Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pediatric Dermatology MCQs
Încărcat de
Dr.TawheedDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pediatric Dermatology MCQs
Încărcat de
Dr.TawheedDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
1
Which treatment choice would be contraindicated in a one-year old child who presents with
monomorphous, nonpruritic flat-topped papules on the face, buttocks, extremities, palms and soles?
1
Advil
2
Acetaminophen
3
Hydration
4
Corticosteroids
5
Observation
Q/Q(M)-476495 Report a Problem
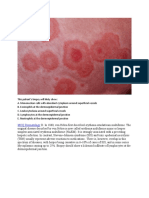
Which treatment choice would be contraindicated in a one-year old child who presents with
monomorphous, nonpruritic flat-topped papules on the face, buttocks, extremities, palms and soles?
4
Corticosteroids
Gianotti-Crosti or papular acrodermatitis of childhood is associated with a variety of viral infections.
Patients have a typical cutaneous manifestation, low-grade fever, mild lymphadenopathy and diarrhea.
Corticosteroids should be avoided as they may have an adverse effect.
Q/Q(M)-476495 Report a Problem
Most common malignancy associated with multiple lesions similar to the attached image is:
1
Acute myelogenous leukemia
2
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
3
Acute lymphocytic leukemia
4
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
5
Melanoma
Q/Q(M)-481905 Report a Problem
Most common malignancy associated with multiple lesions similar to the attached image is:
2
Chronic myelogenous leukemia
The image shown is juvenile xanthogranuloma. The most commonly associated malignancy is chronic
myelogenous leukemia. Other associations include Neurofibromatosis type 1 and aquagenic pruritus.
Reference: Zvulunov A, Barak Y, Metzker A. Juvenile xanthogranuloma, neurofibromatosis, and juvenile
chronic myelogenous leukemia. World statistical analysis. Arch Dermatol 1995;131:904-908.
Q/Q(M)-481905 Report a Problem
A newborn has a nodule over his lumbar spine. Skin biopsy reveals a lipoma. The next appropriate step is:
1
Observation
2
2
Excision of the lesion
3
Genetic testing
4
Imaging study
5
Malignancy work up
Q/Q(M)-476957 Report a Problem
A newborn has a nodule over his lumbar spine. Skin biopsy reveals a lipoma. The next appropriate step is:
4
Imaging study
The skin can provide an important clue to the presence of an underlying neural tube defect, such as
meningomyelocele and encephalocele. Cutaneous lesions along the midline of the spine should always
prompt consideration of this possibility. Although, midline neural tube defects are uncommon, early
recognition and diagnosis of a spinal dysraphism can have important implications for early surgical
correction and minimizing loss of neurologic function. Clues to the diagnosis include a midline dimple, tuft
of hair, lipoma, or vascular lesion. In these instances, imaging studies (MRI, CT, ultrasound) should be
promptly initiated.
Q/Q(M)-476957 Report a Problem
A patient presents with multiple juvenile xanthogranulomas, axillary freckling, multiple caf-au-lait
macules, three neurofibromas and a family history of NF-1. What other condition is this patient at
increased risk for?
1
AML
2
CML
3
CLL
4
Medulloblastoma
5
Pancreatic carcinoma
Q/Q(M)-480185 Report a Problem
A patient presents with multiple juvenile xanthogranulomas, axillary freckling, multiple caf-au-lait
macules, three neurofibromas and a family history of NF-1. What other condition is this patient at
increased risk for?
2
CML
A patient with Neurofibromatosis type I and JXGs present is at increased risk for CML.
Medulloblastomas are increased in patients with Basal Cell Nevus syndrome. Pancreatic carcinoma occurs
at an increased risk in patients with mutations in CDKN2A in the familial melanoma syndrome.
Q/Q(M)-480185 Report a Problem
Schimmelpenning-Feuerstein-Mims syndrome may be associated with which of the following:
1
Osteopokilosis
2
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
3
Osteopathia striata
4
Chondrodysplasia punctata
5
Hypophosphatemic rickets
Q/Q(M)-476261 Report a Problem
3
Schimmelpenning-Feuerstein-Mims syndrome may be associated with which of the following:
5
Hypophosphatemic rickets
Epidermal nevus syndrome, also known as Schimmelpenning-Feuerstein-Mims syndrome, may be
associated with hypophospatemic, vitamin D resistant rickets.
Q/Q(M)-476261 Report a Problem
The differential diagnosis of zinc deficiency is least likely to include:
1
Granuloma gluteale infantum
2
Biotin deficiency
3
Multiple carboxylase deficiency
4
Cystic fibrosis
5
Holocarboxylase synthetase deficiency
Q/Q(M)-473684 Report a Problem
The differential diagnosis of zinc deficiency is least likely to include:
1
Granuloma gluteale infantum
All of the options result in an eczematous acrodermatitis enteropathica-like eruption except granuloma
gluteale infantum. As the name suggests, the lesions of granuloma gluteale infantum are granulomatous.
Q/Q(M)-473684 Report a Problem
Multiple cylindromas are associated with:
1
Myotonic dystrophy
2
Cowden syndrome
3
Carney complex
4
Trichoepitheliomas
5
Pilomatrichomas
Q/Q(M)-473703 Report a Problem
Multiple cylindromas are associated with:
4
Trichoepitheliomas
The Brooke-Spigler syndrome is defined by the presence of multiple trichoepitheliomas and cylindromas.
Q/Q(M)-473703 Report a Problem
A full term neonate is noted to have small pustules with no underlying erythema present at delivery. The
pustules are easily removed with clearing of the vernix and a collarette appears. A gram stain is done
showing predominately neutrophils without bacteria. What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Miliaria
2
Erythema toxicum neonatorum
3
Transient neonatal pustular melanosis
4
Congenital candidiasis
5
Urticaria pigmentosa
4
Q/Q(M)-473678 Report a Problem
A full term neonate is noted to have small pustules with no underlying erythema present at delivery. The
pustules are easily removed with clearing of the vernix and a collarette appears. A gram stain is done
showing predominately neutrophils without bacteria. What is the most likely diagnosis?
3
Transient neonatal pustular melanosis
Transient neonatal pustular melanosis typically begins with sterile pustules that leave a characteristic
collarette when ruptured. The lesions heal with hyperpigmented macules.
Q/Q(M)-473678 Report a Problem
Which of the following may be associated?
1
Paronychia
2
Cleft palate
3
AVM
4
Seizure disorder
5
Atrial septal defect
Q/Q(M)-474924 Report a Problem
Which of the following may be associated?
4
Seizure disorder
Nevus sebaceus can very rarely be associated with multiple anomalies. Schimmelpenning syndrome can
include seizure disorder, mental retardation, coloboma, as well as skeletal, cardiac and genitourinary
abnormalities.
Q/Q(M)-474924 Report a Problem
What syndrome can accessory tragi be associated with?
1
Goldenhar syndrome
2
Turner syndrome
3
Neurofibromatosis
4
Ichthyosis
5
Birt Hogg Dube
Q/Q(M)-482064 Report a Problem
5
What syndrome can accessory tragi be associated with?
1
Goldenhar syndrome
Accessory tragus is the most common congenital defect of the external ear and linked to maldevelopment
of the first branchial arch. It can be associated with several syndromes including Goldenhar syndrome, in
which epibulbar dermoid and vertebral defects are also common. An accessory tragus usually it appears as
a small skin-colored tag or nodule arising near the tragus; it is composed of normal epidermis with dermal
adipose tissue, pilosebaceous units, eccrine glands, elastic fibers, and cartilage.
Q/Q(M)-482064 Report a Problem
Which of the following is a potential complication of subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn?
1
Cholestrol clefts in fat cells
2
Hypercalcemia
3
Acute renal failure
4
Hepatitis
5
Elevated uric acid levels
Q/Q(M)-475869 Report a Problem
Which of the following is a potential complication of subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn?
2
Hypercalcemia
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is a rare condition characterized by firm, reddish or purple
nodules which appear on the arms, thighs, buttocks, back and cheeks. This condition is believed to result
from cold injury. Crystallization occurs within the lipocytes, and this can be seen on histopathology with an
associated granulomatous reaction. This is thought to occur due to the higher melting point of neonatal fat,
which contains more saturated fatty acids. Onset of this condition occurs within the first two weeks of life
and usually resolved over a period of weeks to months. Occasionally, lesions heal with atrophy.
Hypercalcemia is an infrequent complication of subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn. Associated
symptoms can include irritability, weight loss, vomiting and failure to thrive. Repeated serum calcium tests
are advised until one month after all the cutaneous lesions have resolved.
Q/Q(M)-475869 Report a Problem
6
What is the most likely diagnosis is this 16 year old patient who developed generalized eruption 2 weeks
after onset of sore throat due to strep infection?
1
Psoriasis
2
Pityriasis rosea
3
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
4
Contact dermatitis
5
Lichen planus
Q/Q(M)-476801 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis is this 16 year old patient who developed generalized eruption 2 weeks
after onset of sore throat due to strep infection?
1
Psoriasis
Although the exact mechanism is not known, there is a well-known correlation between a history of upper
respiratory infection secondary to group A beta-hemolytic streptococci and the subsequent development of
guttate psoriasis. The eruption may resolve spontaneously or with treatment (topical steroids or ultraviolet
therapy). Some portion of these patients eventually develop chronic, plaque-type psoriasis.
Q/Q(M)-476801 Report a Problem
What systemic abnormalities are associated with neonatal lupus?
1
Thrombocytopenia, transaminitis
2
Thrombocythemia, transaminitis
3
Anemia, hypocomplementemia
4
Thrombocytopenia, hypocomplementemia
5
Transaminitis, hypocomplementemia
Q/Q(M)-482854 Report a Problem
What systemic abnormalities are associated with neonatal lupus?
1
Thrombocytopenia, transaminitis
Thrombocytopenia and transaminitis are associated with neonatal lupus and may indicate a worse
prognosis.
7
Q/Q(M)-482854 Report a Problem
What is the best therapeutic option?
1
Oral cephalexin
2
Topical immune modulator
3
Oral acyclovir
4
Topical mupirocin
5
Oral prednisone
Q/Q(M)-474923 Report a Problem
What is the best therapeutic option?
3
Oral acyclovir
The condition shown is eczema herpeticum. The most appropriate treatment is oral acyclovir.
Q/Q(M)-474923 Report a Problem
A full term newborn develops erythematous, indurated plaques on the upper back. Which of the following
tests should be performed?
1
Calcium
2
Complete blood count
3
Blood culture
4
Thyroid function test
5
Alkaline phosphatase
Q/Q(M)-473674 Report a Problem
A full term newborn develops erythematous, indurated plaques on the upper back. Which of the following
tests should be performed?
1
Calcium
The most likely diagnosis is subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn. Hypercalcemia may result and
serum calcium levels should be monitored up to 4 weeks after resolution of the skin.
Q/Q(M)-473674 Report a Problem
The causative agent of Roseola is:
1
A ssDNA virus
8
2
A dsDNA virus
3
A ssRNA virus
4
A dsRNA virus
5
Streptococcus
Q/Q(M)-473695 Report a Problem
The causative agent of Roseola is:
2
A dsDNA virus
Roseola is caused by Human Herpesvirus 6, a double stranded DNA virus.
Q/Q(M)-473695 Report a Problem
GLUT-1 stains placental tissue. What other tissue shows positive GLUT-1 staining?
1
capillary vascular malformation
2
salmon patch
3
glomus tumor
4
infantile hemangioma
5
angel's kiss
Q/Q(M)-482561 Report a Problem
GLUT-1 stains placental tissue. What other tissue shows positive GLUT-1 staining?
4
infantile hemangioma
The correct answer is infantile hemangioma, which reliably displays GLUT-1 positivity. GLUT-1 stains
infantile hemangioma with high sensitivity and specificity. Glomus tumor, capillary vascular malformation
(also called port-wine stain), salmon patch, and angel's kiss are other vascular lesions that do not stain with
GLUT-1.
Q/Q(M)-482561 Report a Problem
Which of the following is not true about Gianotti-Crosti?
