Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
AC Generator Principles Explained
Încărcat de
raviTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AC Generator Principles Explained
Încărcat de
raviDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
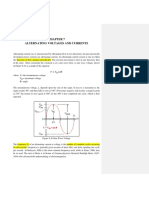
Principle :
A.C. generators or alternators (as they are usually called) operate on the same fundamental
principles of electromagnetic induction as D.C. generators.
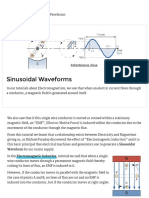
Alternating voltage may be generated by rotating a coil in the magnetic field or by rotating a
magnetic field within a stationary coil. The value of the voltage generated depends onthe number of turns in the coil.
strength of the field.
the speed at which the coil or magnetic field rotates.
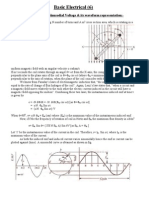
Working :
Consider a rectangular coil having N turns and rotating in a uniform magnetic field with an angular
velocity of w radian/second. Maximum flux m is linked with the coil when its plane coincides with
the X-axis. In time t seconds, this coil rotates through an angle q = wt. In this deflected position , the
component of the flux which is perpendicular to the plane of the coil is = m cos wt. Hence flux
linkage at any time are N=Nm cos wt.
According to Faraday's Laws of Electromagnetic Induction, the e.m.f. induced in the coil is given by
the rate of change of flux linkage of the coil. Hence the value of the induced e.m.f. is
e = - d(N)/dt volt
= - N d(m cos wt) / dt volt
= - Nm w(-sin wt) volt
= wNm sin wt volt
= w Nm sin q volt ----------------------- (i)
When the coil turned through 90 i.e. when q = 90, then sin q = 1, hence e has maximum value,
say Em. Therefore from Eq(i) we get
Em = wNm
= w NBmA = 2pfNBmA volt
where Bm = maximum flux density in Wb/m2.
A = Area of the coil in m2.
f = frequency of rotation of the coil in rev/second.
Substituting this value of Em in Eq(i), we get
e = Em sin q = Em sin wt
Similarly, the equation of the induced alternating current is
i = Im sin wt
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Induction PowerpointDocument48 paginiInduction PowerpointIsaac DunkleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformers: How They Work and Their UsesDocument16 paginiTransformers: How They Work and Their UsestalhawasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous Motors SlidesDocument55 paginiSynchronous Motors SlidesKaye Freyssinet Nermal Abanggan100% (1)
- LLM Cheat Sheet CombineDocument4 paginiLLM Cheat Sheet CombineTim DaviesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternating Current FundamentalsDocument25 paginiAlternating Current Fundamentalsmariamoi suarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsDe la EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANSI IEEE-IEC-ComparisonDocument For TransformersDocument42 paginiANSI IEEE-IEC-ComparisonDocument For TransformersM Kumar Marimuthu50% (2)
- AC Circuits Module 1Document28 paginiAC Circuits Module 1YoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Magnetic CircuitsDocument23 paginiIntroduction To Magnetic Circuitssharad kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Synchronous MachinesDocument45 paginiThree Phase Synchronous MachinesAndrew Lapthorn100% (3)
- Elec 6Document2 paginiElec 6logon_saralÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sinusoidal Waveform or Sine Wave in An AC Circuit PDFDocument16 paginiSinusoidal Waveform or Sine Wave in An AC Circuit PDFshahanbashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Format For The Sinusoidal Voltage or CurrentDocument25 paginiGeneral Format For The Sinusoidal Voltage or CurrentGabriel Carl AlpuertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- القشرياتDocument19 paginiالقشرياتابراهيم عمارÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accircuit1 PartIDocument40 paginiAccircuit1 PartIriddhitadas9Încă nu există evaluări
- e = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceDocument8 paginie = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceReniel MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Laws and ApplicationsDocument10 paginiElectromagnetic Induction: Faraday's Laws and ApplicationsDisha KatariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No. 1 Sine Wave For Single Loop Generator: ObjectiveDocument5 paginiExperiment No. 1 Sine Wave For Single Loop Generator: ObjectiveAnam MugheesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEEE Unit 2-Single Phase Ac Circuits NotesDocument42 paginiBEEE Unit 2-Single Phase Ac Circuits NotesShreyash SargarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter5 Part 3 Sinusoidal Current and VoltageDocument46 paginiChapter5 Part 3 Sinusoidal Current and VoltageJOHN BRYNDON LANDICHOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes 1Document7 paginiLecture Notes 1zed cozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generate Sinusoidal Waveforms Using Electromagnetic InductionDocument10 paginiGenerate Sinusoidal Waveforms Using Electromagnetic InductionrodinooÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC FundamentalsDocument7 paginiAC FundamentalsJayrMenesÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic InductionDocument26 paginiNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic Inductionjaswanth .sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advantages of Purely Sinusoidal WaveformDocument5 paginiAdvantages of Purely Sinusoidal WaveformsurajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ohm's Law & Kirchhoff's LawsDocument18 paginiOhm's Law & Kirchhoff's LawsAkhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic InductionDocument20 paginiNCERT Solutions For Class 12 Physics Chapter 6 Electromagnetic InductionDileep GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Electrical EnggDocument79 paginiModule 3 Electrical EnggAnand AÎncă nu există evaluări
- EM - II - Lecture Notes PDFDocument86 paginiEM - II - Lecture Notes PDFUdayChanderAmbatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of AC CircuitsDocument49 paginiAnalysis of AC CircuitsScrappy WellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase AC CircuitsDocument29 paginiSingle Phase AC Circuitskali hembramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jarryd Price 2009 F.C.C.C Light and MatterDocument2 paginiJarryd Price 2009 F.C.C.C Light and MatterBob BobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mod2 AC Circuits Provided by MaamDocument72 paginiMod2 AC Circuits Provided by Maamanishdeshmukh369Încă nu există evaluări
- NotesDocument55 paginiNotesKhushi TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION BASICSDocument4 paginiELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION BASICSMahesh AbnaveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Engineering (BEEE101L) : Presented byDocument23 paginiBasic Electrical Engineering (BEEE101L) : Presented byAsh wanth100% (1)
- AC GenerationDocument18 paginiAC GenerationHEMACHANDRA REDDY KÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase, AC Circuits, Basics - RMS and Average QuantitiesDocument42 paginiSingle Phase, AC Circuits, Basics - RMS and Average QuantitiesKavitha NaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- LEC 1 Rev1Document35 paginiLEC 1 Rev1Ovie MacatiagÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC CurrentsDocument16 paginiAC CurrentsRoshan RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE 212 - Applied Electricity 2Document78 paginiEEE 212 - Applied Electricity 2noumsi briceÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEEE (Alternating-Current Circuits)Document6 paginiBEEE (Alternating-Current Circuits)Vedu KadamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objective: Apparatus Required:: Reflex Klystron CharacteristicsDocument5 paginiObjective: Apparatus Required:: Reflex Klystron Characteristicsratan lal mouryaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac GeneratorDocument18 paginiAc GeneratorPrathune KailashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cse-I-Basic Electricals Engg. L3 PDFDocument52 paginiCse-I-Basic Electricals Engg. L3 PDFDeeksha NaiduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alternating Current (Ac) CircuitsDocument34 paginiAlternating Current (Ac) CircuitsGabriel Carl AlpuertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 8 PPT - Maxwell.importantDocument15 paginiChapter 8 PPT - Maxwell.importantOsama Hassan100% (1)
- AC CircuitsDocument15 paginiAC CircuitsJayaprasadGollaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 2-Electrical and Electronic InstrumentsDocument147 paginiUNIT 2-Electrical and Electronic InstrumentspoornimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Circuits LectureDocument21 paginiAC Circuits LectureAko si GianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Circuits 2Document231 paginiElectrical Circuits 2RJ MCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic Induction - P2, Week 4Document15 paginiElectromagnetic Induction - P2, Week 4hooloovooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1Document15 paginiChapter 1yibelta abebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- theory midDocument15 paginitheory midSantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ac Fundamentals-NewDocument13 paginiAc Fundamentals-Newlarra100% (2)
- OutputDocument18 paginiOutputakterafuja7Încă nu există evaluări
- Gce o Level 2011 Physics 5058 Paper 1 SolutionsDocument26 paginiGce o Level 2011 Physics 5058 Paper 1 Solutionsjan12th2004Încă nu există evaluări
