Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 15
Încărcat de
Sujay SantraTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 15
Încărcat de
Sujay SantraDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
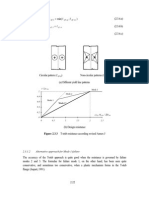
r =
0 ,8 5 F
Ec
(2.1.7)
L ar
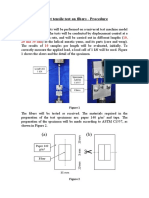
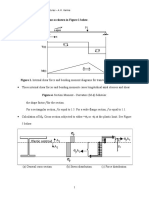
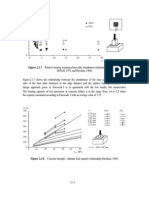
A flexible plate can be expressed in terms of equivalent rigid plate based on the same
deformations. For this purpose, half of a T-stub flange in compression is modelled as shown
in Figure 2.1.5.
cfl
x
E Ip
Figure 2.1.5 A flange of a flexible T-stub
The flange of a unit width is elastically supported by independent springs. The deformation of
the plate is a sine function, which can be expressed as
(x) = sin ( x / cfl )
(2.1.8)
The uniform stress on the plate can then be replaced by the fourth differentiate of the
deformation multiplied by E Ip, where E is the Young's modulus of steel and Ip is the moment
of inertia per unit length of the steel plate with thickness t (Ip = t3 / 12).
(x) = Es Ip ( / c fl )4 sin ( x / c fl ) = Es
12
( / cfl ) 4 sin ( x / c fl ) (2.1.9)
The concrete part should be compatible with this stress
(x) = (x) h ef / E c
(2.1.10)
where hef is the equivalent concrete height of the portion under the steel plate. Assume that
hef = cfl hence
(x) = (x) c fl / Ec
(2.1.11)
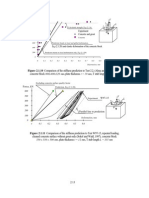
Substitution gives
sin ( x / cfl ) = E t3 / 12 ( / c fl )4 sin ( x / cfl ) c fl / Ec
This may be expressed as
2.7
(2.1.12)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- E9.10 Homework Ofr Advance Material SelectionDocument1 paginăE9.10 Homework Ofr Advance Material SelectionGeorge SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part 04 SET - 481 - 482 - PDFDocument2 paginiPart 04 SET - 481 - 482 - PDFAkshat JoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document37 paginiChapter 4Arun SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of The Seismic Demand Chord Rotations of Structural Reinforced Concrete MembersDocument8 paginiEvaluation of The Seismic Demand Chord Rotations of Structural Reinforced Concrete MembersSEP-PublisherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Use Steel SpesificationDocument7 paginiUse Steel SpesificationiksanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 16Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 16Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Bearing PlatesDocument4 paginiSteel Bearing Platessebastian9033Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 11 Shape Factors in Materials SelectionDocument5 paginiCH 11 Shape Factors in Materials SelectionKristi GonzalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejemplo de Deflexion Aci 435Document4 paginiEjemplo de Deflexion Aci 435OmarJosueLeonCruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aluminum PapeBehavior and Design of Aluminum Flexural Members With Tapered Thicknessr2aDocument22 paginiAluminum PapeBehavior and Design of Aluminum Flexural Members With Tapered Thicknessr2astefanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Materiaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter5Document34 paginiMateriaalkunde 1 Slides Chapter5ahmed11 engyemenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Plate BucklinDocument12 paginiIntroduction To Plate BucklinAndré FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fastener FlexibilityDocument3 paginiFastener FlexibilitySonell ShroffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture - RCIII - RC Hinge Design - 4Document9 paginiLecture - RCIII - RC Hinge Design - 4Rodain NajjarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study Into Optimization of Stiffeners in Plates PDFDocument16 paginiA Study Into Optimization of Stiffeners in Plates PDFJohn PetterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thornton 1990 A Q3Document3 paginiThornton 1990 A Q3Wheni Candra Dewi AsmaralisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FRP Concrete ConfinementDocument3 paginiFRP Concrete ConfinementCesar RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 3 - AE Analysis and Design of Two-Way SlabsDocument111 paginiCH 3 - AE Analysis and Design of Two-Way Slabsephrem100% (3)
- Kara 2015Document46 paginiKara 2015Besian SinaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Czech Technical University, Faculty of Civil Engineering Université de Liège, Institut Du Génie Civil, Département MSMDocument26 paginiCzech Technical University, Faculty of Civil Engineering Université de Liège, Institut Du Génie Civil, Département MSMTiago CunhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of The Collapse Load of An ADocument13 paginiCalculation of The Collapse Load of An ALuminita GeorgetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Initial Soil Springs Stiffness For Laterally Loaded Piles: AbstractsDocument6 paginiInitial Soil Springs Stiffness For Laterally Loaded Piles: Abstractswidayat81Încă nu există evaluări
- Double Tapered FRP Beam For Automotive Suspension: Leaf SprungDocument22 paginiDouble Tapered FRP Beam For Automotive Suspension: Leaf SprungYogesh ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRB CasingDocument2 paginiBRB Casingshanky_77Încă nu există evaluări
- Base Plate and Anchor Bolt DesignDocument30 paginiBase Plate and Anchor Bolt DesignShaikh Muhammad Ateeq100% (1)
- K Design Graphs and Charts For Raft Foundations Spanning Local DepressionsDocument8 paginiK Design Graphs and Charts For Raft Foundations Spanning Local DepressionsPetar ValevÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 The in Uence of Holes: 8.1 Hole Lines On Cylinders, Spheres, and ConesDocument2 pagini8 The in Uence of Holes: 8.1 Hole Lines On Cylinders, Spheres, and ConesBill HubbardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap5 1Document53 paginiChap5 1Fernando LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Closed Form Solution For Predicting The Thick Elastic Plate Behavior of CLT and Timber Panels With GapsDocument16 paginiClosed Form Solution For Predicting The Thick Elastic Plate Behavior of CLT and Timber Panels With GapsTom Van den BosscheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Torsion in Closed SectionsDocument11 paginiTorsion in Closed SectionsJason GarnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tensile Tests - ProcedureDocument3 paginiTensile Tests - ProcedureAna Carolina TrindadeÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main Elasticity Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFDocument9 paginiJEE Main Elasticity Previous Year Questions With Solutions PDFaugustÎncă nu există evaluări
- dθ D pL dA p dF: 1-d. Thin-walled Pressure VesselsDocument3 paginidθ D pL dA p dF: 1-d. Thin-walled Pressure VesselsJasleneDimarananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tapered Power PolesDocument12 paginiTapered Power PolesDon DeolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plates & Shells - 11Document14 paginiPlates & Shells - 11RC Dela RocaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Old Paper On Vierendeel TrussDocument20 paginiOld Paper On Vierendeel TrusssmwassyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear Centre 2 Thin WalledDocument3 paginiShear Centre 2 Thin WalledAdil GhazanfarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete&baseplate PDFDocument18 paginiConcrete&baseplate PDFmitimas2003Încă nu există evaluări