1
It is associated with viral infections like enterocirus, EBV, and CMV
2
It typically affects children between the age of 3 months and 15 years
3
It is characterized by monomorphic symmetric flat topped papules in acral areas
4
It may have associated fevers, lymphadenopathy, and diarrhea
5
Corticosteroids should be given to alleviate the pruritus of the lesions
Q/Q(M)-482241 Report a Problem
Which of the following is not true about Gianotti-Crosti?
5
Corticosteroids should be given to alleviate the pruritus of the lesions
Gianotti-Crosti, or papular acrodermatitis of childhood, is typically nonpruritic and corticosteroids should
be avoided as they may have adverse effect. All the other statements are true. The condition typically
resolves after 2-3 weeks.
Q/Q(M)-482241 Report a Problem
9
Which of the following clinical signs is most likely associated?
1
Clitoral hypertrophy
2
Neurofibromas
3
Axillary freckling
4
Hypertrichosis
5
Alopecia
Q/Q(M)-476798 Report a Problem
Which of the following clinical signs is most likely associated?
1
Clitoral hypertrophy
The coast of Maine caf au lait macule is associated with McCune-Albright syndrome. Endocrine
abnormalities, including precocious puberty and polyostotic fibrous dysplasia are associated features. The
genetic mutation which results in this genodermatosis is due to a post-somatic mutaion in the alpha sub-
unit of stimulatory G-protein.
Q/Q(M)-476798 Report a Problem
The most likely etiology of Jacquets diaper dermatitis is:
1
Candida
2
Trichophyton rubrum
3
Group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus
4
Herpes simplex virus, Type 2
5
Multifactorial
Q/Q(M)-473682 Report a Problem
The most likely etiology of Jacquets diaper dermatitis is:
5
Multifactorial
Jacquets diaper dermatitis is a multifactorial process. Yeast, irritants and moisture all contribute to the
occurrence of this eruption.
Q/Q(M)-473682 Report a Problem
A newborn presents with a well-defined, shiny patch with complete alopecia on the vertex of the scalp
along the suture lines. Which of the following is the first step in diagnosis?
10
1
MRI
2
Calcium
3
Skin biopsy
4
Skull x-ray
5
Fungal culture
Q/Q(M)-473675 Report a Problem
A newborn presents with a well-defined, shiny patch with complete alopecia on the vertex of the scalp
along the suture lines. Which of the following is the first step in diagnosis?
4
Skull x-ray
The newborn most likely has aplasia cutis congenita. A skull x-ray would be the simplest, most cost
effective means of identifying any underlying bony abnormality.
Q/Q(M)-473675 Report a Problem
A child presents with high fever, strawberry tongue, lymphadenopathy, and a polymorphous exanthem.
Approximately how many of these patients will have coronary artery aneurysms if left untreated?
1
Two percent
2
Five percent
3
Ten percent
4
Twenty-five percent
5
Sixty percent
Q/Q(M)-482264 Report a Problem
A child presents with high fever, strawberry tongue, lymphadenopathy, and a polymorphous exanthem.
Approximately how many of these patients will have coronary artery aneurysms if left untreated?
4
Twenty-five percent
This child has Kawasaki's disease, or mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome. Other features include
conjunctival injection and extremity erythema and edema. Twenty-five percent of untreated patients go on
to develop coronary artery aneurysms. Treatment is with IVIG and aspirin.
Q/Q(M)-482264 Report a Problem
A 10 year old girl presents with desquamation of the fingertips. Which exam should be ordered?
1
Renal ultrasound
2
ASO titer
3
EEG
4
Eye exam
5
Chest x-ray
Q/Q(M)-482471 Report a Problem
A 10 year old girl presents with desquamation of the fingertips. Which exam should be ordered?
11
2
ASO titer
Desquamation of the fingertips is commonly associated with infections with group A beta-hemolytic Strep
and Staph aureus, including scarlet fever, perianal Strep, Staph scalded skin syndrome, and toxic shock
syndrome. Thus ASO titer would be indicated in this case. Fingertip desquamation is also a manifestation
of Kawasaki disease.
Q/Q(M)-482471 Report a Problem
Which of the following is not a major criterion for Kawasakis disease:
1
Fever >5 days
2
Palmoplantar erythema > desquamation
3
Cardiac aneurysm
4
Strawberry tongue/ red lips
5
Cervical adenopathy
Q/Q(M)-473697 Report a Problem
Which of the following is not a major criterion for Kawasakis disease:
3
Cardiac aneurysm
Cardiac aneurysm is a serious complication of Kawasakis disease. However, as the cardiovascular
manifestations generally present 1 5 months after presentation, they are not criteria for diagnosis.
Q/Q(M)-473697 Report a Problem
The most common age group for papular-purpuric gloves and socks syndrome is:
1
Newborns
2
Toddlers
3
6-10 year olds
4
Adolescents
5
Elderly
Q/Q(M)-473696 Report a Problem
The most common age group for papular-purpuric gloves and socks syndrome is:
4
Adolescents
This unique presentation of parvovirus infection typically occurs in adolescents and young adults.
Q/Q(M)-473696 Report a Problem
What is the most common tumor associated with this condition?
1
Trichoblastoma
2
Syringocystadenoma papilliferum
3
Sebaceous carcinoma
4
Basal cell carcinoma
5
Trichoadenoma
12
Q/Q(M)-476259 Report a Problem
What is the most common tumor associated with this condition?
1
Trichoblastoma
Recent reviews have identified trichoblastoma as the most common tumor arising within nevus sebaceous.
Q/Q(M)-476259 Report a Problem
An infant presents with yellowish-brown, crusted papules with petechiae in a seborrheic distribution.
Which of the following statements about this entity is likely to be true?
1
This presentation is consistent with Jacquet's dermatitis
2
CD1+, S100+ cells with comma-shaped nuclei should be seen on biopsy
3
This presentation occurs when the infant is weaned off of breast milk
4
An autosomal recessive defect in holocarboxylase synthetase is the cause
5
Maternal-fetal transmission most likely occured in the peripartum period
Q/Q(M)-477791 Report a Problem
An infant presents with yellowish-brown, crusted papules with petechiae in a seborrheic distribution.
Which of the following statements about this entity is likely to be true?
2
CD1+, S100+ cells with comma-shaped nuclei should be seen on biopsy
This infant has Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (Letterer-Siwe disease). Multisystem involvement may be
present. Jacquet's Erosive Dermatitis presents with severe erosive papules in the diaper region, and is
multifactorial in etiology (yeast, irritant dermatitis, moisture). Acrodermatitis enteropathica (zinc
deficiency) presents with brown, orange crusted plaques with vesicles and bullae, especially in perineal and
perioral areas and distal extremities. The inherited form occurs when the infant is weaned off of breast
milk. Biotin deficiency presents similarly; the neonatal form is attributed to an AR defect in
holocarboxylase synthetase.
Q/Q(M)-477791 Report a Problem
An infant presents with the lesion depicted in the photo. What information do you provide the parents
regarding this condition?
1
The lesion will go through rapid growth followed by stabilization and regression
13
2
The lesion will respond to laser therapy
3
The lesion will persist and may grow further
4
The lesion will resolve with antifungal therapy
5
The lesion is associated with a XO karyotype
Q/Q(M)-474920 Report a Problem
An infant presents with the lesion depicted in the photo. What information do you provide the parents
regarding this condition?
3
The lesion will persist and may grow further
The lesion represented in the photo is an arteriovenous vascular malformation. These lesions do not
typically regress.
Q/Q(M)-474920 Report a Problem
Which finding is associated with Pachydermoperiostosis:
1
Cutis verticis gyrata
2
Palmoplantar hyperkeratosis
3
Mucosal keratoses
4
Osteopathia striata
5
Cutis marmorata
Q/Q(M)-476266 Report a Problem
Which finding is associated with Pachydermoperiostosis:
1
Cutis verticis gyrata
The scalp change seen in pachydermoperiostosis is cutis verticis gyrata.
Q/Q(M)-476266 Report a Problem
Which presentation of psoriasis is more common in children:
1
Pustular psoriasis
2
Acrodermatitis continua of Hallopeau
3
Keratoderma blennorragica
4
Erythrodermic psoriasis
5
Guttate psoriasis
Q/Q(M)-476267 Report a Problem
14
Which presentation of psoriasis is more common in children:
5
Guttate psoriasis
The majority of cases of guttate psoriasis occur in persons under the age of 30.
Q/Q(M)-476267 Report a Problem
What deficiency is responsible for this condition?
1
Thiamine
2
Niacin
3
Zinc
4
Vitamin C
5
Vitamin A
Q/Q(M)-476670 Report a Problem
What deficiency is responsible for this condition?
3
Zinc
Acrodermatitis enteropathica is a rare inherited disorder transmitted in an autosomal recessive fashion. The
disorder is caused by an inability to absorb zinc. the clinical syndrome is characterized by acral dermatitis,
alopecia, and diarrhea. Zinc deficiency from other causes (including chronic wasting, poor oral intake, lack
of supplementation in total parenteral nutrition) can cause similar clinical changes.
Q/Q(M)-476670 Report a Problem
All four subtypes of Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis have which feature in common:
1
Nevus spilus
2
Epidermal nevi
3
Nevus flammeus
4
Nevus anemicus
5
Dermal Melanocytosis.
Q/Q(M)-478707 Report a Problem
All four subtypes of Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis have which feature in common:
3
Nevus flammeus
Phakomatosis Pigmentovascularis: Patients with a combination of vascular malformations and melanocytic
or epidermal nevi are grouped into 4 subtypes of this disorder. All have nevus flammeus/capillary
malformation (CM). Type I: CM + epidermal nevus Type II: CM + dermal melanocytosis +/- nevus
anemicus Type III: CM + nevus spilus +/- nevus anemicus Type IV: CM + dermal melanocytosis + nevus
spilus +/- nevus anemicus.
Q/Q(M)-478707 Report a Problem
15
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Psoriasis
2
Pityriasis rosea
3
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
4
Contact dermatitis
5
Lichen planus
Q/Q(M)-476441 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
4
Contact dermatitis
This periumbilical eruption is classic for a contact nickel allergy. The metal snaps on pants are the cause in
this case.
Q/Q(M)-476441 Report a Problem
Which of the following is the most common long term sequelae from congenital rubella syndrome?
1
Macrocephaly
2
Saber shins
3
Deafness
4
Nystagmus
5
Microcephaly
Q/Q(M)-473687 Report a Problem
Which of the following is the most common long term sequelae from congenital rubella syndrome?
3
Deafness
Deafness may occur in up to 50% of infants with congenital rubella syndrome.
Q/Q(M)-473687 Report a Problem
Which of the following is a ssDNA virus:
1
Herpesvirus
2
Parvovirus
3
Picornovirus
16
4
Adenovirus
5
Parapox
Q/Q(M)-473688 Report a Problem
Which of the following is a ssDNA virus:
2
Parvovirus
Parvovirus is the only ssDNA virus listed.
Q/Q(M)-473688 Report a Problem
A newborn infant presents with ring of long, dark, coarse hair surrounding a midline scalp patch of
alopecia. What is associated with this finding?
1
Alopecia areata
2
Ectopic brain tissue
3
Thyroid disease
4
Nevus sebaceus of Jadassohn
5
Deafness
Q/Q(M)-476777 Report a Problem
A newborn infant presents with ring of long, dark, coarse hair surrounding a midline scalp patch of
alopecia. What is associated with this finding?
2
Ectopic brain tissue
The "hair collar sign" is associated with ectopic brain tissue and is thought to arise from a congenital
herniation through the skull. Caution must be used in evaluation as biopsy or needle aspiration may lead to
retrograde infection.
