Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Key Ideas
Încărcat de
api-261372832Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Key Ideas
Încărcat de
api-261372832Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Motion
Section 3
Key Ideas
What do scientists identify as the fundamental
forces of nature?
What happens when there is a net force acting
on an object?
What force always opposes motion?
Why is friction sometimes necessary?
Motion
Section 3
Bellringer
You are driving around and text messaging omg.
Having taken your attention off the road you sped up
from 30 mi/hr to 87mi/hr in 60 seconds. You then get
pulled over by a cop and come to a stop with an
acceleration of -6000 mi/hr^2. Calculate:
1. Your acceleration when you sped up in mi/hr^2.
2. Time it took you to pull over in seconds
Motion
Section 3
Bellringer
In some cases, an applied force is balanced by an opposite force, and
there is no change in motion. In other cases, an applied force is not
balanced by an opposite force, and the result is acceleration in the
direction of the applied force. Look at the following illustrations, and
identify the forces and motion in each one.
Motion
Section 3
Fundamental Forces
What do scientists identify as the fundamental
forces of nature?
These forces are the force of gravity, the
electromagnetic force, the strong nuclear force,
and the weak nuclear force.
The strong and weak nuclear forces act only over a short
distance.
The force of gravity is a force that you feel every day.
Other everyday forces, such as friction, are a result of the
electromagnetic force.
Motion
Section 3
Fundamental Forces, continued
Fundamental forces vary in strength.
The fundamental forces vary widely in strength and
the distance over which they act.
Forces can act through contact or at a distance.
Pushes and pulls are examples of contact forces.
Field forces (like the force of gravity) do not require
that the objects touch each other.
Both contact and field forces can cause an object to
move or to stop moving.
Motion
Forces
Forces are always
acting on us.
A force is simply a
push or a pull
Section 3
Motion
Section 3
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces
What happens when there is a net force acting
on an object?
Whenever there is a net force acting on an
object, the object accelerates in the direction of
the net force.
net force: the combination of all forces acting on an
object
Motion
Section 3
Tug of war
Balanced forces on the rope (one person each side)
No Acceleration, No Net Force
Force Left =
Force right
Unbalanced Forces on the rope (3 on 1)
Acceleration to the right, Net Force to the right
Force Left smaller than Force right
Motion
Section 3
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces,
continued
Balanced forces do not change motion.
Forces are balanced when the net force is zero.
EX. Car on the expressway force diagram
Motion
Section 3
Balanced and Unbalanced Forces,
continued
Unbalanced forces do not cancel completely.
Forces are unbalanced when the net force is
greater than zero.
The object will accelerate in the direction of
the net force.
Example: Deer runs out in front of you
Motion
Visual Concept: Force
Section 3
Motion
Section 3
The Force of Friction
What force always opposes motion?
The force of friction always opposes the motion.
friction: a force that opposes motion between two
surfaces that are in contact
Motion
Section 3
The Force of Friction, continued
Static friction is greater than kinetic friction.
static friction: the force that resists the initiation of sliding
motion between two surfaces that are in contact and at rest
(Static means at rest)
kinetic friction: the force that opposes the movement of two
surfaces that are in contact and are moving over each other.
(Kinetic means in motion)
Have you noticed that Static Friction is usually higher
than Kinetic friction!
Phet
Motion
Section 3
Visual Concept: The Force of Friction
Motion
Section 3
The Force of Friction, continued
Not all kinetic friction is the same.
sliding friction: when objects slide past each other
Try rubbing your hands together
rolling friction: when a rounded object rolls over a flat
surface
BBall
in general, rolling friction < sliding friction
Motion
Section 3
Visual Concept: Types of Friction
Motion
Section 3
Friction and Motion
Why is friction sometimes necessary?
Friction is necessary for many everyday tasks to
work correctly.
