Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Phe Presentation
Încărcat de
api-240613752Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Phe Presentation
Încărcat de
api-240613752Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Excessive Carbohydrate
Intake
Agung, Audrey, Deo
9.2
Physical and Health Education
Types of Carbohydrate Foods
Excessive Fat / Obesity
Fat stores up in the body
Increased chance of stroke, blood pressure
related problems, blood vessel damage, heart
attack or heart failure, and kidney failure
PREVENTION
Eat healthy food (fruits and vegetables), less junk
food, more exercise
RISK FACTORS
Not enough rest/sleep
Blood Glucose
Blood glucose is caused by the
consumption of a lot of carbohydrates.
Causes diabetes (type 2 diabetes)
Over a year, muscles and cells inside your
body will stop responding and it will make
like Insulin Resistance
Insulin is like a hormone produced in the
pancreas which stable the sugar in your
body and by insulin resistance, diabetes
can happen.
GI Distress
Gastrointestinal Distress
Bloating
Constipation
Heartburn
Indigestion
Intensive exercise
Prevention:
Stay hydrated
Less intake of carbohydrates
Increased Cancer Risk
Gallbladder
Kidney
Colon (women)
Cervix (women)
Thyroid
Ovary (women)
Breast (women)
Rectum
Atherosclerosis
Plaque builds up in the arteries.
Made up of fat, cholesterol, calcium
Hardens and narrows
Limits flow
Leads to heart attack/CHD, stroke,
death
RISK FACTORS
No physical activity, constant
smoking, unhealthy diet
Testimony
Although people are aware that obesity has adverse health
consequences...mostly seen as negatively affecting physical appearance...few
people realise that without proper diet and exercise they put themselves at risk
of many types of cancer, and premature illness or death.
Dr Sawsan Al Madhi (secretary general of Friends of
Cancer
Patients society)
The higher the body mass index of a person, the higher the risk of cancer is in
general and in certain site-specific cancers.
Dr Andre Rizk (chief of medical oncology at Gulf
International
Cancer Centre in Abu Dhabi)
Works Cited
"Carbohydrates and Blood Sugar." The Nutrition Source. Web. 29 Sept. 2014.
<http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/carbohydrates/carbohydrates-and-blood-sugar/>.
"Diabetes." Jamaica Scientific Research Institute. N.p., n.d. Web. 01 Oct. 2014.
<http://www.jascires.com/diabetes.html>."Obesity Causes." Obesity Prevention Source. Web. 29 Sept.
2014. <http://www.hsph.harvard.edu/obesity-prevention-source/obesity-causes/>.
"GASTROINTESTINAL DISTRESS."GASTROINTESTINAL DISTRESS. N.p., n.d. Web. 1 Aug. 2014.
<http://www.endurancedoc.com/Racing/Racing_Gastrointestinal_Distress.htm>.
How Does Insulin Work?" How Insulin Works. N.p., n.d. Web. 28 Sept. 2014.
<http://www.lillydiabetes.com/Pages/how-does-insulin-work.aspx>.
Rizvi, Anam. "Obesity Increases Vulnerability to Cancer, Say UAE Doctors."The National. Abu Dhabi
Media, 6 Sept. 2014. Web. 28 Sept. 2014. <http://www.thenational.ae/uae/health/obesity-increases-
vulnerability-to-cancer-say-uae-doctors>.
Swan, Teal. "The Cause of Obesity." Teals Blog. Web. 01 Oct. 2014.
<http://blog.thespiritualcatalyst.com/the-cause-of-obesity/>.
"What Is Atherosclerosis?" NHLBI, NIH. National Institutes of Health, 01 June 2011. Web. 26 Sept. 2014.