Q/Q(M)-476777 Report a Problem
The association of Port-wine stains on a limb with soft tissue swelling with or without bony over growth is:
1
Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome
2
Goldenhar's syndrome
3
Sturge-Weber syndrome
4
Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome
5
Proteous syndrome
Q/Q(M)-478735 Report a Problem
The association of Port-wine stains on a limb with soft tissue swelling with or without bony over growth is:
4
Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome
The association of port-wine stain on a limb with soft tissue swelling with or without bony overgrowth is
Klippel-Trenuanay syndrome. Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome is characterized by the Triad of port-wine
malformations in association with deep venous system malformations, superficial varicosities, and bony
and soft tissue hypertrophy. Sturge-Weber syndrome has 2 essential components: Facial port-wine stain
and homolateral leptomeningeal angiiomattosis. The port wine stain most commonly involves the areas
innervated by the ophthalmic(V1) and maxillary (V2) divisions of the trigeminal nerve. Complications of
leptomeningeal angiomatosis are epilepsy, mental retardation, and occasionally, contralateral hemiplegia.
Proteus Syndrome is characterized by vascular malformations including nevus flammeus,
17
hemihypertrophy, macrodactyly, verrucous epidermal nevus, soft-tissue subcutaneous masses, and
cerebriform overgrowth of the plantar surface. Bannayan Riley Ruvalcaba syndrome may include multiple
cutaneous and visceral venous, capillary, and lympathtic malformations, macroephaly, pseudopapilledema,
systemic lipoangiomatosis, spotted pigmentation of the penis, hamartomatous intestinal polyps, and rarely
trichilemmonmas. (multiple subcutaneous lipomas as well as acanthosis nigricans).
Q/Q(M)-478735 Report a Problem
What is the most common cause of neonatal purpura fulminans?
1
Strep
2
Staph
3
Varicella
4
Protein C deficiency
5
Factor V Leiden deficiency
Q/Q(M)-482247 Report a Problem
What is the most common cause of neonatal purpura fulminans?
4
Protein C deficiency
In children, purpura fulminans may have several causes. It is a highly characteristic feature of
meningococcal septicemia and may occur as a sequel to a number of infections, including streptococcal
infections, varicella, and measles. In the neonate, however, its occurrence is highly suggestive of
homozygous protein C deficiency.
Q/Q(M)-482247 Report a Problem
Pachyonychia congenita type 2 is most commonly associated with which of the following:
1
Increased risk of malignancy
2
Poikiloderma
3
Natal teeth
4
Aplastic nails
5
Deafness
Q/Q(M)-476264 Report a Problem
Pachyonychia congenita type 2 is most commonly associated with which of the following:
3
Natal teeth
Pachyonychia congenita type 2 may be associated with natal teeth and steatocystoma. Pachyonychia
congenita type 1 is associated with benign leukoplakia.
Q/Q(M)-476264 Report a Problem
In a child with zinc deficiency, yet normal or near normal zinc levels, which test could be a valuable
adjunctive test?
1
Magnesium
2
Niacin
3
Manganese
4
Alkaline phosphatase
18
5
Iron
Q/Q(M)-477753 Report a Problem
In a child with zinc deficiency, yet normal or near normal zinc levels, which test could be a valuable
adjunctive test?
4
Alkaline phosphatase
The diagnosis of zinc deficiency should be consideredi in at-risk individuals with acral or periorificial
dermatitis. Chronic diaper dermatitis in an infant should lead to the evaluation for zinc deficiency. A low
serum zinc level can usually confirm the diagnosis. If normal or near normal a low serum alkaline
phosphatase, a zinc-dependent enzyme, may be a valuable adjunctive test.
Q/Q(M)-477753 Report a Problem
Menkes kinky hair syndrome is associated most commonly with:
1
Trichorrhexsis invaginata
2
Trichostasis spinulosa
3
Pili multigemini
4
Pili torti
5
Plica neuropathica
Q/Q(M)-473701 Report a Problem
Menkes kinky hair syndrome is associated most commonly with:
4
Pili torti
The X-linked recessive Menkes kinky hair syndrome is associated with multiple hair shaft abnormalities,
most characteristically, pili torti.
Q/Q(M)-473701 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis:
1
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
2
Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica
3
Pemphigus vulgaris
4
Linear bullous IgA disease
5
Facticial dermatosis
Q/Q(M)-474922 Report a Problem
19
What is the most likely diagnosis:
1
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
The bullous lesions represented are nonscarring and are associated with obvious nail dystrophy.
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex, Dowling-Meara type, is the best option.
Q/Q(M)-474922 Report a Problem
816 activating mutation in c-kit are found most often in which subset of patients with mastocytosis?
1
Adults with systemic disease refractory to imantinib
2
Adults with systemic disease associated with eosinophilia
3
Patients with familial history of mastocytosis
4
Adults with Telangiectasia Macularis Eruptiva Perstans
5
As a mosaic mutation in children with solitary cutaneous mastocytoma
Q/Q(M)-482220 Report a Problem
816 activating mutation in c-kit are found most often in which subset of patients with mastocytosis?
1
Adults with systemic disease refractory to imantinib
Almost all sporadic adult onset mastocytosis patients demonstrate mutations in c-kit. Most of these are
activating mutations linked to the 816 codon. Unfortunately, patients with this specific mutation tend to not
respond to systemic therapy with oral imantinib, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Q/Q(M)-482220 Report a Problem
Which of the following is most likely associated?
1
No additional abnormality
2
Deafness
3
Coarctation of the aorta
4
Bifid rib
5
Alopecia
Q/Q(M)-476251 Report a Problem
20
Which of the following is most likely associated?
1
No additional abnormality
The majority of patients with accessory tragii do not have any associated abnormalities. Multiple
anomalies, including deafness and midline defects, have been reported but are rare.
Q/Q(M)-476251 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Incontinentia pigmenti
2
Bullous pemphigoid of infancy
3
Herpes zoster
4
Disseminated herpes simplex
5
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
Q/Q(M)-474927 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Incontinentia pigmenti
The vesicular lesions following the lines of Blaschko are typical for incontinentia pigmenti.
Q/Q(M)-474927 Report a Problem
Pastias lines are characteristic for which eruption:
1
Measles
2
Scarlet fever
3
Rubella
4
Kawasakis disease
5
Mumps
Q/Q(M)-473689 Report a Problem
Pastias lines are characteristic for which eruption:
2
Scarlet fever
21
Pastias lines are defined as a linear accentuation of the erythematous sandpaper rash within the flexures.
This is classically described with scarlet fever.
Q/Q(M)-473689 Report a Problem
What disorder is associated with a defect in LMX1B?
1
Nail patella syndrome
2
Steatocystoma
3
Monilithrix
4
Lhermitte-Duclos syndrome
5
Chediak-Higashi syndrome
Q/Q(M)-473699 Report a Problem
What disorder is associated with a defect in LMX1B?
1
Nail patella syndrome
A LMX1B gene defect is associated with nail patella syndrome.
Q/Q(M)-473699 Report a Problem
An infant presents with the lesion depicted in the photo. Which of the following is least likely?
1
Sternal clefting
2
Supraumbilical raphe
3
Dandy-Walker malformation
4
Seizure disorder
5
Congenital cataracts
Q/Q(M)-474926 Report a Problem
An infant presents with the lesion depicted in the photo. Which of the following is least likely?
4
Seizure disorder
Extensive facial hemangiomas are a component of the PHACES syndrome. Seizure disorder has not been
described.
Q/Q(M)-474926 Report a Problem
The risk of fetal death with intrauterine parvovirus infection may occur with infection in which trimester:
1
First
2
Second
22
3
Third
4
First, Second and Third
5
None of these answers are correct
Q/Q(M)-473691 Report a Problem
The risk of fetal death with intrauterine parvovirus infection may occur with infection in which trimester:
4
First, Second and Third
Fetal hydrops may occur with parvovirus infection during all three trimesters although the greatest risk is
during the second trimester. Congenital anomalies are not a feature.
Q/Q(M)-473691 Report a Problem
A young girl presents with enlarged tongue, exomphalmos, and organomegaly and has history of Wilm's
tumor. What cutaneous finding is most likely on physical exam?
1
Palmoplantar keratoderma
2
Lymphatic malformation
3
Acral edema
4
Midline capillary malformation
5
Angiokeratoma
Q/Q(M)-482385 Report a Problem
A young girl presents with enlarged tongue, exomphalmos, and organomegaly and has history of Wilm's
tumor. What cutaneous finding is most likely on physical exam?
4
Midline capillary malformation
This patient has Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, a sporadic condition that is also known as exomphalos-
macroglossia-gigantism syndrome. It also features a midline capillary malformation, linear earlobe creases,
intestinal malrotation, and other tumors such as rhabdomyosarcoma an hepatoblastoma.
Q/Q(M)-482385 Report a Problem
This patient had significantly elevated serum CPK. The likely diagnosis is:
1
Dermatomyositis
2
Lupus erythematosus
3
Psoriasis
4
Atopic dermatitis
5
Lichen planus
Q/Q(M)-474880 Report a Problem
This patient had significantly elevated serum CPK. The likely diagnosis is:
1
Dermatomyositis
23
The answer is dermatomyositis with the heliotrope color and distribution of erythema or violaceous color.
The skin over the metacarpal and proximal interphalangeal joints can become inflamed and erythematous
forming Gottrons papules.
Q/Q(M)-474880 Report a Problem
A neonate presents with a large segmental hemangioma of the V1 distribution. What are features may be
associated with this finding?
1
Tram-track calcifications
2
Anterior fossa defect
3
Posterior fossa defect
4
M-paraproteinemia
5
Muscular dystrophy
Q/Q(M)-476778 Report a Problem
A neonate presents with a large segmental hemangioma of the V1 distribution. What are features may be
associated with this finding?
3
Posterior fossa defect
PHACES syndrome consists of posterior fossa defect, hemangiomas (often segmental and large), arterial
defects, cardiac defects, eye abnormaliteis, and sternal clefting. Posterior fossa defects include the Dandy-
Walker malformtion.
Q/Q(M)-476778 Report a Problem
POEMS syndrome is associated with which of the following:
1
Premature aging
2
Odontogenic cysts
3
Eye abnormalities
4
M protein
5
Saddle nose deformity
Q/Q(M)-476263 Report a Problem
POEMS syndrome is associated with which of the following:
4
M protein
The acronym POEMS stands for polyneuropathy, organomegaly, endocrinopathy, M-protein, and skin
changes.
Q/Q(M)-476263 Report a Problem
An infant with failure to thrive has multiple xanthomas on skin exam and foamy histiocytes on bone
marrow biopsy. Your diagnosis is:
1
Gauchers disease
2
Tay-Sachs disease
3
Niemann-Pick disease
4
Fabrys disease
5
Hunters syndrome
24
Q/Q(M)-477194 Report a Problem
An infant with failure to thrive has multiple xanthomas on skin exam and foamy histiocytes on bone
marrow biopsy. Your diagnosis is:
3
Niemann-Pick disease
Niemann-Pick disease is an autosomal recessive disease caused by mutations in sphingomyelin
phosphodiesterase-1. Patients with Type A Niemann-Pick disease may have xanthomas, progressive
psychomotor deterioration, hepatosplenomegaly, blindness, cherry red spots, and deafness.
Q/Q(M)-477194 Report a Problem
A patient presents with an epidermal nevus of the lower abdomen. You take a skin biopsy to confirm the
diagnosis. The pathology report indicates that there were findings of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Which
of the following defects is her offspring at risk for based on these findings?
1
Transglutaminase
2
Keratin 6a/16
3
Keratin 6b/17
4
Keratin 1/10
5
Keratin 2e
Q/Q(M)-473797 Report a Problem
A patient presents with an epidermal nevus of the lower abdomen. You take a skin biopsy to confirm the
diagnosis. The pathology report indicates that there were findings of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Which
of the following defects is her offspring at risk for based on these findings?
4
Keratin 1/10
Women with epidermal nevi with epidermolytic hyperkeratosis histologically are at risk for offspring with
the full-blown epidermolytic hyperkeratosis syndrome, which is due to Keratin 1/10 defects.
Transglutaminase defects are seen in lamellar ichthyosis, Keratin 6a/16 and 6b/17 in Pachyonychia
congenita types I and II and Keratin 2e in Ichthyosis bullosa of Siemens.
Q/Q(M)-473797 Report a Problem
An 8 year-old boy presents with pink, flushed cheeks and a low-grade fever. On week later, the following
lacy eruption appeared. What is the most likely etiology?
