Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
Încărcat de
api-264090670Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes
Încărcat de
api-264090670Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
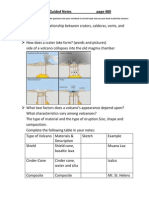
What is the relationship between craters, calderas, vents, and
magma? Craters, calderas, vents, and magma all are formed due
to a volcano
How does a crater lake form? (words and pictures)A crater lake is
formed when the summit or side of a volcano collapses into the
magma chamber that once fueled the volcano
What two factors does a volcanos appearance depend upon? The
type of material that forms the volcano, and the type of eruptions
that occur.
What characteristics vary among volcanoes? Each volcano differs
in size, shape, and composition.
Complete the following table in your notes:
Type of
Volcano
Materials &
Description
Sketch Example
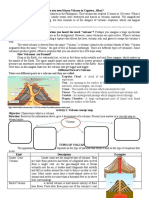
Shield
A mountain with
broad, gently
sloping sides and
a nearly circular
base. Shield
volcanoes form
when layer upon
layer of basaltic
lave accumulates
during non
explosive
eruptions.
Mauna
Loa
which is
on a
Hawaii
Island
Cinder-Cone
Form when
material is
ejected high into
the air falls back
to Earth and
piles up around
the vent. These
volcanoes have
steep sides and
are mostly less
Izalco
volcano
in El
Savador
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
than 500m high.
They contain
magma that has
more water and
silica which
makes cinder-
cone volcanoes
more explosive
in nature.
Composite
(Stratovolcano)
Composite
volcanoes form
when layers of
volcanic
fragments
alternate with
lava. Composite
volcano magma
has the same
composition as
Cinder-cone
magma.
Composite
volcanoes are
large and are
potentially
dangerous to
humans and the
environment.
Mount
St.
Helens
How do the volcanoes compare in terms of size and slope? Shield
volcanoes are the largest, and then composite, and then cinder-
cone volcanoes.
What factors cause differences in size and slope? Some factors
that cause differences in size and slope are materials that make
up volcano, vegetation on volcanoes slope, local climate, and
eruptive history of the volcano.
What is tephra? Tephra is rock fragments that are thrown into the
air during a volcanic eruption.
Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes page 480
Do not write on this copy. Transfer the questions into your notebook in Cornell style and use your book to find the answers.
What is a pyroclastic flow? Pyroclastic flow is rapidly moving
volcanic material.
Where are most volcanoes found? Most volcanoes form at plate
boundaries. Most volcanoes are found on two distinct volcanic
belts, the Circum-Pacific belt and the Mediterranean belt.
Use the maps provided to show: (1) the Circum Pacific Belt and the
Mediterranean Belt where convergent volcanism occur and (2) the
Hawaiian Emperor Volcanic Chain.
How do hotspots form? Hot spots are unusually hot regions of
Earths mantle where high temperature plumes of mantle
material rise toward the surface.
What do hotspots tell us about tectonic plates? Hotspots tell us
important provide important information about plate
tectonics. The rate and direction of motion can be calculated
from the positions of these volcanoes.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330464848Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330050027Încă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes NotesDocument4 paginiVolcanoes Notesapi-264874516Încă nu există evaluări
- Volcano Guided NotesDocument4 paginiVolcano Guided Notesapi-330490538100% (1)
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument2 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264220672Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument4 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330049909Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument4 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330085018Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of VolcanoesDocument3 paginiTypes of Volcanoesapi-265544103Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330049903Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument3 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-264099976Încă nu există evaluări
- Voolcanoes Guided NotesDocument3 paginiVoolcanoes Guided Notesapi-264885511Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330092916Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument4 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330042011Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument5 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330050095Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided Notes 1Document4 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notes 1api-330067833Încă nu există evaluări