<http://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/health-topics/topics/atherosclerosis/>.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Detox for Women: An All New Approach for a Sleek Body and Radiant Health in 4 WeeksDe la EverandDetox for Women: An All New Approach for a Sleek Body and Radiant Health in 4 WeeksEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Body Weight Loss for Your Well Being: Through Helpful Medicinal Alkaline Diets, Water & Herbs to Vitalize, Detox, Cleanse, Remove Plus Fats From Your Body & Free From DiseasesDe la EverandBody Weight Loss for Your Well Being: Through Helpful Medicinal Alkaline Diets, Water & Herbs to Vitalize, Detox, Cleanse, Remove Plus Fats From Your Body & Free From DiseasesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oversaturated: A Guide to Conversations About Fats With Your PatientsDe la EverandOversaturated: A Guide to Conversations About Fats With Your PatientsÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to Choose Types of Diets: The Best Guide on Types of Healthy and Losing Weight DietsDe la EverandHow to Choose Types of Diets: The Best Guide on Types of Healthy and Losing Weight DietsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Insulin Resistance Solution: Reverse Pre-Diabetes, Repair Your Metabolism, Shed Belly Fat, Prevent DiabetesDe la EverandThe Insulin Resistance Solution: Reverse Pre-Diabetes, Repair Your Metabolism, Shed Belly Fat, Prevent DiabetesEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Contents:: 200 Vegan Health StudiesDocument25 paginiContents:: 200 Vegan Health StudiesCaron RussÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Low-GI Slow Cooker: Delicious and Easy Dishes Made Healthy with the Glycemic IndexDe la EverandThe Low-GI Slow Cooker: Delicious and Easy Dishes Made Healthy with the Glycemic IndexÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fresh & Healthy DASH Diet Cooking: 101 Delicious Recipes for Lowering Blood Pressure, Losing Weight and Feeling GreatDe la EverandFresh & Healthy DASH Diet Cooking: 101 Delicious Recipes for Lowering Blood Pressure, Losing Weight and Feeling GreatÎncă nu există evaluări
- American Medical Association Complete Guide to Prevention and Wellness: What You Need to Know about Preventing Illness, Staying Healthy, and Living LongerDe la EverandAmerican Medical Association Complete Guide to Prevention and Wellness: What You Need to Know about Preventing Illness, Staying Healthy, and Living LongerEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- The Effective Mediterranean Diet for Beginners: A Complete Guide Plus 60 Easy & Delicious RecipesDe la EverandThe Effective Mediterranean Diet for Beginners: A Complete Guide Plus 60 Easy & Delicious RecipesEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (4)
- Mediterranean Diet Recipes for Beginners: Top 51 Delicious Mediterranean Recipes for Weight Loss HealthyDe la EverandMediterranean Diet Recipes for Beginners: Top 51 Delicious Mediterranean Recipes for Weight Loss HealthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Amazing Fiber-rich Cookbook: Simple, Easy and Delightful Recipes Rich in Fiber to Keep You Devoted to a Healthier LifestyleDe la EverandThe Amazing Fiber-rich Cookbook: Simple, Easy and Delightful Recipes Rich in Fiber to Keep You Devoted to a Healthier LifestyleEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Esl 4230 Informative Paper d3 0417Document8 paginiEsl 4230 Informative Paper d3 0417api-356002030Încă nu există evaluări
- Cholesterol: Heart-Healthy Eating: The most important information you need to improve your healthDe la EverandCholesterol: Heart-Healthy Eating: The most important information you need to improve your healthÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ultimate Mediterranean Diet Cookbook: Harness the Power of the World's Healthiest Diet to Live Better, LongerDe la EverandThe Ultimate Mediterranean Diet Cookbook: Harness the Power of the World's Healthiest Diet to Live Better, LongerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (6)
- Eat Well, Feel Well: Fighting Cancer with NutritionDe la EverandEat Well, Feel Well: Fighting Cancer with NutritionEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- The Mediterranean Diet For Beginners: Start Your Ideal 7-Day Mediterranean Diet Plan To Lose Weight and Live An Healthy LifestyleDe la EverandThe Mediterranean Diet For Beginners: Start Your Ideal 7-Day Mediterranean Diet Plan To Lose Weight and Live An Healthy LifestyleÎncă nu există evaluări