- Ese Som Pyq Chapter 1Document38 paginiEse Som Pyq Chapter 1Krishna GovindÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pengaruh Rasio Tulangan-Balok T - AkmaluddinDocument13 paginiPengaruh Rasio Tulangan-Balok T - Akmaluddinakmal2k4Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural BracingDocument4 paginiStructural BracingjohnnybebadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength Curves For Web Crippling DesignDocument6 paginiStrength Curves For Web Crippling Designuhu_plus6482Încă nu există evaluări
- Deflection Calculations FLAT SLABDocument12 paginiDeflection Calculations FLAT SLABscshekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element Static and Dynamic Analyses of Folded Plates: Asokendu Samanta, Madhujit MukhopadhyayDocument11 paginiFinite Element Static and Dynamic Analyses of Folded Plates: Asokendu Samanta, Madhujit MukhopadhyayJogger JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISTAM - Stress Concentration Factor Convergence Study of A Thin PlateDocument7 paginiISTAM - Stress Concentration Factor Convergence Study of A Thin PlateKanak_KalitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Static Analysis of Isotropic & Orthotropic Plates With Central CutoutDocument7 paginiStatic Analysis of Isotropic & Orthotropic Plates With Central CutoutKanak_KalitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Elements in Analysis and Design: S. Haldar, A.H. SheikhDocument9 paginiFinite Elements in Analysis and Design: S. Haldar, A.H. SheikhJogger JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beam DesignDocument30 paginiBeam DesignSarat Srinivas BeesettiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABC Moments in The Beams As Shown in Figure 1 Below.: Plastic Centroid. A A A Plastic Centroid. A A ADocument21 paginiABC Moments in The Beams As Shown in Figure 1 Below.: Plastic Centroid. A A A Plastic Centroid. A A ATabish IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elastic Buckling of Plates With HoleDocument16 paginiElastic Buckling of Plates With Hole201087Încă nu există evaluări
- Inelastic Buckling of Beam-Columns With Unequal End Moments: J. Construct. Steel Research 5 (1985) 195-212Document18 paginiInelastic Buckling of Beam-Columns With Unequal End Moments: J. Construct. Steel Research 5 (1985) 195-212juan carlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Point Bending Test 1Document18 paginiThree Point Bending Test 1dinesh ramratanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AECT210 Lecture 6Document7 paginiAECT210 Lecture 6nony321Încă nu există evaluări
- Composite BeamsDocument5 paginiComposite BeamsbertinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsDe la EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperbolic Functions: with Configuration Theorems and Equivalent and Equidecomposable FiguresDe la EverandHyperbolic Functions: with Configuration Theorems and Equivalent and Equidecomposable FiguresÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Wave Concept in Electromagnetism and Circuits: Theory and ApplicationsDe la EverandThe Wave Concept in Electromagnetism and Circuits: Theory and ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianDe la EverandThe Plasma Dispersion Function: The Hilbert Transform of the GaussianEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Stress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsDe la EverandStress in ASME Pressure Vessels, Boilers, and Nuclear ComponentsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationDe la EverandTunnel Field-effect Transistors (TFET): Modelling and SimulationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 41Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 41Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 17Document12 paginiCH 17SergejjjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 42Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 42Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 43Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 43Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 42Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 42Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Shear Connector For StringerDocument32 paginiDesign of Shear Connector For StringerSujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 29Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 29Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 39Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 39Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 41Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 41Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 31Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 31Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 32Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 32Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 18Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 18Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 193801063-Base-Plates-Practicase-Details-in-Steel-Structures 40 PDFDocument1 pagină193801063-Base-Plates-Practicase-Details-in-Steel-Structures 40 PDFSujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 30Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 30Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 21Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 21Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 27Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 27Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 28Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 28Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 23Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 23Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 25Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 25Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 25Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 25Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 20Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 20Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 19Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 19Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 22Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 22Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 27Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 27Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 17Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 17Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 18Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 18Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 16Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 16Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 13Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 13Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Base Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 14Document1 paginăBase Plates Practicase Details in Steel Structures 14Sujay SantraÎncă nu există evaluări