- Types of Volcanoes Guided NotesDocument4 paginiTypes of Volcanoes Guided Notesapi-330102217Încă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesDe la EverandVolcanoes The Ultimate Book: Experience the Heat, Power, and Beauty of VolcanoesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateDocument11 paginiMary Drury - VOLCANOES TemplateMary DruryÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoDocument78 paginiVolcanoGen BautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanic LandformDocument12 paginiVolcanic LandformJoseph ZotooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wonders of Creation: A Descriptive Account of Volcanoes and Their PhenomenaDe la EverandWonders of Creation: A Descriptive Account of Volcanoes and Their PhenomenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcano: Go To Australian Volcanos Go To Volcanic Hazards and Case Studies Go To Volcano TypesDocument14 paginiVolcano: Go To Australian Volcanos Go To Volcanic Hazards and Case Studies Go To Volcano TypesTulika ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A VolcanoDocument3 paginiWhat Is A VolcanoDarlyn Llabore SueltoÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoesDocument8 paginiVolcanoesShah KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes EarthquakeDocument83 paginiVolcanoes EarthquakeMeshal M ManuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Volcano?: Mount Fuji in Japan, and Mount Rainier, Washington, U.S.ADocument2 paginiWhat Is A Volcano?: Mount Fuji in Japan, and Mount Rainier, Washington, U.S.ADarlyn Llabore SueltoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleDocument18 paginiScience9 Q3 Week1 Romo AmabelleGrace OroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Power PointDocument18 paginiScience Power PointpatriciangbenaohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quarter 3 - Module 1 VOLCANOESDocument39 paginiQuarter 3 - Module 1 VOLCANOESRubeliza LawengÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoDocument3 paginiVolcanoRhienzane L. MarasiganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcano WebquestDocument3 paginiVolcano WebquestRichard Muchow100% (1)
- Types of VolcanoesDocument21 paginiTypes of VolcanoesAgaManlapazMacasaquitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science VolcanoDocument48 paginiScience Volcanojosemaria tabliganÎncă nu există evaluări
- This Article Is About The Geological Feature. For Other Uses, See and - For Broader Coverage of This Topic, SeeDocument27 paginiThis Article Is About The Geological Feature. For Other Uses, See and - For Broader Coverage of This Topic, SeeMichael FelicianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoDocument84 paginiVolcanoJM LomoljoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of VolcanoesDocument15 paginiTypes of VolcanoesSally PocamasÎncă nu există evaluări
- VOLCANOESDocument10 paginiVOLCANOESYesha ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoesDocument75 paginiVolcanoesMeleen ConstantinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forces Within The EarthDocument56 paginiForces Within The EarthTHE HATE FARMERÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Study Guide: Volcanoes and Volcanic Activity: ObjectivesDocument7 paginiLecture Notes Study Guide: Volcanoes and Volcanic Activity: ObjectivesRonaldo ManaoatÎncă nu există evaluări
- VOLCANESDocument10 paginiVOLCANESJahnisel A. CordovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes NotesDocument13 paginiVolcanoes NotesNavya RaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Types of Volcanic ConesDocument2 pagini3 Types of Volcanic ConesKirsten Colin BermejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Different Types of VolcanoesDocument3 paginiWhat Are The Different Types of VolcanoesBenes Salamanca BolascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary Volcanic Landforms: Shan de SilvaDocument25 paginiPrimary Volcanic Landforms: Shan de SilvaAlvaro Zavala VásquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- For Earth Science !! 33Document91 paginiFor Earth Science !! 33art2rugraceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes, Frankenstein, and The ScreamDocument33 paginiVolcanoes, Frankenstein, and The ScreamAishwarya KokateÎncă nu există evaluări
- VOLCANODocument69 paginiVOLCANOchristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Science Reviewer VolcanoesDocument7 paginiEarth Science Reviewer VolcanoesAndrea Grace Bayot AdanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Types of VolcanoesDocument9 pagini5 Types of VolcanoesQasim IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualDocument11 paginiEarth Science Tarbuck 14th Edition Solutions ManualAntonioCohensirt100% (32)