1
Paramyxovirus
2
Togavirus
3
Group A streptococcus
4
HHV6
5
Parvovirus
Q/Q(M)-474932 Report a Problem
An 8 year-old boy presents with pink, flushed cheeks and a low-grade fever. On week later, the following
lacy eruption appeared. What is the most likely etiology?
5
Parvovirus
Fifth disease is caused by Parvovirus B19. Most cases start with prodrome of fever, malaise, headache and
25
rhinorrhea. Cutaneous reaction follows approximately 5-7 days later with erythema of the cheeks ("slapped
cheeks") and reticulate rash of the trunk and extremities.
Q/Q(M)-474932 Report a Problem
The disorder caused by a defect in intestinal zinc-specific transporter SLC39A4 is most likely to present:
1
At birth
2
Upon weaning from breast milk
3
Upon weaning from formula
4
In childhood
5
In adulthood
Q/Q(M)-473680 Report a Problem
The disorder caused by a defect in intestinal zinc-specific transporter SLC39A4 is most likely to present:
2
Upon weaning from breast milk
In acrodermatitis enteropathica, there is decreased absorption of zinc from the infants gastrointestinal
tract. The zinc in breast milk has greater availability than nonmaternal sources thus protecting the child
from disease expression until weaning.
Q/Q(M)-473680 Report a Problem
2 year old female with the skin eruption, also history of joint swelling, painful movement and mucosal
lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Pustular psoriasis
2
PAPA syndrome
3
Familial Mediterranean fever
4
DIRA
5
Subcorneal pustular dermatosis
Q/Q(M)-482881 Report a Problem
2 year old female with the skin eruption, also history of joint swelling, painful movement and mucosal
lesions. What is the most likely diagnosis?
4
DIRA
Deficiency of the IL-1 receptor antagonist(DIRA). These patients, early in their lives, present with severe
pustulosis and ichthyosiform skin eruptions. Also they can have joint pains and oral mucosal lesions. DIRA
is a new addition to the spectrum of autoinflammatory disorders. It will not be encountered often, but its
origin highlights the importance of IL-1? in skin function.
Q/Q(M)-482881 Report a Problem
Osteopathia striata is found in which disorder?
1
McCune-Albright syndrome
2
Neurofibromatosis I
3
Buschke-Ollendorff syndrome
4
Gorlin's syndrome
26
5
Focal dermal hypoplasia
Q/Q(M)-477631 Report a Problem
Osteopathia striata is found in which disorder?
5
Focal dermal hypoplasia
Osteopathia striata (vertical striations in the metaphysis of long bones on x-ray) is seen is greater than 80%
of cases of focal dermal hypoplasia (or Goltz syndrome). Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia with recurrent
fractures is seen in McCune-Albright syndrome. Sphenoid wing dysplasia and thinning of long bone cortex
is found in neurofibromatosis I. Osteopoikilosis is an asymptomatic x-ray finding in patients with Buschke-
Ollendorf syndrome. Osteopoikilosis reflects ectopic calcification that does not increase risk of fracture.
Bifid ribs, vertebral fusion/Sprengel deformity of the spine, and kyphoscoliosis can be seen in basal cell
nevus syndrome (Gorlin's syndrome).
Q/Q(M)-477631 Report a Problem
Which enanthem is most commonly seen in association with Exanthem subitum?
1
Koplik spots
2
Red strawberry tongue
3
Chapped lips; dry, red mucosa
4
Red macules and streaks on the soft palate
5
Palatal erosions
Q/Q(M)-477795 Report a Problem
Which enanthem is most commonly seen in association with Exanthem subitum?
4
Red macules and streaks on the soft palate
Exanthem subitum (roseola or Sixth disease) is caused by HHV6, a dsDNA virus. It presents with high
fever for several days followed by an exanthem of erythematous macules and papules on the trunk that
begins as the fever ends. An associated enanthem of red macules/streaks on the soft palate may be seen.
Koplik spots are seen in measles; the red strawberry tongue (following the white strawberry tongue) is seen
in Scarlet fever; chapped lips and dry, red mucosa may be seen in Kawasaki's disease; palatal erosions may
be seen in Papular-purpuric gloves and socks syndrome.
Q/Q(M)-477795 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Traction alopecia
2
Tinea capitis
3
Aplasia cutis congenita
4
Nevus sebaceous
5
Alopecia areata
Q/Q(M)-476797 Report a Problem
27
What is the most likely diagnosis?
3
Aplasia cutis congenita
Aplasia cutis congenita is characterized by the absence of a portion of skin, most commonly presenting as a
solitary defect on the scalp, but sometimes it may occur as multiple lesions. The lesions are non-
inflammatory and well demarcated appear as an atrophic, membranous, ulcerated area with alopecia. The
condition may be associated with other physical anomlies.
Q/Q(M)-476797 Report a Problem
This condition may be associated with which of the following:
1
Hypercalcemia
2
Hyperlipidemia
3
Vitiligo
4
Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica
5
Perinatal trauma
Q/Q(M)-474919 Report a Problem
This condition may be associated with which of the following:
4
Epidermolysis bullosa dystrophica
Aplasia cutis congenita may be associated with dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (Bart syndrome.)
Q/Q(M)-474919 Report a Problem
A 6-year-old boy presents with osteoma cutis on his face. Which of the following genes is most likely
defective?
1
GNAS
2
NSDHL
3
PTEN
4
SPINK5
5
SLURP1
Q/Q(M)-480188 Report a Problem
28
A 6-year-old boy presents with osteoma cutis on his face. Which of the following genes is most likely
defective?
1
GNAS
Osteoma cutis in a child is associated with Albrights hereditary osteodystrophy
(pseudohypoparathyroidism), which is caused by a mutation in GNAS1. Albright hereditary
osteodystrophy is characterized by including short stature, obesity, round facies, subcutaneous
ossifications, brachydactyly, and other skeletal anomalies. Some patients have mental retardation. AHO is
often associated with pseudohypoparathyoidism, hypocalcemia, and elevated PTH levels (PHP Ia) (OMIM,
103580). NSDHL is defective in CHILD syndrome, PTEN in Cowdens syndrome, SPINK5 in
Nethertons syndrome and SLURP1 in Mal de Maleda.
Q/Q(M)-480188 Report a Problem
A 2 day-old full term neonate develops blotchy erythematous macules with small central pustules over the
upper trunk and extremities. A gram stain reveals predominantly eosinophils. What is the most likely
diagnosis?
1
Erythema toxicum neonatorum
2
Incontinentia pigmenti
3
Urticaria pigmentosa
4
Transient neonatal pustular melanosis
5
Miliaria
Q/Q(M)-473677 Report a Problem
A 2 day-old full term neonate develops blotchy erythematous macules with small central pustules over the
upper trunk and extremities. A gram stain reveals predominantly eosinophils. What is the most likely
diagnosis?
1
Erythema toxicum neonatorum
Erythema toxicum neonatorum is a very common eruption in healthy newborns. A gram stain reveals
sterile pustules containing eosinophils.
Q/Q(M)-473677 Report a Problem
A deficiency of the surface glycoprotein sialophorin is seen in which immunedeficient disease?
1
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
2
Chronic granulomatous disease
3
Job syndrome
4
Severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome
5
Leiners disease
Q/Q(M)-477199 Report a Problem
A deficiency of the surface glycoprotein sialophorin is seen in which immunedeficient disease?
1
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by mutations in WAS gene. Patients
with Wiskott-Aldrich may have unstable sialoglycoprotein CD 43 on the surface of lymphocytes. Patients
with Wiskott-Aldrich have atopic dermatitis with increased risks for secondary infection,
thrombocytopenia, and recurrent bacterial infections. They are also at an increased risk for lymphoreticular
malignancy (20%).
29
Q/Q(M)-477199 Report a Problem
A healthy, full-term infant develops a pustular, erythematous eruption on her face and trunk on the third
day of life. A smear taken from one of these pustules would show:
1
Gram-positive bacteria
2
Predominantly neutrophils
3
Multi-nucleated giant cells
4
Predominantly eosinophils
5
Hyphae
Q/Q(M)-477632 Report a Problem
A healthy, full-term infant develops a pustular, erythematous eruption on her face and trunk on the third
day of life. A smear taken from one of these pustules would show:
4
Predominantly eosinophils
This baby has developed erythema toxicum neonatorum, a benign, self-limited eruption that occurs in the
majority of healthy, full-term infants. Erythema toxicum usually develops on the second or third day of life
and resolves by day 10. A smear taken from one of the pustules will demonstrate eosinophils, which is
sufficient to make the diagnosis. Viral infections of the skin may demonstrate multi-nucleated giant cells
on Tzanck smear. Transient neonatal pustular melanosis is present at birth; neonates present with small,
superficial pustules that rupture easily. Some may have ruptured in utero, leaving pigmented macules. The
pigmentation may persist for weeks to months in darkly-complexed infants. A smear of the
intracorneal/subcorneal pustule will show mostly neutrophils, but eosinophils may also be present.
Q/Q(M)-477632 Report a Problem
A 3 month-old girl with multiple hemangiomas along her right jaw is at increased risk for:
1
Bleeding complications
2
Underlying bone abnormalities
3
Subglottic hemangioma
4
Oral obstruction
5
Hearing defecits
Q/Q(M)-477334 Report a Problem
A 3 month-old girl with multiple hemangiomas along her right jaw is at increased risk for:
3
Subglottic hemangioma
Hemangiomas are benign vascular tumors which have proliferating phase and then a spontaneous
involution phase. Depending upon the location, some hemangiomas may have more long term sequelae
such as scarring or structural malformation, and rarely, consumptive coagulopathy. Infants with
hemangiomas of the beard distribution should be evaluated for subglottic hemangiomas which may
lead to airway obstruction.
Q/Q(M)-477334 Report a Problem
What the most likely diagnosis?
1
Atopic dermatitis
30
2
Lamellar ichthyosis
3
Rud syndrome
4
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
5
Keratosis pilaris
Q/Q(M)-474935 Report a Problem
What the most likely diagnosis?
1
Atopic dermatitis
Ichythosis vulgaris and hyperlinear palms are both independent minor criteria for the diagnosis of atopic
dermatitis in both children and infants.
Q/Q(M)-474935 Report a Problem
Rhinorrhea, condylomata lata, and mucous patches are all seen with which congenital disorder?
1
Rubella
2
Toxoplasmosis
3
Herpes simplex virus
4
Syphilis
5
Human papillomavirus infection
Q/Q(M)-473686 Report a Problem
Rhinorrhea, condylomata lata, and mucous patches are all seen with which congenital disorder?
4
Syphilis
Signs of congenital syphilis include rhinorrhea, snuffles, rhagades, condylomata lata, and mucous patches.
Condylomata lata or a generalized papulosquamous eruption of secondary syphilis may be present in diaper
area.
Q/Q(M)-473686 Report a Problem
An infant who presents with this abnormality will often have the following:
1
The lesion will be on the left-side in a segmental distribution
2
Airway restriction
3
Have multiple liver hemangiomas
31
4
Most likely be a male infant
5
An anterior fossa malformation
Q/Q(M)-480558 Report a Problem
An infant who presents with this abnormality will often have the following:
1
The lesion will be on the left-side in a segmental distribution
PHACES syndrome represents posterior fossa malformations, hemangiomas, arterial abnormalities, cardiac
abnormalities, eye abnormalities, and sternal defects. Facial hemangiomas are most often on the left-side of
the face. The majority of reported cases are female.
Q/Q(M)-480558 Report a Problem
The genetic disorder depicted in this photo is caused by a mutation in:
1
MASH2
2
STK11
3
PTEN
4
Patched
5
TSC1
Q/Q(M)-474931 Report a Problem
The genetic disorder depicted in this photo is caused by a mutation in:
2
STK11
The multiple labial lentigo seen on this young boy are seen with Peutz-Jegher syndrome. A defect in the
STK11 gene is responsible.
Q/Q(M)-474931 Report a Problem
A 4 month-old with diffuse blisters and erosions has a skin biopsy diagnostic of generalized mastocytosis.
Which topical dressing should be avoided in this patient?