- User's Guide to Preventing & Reversing Diabetes NaturallyDe la EverandUser's Guide to Preventing & Reversing Diabetes NaturallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthy Living Guide:Healthy Diets Prevent DiseasesDe la EverandHealthy Living Guide:Healthy Diets Prevent DiseasesÎncă nu există evaluări
- A New Look at Vegetarianism: Health & Spiritual SeriesDe la EverandA New Look at Vegetarianism: Health & Spiritual SeriesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Mediterranean Diet:The Complete Guide with Meal Plan and Recipes for Normal People Who Want to Eat Healthy and Lose WeightDe la EverandMediterranean Diet:The Complete Guide with Meal Plan and Recipes for Normal People Who Want to Eat Healthy and Lose WeightÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 30-minute Mediterranean Diet Cookbook: 101 Easy, Flavorful Recipes for Lifelong HealthDe la EverandThe 30-minute Mediterranean Diet Cookbook: 101 Easy, Flavorful Recipes for Lifelong HealthEvaluare: 2.5 din 5 stele2.5/5 (4)
- Zest for Life: The Mediterranean Anti-Cancer DietDe la EverandZest for Life: The Mediterranean Anti-Cancer DietÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dietas para Enfermedades Crónicas: Cómo Alimentarte para una Vida SaludableDe la EverandDietas para Enfermedades Crónicas: Cómo Alimentarte para una Vida SaludableÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Science of Mediterranean Diet: A Simple Beginner's Guide to Burn Fat, Lose Weight & Live Healthily Without SufferingDe la EverandThe Science of Mediterranean Diet: A Simple Beginner's Guide to Burn Fat, Lose Weight & Live Healthily Without SufferingEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (3)
- The Keys to Healthy Living with Chronic Diseases for African Americans: A Primer for Nutrition Therapy in the Primary Care SettingDe la EverandThe Keys to Healthy Living with Chronic Diseases for African Americans: A Primer for Nutrition Therapy in the Primary Care SettingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extended Summary - How Not To Die: Based On The Book By Michael Greger Y Gene StoneDe la EverandExtended Summary - How Not To Die: Based On The Book By Michael Greger Y Gene StoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mother Nature's Garden: Healthy Vegan CookingDe la EverandMother Nature's Garden: Healthy Vegan CookingEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Reader's Digest Food Cures New EditionDe la EverandReader's Digest Food Cures New EditionReader's DigestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes: How Food and Alcohol Affect Diabetes: The most important information you need to improve your healthDe la EverandDiabetes: How Food and Alcohol Affect Diabetes: The most important information you need to improve your healthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dash Diet for Beginners: Lower Blood Pressure, Reduce Cholesterol and Manage Diabetes NaturallyDe la EverandDash Diet for Beginners: Lower Blood Pressure, Reduce Cholesterol and Manage Diabetes NaturallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Plant-Powered Diet: The Lifelong Eating Plan for Achieving Optimal Health, Beginning TodayDe la EverandThe Plant-Powered Diet: The Lifelong Eating Plan for Achieving Optimal Health, Beginning TodayEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Let’S Stop ''Killing'' Our Children: Disease Prevention Starting from the Crib | a Simplified Survival Guide for Parents and Society to Save Our ChildrenDe la EverandLet’S Stop ''Killing'' Our Children: Disease Prevention Starting from the Crib | a Simplified Survival Guide for Parents and Society to Save Our ChildrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Not to Die - Summarized for Busy People: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse Disease: Based on the Book by Michael Greger and Gene StoneDe la EverandHow Not to Die - Summarized for Busy People: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse Disease: Based on the Book by Michael Greger and Gene StoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Essential Cardiac Diet Cookbook ;The Perfect Nutrition Guide For Better Heart Health With Diet Tips, Meal Plan And Nutritious Heart-Healthy RecipesDe la EverandThe Essential Cardiac Diet Cookbook ;The Perfect Nutrition Guide For Better Heart Health With Diet Tips, Meal Plan