Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
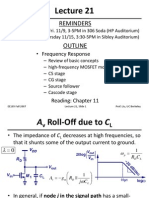
Discussion 3 Large Signal vs. Small Signal Analysis: D S BE T
Încărcat de
prasanna810243Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Discussion 3 Large Signal vs. Small Signal Analysis: D S BE T
Încărcat de
prasanna810243Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Discussion3
LargeSignalvs.SmallSignalAnalysis
LargeSignal: 1.DCAnalysis;findingoperatingpointandthebiasconditions(Voltagesand
Currentsatdifferentnodes)ofcircuit.
2.Usecurrentandvoltageequationsthatgovernthebehaviorofthedevice
(e.g.I
D
=I
s
(exp(V
BE
/V
T
)1),andKVL/KCLtofindthebiaspoints.
3.Largesignalvaluesareusedtofindsmallsignalparameters.
*NOTE:Circuitmaycontainnonlineardevices(e.g.diodes,BJTs),so
neverlinearizethesedevices,i.e.donotthinkofthemasdependentsources
orresistors.
4.Voltagesappliedhereareusuallyseveralvoltstoseveraltensofvolts.They
arelargevalues.
SmallSignal: 1.ACAnalysis;tweakaroundthebiascondition,i.e.aroundtheDCbiasofthe
circuit,addasmallACsourcethatslightlyincreasesanddecreasesthebias
point.
2.Linearizethedevice.Replacethenonlineardevicewithlinearones.Why
canyoutreatnonlineardevicesaslinearwhensmallsignalvaluesareapplied?
BecauseifyoutaketheinstantaneousslopeoftheIVcurveataparticularDC
pointandzoomintoit,forvaluesveryclosetothisDCpoint,theIVcurvelooks
quitelinear.
3.Constructthesmallsignalmodelusingvaluesfortheparametersthatyou
foundinStep3ofLargeSignalAnalysis.
4.Usethismodeltofindthingslikegain,inputandoutputresistances.
LargeSignalandSmallSignalAnalysisonBJTs
DCEquationsforBJTs:(Reminder)
I
C
= I
S
(c
(v
BE
v
T)
-1)
I
C
= [I
B
I
L
= I
C
+I
B
= (1 +[)I
B
SmallSignalParamtersforBJTs:(Reminder)
*Ifthereistime,youmaywanttodrawI
C
vs.V
CE
curvesfor3differentV
BE
valuesandpickonepointas
theDCoperatingpointandshowhowincrementalchangesinV
BE
,i.e.ifthenewV
be
becomesV
BE
+v
be
,
changesI
c
toI
C
+i
c
andshowhowthisismodeledasavoltagedependentcurrentsource,g
m
v
be
.Similarly,
youcandothisforincrementalchangesinV
CE
andshowitseffectandwhythatsaresistor.So,basically
derivewherethesmallsignalmodelcomesfrom.
g
m
=
I
c
I
1
r
n
=
[
g
m
r
o
=
I
A
I
C
Ex.1
Forthecircuitbelow,findtheDCoperatingpoint,i.e.findI
C
andV
BE,1
andV
BE,2
,suchthatV
out
is3V.
(SupposeV
CC
andR
1
valuesaregiven).*Youdontactuallyneedtofindnumbers,justgothroughthe
KVL/KCLanddevicebehaviorequationsthatwouldprovidethefinalanswerforI
C
,V
BE,1
,andV
BE,2
.
Then,evaluatethesmallsignalparameters.*Again,justgothroughthestepsofhowyouwouldfind
theseparameters.
Finally,drawthesmallsignalmodel.*Drawtheentiremodelout.Note:Youcanreplaceg
m
V
BE
dependentcurrentsourceforQ2witharesistorhavingavalue1/g
m
sincethecollectorandbasearetied
together.
Amplifiers:Introductionto2portmodelsandgoingoveridealvoltageamplifiers,idealcurrent
amplifiers,idealtransconductanceamplifiers,andidealtransresistanceamplifiers,i.e.whatshouldR
in
andR
out
be(largeorsmall)foreachoftheseidealamplifiers.*Youmaywanttouseananalogyof2port
modelwithTheveninandNortonequivalentcircuits.
