document28 paginiThe Stony Brook Press - Volume 11, Issue 4The Stony Brook PressÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Evolution SE Skull Analysis GizmoDocument9 paginiHuman Evolution SE Skull Analysis GizmoTamia WashingtonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamental Unit of Life 1-25Document25 paginiFundamental Unit of Life 1-25Anisha PanditÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicina 57 00032 (01 14)Document14 paginiMedicina 57 00032 (01 14)fauzan nandana yoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Articulo de Las 3 Tesis Por BrowDocument30 paginiArticulo de Las 3 Tesis Por BrowJHIMI DEIVIS QUISPE ROQUEÎncă nu există evaluări
- JIDMR SCOPUS Ke 4 Anwar MallongiDocument4 paginiJIDMR SCOPUS Ke 4 Anwar Mallongiadhe yuniarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive ROMDocument3 paginiPassive ROMCzarina FayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Access Control Quiz3 PDFDocument2 paginiNetwork Access Control Quiz3 PDFDaljeet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- 006R5-WMS-JI-MI-MAU-ACS-II-23 Working Method - Pile CapDocument20 pagini006R5-WMS-JI-MI-MAU-ACS-II-23 Working Method - Pile CapEko Budi HartantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Msla Business FeesDocument1 paginăMsla Business FeesNBC MontanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODEL 1332 MODEL 1432: Slide LengthDocument8 paginiMODEL 1332 MODEL 1432: Slide LengthFabian FragosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meyer-Andersen - Buddhism and Death Brain Centered CriteriaDocument25 paginiMeyer-Andersen - Buddhism and Death Brain Centered Criteriautube forÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stas Final ReviewerDocument8 paginiStas Final ReviewerShane SaynoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evolution Practice Test 2 With AnswersDocument10 paginiEvolution Practice Test 2 With AnswersSuhani SinhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Io (Jupiter Moon)Document2 paginiIo (Jupiter Moon)FatimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Quantity Estimation PDFDocument3 paginiWater Quantity Estimation PDFOladunni AfolabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hijama Cupping A Review of The EvidenceDocument5 paginiHijama Cupping A Review of The EvidenceDharma Yoga Ayurveda MassageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dyestone Blue MX SDS SA-0186-01Document5 paginiDyestone Blue MX SDS SA-0186-01gede aris prayoga mahardikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac PacemakerDocument25 paginiCardiac PacemakerDhvij KmlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Public Health Interventions: Applications For Public Health Nursing PracticeDocument249 paginiPublic Health Interventions: Applications For Public Health Nursing PracticeJemimah AdaclogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kerala Medico Legal Code - Annexure2Document19 paginiKerala Medico Legal Code - Annexure2doctor82Încă nu există evaluări
- Barangay Clearance SampleDocument1 paginăBarangay Clearance SampleBarangay Onse Malaybalay100% (3)
- Lab Safety RulesDocument2 paginiLab Safety RulesChristine ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Textile Reinforced - Cold Splice - Final 14 MRCH 2018Document25 paginiTextile Reinforced - Cold Splice - Final 14 MRCH 2018Shariq KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dolor Postoperatorio y Efectos Secundarios de La Uvulo Palstia Con Radiofrecuencia en Roncopatia Primaria.Document5 paginiDolor Postoperatorio y Efectos Secundarios de La Uvulo Palstia Con Radiofrecuencia en Roncopatia Primaria.Alejandro RuizÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6 Adjective ClauseDocument16 pagini6 Adjective ClauseMaharRkpÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5219-PRP Support Tool CounsellingDocument10 pagini5219-PRP Support Tool CounsellingRodhi AnshariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schengen Certificate ExampleDocument2 paginiSchengen Certificate ExampleGabriel Republi CanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- GLYSANTIN+G48+bg+IN 000000000030667689 SDS GEN US en 8-1Document11 paginiGLYSANTIN+G48+bg+IN 000000000030667689 SDS GEN US en 8-1Ali RidloÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEM F313: Instrumental Methods of Analysis: Flame Photometry & Atomic Absorption SpectrosDocument26 paginiCHEM F313: Instrumental Methods of Analysis: Flame Photometry & Atomic Absorption SpectrosHARSHVARDHAN KHATRIÎncă nu există evaluări