Motion
Section 3
Friction and Motion, continued
Unwanted friction can be lowered.
using low-friction materials, such as nonstick coatings
on cooking pans
using lubricants, such as motor oil, wax, and grease
Helpful friction can be increased.
scattering sand on icy roads to keep cars from
skidding
wearing textured batting gloves when playing
baseball to make it easier to grip the bat
Motion
Section 3
Visual Concept: Ways to Reduce or Increase
Friction
Motion
Section 3
Friction and Motion, continued
Cars could not move without friction.
Without friction between the tires and the
road, the tires would not be able to push
against the road and the car would not move
forward.
The force pushing the car forward must be
greater than the force of friction that opposes
the cars motion.
Motion
Section 3
Friction and Motion, continued
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Force & MotionDocument34 paginiForce & MotionMhimi Viduya100% (1)
- PEDH Volume 1 2013-14 PDFDocument421 paginiPEDH Volume 1 2013-14 PDFSaurabh Gupta100% (2)
- Force and MotionDocument33 paginiForce and MotionEdric S100% (1)
- Law of MotionDocument76 paginiLaw of MotionLove With Books 2470% (1)
- Group3 PhysicsDocument26 paginiGroup3 PhysicsCarl Eric Amora Velasco IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harmonic Patterns GuideDocument51 paginiHarmonic Patterns GuideUNSA MANI SAON88% (8)
- P WEEK IV Force and Pressure VIIIDocument22 paginiP WEEK IV Force and Pressure VIIISesha Sai KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- CM P1 11604 14 EN Vibration Sensor Catalog PDFDocument138 paginiCM P1 11604 14 EN Vibration Sensor Catalog PDFjesushuamantunagrandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Final Revision Notes Based On Advanced InformationDocument100 paginiIgcse Final Revision Notes Based On Advanced Informationsohaila ibrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laws of MotionDocument64 paginiLaws of MotionArnel A. JulatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- SBC Detailed ReportDocument36 paginiSBC Detailed ReportPraneeth Kumar100% (1)
- Tugas VeigaDocument17 paginiTugas VeigaPutra Tresna100% (2)
- Erico System 3000Document12 paginiErico System 3000Juan E Torres M67% (3)
- 2-Plasticiy Theory and Application - A. MENDELSON - 3Document368 pagini2-Plasticiy Theory and Application - A. MENDELSON - 3Ardeshir GholamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metrology - Book - Hari PDFDocument212 paginiMetrology - Book - Hari PDFKallol ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Slag Fundamentals Under 40 CharactersDocument38 paginiIntroduction to Slag Fundamentals Under 40 CharactersNicole Altamirano Catalán100% (1)
- Balanced and Unbalanced ForcesDocument31 paginiBalanced and Unbalanced ForcesInah MasubayÎncă nu există evaluări
- DynamicsDocument100 paginiDynamicsRAMAN KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch11 Sec3 Motion and ForceDocument15 paginich11 Sec3 Motion and Forceapi-266280305Încă nu există evaluări
- General Physics 1: Newton's Laws and ApplicationsDocument6 paginiGeneral Physics 1: Newton's Laws and ApplicationsAllen Simon BaulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 SLOsDocument35 paginiChapter 3 SLOsNoman Qadeer100% (1)
- Chapter 3 DynamicsDocument5 paginiChapter 3 DynamicsLakhan VaishnavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5 - Newton's Laws of MotionDocument5 paginiModule 5 - Newton's Laws of MotionAllen Simon BaulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHY 111 Forces and Motion LectureDocument72 paginiPHY 111 Forces and Motion LectureDeborah ChiramboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key IdeasDocument20 paginiKey Ideasapi-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics PPT NotesDocument15 paginiDynamics PPT NotesFaiq IrfanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 5 (Forces and Netwons Laws)Document73 paginiLesson 5 (Forces and Netwons Laws)Francis Perito50% (2)
- Force and MotionDocument34 paginiForce and MotionJoric MagusaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics L 9Document50 paginiPhysics L 9AkshithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demo - Newtons Laws of MotionDocument29 paginiDemo - Newtons Laws of MotionYomiko Danise P. EloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Dynamics of TranslationDocument23 pagini2 Dynamics of TranslationGia SaysonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 13 VDocument5 paginiLecture 13 VLucian NicolauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elements of Mechanical EngineeringDocument14 paginiElements of Mechanical EngineeringVivekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics (Forces)Document3 paginiPhysics (Forces)TVÎncă nu există evaluări