32
1
Mupirocin ointment
2
Polymyxin B ointment
3
Petrolatum
4
Neomycin ointment
5
Silver sulfadiazine
Q/Q(M)-477328 Report a Problem
A 4 month-old with diffuse blisters and erosions has a skin biopsy diagnostic of generalized mastocytosis.
Which topical dressing should be avoided in this patient?
2
Polymyxin B ointment
Mastocytosis comprises a group of diseases characterized by increased number of mast cells in the skin and
other organs. Seventy-five percent of cases occur before the age of 2. Patients with mastocytosis should
avoid potential mast degranulators including aspirin, codeine, opiates, procaine, spicy foods, cheese,
alcohol, polymyxin B.
Q/Q(M)-477328 Report a Problem
Which of the following is a sign of EARLY postnatal congenital syphilis?
1
Clutton's joints
2
Higoumenaki's sign
3
Hutchinson's teeth
4
Saber shins
5
Wimberger's sign
Q/Q(M)-482501 Report a Problem
Which of the following is a sign of EARLY postnatal congenital syphilis?
5
Wimberger's sign
Wimberger's sign is a sign of early postnatal congenital syphilis (occurs < 2 years old). All other choices
are signs of late postnatal congenital syphilis. Wimberger's sign is a radiographic sign showing a sawtooth
appearance of the proximal tibia. Clutton's joints are nontender and represent synovitis with effusions of
the knees and elbows. Higoumenaki's sign is a unilateral clavicular enlargement secondary to periostitis.
Hutchinson's teeth are centrally notched, wide spaced, peg shaped upper incisors. Saber shins are anterior
bowing of the tibia.
Q/Q(M)-482501 Report a Problem
An eight year-old boy presents with pink, flushed cheeks and a low-grade fever. Eruptions then appeared.
What is the most likely etiology?
1
Paramyxovirus
2
Togavirus
3
Group A streptococcus
4
HHV6
5
Parvovirus
Q/Q(M)-476796 Report a Problem
33
An eight year-old boy presents with pink, flushed cheeks and a low-grade fever. Eruptions then appeared.
What is the most likely etiology?
5
Parvovirus
Fifths Disease or erythema infectiosum, is caused by parvovirus B19, a single-stranded DNA virus. There
are a few clinical presentations including, diffuse lacy rash on the trunk that spreads gradually toward the
distal extremities, papular-pruritic "gloves-and-socks" syndrome and aplastic crisis which does not have
concomitant rash.
Q/Q(M)-476796 Report a Problem
The lesion depicted is most often associated with:
1
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
2
Chondrodysplasia punctata
3
Sphenoid wing hypoplasia
4
Cleft palate
5
Osteopoikilosis
Q/Q(M)-474921 Report a Problem
The lesion depicted is most often associated with:
1
Polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
The coast of Maine caf au lait macule is associated with McCune-Albright syndrome and
polyostotic fibrous dysplasia.
Q/Q(M)-474921 Report a Problem
What syndrome is the disorder shown in the photo associated with?
1
Turner syndrome
2
Down syndrome
3
Noonan syndrome
4
Griscelli syndrome
5
Bloom syndrome
Q/Q(M)-474928 Report a Problem
34
What syndrome is the disorder shown in the photo associated with?
3
Noonan syndrome
The photo shows keratosis pilaris atrophicans faceii and surgically corrected ptosis. Both of these findings
are associated with Noonan syndrome.
Q/Q(M)-474928 Report a Problem
Psammomatous melanotic schwannomas are associated with:
1
Bloom syndrome
2
Carney complex
3
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
4
Neurofibromatosis Type 2
5
Tuberous sclerosis
Q/Q(M)-473702 Report a Problem
Psammomatous melanotic schwannomas are associated with:
2
Carney complex
Psammomatous melanotic schwannomas have been described in the Carney complex, a defect in the tumor
suppressor gene, PRKAR1A.
Q/Q(M)-473702 Report a Problem
What is the diagnosis?
1
Unilateral laterothoracic exanthem
2
Roseola
3
Rubella
4
Urticaria
5
Contact dermatitis
Q/Q(M)-474929 Report a Problem
35
What is the diagnosis?
1
Unilateral laterothoracic exanthem
The child in the photo depicts the Statue of Liberty sign of unilateral laterothoracic exanthem.
Q/Q(M)-474929 Report a Problem
Which of followings syndromes characterized by Seborrheic-like or exfoliative dermatitis
1
Leiner's disease
2
Hyperimmunoglobulinemia E syndrome
3
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
4
Chronic granulomatous disease
5
X-linked agammaglobulinemia
Q/Q(M)-482136 Report a Problem
Which of followings syndromes characterized by Seborrheic-like or exfoliative dermatitis
1
Leiner's disease
Immunodeficiency disorders may be associated with a variety of cutaneous abnormalities, and recognition
of these clinical features may allow an early diagnosis of primary immunodeficiency. Cutaneous
abnormalities may include cutaneous infections, atopic- or seborrheic-like dermatitis, macular erythemas,
alopecia, poor wound healing, purpura, petechiae, telangiectasias, pigmentary dilution, cutaneous
granulomas, extensive warts, angioedema, and lupus-like changes. Leiner's disease or erythroderma
desquamativum is a complication of seborrheic dermatitis in infants (dermatitis seborrhoides infantum)
There is usually a sudden confluence of lesions, leading to a universal scaling redness of the skin
(erythroderma). The young patients are severely ill with anemia, diarrhea, and vomiting.The disease is both
a familial and a nonfamilial form. The former is noted for having a functional deficiency of C5
complement, resulting in defective opsonization. These patients respond to antibiotics and infusions of
fresh frozen plasma or whole blood. The other choices in the questions can all be associated with atopic-
like dermatitis.
Q/Q(M)-482136 Report a Problem
Which of the following can present as collodion baby?
1
Ichthyosis vulgaris
2
X-linked ichthyosis
3
Lamellar ichthyosis
36
4
Bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma
5
Sjogren-Larsson syndrome
Q/Q(M)-477629 Report a Problem
Which of the following can present as collodion baby?
3
Lamellar ichthyosis
The most common presentation of collodion baby is lamellar ichthyosis, followed by congenital
ichthyosiform erythroderma. Patients with ichthyosis vulgaris and x-linked ichthyosis are normal at birth.
Bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma or epidermolytic hyperkeratosis presents with widespread
bullae, erthroderma, and denuded skin. Sjogren-Larsson presents with generalized ichthyosis and
erythroderma in infancy. It is important to know the at-birth presentations of all the disorders of
cornification.
Q/Q(M)-477629 Report a Problem
What is the function of the gene which is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia?
1
Gap junction protein
2
Cross-linking of structural proteins in the protein and lipid envelope of the upper epidermis
3
Pathway of cholesterol biosynthesis
4
DNA repair protein
5
Tumor supressor protein
Q/Q(M)-477630 Report a Problem
What is the function of the gene which is defective in ataxia-telangiectasia?
4
DNA repair protein
The defective gene is ataxia-telangiectasia (Louis-Bar syndrome) is the ATM gene, which is responsible
for DNA repair, especially after ionizing radiation. Tumor suppressor genes mutations are responsible for
basal cell nevus syndrome, xeroderma pigmentosum, Muir-Torre syndrome, dyskeratosis congenital,
Gardner syndrome, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, Cowden syndrome, and MEN syndromes. Connexins are gap
junction proteins that are responsible for intercellular communication and signaling. Mutations in
connexins are responsible for Vohwinkel syndrome and erythrokeratoderma variabilis. Mutations in the
cholesterol biosynthesis pathways cause CHILD syndrome and Conradi-Hunermann syndrome.
Tranglutaminase 1 (TGM 1) is involved in the normal cross-linking of structural proteins in the protein and
lipid envelope of the upper epidermis. TGM 1 is mutated in lamellar ichthyosis and congenital
ichthyosiform erythroderma.
Q/Q(M)-477630 Report a Problem
A 24 month-old infant presents with yellowish-brown, crusted papules with petechiae in a seborrheic
distribution. A biopsy is done to confirm a diagnosis. Which histologic picture is most likely?
1
CD1-, S100- cells with reniform nuclei
2
Foamy histiocytes with Touton giant cells
3
CD1+, S100+ cells with reniform nuclei
4
Mixed cellular infiltrate in a ball and claw pattern
5
Superficial perivascular infiltrate with mild spongiosis and neutrophil containing scale crust
Q/Q(M)-473681 Report a Problem
37
A 24 month-old infant presents with yellowish-brown, crusted papules with petechiae in a seborrheic
distribution. A biopsy is done to confirm a diagnosis. Which histologic picture is most likely?
3
CD1+, S100+ cells with reniform nuclei
Langerhans cells are CD1 and S100 positive. The nuclei are described as kidney shaped, or reniform.
Q/Q(M)-473681 Report a Problem
Posterior auricular adenopathy is a common feature of which exanthem:
1
Measles
2
Mumps
3
Scarlet fever
4
Rubella
5
Erythema infectiosum
Q/Q(M)-473690 Report a Problem
Posterior auricular adenopathy is a common feature of which exanthem:
4
Rubella
Lymphadenopathy with 1-7 days of malaise is commonly described with rubella infection. The rose-pink
macular rash follows the prodrome.
Q/Q(M)-473690 Report a Problem
A 2 week-old infant is brought to the ER with a rash on her face. She is found to have a 3rd degree heart
block. What is the risk that a second child born to this mother will have the same diagnosis?
1
5%
2
10%
3
25%
4
50%
5
100%
Q/Q(M)-477634 Report a Problem
A 2 week-old infant is brought to the ER with a rash on her face. She is found to have a 3rd degree heart
block. What is the risk that a second child born to this mother will have the same diagnosis?
3
25%
The diagnosis here is neonatal lupus erythematosus. Babies are normal at birth and develop skin lesions
within the few months of life. About half of these babies will have an associated congenital heart block,
usually 3rd degree, which is permanent. Most infants with NLE are girls and are born to mothers who are
Ro/La positive. There is a 25% chance that a second child with have NLE.
Q/Q(M)-477634 Report a Problem
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is usually treated with:
1
Aspirin
2
Topical calcipitriol
3
Excision
4
Observation
38
5
Retinoids
Q/Q(M)-479620 Report a Problem
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is usually treated with:
4
Observation
Subcutaneous fat necrosis of the newborn is rare and self-limited. It is thought to result from perinatal
stress and resolves in 3-6 months. Treatment is usually not necessary unless hypercalcemia develops.
Q/Q(M)-479620 Report a Problem
A 10 year-old male presents with new pink-red papules distributed on his bilateral cheeks, elbows, knees,
and buttocks. The lesions are not pruritic. His mother notes he has suffered from low grade fevers over the
past few days, but is otherwise healthy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
1
rubella
2
rubeola
3
roseola
4
papular acrodermatitis of childhood
5
dermatitis herpetiformis
Q/Q(M)-482829 Report a Problem
A 10 year-old male presents with new pink-red papules distributed on his bilateral cheeks, elbows, knees,
and buttocks. The lesions are not pruritic. His mother notes he has suffered from low grade fevers over the
past few days, but is otherwise healthy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
4
papular acrodermatitis of childhood
Papular acrodermatitis of childhood (Gianotti-Crosti syndrome) typically affects children 6 months to 10
years of age, and is characterized by symmetric papules (and sometimes papulovesicles) involving the face
and buttocks (four cheeks) and extensor surfaces of the upper and lower extremities. Lesions tend to
be asymptomatic. Multiple infectious etiologies have been implicated, including Epstein-Barr virus (most
common in the U.S.) and hepatitis B (most common in Europe). However, the eruption is most often self-
limited, resolving in 4 to 8 weeks, and thus further work-up (e.g. testing for hepatitis) is indicated only if
additional clinical symptoms are present.
Q/Q(M)-482829 Report a Problem
Hemangiomas of infancy are more likely to be:
1
GLUT-1 negative
2
Merosin positive but GLUT-1 negative
3
Lewis Y antigen positive, merosin negative
4
Glut-1 positive, merosin positive, Lewis Y antigen negative
5
Glut-1 positive, merosin positive, Lewis Y antigen positive
Q/Q(M)-482865 Report a Problem
Hemangiomas of infancy are more likely to be:
5
Glut-1 positive, merosin positive, Lewis Y antigen positive
Hemangiomas show GLUT-1 positivity and stain positively with placental markers.