- Types of VolcanoesDocument26 paginiTypes of VolcanoesMatt PayawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre-Assessment: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerDocument60 paginiPre-Assessment: Choose The Letter of The Best AnswerheartÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explosions. Materials, Such As Magma, Can EscapeDocument2 paginiExplosions. Materials, Such As Magma, Can EscapeAlexis John Hisula VillahermosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolvanoDocument6 paginiVolvanoZarinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4: Volcanism: After Having Learnt This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToDocument4 paginiChapter 4: Volcanism: After Having Learnt This Chapter, You Should Be Able ToVaansh DhirwaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of VolcanoesDocument5 paginiClassification of Volcanoesmark.mendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acid Rain Virtual Lab Worksheet 1Document4 paginiAcid Rain Virtual Lab Worksheet 1api-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- Climate Notes Glencoe 14 1 14 2Document3 paginiClimate Notes Glencoe 14 1 14 2api-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- Atmosphere Basics Websquest 2Document3 paginiAtmosphere Basics Websquest 2api-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- Airmassandfrontsawebquest 4Document4 paginiAirmassandfrontsawebquest 4api-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Lab-Water QualityDocument7 paginiVirtual Lab-Water Qualityapi-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- Recyclecity FinalDocument2 paginiRecyclecity Finalapi-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- Earthquake Guided NotesDocument3 paginiEarthquake Guided Notesapi-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- SeasonswebquestDocument3 paginiSeasonswebquestapi-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- Rocks and Minerals Webquest 3Document4 paginiRocks and Minerals Webquest 3api-264090670Încă nu există evaluări
- Volcano Destabilization by Magma InjectiDocument5 paginiVolcano Destabilization by Magma Injecticarlos camargoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Q SCIENCE 9Document15 pagini3rd Q SCIENCE 9marvin agubanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of VolcanoesDocument38 paginiEffects of Volcanoesmonch1998Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan Viscosity RaceDocument2 paginiLesson Plan Viscosity RaceQueencess Ara TorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 Quarter 3 - Module 1Document9 paginiScience 9 Quarter 3 - Module 1HPLaptop ReymarkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science9 Q3 SLM2Document15 paginiScience9 Q3 SLM2Zandra Musni Delos ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- OLD1 - Earth Lab Volcanoes FillableDocument2 paginiOLD1 - Earth Lab Volcanoes FillableNeon ZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1: Statements ExpectationDocument12 paginiLesson 1: Statements ExpectationNeneth Saguin SionomioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 04Document5 paginiWorksheet 04Kartavya Jhunjhunwala 9AÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolcanoesDocument36 paginiVolcanoesjhoms8Încă nu există evaluări
- Science9 q3 Mod1 Week1 typesofvolcanoandvolcaniceruptions-LOCALLY-DEVELOPED-MODULESDocument32 paginiScience9 q3 Mod1 Week1 typesofvolcanoandvolcaniceruptions-LOCALLY-DEVELOPED-MODULESSubicAmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcano ReviewerDocument3 paginiVolcano ReviewerKelvin Ignacio100% (1)
- Chapter 9 VolcanoesDocument19 paginiChapter 9 VolcanoesaaahhhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q3M1 Regular Science FVRNHS Volcanoes PDFDocument25 paginiQ3M1 Regular Science FVRNHS Volcanoes PDFJensen Kay NorteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Q3 SciDocument20 pagini1 - Q3 Scimaximo meridaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson Plan in Science Type of VolcanoesDocument8 paginiDetailed Lesson Plan in Science Type of Volcanoesirene ilustrisimo92% (13)
- Division School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesDocument11 paginiDivision School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesKwen Ann OrtigzÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Rs Final Mineral ReportDocument95 paginiAn Rs Final Mineral ReportYohannes Woldekidan100% (3)
- Volcano DataDocument30 paginiVolcano DataAbdul Haris Manggala PutraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes Definition TypesDocument62 paginiVolcanoes Definition TypesNota BelzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dissertation On Effects of Earthquake, Volcano & TsunamiDocument217 paginiDissertation On Effects of Earthquake, Volcano & TsunamiumzzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailed Lesson PlanDocument7 paginiDetailed Lesson PlanIrish Buaya Gementiza100% (1)
- Strategic Intervention Material VolcanoDocument26 paginiStrategic Intervention Material VolcanoShena Jalalon Peniala100% (2)
- QUARTER 3 Summative Test G9Document6 paginiQUARTER 3 Summative Test G9Angelita MenesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 9-Q3 M-EDocument3 paginiScience 9-Q3 M-Enelson dante jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- Volcanoes HandoutsDocument30 paginiVolcanoes HandoutssamanthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- - - What is a volcano - نسخةDocument13 pagini- - What is a volcano - نسخةSafa AlzamelÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Volcano?Document4 paginiWhat Is A Volcano?Sriram SusarlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appsc Static Quiz - 2023Document115 paginiAppsc Static Quiz - 2023tejeswararaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal Latihan Simulasi Un Bahasa Inggris (Ahmad)Document9 paginiSoal Latihan Simulasi Un Bahasa Inggris (Ahmad)AsepÎncă nu există evaluări