IdealVoltageAmplifier:(HighR
in
,LowR
out
)
IdealCurrentAmplifier:(LowR
in
,HighR
out
)
IdealTransconductanceAmplifier:(HighR
in
,HighR
out
)
IdealTransresistanceAmplifier:(LowR
in
,LowR
out
)
CalculatingA
v
,A
i
,G
m
,R
m
,R
in
,R
out
:
A
v
: Applyidealvoltagesourceattheinput(i.e.asourcewithnosourceresistance),andmeasure
theopencircuitoutputvoltage.
A
i
: Applyidealcurrentsourceattheinput(i.e.asourcewithnosourceresistance),andmeasure
theshortcircuitoutputcurrentgoingbackintothecircuit.
G
m
: Applyidealvoltagesourceattheinput(i.e.asourcewithnosourceresistance),andmeasure
theshortcircuitoutputcurrentgoingbackintothecircuit.
R
m
: Applyidealcurrentsourceattheinput(i.e.asourcewithnosourceresistance),andmeasure
theopencircuitoutputvoltage.
R
in
: Applyidealvoltagesourceattheinput(i.e.asourcewithnosourceresistance),keepR
L
attached
attheoutput,andmeasurethecurrentthatflowsoutofthisidealinputsource.
A
v
: Applyidealvoltagesourceattheoutput(i.e.asourcewithnosourceresistance),zeroanyinput
source(voltagesourcesbecomeshortandcurrentsourcesbecomeopen),keepR
s
attachedat
theinput,andmeasurethecurrentthatflowsoutofthisidealoutputsource:
*Ifthereismoretime,doanexampleofasimpleCommonEmitterAmplifiergoingthroughthestepsof
findingA
v
,R
in
,andR
out
.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Principles of Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21Document68 paginiPrinciples of Electrical Engineering Lab 2020-21riko.mori.toi22Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument10 paginiBasic Electronic ComponentsEDEN JIMENEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- WS 1020Document44 paginiWS 1020Sunil Sree NathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narrative Report in Physics MidtermDocument5 paginiNarrative Report in Physics MidtermAshner NovillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eec 115 Experiment I & IiDocument12 paginiEec 115 Experiment I & IiOreoluwa OmiyaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical EngineeringDocument7 paginiStudy of Various Basic Instruments and Components of Electrical Engineeringnational printersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ammeter: ObjectiveDocument26 paginiAmmeter: ObjectiveAnkhi BaroiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument9 paginiBasic Electronic ComponentsMackRoss PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lessons in Electric Circuit2Document84 paginiLessons in Electric Circuit2jun deeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voltage Detector Using Any 555 ICDocument8 paginiVoltage Detector Using Any 555 ICPiyush chaudhari100% (2)
- Liquid Crystal Display (LCD)Document6 paginiLiquid Crystal Display (LCD)MURUGESANM MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuits 1Document110 paginiCircuits 1Mark Ian Tanangonan Maravilloso100% (1)
- Attachment - 1434787422739 - Familarization With Discrete ComponentsDocument14 paginiAttachment - 1434787422739 - Familarization With Discrete ComponentsRajan SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2: Circuits and Electrical Components: Lesson 1: Circuit Elements and Constitutive RelationshipsDocument10 paginiModule 2: Circuits and Electrical Components: Lesson 1: Circuit Elements and Constitutive RelationshipsCerealÎncă nu există evaluări
- SpaDocument5 paginiSpamillionÎncă nu există evaluări
- BCM Practical 1 2Document9 paginiBCM Practical 1 2Adi KhardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complect PresntionDocument13 paginiComplect PresntionKubra ĖdrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Chapter 1 SolutionDocument11 paginiFundamentals of Electrical and Electronics Engineering: Chapter 1 SolutionsegsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report of Project-1Document12 paginiReport of Project-103061341753 03061341753Încă nu există evaluări
- Essential Electrical Components and How They Work Together To Create Incredible Modern Electrical SystemsDocument13 paginiEssential Electrical Components and How They Work Together To Create Incredible Modern Electrical SystemsSolomon GodwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEEEDocument56 paginiFEEEnetra msajjan100% (1)
- Basic Electronics NotesDocument5 paginiBasic Electronics NotesRolando Carlos FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Sheets 6.1.4Document12 paginiInformation Sheets 6.1.4api-196541959Încă nu există evaluări
- WPC Practical No. 5Document4 paginiWPC Practical No. 5166CMYashvardhan ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No: 1Document7 paginiExperiment No: 1naeemullah786057Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics L1Document19 paginiBasic Electronics L1msellereneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Electronic ComponentsDocument41 paginiCommon Electronic ComponentsangelynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1 ElectricalDocument5 paginiExperiment 1 ElectricalUsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ass 1 FEEDocument3 paginiAss 1 FEE21-04126Încă nu există evaluări