39
Q/Q(M)-482865 Report a Problem
Late onset subungual keratotic tumors are associated with:
1
Incontinentia pigmenti
2
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
3
Carney complex
4
Cowden syndrome
5
Basal cell nevus syndrome
Q/Q(M)-473704 Report a Problem
Late onset subungual keratotic tumors are associated with:
1
Incontinentia pigmenti
A NEMO gene defect can cause subungual keratotic growths. The typical age of presentation is early
adulthood.
Q/Q(M)-473704 Report a Problem
Variants of xeroderma pigmentosum are due to all of the following defects except:
1
Nucleotide excision repair
2
Helicase
3
Endonuclease
4
Thymidine kinase
5
Postrepliction repair
Q/Q(M)-473698 Report a Problem
Variants of xeroderma pigmentosum are due to all of the following defects except:
4
Thymidine kinase
The photosensitivity of xeroderma pigmentosum is caused by defect in DNA repair mechanisms.
Thymidine kinase is not affected.
Q/Q(M)-473698 Report a Problem
Rapp-Hodgkin is caused by a defect in the following gene:
1
Plakophilin
2
Desmoglein 1
3
Ectodysplasin A
4
P63
5
Connexin 30
Q/Q(M)-476265 Report a Problem
Rapp-Hodgkin is caused by a defect in the following gene:
40
4
P63
Rapp-Hodgkin, along with the other ectodermal dysplasia-clefting syndromes, is reportedly caused by a
defect in the p63 gene.
Q/Q(M)-476265 Report a Problem
Individuals with which of the following syndromes characteristically present with photosensitivity, mental
retardation, a "wizened" appearance, "bird-headed" facies, and "Mickey Mouse" ears?
1
Tay Syndrome
2
Rothmund-Thomson Syndrome
3
Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome
4
Cockayne Syndrome
5
Werner Syndrome
Q/Q(M)-478060 Report a Problem
Individuals with which of the following syndromes characteristically present with photosensitivity, mental
retardation, a "wizened" appearance, "bird-headed" facies, and "Mickey Mouse" ears?
4
Cockayne Syndrome
Cockayne Syndrome is AR, caused by defective excision repair, cross-complementing group 8 gene
(ERCC8). It presents with photosensitivity, mental retardation, and cachectic dwarfism. Patients have a
characteristic "wizened" appearance, "bird-headed" facies, and "Mickey Mouse" ears. Cataracts, deafness,
pigmentary retinopathy, dental caries, and skeletal, GU, and endocrine abnormalities may be seen.
Q/Q(M)-478060 Report a Problem
A 2 year-old has a high fever for three days, as the fever breaks, a generalized rash appears on the trunk.
The most likely diagnosis is:
1
Measles
2
Mumps
3
Rubella
4
Erythema infectiosum
5
Roseola
Q/Q(M)-473694 Report a Problem
A 2 year-old has a high fever for three days, as the fever breaks, a generalized rash appears on the trunk.
The most likely diagnosis is:
5
Roseola
Roseola typically appears in toddlers. A high fever followed by a generalized maculopapular rash is
characteristic for this HHV6 infection.
Q/Q(M)-473694 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
41
1
Papular acrodermatitis of childhood
2
Mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome
3
German measles
4
Letterer-Siwe disease
5
Exanthem subitum
Q/Q(M)-475959 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Papular acrodermatitis of childhood
Gianotti-Crosti syndrome is also known as papular acrodermatitis of childhood. The eruption is
characterized by lichenoid papules in an acral distribution.
Q/Q(M)-475959 Report a Problem
Ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum is seen with a defect in:
1
Plakophilin
2
Plakoglobin
3
Desmoglein
4
C-kit
5
p63
Q/Q(M)-473705 Report a Problem
Ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum is seen with a defect in:
5
p63
The ectodermal-clefting syndromes are caused by a defect in the p63 gene. Specifically, AEC or Hay-Wells
syndrome is comprised of ankyloblepharon filiforme adnatum, ectodermal dysplasia and clefting.
Q/Q(M)-473705 Report a Problem
Which of the following is characteristic of Wooly Hair Nevus:
42
1
Typically occurs in the 5th decade
2
Ocular abnormalities may be associated
3
There are no nevi associated with this hair abnormality
4
Sponteneous improvement never occurs
5
It is hereditary
Q/Q(M)-478697 Report a Problem
Which of the following is characteristic of Wooly Hair Nevus:
5
It is hereditary
Wooly Hair Nevus is the presence of Negroid hair on the scalp of persons of non-Negroid inheritance. The
unruly hair presents at birth or in infancy, usually as a solitary problem inherited in an autosomal dominant
fashion.
Q/Q(M)-478697 Report a Problem
Which of the following should be the next step in the management of this patient?
1
Barium swallow
2
spine x-ray
3
Cardiac evaluation
4
Administration of oral antibiotics
5
Pulmonary function studies
Q/Q(M)-477846 Report a Problem
Which of the following should be the next step in the management of this patient?
3
Cardiac evaluation
This patient must be evaluated thoroughly for PHACES syndrome. PHACES is an acronym for Posterior
fossa malformations (Dandy-Walker malformation is most common), Hemangiomas, Arterial anomalies,
Coarctation of the aorta, Eye abnormalities, and Sternal cleft defects. This patient should have a complete
cardiac evaluation, neuroimaging, and ophthalmologic exam. If the facial hemangioma involves the beard
area, this may indicate laryngeal involvement and appropriate imaging and evaluation is mandated.
Systemic steroids at high doses (5 mg/kg) are usually administered. If caught early, the sequelae of
PHACES syndrome can be minimized.
Q/Q(M)-477846 Report a Problem
43
A boy is noted at birth to have coarse scales over his trunk and extremities. The face, palms, soles and
flexures are spared. What is the least likely association?
1
Corneal opacities
2
Cryptorchidism
3
Ectropion
4
Prolonged maternal labor
5
Neurologic abnormality
Q/Q(M)-474934 Report a Problem
A boy is noted at birth to have coarse scales over his trunk and extremities. The face, palms, soles and
flexures are spared. What is the least likely association?
3
Ectropion
X-linked ichthyosis is characterized by small, dark, firmly adherent scales accentuated on the sides of the
neck and trunk. The face, palms, soles, antecubital and popliteal flexures are generally spared. Associated
extracutaneous findings include corneal opacities (50%), undescended testes (20%), and prolonged
maternal labor (usual). Neurological or mental retardation are rare but documented associations as XLI can
be associated with a contiguous gene syndrome with Kallman syndrome, mental retardation and X linked
recessive chrondrodysplasia punctata.
Q/Q(M)-474934 Report a Problem
What is the best test to confirm a diagnosis?
1
DsDNA antibody
2
Anti Ro antibody
3
Biopsy
4
KOH
5
Gram stain
Q/Q(M)-476258 Report a Problem
What is the best test to confirm a diagnosis?
44
4
KOH
The picture depicts tinea faceii. A KOH exam should be performed to look for hyphae.
Q/Q(M)-476258 Report a Problem
What is the best treatment option?
1
Oral cephalexin
2
Oral acyclovir
3
Observation
4
Topical tretinoin
5
Topical ketoconazole
Q/Q(M)-476794 Report a Problem
What is the best treatment option?
4
Topical tretinoin
The lesions shown in the photo are comedones of infantile acne. Topical tretinoin would be the best
treatment option.
Q/Q(M)-476794 Report a Problem
A young boy presents with a port-wine stain, a Mongolian spot, and a nevus spilus. Which phakomatosis
pigmentovascularis does he have?
1
Type I
2
Type II
3
Type III
4
Type IV
5
Type V
Q/Q(M)-482384 Report a Problem
A young boy presents with a port-wine stain, a Mongolian spot, and a nevus spilus. Which phakomatosis
pigmentovascularis does he have?
4
Type IV
This patient has type IV phakomatosis pigmentovascularis characterized by a port-wine stain, Mongolian
spot, and nevus spilus. All types have a nevus flammeus. In addition, type II demonstrates a Mongolian
spot (may be associated with granular cell tumor), type II a speckled nevus, and type V cutis marmorata
telangiectasia. Type II-IV can also have a nevus amenicus. Phakomatosis pigmentovascularis is thought to
be caused by the "twin spot" phenomenon.
Q/Q(M)-482384 Report a Problem
45
Which of the following is the most common complication associated with cutis marmorata telangectatica
congenita?
1
Seizure disorder
2
Atrial septal defect
3
Systemic lupus erythematosus
4
Hypercalcemia
5
Limb hypertrophy or atrophy
Q/Q(M)-473676 Report a Problem
Which of the following is the most common complication associated with cutis marmorata telangectatica
congenita?
5
Limb hypertrophy or atrophy
Hypertrophy or atrophy of the affected limb is the most likely consequence of cutis marmorata
telangectatica congenita. Orthopedic evaluation should be a part of the patients routine management.
Q/Q(M)-473676 Report a Problem
Juvenile self-healing papular mucinosis is associated with which of the findings?
1
Arthralgias
2
Cataracts
3
Type I diabetes
4
Calcinosis cutis
5
Xeropthalmia
Q/Q(M)-482478 Report a Problem
Juvenile self-healing papular mucinosis is associated with which of the findings?
1
Arthralgias
Self-healing papular mucinosis is a rare disorder characterized by small, nontender, flesh-colored papules
commonly seen on the head, neck, trunk, and periarticular areas of children. Self-healing papular mucinosis
is associated with systemic findings during acute stages, including fever, arthralgias, weakness, and often
carpal tunnel syndrome. A handful of cases have been reported in adults, although systemic symptoms are
not typically found in this population.
Q/Q(M)-482478 Report a Problem
Which of the following syndromes is associated with development of giant cell epulides?
1
Cherubism
2
Gardner syndrome
3
Cowden syndrome
4
Multiple hamartoma syndrome
5
CHILD syndrome
Q/Q(M)-482834 Report a Problem
Which of the following syndromes is associated with development of giant cell epulides?
1
Cherubism
46
Cherubism is an autosomally-dominant inherited disorder characterized by asymptomatic fibro-osseous
hyperplasia and replacement of normal bone which commences in childhood. Typically the mandible is
affected, leading to progressive enlargement and swollen cherub-like cheeks. Similar involvement of
maxillary bones results in periorbital enlargement, resulting in the tendency of affected individuals to
look up towards the sky. Frequently the disorder is self-limited and self-regressive. Mutations in
SH3BP2 have been identified as a candidate gene defect. Affected individuals may also present with single
or multiple giant cell epulides (singular: epulis), which is a benign, bluish-red nodule arising on the
gingiva, near deciduous incisors or bicuspids. It bears histologic similarity to giant cell tumor of the tendon
sheath.
Q/Q(M)-482834 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Psoriasis
2
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
3
Seborrheic dermatitis
4
Contact dermatitis
5
Perianal streptococcal disease
Q/Q(M)-476793 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Psoriasis
The well-defined erythematous plaque is an example of psorisis in the diaper area. The moist nature of the
diaper environment results in a loss of the classic silvery scale.
Q/Q(M)-476793 Report a Problem
Neonatal acne is associated with species of which organism:
1
Staphylococcus
2
Propionibacterium
3
Candida
4
Malassezia
5
Streptococcus
Q/Q(M)-475879 Report a Problem
47
Neonatal acne is associated with species of which organism:
4
Malassezia
Acne which develops within the first 30 days of life is termed neonatal acne. Neonatal acne has a
predilection for the face, chest, back and groin appearing as small, discrete papules at 2 to 4 weeks of age,
and persisting for up to 8 months. As these lesions are self-resolving, no treatment is necessary, though
2.5% benzoyl peroxide may hasten resolution. Neonatal acne is quite common and is postulated to occur as
a result of hyperplasia of premature sebaceous glands coupled with transient increases in circulating
androgens. More recent data suggests that Malassezia species may be implicated at etiologic factors in
neonatal acne. These organisms have been cultured from the skin of affected patients, though their exact
role in unclear.