And Nutritious Heart-Healthy RecipesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mediterranean Diet: Your Path to a Healthier LifeDe la EverandMediterranean Diet: Your Path to a Healthier LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast Cancer Smoothies: 100 Delicious, Research-Based Recipes for Prevention and RecoveryDe la EverandBreast Cancer Smoothies: 100 Delicious, Research-Based Recipes for Prevention and RecoveryÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Not To Die From Heart Disease - Based On The Teachings Of Michael Greger: Your Guide To Heart Health And WellnessDe la EverandHow Not To Die From Heart Disease - Based On The Teachings Of Michael Greger: Your Guide To Heart Health And WellnessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary of Eat to Beat Disease by Dr. William LiDe la EverandSummary of Eat to Beat Disease by Dr. William LiEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (4)
- A Joosr Guide to... How Not To Die by Michael Greger with Gene Stone: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseDe la EverandA Joosr Guide to... How Not To Die by Michael Greger with Gene Stone: Discover the Foods Scientifically Proven to Prevent and Reverse DiseaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essay 3 Second DraftDocument5 paginiEssay 3 Second Draftapi-610022486Încă nu există evaluări
- Insulin ResistanceDocument4 paginiInsulin ResistanceHannah Denise BatallangÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Dash Diet Made Easy: A Beginner's Guide to Improving Overall Health, Weight Loss, and Preventing High Blood Pressure, Cancer, Diabetes and Heart ConditionsDe la EverandThe Dash Diet Made Easy: A Beginner's Guide to Improving Overall Health, Weight Loss, and Preventing High Blood Pressure, Cancer, Diabetes and Heart ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low-Carbohydrate Mania: The Fantasies, Delusions, and MythsDe la EverandLow-Carbohydrate Mania: The Fantasies, Delusions, and MythsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lose Weight in 30 Days: At Home Weight Loss Diets, Carb Cycling and Exercise Plans to Get in Shape in A MonthDe la EverandLose Weight in 30 Days: At Home Weight Loss Diets, Carb Cycling and Exercise Plans to Get in Shape in A MonthEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Online Assignment: Submitted byDocument14 paginiOnline Assignment: Submitted byPrasant NatarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ItineraryDocument2 paginiItineraryapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Artificial Propagation Research PaperDocument6 paginiArtificial Propagation Research Paperapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Deo Reflectiveessay IduDocument3 paginiDeo Reflectiveessay Iduapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Design DeoDocument5 paginiExperimental Design Deoapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Globalization Effect Samuel DeoDocument6 paginiGlobalization Effect Samuel Deoapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Create and Review Nutritional PlanDocument6 paginiCreate and Review Nutritional Planapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- LifeafterirskitDocument5 paginiLifeafterirskitapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Oral Presentation Propaganda RepetitionDocument1 paginăOral Presentation Propaganda Repetitionapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- CivicsstatedefenseessayDocument5 paginiCivicsstatedefenseessayapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Music AnalyzationDocument4 paginiMusic Analyzationapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Civics State Defence DeosamsaurishDocument8 paginiCivics State Defence Deosamsaurishapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Le Bon Roi Dagobert French Traditional SongDocument14 paginiLe Bon Roi Dagobert French Traditional Songapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Path of Principle ReflectionDocument1 paginăPath of Principle Reflectionapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- The Understanding of Chokmah RevisionDocument1 paginăThe Understanding of Chokmah Revisionapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Schedule Field TripDocument2 paginiSchedule Field Tripapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Field Trip BrochureDocument2 paginiField Trip Brochureapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Atl Scope and SequenceDocument4 paginiAtl Scope and Sequenceapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Criterion D CreateDocument1 paginăCriterion D Createapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Gantt ChartDocument2 paginiGantt Chartapi-240613752Încă nu există evaluări