- BuzzerDocument5 paginiBuzzerHehe_09Încă nu există evaluări
- Circuits, EC, Symbols, SchematicDocument7 paginiCircuits, EC, Symbols, SchematicKyle Angelo SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesDocument18 pagini1 Basic Electronics P1 NotesEphraem RobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic One Introduction To ElectronicsDocument22 paginiTopic One Introduction To ElectronicsBlueprint MihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ia T 3 Two Marks Q & ADocument2 paginiIa T 3 Two Marks Q & ARAMESH BABU EEEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics: (Small Scale Electrical Circuits)Document24 paginiBasic Electronics: (Small Scale Electrical Circuits)aspectÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workshop Training Manual COURSE: WS1020: Central Workshop Indian Institute of Technology Madras CHENNAI - 600036, INDIADocument44 paginiWorkshop Training Manual COURSE: WS1020: Central Workshop Indian Institute of Technology Madras CHENNAI - 600036, INDIAhariharanhemanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Electronic ComponentsDocument24 paginiIntroduction To Electronic ComponentsVincent AveryÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student VersionDocument25 paginiELECTRIC WORKSHOP Student Versionnaqirustambajwa90Încă nu există evaluări
- Signals, Circuits, and Computers: Part BDocument21 paginiSignals, Circuits, and Computers: Part BVeron Taguinod BungagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2. Electronics Project #1: 1. Resistance (Ohm)Document25 paginiUnit 2. Electronics Project #1: 1. Resistance (Ohm)api-299438748Încă nu există evaluări
- Research Electronics 4 19 9 19Document7 paginiResearch Electronics 4 19 9 19HarshilÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTRONOTES.comDocument8 paginiELECTRONOTES.comJairus TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics PowerpointDocument16 paginiBasic Electronics PowerpointYamanappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electronics PowerpointDocument16 paginiBasic Electronics PowerpointVo Minh Thong100% (1)
- Basic Electronics PowerpointDocument16 paginiBasic Electronics PowerpointKienzer San Agustin100% (1)
- Basic Electronics PowerpointDocument16 paginiBasic Electronics Powerpointmayada ahmed100% (2)
- Basic Electronics PowerpointDocument16 paginiBasic Electronics PowerpointEarle Sean MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wires and ConnectionsDocument22 paginiWires and ConnectionsDanilo AlbayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Testing of Continuity in Switches and LoadDocument7 paginiTesting of Continuity in Switches and LoadVikas UpadhyayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of ElectronicsDocument15 paginiBasics of ElectronicsAbdul RazzakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Practices Laboratory: Lab ManualDocument51 paginiEngineering Practices Laboratory: Lab ManualKarthikeyan100% (1)
- Analog Communication Final WorkDocument23 paginiAnalog Communication Final Worktoa2bÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No: 1 Familiarization of Electronic Components AimDocument49 paginiExperiment No: 1 Familiarization of Electronic Components Aimarun joseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1. Electronic Components & SignalsDocument12 paginiChapter 1. Electronic Components & SignalsPavankumar Gosavi100% (2)
- Basic Electrical LabDocument32 paginiBasic Electrical Labsrinu247Încă nu există evaluări
- Mod 2 - 3 - 4Document17 paginiMod 2 - 3 - 4Georji kairuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod 2 - 3 - 4 - 5Document26 paginiMod 2 - 3 - 4 - 5Georji kairuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Engineering - Leacture NotesDocument29 paginiBasic Electrical Engineering - Leacture NotesEngineer Zeeshan RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interview Questions On ElectronicsDocument4 paginiInterview Questions On ElectronicsInstrumentation ToolsÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIGO Vacuum Compatible Materials List: LIGO Laboratory / LIGO Scientific CollaborationDocument15 paginiLIGO Vacuum Compatible Materials List: LIGO Laboratory / LIGO Scientific CollaborationMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Herbs Mooligai Uses in TamilDocument88 paginiHerbs Mooligai Uses in Tamilscribdlinus83% (6)