Q/Q(M)-475879 Report a Problem
Most common location of cutaneous lesions in neonatal lupus erythrematosus is
1
Cheeks
2
Nose
3
Scalp
4
Perioral
5
Periorbital
Q/Q(M)-482134 Report a Problem
Most common location of cutaneous lesions in neonatal lupus erythrematosus is
5
Periorbital
neonatal lupus erythrematosus(NLE) is a form of subacute cutaneous lupus erythrematosus(SCLE) that
occur in infants whose mothers have anti-Ro autoantibodies. Unlike SCLE in adults, lesions of NLE have a
predilection for the face especially periorbital region. Other sites include scalp, arms, legs, trunk and groin.
Q/Q(M)-482134 Report a Problem
A 3 month old baby girl is brought to your office for consultation. You note an infantile hemangioma on
the tip of the nose. Imaging reveals no underlying structural anomalies in the cerebro-vasculature. You
discuss starting propranolol. What side effect do you need to monitor for?
1
Hypertension
2
Hypercalcemia
3
Hypoglycemia
4
Tachycardia
5
Hypernatremia
Q/Q(M)-482515 Report a Problem
A 3 month old baby girl is brought to your office for consultation. You note an infantile hemangioma on
the tip of the nose. Imaging reveals no underlying structural anomalies in the cerebro-vasculature. You
discuss starting propranolol. What side effect do you need to monitor for?
3
Hypoglycemia
In the treatment of infantile hemangiomas with propranolol, the most common serious adverse effects are
bradycardia and hypotension. Other potential adverse effects include bronchospasm and hypoglycemia.
Sustained hypoglycemia in infancy has been associated with longterm neurologic sequelae. Infants with
very large hemangiomas or miliary hemangiomatosis are also at risk for high-output cardiac compromise.
Q/Q(M)-482515 Report a Problem
48
An infant presents with red-purple, granulomatous nodules occurring in the diaper area. The etiology is
secondary to local irritation, maceration and Candida albicans. What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Granuloma gluteale infantum
2
Langerhans cell histiocytosisc.
3
Seborrheic dermatitis
4
Biotin deficiency
5
Psoriasis
Q/Q(M)-473683 Report a Problem
An infant presents with red-purple, granulomatous nodules occurring in the diaper area. The etiology is
secondary to local irritation, maceration and Candida albicans. What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Granuloma gluteale infantum
The etiology of granuloma gluteale infantum is multifactorial, resulting from the unique environment of the
diaper area. Treatment consists of topical antifungal agents, barrier creams, and anti-inflammatory agents
as needed.
Q/Q(M)-473683 Report a Problem
The Carney complex is associated with a defect in:
1
PRKAR1A
2
LYST
3
PTEN
4
MASH2
5
MLH1
Q/Q(M)-473700 Report a Problem
The Carney complex is associated with a defect in:
1
PRKAR1A
A PRKAR1A gene defect is associated with the Carney complex.
Q/Q(M)-473700 Report a Problem
Koplik spots typically appear:
1
Before the exanthem
2
At the same time as the exanthem
3
1 week after the exanthem
4
6 weeks after the exanthem
5
8 weeks after the exanthem
Q/Q(M)-473693 Report a Problem
oplik spots typically appear:
1
Before the exanthem
The enanthem of measles precedes the morbilliform eruption.
Q/Q(M)-473693 Report a Problem
49
What is the diagnosis?
1
Transient neonatal pustular melanosis
2
Acropustulosis of infancy
3
Neonatal cphalic pustulosis
4
Miliaria
5
Erythema toxicum neonatorum
Q/Q(M)-476868 Report a Problem
What is the diagnosis?
3
Neonatal cphalic pustulosis
In neonatal cephalic pustulosis (neonatal acne), papules and pustules are present but comedones are absent.
Spontaneous remission occurs.
Q/Q(M)-476868 Report a Problem
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Psoriasis
2
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
3
Granuloma gluteale infantum
4
Contact dermatitis
5
Perianal streptococcal disease
Q/Q(M)-476438 Report a Problem
50
What is the most likely diagnosis?
5
Perianal streptococcal disease
The bright red erythema of perianal streptococcal disease can also involve the creases of the groin and
axillae.
Q/Q(M)-476438 Report a Problem
Hemangiomas of infancy are more likely to occur:
1
a. In males
2
b. In Asians
3
c. In children who are large for gestational age
4
d. In multiple gestation
5
e. In post term infants
Q/Q(M)-482873 Report a Problem
Hemangiomas of infancy are more likely to occur:
4
d. In multiple gestation
D. is Correct. Hemangiomas of infancy occur more commonly in girls, in Caucasians, in babies who are
premature and low birth weight. They are more likely to occur in multiple gestation
Q/Q(M)-482873 Report a Problem
A 6 month-old presents with orange-brown crusted plaques around the mouth and groin. Several bullae are
present on the fingers and toes. Which of the following laboratory values is likely to be abnormal?
1
Hematocrit
2
Calcium
3
Platelet count
4
ALT
5
Alkaline phosphatase
Q/Q(M)-473679 Report a Problem
A 6 month-old presents with orange-brown crusted plaques around the mouth and groin. Several bullae are
present on the fingers and toes. Which of the following laboratory values is likely to be abnormal?
5
Alkaline phosphatase
The most likely diagnosis is acrodermatitis enteropathica. Alkaline phosphatase is a zinc dependant
enzyme that is decreased in response to low serum zinc levels.
Q/Q(M)-473679 Report a Problem
Trichothiodystrophy classically includes which of the following findings:
1
Trichostasis
2
Trichoschisis
3
Pili torti
4
Trichorrhexis invaginata
5
Trichorrhexis nodosa
Q/Q(M)-476262 Report a Problem
Trichothiodystrophy classically includes which of the following findings:
51
2
Trichoschisis
Trichothiodystrophy or PIBIDS is associated with the tiger-tail abnormality of trichoschisis.
Q/Q(M)-476262 Report a Problem
Slapped cheeks followed by a lacy eruption on extremities:
1
ssDNA virus
2
dsDNA virus
3
ssRNA virus
4
dsRNA virus
5
Streptococcus
Q/Q(M)-473692 Report a Problem
Slapped cheeks followed by a lacy eruption on extremities:
1
ssDNA virus
The erythematous eruption on the cheeks precedes the generalized lacy rash of Fifth disease. The causative
agent is parvovirus B19, a single stranded DNA virus.
Q/Q(M)-473692 Report a Problem
Which of the following bullous disorders is due to a target antigen that is a 97 kD protein which is a
member of BPAG-2?
1
Bullous Dermolysis of the Newborn
2
Neonatal Pemphigus
3
Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis
4
Junctional epidermolysis bullosa (Herlitz)
5
Epidermolysis bullosa simplex
Q/Q(M)-477809 Report a Problem
Which of the following bullous disorders is due to a target antigen that is a 97 kD protein which is a
member of BPAG-2?
3
Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis
Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis is due to a target antigen that is a 97 kD protein which is a member of
BPAG-2. Transient bullous dermolysis of the newborn is due to a transient defect in intracytoplasmic
packaging or in the transport of type VII collagen within basal keratinocytes. Neonatal pemphigus is due to
maternal transfer of IgG antibodies reacting to Desmoglein 3 (pemphigus vulgaris). Epidermolysis bullosa
simplex is due to keratin 5/14 abnormalities and junctional EB (Herlitz) is due to defects in Laminin 5.
Q/Q(M)-477809 Report a Problem
A newborn presents with a pustular rash, joint swelling, oral mucosal lesions, and pain with movement.
Over time, cutaneous pustulosis, ranging from discrete crops of pustules to generalized severe pustulosis
and ichthyosiform lesions develop. In addition the newborn develops sterile multifocal osteomyelitis and
periostitis. What is this condition?
1
Muckle-Wells syndrome
2
Deficiency of the interleukin-1-receptor antagonist (DIRA)
3
Familial Mediterranean fever
4
Hyper-IgD syndrome
52
5
PAPA syndrome
Q/Q(M)-482549 Report a Problem
A newborn presents with a pustular rash, joint swelling, oral mucosal lesions, and pain with movement.
Over time, cutaneous pustulosis, ranging from discrete crops of pustules to generalized severe pustulosis
and ichthyosiform lesions develop. In addition the newborn develops sterile multifocal osteomyelitis and
periostitis. What is this condition?
2
Deficiency of the interleukin-1-receptor antagonist (DIRA)
This condition is deficiency of the interleukin-1-receptor antagonist (DIRA) and due to a mutation in the
IL1RN gene. Muckle-Wells syndrome is due to a mutation in the CIAS1 gene and presents with
sensorineural deafness, recurrent hives, and amyloidosis. Familial Mediterranean fever is most often due to
a mutation in the MEFV gene. Hyper-IgD syndrome is a rare periodic fever syndrome characterised by
attacks of fever, arthralgia, skin lesions including cyclical mouth ulcers, and diarrhea due to mutations in
the mevalonate kinase gene. PAPA syndrome presents with pyogenic arthritis, pyoderma gangrenosum and
acne and is associated with mutations in the CD2 binding protein 1 (CD2BP1).
Q/Q(M)-482549 Report a Problem
Which of the following disorders is more likely to occur in children with chronic fecal incontinence?
1
Langerhans cell histiocytosis
2
Perianal pseudoverrucous papules and nodules
3
Perianal streptococcal disease
4
Granuloma gluteale infantum
5
Seborrheic dermatitis
Q/Q(M)-473685 Report a Problem
Which of the following disorders is more likely to occur in children with chronic fecal incontinence?
2
Perianal pseudoverrucous papules and nodules
The warty papules of perianal pseudoverrucous papules and nodules are seen more commonly in the setting
of chronic fecal incontinence.
Q/Q(M)-473685 Report a Problem
A 12 y/o female with autoimmune hepatitis on oral prednisone now with eruption on the face for 3 weeks.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1
Tinea facei
2
Acne vulgaris
3
Keratosis pilaris
4
Pityrosporum Folliculitis
5
Diagnosis not listed
Q/Q(M)-482890 Report a Problem
A 12 y/o female with autoimmune hepatitis on oral prednisone now with eruption on the face for 3 weeks.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
4
Pityrosporum Folliculitis
It presents as 1-2mm pruritic monomorphic papules and pustules on chest, back, upper arms, sometimes
53
face. The presence of pruritus may help to distinguish this entity from acne. It has been associated with oral
cortico-steroid use, diabetes and other immune suppressed states.
Q/Q(M)-482890 Report a Problem
Which of the following diseases with immunodeficiency has an increased risk of lymphoreticular
malignancy?
1
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
2
Chronic granulomatous disease
3
Job syndrome
4
Severe combined immunodeficiency syndrome
5
Leiners disease
Q/Q(M)-477213 Report a Problem
Which of the following diseases with immunodeficiency has an increased risk of lymphoreticular
malignancy?
1
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome is an X-linked recessive disorder caused by mutations in WAS gene. Patients
with Wiskott-Aldrich have atopic dermatitis with increased risks for secondary infection,
thrombocytopenia, and recurrent bacterial infections. They are also at an increased risk for lymphoreticular
malignancy (20%).
Q/Q(M)-477213 Report a Problem
The standard of care of patients with acute Kawasakis disease is:
1
Prednisone
2
Supportive care
3
Aspirin and IVIG
4
Penicillin
5
Acetaminophen and IVIG
Q/Q(M)-477150 Report a Problem
The standard of care of patients with acute Kawasakis disease is:
3
Aspirin and IVIG
Kawasaki disease, also called mucocutaneous lymph node syndrome, is an acute febrile disorder based on
the clinical criteria of changes in peripheral extremities, polymorphous exanthema, conjunctival injection
without exudates, changes in the lips or oral cavity, acute cervical lymphadenopathy. Fever must be
present, lasting more than 5 days. Treatment is aimed to prevent coronary aneurysms and myocardial
infarction. Treatment for acute Kawasaki disease is intravenous immunoglobulin 2 g/kg over 10-12 hours
and aspirin therapy.