- EN3: Introduction to Engineering Statics and Reaction ForcesDocument62 paginiEN3: Introduction to Engineering Statics and Reaction ForcesAnkitnautyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsDocument5 paginiNewton's First Law of Motion Is Often Stated AsRowena Abdula BaronaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8P2A.3 & 4 Newton's Laws of Motion PPT 2017Document52 pagini8P2A.3 & 4 Newton's Laws of Motion PPT 2017Jerome Nicolas Jr. MoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - Applying Newton's LawsDocument20 paginiChapter 5 - Applying Newton's Lawshammygoraya2226Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 Laws of Motion NotesDocument13 paginiChapter 4 Laws of Motion NotesSparkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Force - Summary Notes: Noncontact Forces, E.g., Gravitational Force, Electrical Force, and Magnetic ForceDocument3 paginiForce - Summary Notes: Noncontact Forces, E.g., Gravitational Force, Electrical Force, and Magnetic ForceVenu GopalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument28 paginiNewton's Laws of Motion ExplainedLeah Mae GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Form 2 Physics Topic 3 Forces - 061604Document33 paginiForm 2 Physics Topic 3 Forces - 061604Anotidaishe GurureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Newton'sLawsofMotionDocument44 paginiPhysics Newton'sLawsofMotionCamela LacsamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Concepts of Equilibrium Bragais Ludangco PormalejoDocument85 paginiThe Concepts of Equilibrium Bragais Ludangco PormalejoJANE CASSANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Chapter 5Document38 paginiPhysics Chapter 5Jamie NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Notes For Forces and MotionDocument6 paginiScience Notes For Forces and Motiontoe masterÎncă nu există evaluări
- VND - Openxmlformats Officedocument - PresentationmlDocument49 paginiVND - Openxmlformats Officedocument - PresentationmlwongtuitiondocumentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics MomentumDocument31 paginiPhysics MomentumRado JaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 Notes - Engineering Level 3 CtechDocument11 paginiUnit 3 Notes - Engineering Level 3 CtechHadley PeckÎncă nu există evaluări
- FORCESDocument6 paginiFORCESlemoniteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's First and Second LawDocument26 paginiNewton's First and Second LawDanica DelarosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Laws of Motion SummaryDocument32 paginiNewton's Laws of Motion SummarySonny Boy SajoniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Froces Notes Dynamics+Deformation+MomentsDocument13 paginiFroces Notes Dynamics+Deformation+MomentsFaiq IrfanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction Forces ExplainedDocument6 paginiFriction Forces ExplainedAnoop Mohan ChemnikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton'S Laws of Motion: DynamicsDocument18 paginiNewton'S Laws of Motion: DynamicsOshene TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sci8 Q1-M1 Laws of MotionDocument30 paginiSci8 Q1-M1 Laws of MotionPagudpud National HSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawsDocument40 paginiPhysics in Life Science: Force and Motion: Newton's LawssosatukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ForcesDocument68 paginiForcesJohn Mark MadrazoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Laws of Motion and Forces ExplainedDocument26 paginiNewton's Laws of Motion and Forces ExplainedcookingÎncă nu există evaluări
- ForceDocument50 paginiForceAaron Manuel MunarÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION EXPLAINEDDocument63 paginiNEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION EXPLAINEDWeah Zarraine RosacenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Laws of Motion Finalppt 0914Document62 paginiNewton's Laws of Motion Finalppt 0914Jai SanatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics PPT 9knyDocument18 paginiPhysics PPT 9knyÉva HuszárÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 2 - NM - (B) DynamicsDocument117 paginiCH 2 - NM - (B) DynamicsHush PereraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Laws of Motion - Version 2Document43 paginiNewton's Laws of Motion - Version 2zhareenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sharma CH 02 Phy SciDocument68 paginiSharma CH 02 Phy SciCarlyn VarelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Law PDFDocument6 paginiNewton's Law PDFArslan RajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Friction: General Physics 1Document13 paginiFriction: General Physics 1lalabee19Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 20Document1 paginăWeek 