- Atom Resolved Surface Reactions. NanocatalysisDocument240 paginiAtom Resolved Surface Reactions. Nanocatalysisrace egrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vacuum Stepper Motors: Arun Microelectronics LimitedDocument3 paginiVacuum Stepper Motors: Arun Microelectronics LimitedMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cryogenic SPM PDFDocument4 paginiCryogenic SPM PDFMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extraction Methods Natural Essential OilDocument17 paginiExtraction Methods Natural Essential OilDonatos Dinis100% (1)
- Aromatic Plant Extr MethodsDocument28 paginiAromatic Plant Extr Methodsdadduuudd0% (1)
- The Guide For International Researchers Moving To The UKDocument96 paginiThe Guide For International Researchers Moving To The UKMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Offer Conditions BookletDocument32 paginiOffer Conditions BookletMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Netherland SalDocument4 paginiNetherland SalMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Case TypesDocument3 paginiNew Case TypesRamasubramanian BairavasubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low-Noise Amplifiers: EE215C B. Razavi Win. 10 HO #2Document13 paginiLow-Noise Amplifiers: EE215C B. Razavi Win. 10 HO #2Muraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deed of Partition Betwee... of A Joint Hindu FamilyDocument8 paginiDeed of Partition Betwee... of A Joint Hindu FamilyMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CASTEP StartupDocument38 paginiCASTEP StartupMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elphy Plus ManualDocument207 paginiElphy Plus ManualMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Noise AmplifierDocument115 paginiLow Noise AmplifierIris ShtraslerÎncă nu există evaluări
- E - LiNE Software Operation ManualDocument116 paginiE - LiNE Software Operation ManualMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTspiceGettingStartedGuide PDFDocument53 paginiLTspiceGettingStartedGuide PDFRichard ZerpaÎncă nu există evaluări
- E - LiNE Software Operation ManualDocument116 paginiE - LiNE Software Operation ManualMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method For Mass Production of Graphene-Based Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) Developed - KurzweilAIDocument3 paginiMethod For Mass Production of Graphene-Based Field-Effect Transistors (FETs) Developed - KurzweilAIMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1MA178 1E The Y Factor TechniqueDocument31 pagini1MA178 1E The Y Factor TechniqueMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 12 02 Nanosystems AgendaDocument3 pagini2013 12 02 Nanosystems AgendaMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 005 Keiji MorokumaDocument43 pagini005 Keiji MorokumaMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Noise in AmplifierDocument16 pagini2 Noise in AmplifierMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 21Document27 paginiLecture 21Muraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lattice ParamentersDocument5 paginiLattice ParamentersMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Langton Fob 3ce Ch05Document45 pagini05 Langton Fob 3ce Ch05Ruchita SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estate Goals Mission Values Overview - ProDairy 17pgDocument17 paginiEstate Goals Mission Values Overview - ProDairy 17pgMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team Leadership: Stephen J. Zaccaro, Andrea L. Rittman, Michelle A. MarksDocument33 paginiTeam Leadership: Stephen J. Zaccaro, Andrea L. Rittman, Michelle A. MarksMuraleetharan BoopathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th Sem ECDocument54 pagini4th Sem ECAnup BhowmickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Answer QuestionsDocument24 paginiLong Answer Questionsashok pradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARPLDocument18 paginiARPLLily SternÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memorex MT1191V - MT1131A-32176 PDFDocument23 paginiMemorex MT1191V - MT1131A-32176 PDFdomador1624Încă nu există evaluări
- Sensors and Transducers Lab ManualDocument34 paginiSensors and Transducers Lab ManualRahulMuntha80% (5)
- Schema Electrica Convertor 2Vcc in 30VccDocument16 paginiSchema Electrica Convertor 2Vcc in 30VccDragos DragoshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Collection System of EEG Based On USB InterfaceDocument4 paginiData Collection System of EEG Based On USB InterfaceAdonis LealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eea Pam 535 C 32 PDFDocument5 paginiEea Pam 535 C 32 PDFjorge130494Încă nu există evaluări