Q/Q(M)-477150 Report a Problem
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Genodermatosis MCQsDocument152 paginiGenodermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- General Dermatology MCQsDocument197 paginiGeneral Dermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed95% (19)
- Cutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Diseaes MCQsDocument58 paginiCutaneous Manifestations of Systemic Diseaes MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Geno MCQDocument60 paginiGeno MCQalh bashar100% (1)
- Histopathology ETASDocument89 paginiHistopathology ETASDr.Tawheed75% (4)
- An Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDocument111 paginiAn Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed67% (6)
- Skin Tumor MCQDocument73 paginiSkin Tumor MCQDr.Tawheed92% (13)
- MCQ DermatologyDocument2 paginiMCQ DermatologyDr.Tawheed100% (7)
- Derma MCQ Ch01Document20 paginiDerma MCQ Ch01Rasha Dabbagh75% (4)
- Med Dermatology Questions-75Document67 paginiMed Dermatology Questions-75Khalifa AL-Wishahi75% (4)
- Dermatology MCQ With AnswersDocument27 paginiDermatology MCQ With Answershesham0% (1)
- Quiz Review Exam ETASDocument183 paginiQuiz Review Exam ETASDr.Tawheed92% (12)
- Immunedermatology MCQsDocument73 paginiImmunedermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Vesicular and Bullous Dermatosis MCQsDocument59 paginiVesicular and Bullous Dermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- 11Document3 pagini11faresaltaii100% (2)
- Dermatology MCQ With ExplinationsDocument46 paginiDermatology MCQ With ExplinationsheshamÎncă nu există evaluări
- DermatologyDocument17 paginiDermatologyEbn Seena75% (4)
- Dermatology RecertificatDocument8 paginiDermatology RecertificatKhalifa AL-WishahiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dermatology QuizDocument7 paginiDermatology QuizFaddy OrahaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)Document17 paginiMCQ IN DERMATOLOGY NMT 08 - مركز إبن الاسلام ... (20ebooks.com)R Ratheesh100% (9)
- Dermatology MCQ 1700Document45 paginiDermatology MCQ 1700Dr-Jahanzaib Gondal100% (1)
- Photodermatology MCQsDocument53 paginiPhotodermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Mcqs of Icthyosis With KeyDocument7 paginiMcqs of Icthyosis With KeysaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part I 2016 - Dermatology MCQDocument9 paginiPart I 2016 - Dermatology MCQEmma Dawod100% (1)
- Dermatology MCQDocument9 paginiDermatology MCQNiwashiny CnyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dermatology QuestionsDocument3 paginiDermatology QuestionsMuziki Wa KiafrikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Document31 paginiMCQ Dermatology (Dr. Asaf K.)Dinesh JadhavÎncă nu există evaluări
- DermatologyDocument121 paginiDermatologyjimisurgon83100% (4)
- MCQ Derm1Document5 paginiMCQ Derm1hesham100% (4)
- ETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Document672 paginiETAS MCQ 2015 - Derm-In-Review Volume 1Muhammad Javed Gaba100% (1)
- MCQ DermatologyDocument42 paginiMCQ Dermatologydraik71100% (5)
- Dermatology MCQ FRCPDocument101 paginiDermatology MCQ FRCPhesham89% (19)
- Dermatology Essay QuestionsDocument2 paginiDermatology Essay QuestionsPeter Abikoye100% (1)
- Dermatology QuestionsDocument19 paginiDermatology QuestionsBenjamin Nelson50% (2)
- MCQs Ch07-45651100rdzDocument27 paginiMCQs Ch07-45651100rdzKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (2)
- Derma CD McqsDocument22 paginiDerma CD McqsheshamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prometric Book 2nd EditionDocument207 paginiPrometric Book 2nd Editionsajitha100% (2)
- Dermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2Document56 paginiDermatology Postgraduate MCQs and Revision Notes2hesham50% (2)
- Photo QuizDocument21 paginiPhoto Quizabas_maytham1021100% (3)
- Dermatology Quiz 2015 AnswersDocument40 paginiDermatology Quiz 2015 Answerspoorva shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dermatology Written Exam 2007Document6 paginiDermatology Written Exam 2007Abdullah Matar BadranÎncă nu există evaluări
- DermatologyDocument3 paginiDermatologyDrkhslid890% (1)
- Dermatopathology Q - ADocument55 paginiDermatopathology Q - AKhalifa AL-Wishahi100% (7)
- End Round of Dermatology, MCQsDocument20 paginiEnd Round of Dermatology, MCQsMuhdZaeed100% (2)
- Dermatology QuizDocument10 paginiDermatology QuizSyed Ali Haider0% (1)
- Pics MCQSDocument22 paginiPics MCQStania100% (1)
- Basic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDocument92 paginiBasic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (16)
- Dermatology Board Review 2007 Part 3Document42 paginiDermatology Board Review 2007 Part 3hifuka100% (1)
- Dermatology MnemonicDocument16 paginiDermatology MnemonicAhmed RamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prometric Exam March 2020Document250 paginiPrometric Exam March 2020Sally dossÎncă nu există evaluări
- Derma MCQ Ch01 PDFDocument20 paginiDerma MCQ Ch01 PDFShah NawazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viva Questions DermatologyDocument5 paginiViva Questions DermatologyRavva0% (1)
- 1-Dermatological Case PresentationDocument41 pagini1-Dermatological Case Presentationnaimat007Încă nu există evaluări
- 101-Normal Skin MCQsDocument25 pagini101-Normal Skin MCQsHybat ElsheikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dermatology MCQDocument18 paginiDermatology MCQR Ratheesh100% (2)
- Genetics 50qDocument62 paginiGenetics 50qAnonymous 4txA8N8etÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMJ Mcqs+Key To RMBR 14-09-2023Document13 paginiBMJ Mcqs+Key To RMBR 14-09-2023Kiran ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Pearls DermatologíamatologyDocument4 paginiClinical Pearls DermatologíamatologyMaritza24Încă nu există evaluări
- Keratitis NeurotropikDocument9 paginiKeratitis NeurotropikHengky_FandriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology MCQsDocument88 paginiPharmacology MCQsDr.Tawheed86% (7)
- Photodermatology MCQsDocument53 paginiPhotodermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (8)
- Hair and Nail Disorders MCQsDocument67 paginiHair and Nail Disorders MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Vesicular and Bullous Dermatosis MCQsDocument59 paginiVesicular and Bullous Dermatosis MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (8)
- Skin Tumor MCQDocument73 paginiSkin Tumor MCQDr.Tawheed92% (13)
- Immunedermatology MCQsDocument73 paginiImmunedermatology MCQsDr.Tawheed90% (10)
- Plant and Creature of Dermatological Significance MCQsDocument50 paginiPlant and Creature of Dermatological Significance MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (2)
- Mycology MCQsDocument48 paginiMycology MCQsDr.Tawheed100% (11)
- Dermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryDocument77 paginiDermatologic and Cosmetic SurgeryDr.Tawheed100% (3)
- MCQ DermatologyDocument2 paginiMCQ DermatologyDr.Tawheed100% (7)
- Basic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDocument92 paginiBasic Science and Sructure of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed88% (16)
- Quiz Review Exam ETASDocument183 paginiQuiz Review Exam ETASDr.Tawheed92% (12)
- An Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDocument111 paginiAn Infectious Disease of Skin MCQsDr.Tawheed67% (6)
- BP TB A2PlusDocument209 paginiBP TB A2PlusTAMER KIRKAYA100% (1)
- Engineeringinterviewquestions Com Virtual Reality Interview Questions Answers PDFDocument5 paginiEngineeringinterviewquestions Com Virtual Reality Interview Questions Answers PDFKalyani KalyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- W 26728Document42 paginiW 26728Sebastián MoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Print Isang Beses LangDocument11 paginiPa Print Isang Beses LangGilbert JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gee 103 L3 Ay 22 23 PDFDocument34 paginiGee 103 L3 Ay 22 23 PDFlhyka nogalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Behavioral Interview QuestionsDocument3 paginiSample Behavioral Interview QuestionssanthoshvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Port of Surigao Guide To EntryDocument1 paginăPort of Surigao Guide To EntryNole C. NusogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roman Roads in Southeast Wales Year 3Document81 paginiRoman Roads in Southeast Wales Year 3The Glamorgan-Gwent Archaeological Trust LtdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rebecca Young Vs CADocument3 paginiRebecca Young Vs CAJay RibsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entrep Bazaar Rating SheetDocument7 paginiEntrep Bazaar Rating SheetJupiter WhitesideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Document11 paginiAlice (Alice's Adventures in Wonderland)Oğuz KarayemişÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Document37 paginiNutrition and Metabolism: (Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein)Trishia BonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narcissist's False Self vs. True Self - Soul-Snatching - English (Auto-Generated)Document6 paginiNarcissist's False Self vs. True Self - Soul-Snatching - English (Auto-Generated)Vanessa KanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- JD For Library Interns Sep 2023Document2 paginiJD For Library Interns Sep 2023Bharat AntilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logo DesignDocument4 paginiLogo Designdarshan kabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- RSA ChangeMakers - Identifying The Key People Driving Positive Change in Local AreasDocument29 paginiRSA ChangeMakers - Identifying The Key People Driving Positive Change in Local AreasThe RSAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charles P. Jones, Investments: Analysis and Management, Eleventh Edition, John Wiley & SonsDocument20 paginiCharles P. Jones, Investments: Analysis and Management, Eleventh Edition, John Wiley & SonsRizki AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSC in Healthcare Management (Top-Up) Degree From ARU - Delivered Online by LSBR, UKDocument19 paginiMSC in Healthcare Management (Top-Up) Degree From ARU - Delivered Online by LSBR, UKLSBRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Financial PlanDocument38 paginiSample Financial PlanPatrick IlaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Comprehensive Guide To HR Best Practices You Need To Know This Year (Infographic)Document42 paginiA Comprehensive Guide To HR Best Practices You Need To Know This Year (Infographic)MALATHI MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Security Questions in UPSC Mains GS 3 2013 2020Document3 paginiSecurity Questions in UPSC Mains GS 3 2013 2020gangadhar ruttalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tangazo La Kazi October 29, 2013 PDFDocument32 paginiTangazo La Kazi October 29, 2013 PDFRashid BumarwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept of HalalDocument3 paginiConcept of HalalakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasDocument30 paginiNetwork Function Virtualization (NFV) : Presented By: Laith AbbasBaraa EsamÎncă nu există evaluări
- TEsis Doctoral en SuecoDocument312 paginiTEsis Doctoral en SuecoPruebaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL LayoutDocument4 paginiDLL LayoutMarife GuadalupeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9francisco Gutierrez Et Al. v. Juan CarpioDocument4 pagini9francisco Gutierrez Et Al. v. Juan Carpiosensya na pogi langÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics Experiment No 1 Specific Gravity of LiquidsDocument3 paginiHydraulics Experiment No 1 Specific Gravity of LiquidsIpan DibaynÎncă nu există evaluări
- SANDHU - AUTOMOBILES - PRIVATE - LIMITED - 2019-20 - Financial StatementDocument108 paginiSANDHU - AUTOMOBILES - PRIVATE - LIMITED - 2019-20 - Financial StatementHarsimranSinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- De Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Document106 paginiDe Luyen Thi Vao Lop 10 Mon Tieng Anh Nam Hoc 2019Mai PhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossDe la EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsDe la EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeDe la EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityDe la EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (24)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaDe la EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (42)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedDe la EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (80)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDDe la EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Self-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!De la EverandSelf-Care for Autistic People: 100+ Ways to Recharge, De-Stress, and Unmask!Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsDe la EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.De la EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (110)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerDe la EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (392)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityDe la EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsDe la EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (169)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryDe la EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessDe la EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (328)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsDe la EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisDe la EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Sleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningDe la EverandSleep Stories for Adults: Overcome Insomnia and Find a Peaceful AwakeningEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- Gut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)De la EverandGut: The Inside Story of Our Body's Most Underrated Organ (Revised Edition)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (378)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceDe la EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (51)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlDe la EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (58)