20api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 26Document1 paginăWeek 26api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 19Document1 paginăWeek 19api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 27Document1 paginăWeek 27api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 19Document1 paginăWeek 19api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 16Document1 paginăWeek 16api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 17Document1 paginăWeek 17api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 19Document1 paginăWeek 19api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 36Document1 paginăWeek 36api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 36Document1 paginăWeek 36api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 17Document1 paginăWeek 17api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 36Document1 paginăWeek 36api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 16Document1 paginăWeek 16api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 30Document1 paginăWeek 30api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 14Document1 paginăWeek 14api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 13Document1 paginăWeek 13api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 12Document1 paginăWeek 12api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 15Document1 paginăWeek 15api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 14Document1 paginăWeek 14api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 14Document1 paginăWeek 14api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 11Document1 paginăWeek 11api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 13Document1 paginăWeek 13api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 30Document1 paginăWeek 30api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 30Document1 paginăWeek 30api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 13Document1 paginăWeek 13api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 11Document1 paginăWeek 11api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 12Document1 paginăWeek 12api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 10Document1 paginăWeek 10api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 30Document1 paginăWeek 30api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 10Document1 paginăWeek 10api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- 4 ESO Academics - Unit 01 - Exercises 1.2.Document10 pagini4 ESO Academics - Unit 01 - Exercises 1.2.GoheimÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00285Document7 pagini00285kishan patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1429 (Math and State)Document2 pagini1429 (Math and State)Zameer HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Bearing 1Document30 paginiAir Bearing 1YashOdeepAthawaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Module Form AnswersDocument3 paginiScience Module Form AnswersVedaroobanVijayakumaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 4 Inverse of MatrixDocument13 pagini7 4 Inverse of MatrixEbookcrazeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSDSDocument6 paginiMSDSMAHABEER INDUSTRIESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Imaging TechnologyDocument3 paginiSeismic Imaging TechnologyrasulbabazadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Numerical Scheme To Modeling Open Channels-5 PDFDocument10 paginiNumerical Scheme To Modeling Open Channels-5 PDFOdalis MatuteÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANSYS Polystat Users GuideDocument180 paginiANSYS Polystat Users GuideShady Adel AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gas Chromatography & Liquid Chromatography: Dr. Jenny Jacob School of Bioscience MacfastDocument31 paginiGas Chromatography & Liquid Chromatography: Dr. Jenny Jacob School of Bioscience MacfastJenny Jose100% (1)
- Effect of Motion On Packing EfficiencyDocument14 paginiEffect of Motion On Packing EfficiencydonkosarevÎncă nu există evaluări
- IwnDocument76 paginiIwnAzizur RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AL6061 SiCDocument36 paginiAL6061 SiCmayankÎncă nu există evaluări
- GC Validation TCDDocument6 paginiGC Validation TCDRajan Chidambaram SivaÎncă nu există evaluări
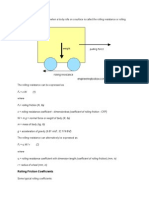
- Rolling Friction CoefficientsDocument3 paginiRolling Friction CoefficientsChypraÎncă nu există evaluări
- AttachmentDocument46 paginiAttachmentaaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW 1 SolutionDocument12 paginiHW 1 SolutionESTUDIANTE JOSE DAVID MARTINEZ RODRIGUEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics K12Document710 paginiPhysics K12skmrrl100% (3)
- Pressure Meter and Dila To MeterDocument34 paginiPressure Meter and Dila To MeterNagarajHB100% (1)