- LM3886 Gainclone 2x68 Watt Full Amplifier ProjectDocument5 paginiLM3886 Gainclone 2x68 Watt Full Amplifier ProjectJustin AntonioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coruspro Katalog enDocument8 paginiCoruspro Katalog enBibi DanilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Single Stage Transistor Amplifier.Document3 paginiStudy of Single Stage Transistor Amplifier.Akib Hasan NiloyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modulation Part 8 of 10Document4 paginiModulation Part 8 of 10nonotjenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kidde AEGIS 2 0 Conventional Fire Alarm-Suppression Control Unit K-84-200 PDFDocument6 paginiKidde AEGIS 2 0 Conventional Fire Alarm-Suppression Control Unit K-84-200 PDFModesto Galicia Martinez-lllÎncă nu există evaluări
- 180 Ma Low-Noise LDO Regulator: Features General DescriptionDocument22 pagini180 Ma Low-Noise LDO Regulator: Features General DescriptionJoão AlmeidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Darlington PairDocument3 paginiDarlington Pairlakka srinivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual Cat994f STMGDocument187 paginiManual Cat994f STMGAlejandroZappa100% (1)
- Acelerômetros 9000Document34 paginiAcelerômetros 9000Andre NilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- CT LAB MannualDocument53 paginiCT LAB MannualVSMSRKIT IICÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC CouplingDocument9 paginiRC CouplingNoriel Louis SoteloÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECM Pre AmplifierDocument4 paginiECM Pre Amplifierksay1504Încă nu există evaluări
- Kenwood Kac-M1804 Car Audio Amplifier SMDocument23 paginiKenwood Kac-M1804 Car Audio Amplifier SMmarius tanjalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Line Follower ReportDocument23 paginiLine Follower Reportatul mishra88% (8)
- Acm Instruments BrochureDocument12 paginiAcm Instruments BrochuresoldadouniverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual AS50R PDFDocument5 paginiManual AS50R PDFJUNIOR700Încă nu există evaluări
- Crystal Oscillators - Alexander Schure PDFDocument68 paginiCrystal Oscillators - Alexander Schure PDFDiego García MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- KMA 20 Mant. ManualDocument91 paginiKMA 20 Mant. Manualmglem100% (2)
- TDA7286 Single Chip Preamplifier For Double Deck Radio CasseDocument6 paginiTDA7286 Single Chip Preamplifier For Double Deck Radio CasseDunatoMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application Note AN-1144: IRS20957S Functional DescriptionDocument18 paginiApplication Note AN-1144: IRS20957S Functional DescriptionGerry GuadarramaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDC 2017 PaperDocument29 paginiEDC 2017 Paperlucky jÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialDe la EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeDe la EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (9)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosDe la EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceDe la EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesDe la EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonDe la EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionDe la EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (543)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsDe la EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Upcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)De la EverandUpcycled Technology: Clever Projects You Can Do With Your Discarded Tech (Tech gift)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- The Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesDe la EverandThe Phone Fix: The Brain-Focused Guide to Building Healthy Digital Habits and Breaking Bad OnesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Wearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsDe la EverandWearable Sensors: Fundamentals, Implementation and ApplicationsEdward SazonovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Current Interruption Transients CalculationDe la EverandCurrent Interruption Transients CalculationEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Practical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionDe la EverandPractical Electronics for Inventors, Fourth EditionEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (3)
- ARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)De la EverandARDUINO CODE: Mastering Arduino Programming for Embedded Systems (2024 Guide)Încă nu există evaluări
- Build Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionDe la EverandBuild Your Own Electric Vehicle, Third EditionEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Understanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveDe la EverandUnderstanding Automotive Electronics: An Engineering PerspectiveEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (16)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionDe la EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (15)