- Anthem Classic PPO 250-20-20Document4 paginiAnthem Classic PPO 250-20-20PhilippÎncă nu există evaluări
- TCCC Quick Reference Guide 2017Document54 paginiTCCC Quick Reference Guide 2017https://www.t-medical.orgÎncă nu există evaluări
- GR No. 168512 Garcia v. Salvador, 20 March 2007Document2 paginiGR No. 168512 Garcia v. Salvador, 20 March 2007Niña VillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomarkers in Kidney Disease PDFDocument1.212 paginiBiomarkers in Kidney Disease PDFAndreea AdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 27 Study GuideDocument8 paginiCHAPTER 27 Study GuideShaline MyrtilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canadian Contraception Consensus PDFDocument92 paginiCanadian Contraception Consensus PDFMacarena RijoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal Health - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument13 paginiMaternal Health - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaNurul ShahirahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hospital Operations ManagementDocument12 paginiHospital Operations ManagementJay ZatakiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMXX Marketing Sample SecuredDocument12 paginiFMXX Marketing Sample SecuredMuneeb ShahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infusion Set and Blood Transfusion SetDocument56 paginiInfusion Set and Blood Transfusion Setsaahil_goje1400Încă nu există evaluări
- AOM CPG RevisedDocument26 paginiAOM CPG Revisedmefav7778520Încă nu există evaluări
- Special Mouth Care: DefinitionDocument3 paginiSpecial Mouth Care: DefinitionSHELLAH MARIE MAMAWAG100% (1)
- ColposDocument41 paginiColposjumgzb 10Încă nu există evaluări
- Pelvic Floor ExercisesDocument11 paginiPelvic Floor ExercisespriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standardized Nursing TerminologyDocument5 paginiStandardized Nursing TerminologyDaniel WainainaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Nursing Post Test Nov. 2016Document5 paginiFundamentals of Nursing Post Test Nov. 2016Jay Abasolo0% (1)
- Controversiesin Anesthesiafororaland Maxillofacialsurgery: Brett J. King,, Adam LevineDocument9 paginiControversiesin Anesthesiafororaland Maxillofacialsurgery: Brett J. King,, Adam LevineAB MISHRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazard Identification and Prevention: (Ndlon-Osha)Document12 paginiHazard Identification and Prevention: (Ndlon-Osha)Eugine BalomagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical ATO Ukraine, April, 2015Document27 paginiMedical ATO Ukraine, April, 2015Patrick Chellew100% (1)
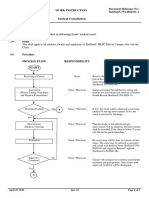
- WI-HSD-01 MALVAR Medical ConsultationDocument2 paginiWI-HSD-01 MALVAR Medical ConsultationVictor BaluyotÎncă nu există evaluări
- HPN DMDocument36 paginiHPN DMFebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessing EarsDocument11 paginiAssessing EarsRhea Mae Visda RoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Needle Stick and Sharp Injuries Among Health Care Workers in Central Zone of Tigray, Northern EthiopiaDocument6 paginiAssessment of Needle Stick and Sharp Injuries Among Health Care Workers in Central Zone of Tigray, Northern Ethiopiashofia andriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Altered Mental StateDocument2 paginiAltered Mental Stateizzati94Încă nu există evaluări
- AmazonDocument8 paginiAmazonKlaudia KałużnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- USFDA A To Z DefinationDocument26 paginiUSFDA A To Z DefinationRishikesh ChakorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dissecting Racial Bias in An Algorithm Used To Manage The HealthDocument4 paginiDissecting Racial Bias in An Algorithm Used To Manage The HealthMUHAMMAD ADAM LUQMAN MOHAMMAD ISMAILÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iasp Finalpreview - PHP Absnum 107579Document2 paginiIasp Finalpreview - PHP Absnum 107579eswar110582Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 08 - ISHADocument2 paginiAssignment 08 - ISHAerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Surgery Mcqs Along With KeyDocument8 paginiSurgery Mcqs Along With KeyFaizan Khan100% (3)