- Generator Write UpDocument14 paginiGenerator Write UpJerome B. PioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sinusoidal Waveform or Sine Wave in An AC Circuit PDFDocument16 paginiSinusoidal Waveform or Sine Wave in An AC Circuit PDFDemudu DonkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CL-12 Chapter 4 Magnetism PhysicsDocument15 paginiCL-12 Chapter 4 Magnetism PhysicsSomila SchoolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energy ConversionDocument98 paginiEnergy ConversionLouise UmaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formulae Magnetic Effect of CurrentDocument14 paginiFormulae Magnetic Effect of CurrentNathanian81% (16)
- Computer Architecture 1.1Document151 paginiComputer Architecture 1.1Ho Trong Nghia (K17 QN)Încă nu există evaluări
- Unitrol 1000Document4 paginiUnitrol 1000irfanWPKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eaton Cutler HammerDocument174 paginiEaton Cutler Hammerlj_treels100% (1)
- Philips Trade - Lighting - DONEDocument71 paginiPhilips Trade - Lighting - DONEKundan DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety Switches and Sens - Control - Safe Control SolutionsDocument24 paginiSafety Switches and Sens - Control - Safe Control SolutionsGl ZseÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEA Electrical EstimateDocument40 paginiNEA Electrical EstimateSurendra MaharjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ifm Electronic Part Number List & Price List 型号清单和价格表Document85 paginiIfm Electronic Part Number List & Price List 型号清单和价格表Bonnie Comen KimTai0% (1)
- Compact motorbike security system featuresDocument4 paginiCompact motorbike security system featuresbarbastylÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fabrication of Bladeless Wind Turbine-1Document10 paginiFabrication of Bladeless Wind Turbine-1SHAJAKHAN RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stock March 2023Document6 paginiStock March 2023manojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amplifier Audio Transistor Guitar Pre-Amp Circuit Simplest Operating Self BiasDocument2 paginiAmplifier Audio Transistor Guitar Pre-Amp Circuit Simplest Operating Self Biasdreyes2288Încă nu există evaluări
- Applications For Distributed Raman AmplificationDocument7 paginiApplications For Distributed Raman Amplificationalaki1000Încă nu există evaluări
- Module On Electrical Circuits and Electrical SafetyDocument17 paginiModule On Electrical Circuits and Electrical SafetyJomel HerrasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety SwitchesDocument56 paginiSafety SwitchesaglegarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- s7300 Failsafe Signal Modules Hardware Manual en-US en-US PDFDocument372 paginis7300 Failsafe Signal Modules Hardware Manual en-US en-US PDFJimy MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PERKOTEK Product Catalogue - 01.2023.1Document24 paginiPERKOTEK Product Catalogue - 01.2023.1android itelÎncă nu există evaluări
- FormulaDocument7 paginiFormulahelenarajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Week 1 Introduction To MicroprocessorDocument51 paginiLecture Notes Week 1 Introduction To Microprocessormargetrie100% (1)
- Lab 1 - Modeling Photovoltaic Module in Matlab-SimulinkDocument4 paginiLab 1 - Modeling Photovoltaic Module in Matlab-SimulinkJofy GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Reasons To Turn Down The Transmit Power of YourDocument3 pagini8 Reasons To Turn Down The Transmit Power of YourvdevanaiduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datasheet Tic116dDocument6 paginiDatasheet Tic116dJ Andres CMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cri-1000 2Document5 paginiCri-1000 2Zeeshan AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1763 Aprilia RSV 1000R 1000RFactory 2004 2008 100 EngDocument4 pagini1763 Aprilia RSV 1000R 1000RFactory 2004 2008 100 Engjesus de bergeracÎncă nu există evaluări
- Z77MA-G45/ Z75MA-G45 Seres: MS-7759 (v1.x) ManboardDocument146 paginiZ77MA-G45/ Z75MA-G45 Seres: MS-7759 (v1.x) ManboardSimon Dominguez ArangurenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rundown Conference PJB Connect Update 26 September 2022Document5 paginiRundown Conference PJB Connect Update 26 September 2022Bahim BahimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report On Final All WTG Description 111113Document35 paginiReport On Final All WTG Description 111113Jiaqing SuÎncă nu există evaluări
- DESIGNING THE PROPORTIONAL (P) AND PROPORTIONAL-INTEGRAL (PI) CONTROLLERS Control SystemDocument7 paginiDESIGNING THE PROPORTIONAL (P) AND PROPORTIONAL-INTEGRAL (PI) CONTROLLERS Control SystemjayxcellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Facade LightingDocument11 paginiFacade LightingsasikalaÎncă nu există evaluări