Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
C 4 S 1
Încărcat de
api-261372832Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
C 4 S 1
Încărcat de
api-261372832Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Atoms
Section 1
Key Ideas
Who came up with the first theory of atoms?
What did Dalton add to the atomic theory?
How did Thomson discover the electron?
What is Rutherfords atomic model?
Atoms
Section 1
Bellringer
When scientists wanted to find out what an atom was, they
were not able to look directly at what the atom was made
of. They had to make inferences from the results of many
different experiments. It was like trying to describe a
picture, such as the one on the next slide, with only small
portions visible.
Atoms
Section 1
1. Write a description what you can see of the above
picture.
2. What information or parts of the picture would make
your descriptions more accurate without revealing
the entire picture?
Atoms
Section 1
The Beginnings of Atomic Theory
Who came up with the first theory of atoms?
In the fourth century BCE, the Greek philosopher
Democritus suggested that the universe was
made of indivisible units called atoms.
Democritus did not have evidence for
his atomic theory.
Atoms
Section 1
Atoms
Section 1
Daltons Atomic Theory
What did Dalton add to the atomic theory?
According to Dalton, all atoms of a given
element were exactly alike, and atoms of
different elements could join to form compounds.
Atoms
Section 1
Atoms
Section 1
Daltons Atomic Theory, continued
Dalton used experimental evidence.
Law of definite proportions: A chemical compound always
contains the same elements in exactly the same proportions by
weight or mass.
Daltons theory did not fit all observations.
Atoms
Section 1
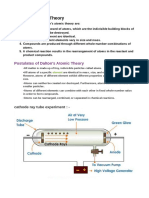
Thomsons Model of the Atom
How did Thomson discover the electron?
Thomsons cathode-ray tube experiment
suggested that cathode rays were made of
negatively charged particles that came from
inside atoms.
Atoms
Section 1
Visual Concept: Thomsons Cathode-Ray
Tube Experiment
Atoms
Section 1
Thomsons Model of the Atom, continued
Thomson developed the plum-pudding model.
In his cathode-ray tube experiment, Thomson had
discovered electrons.
electron: a subatomic particle that has a negative
charge
Thomsons plum-pudding model: electrons are spread
throughout the atom, like blueberries in a muffin
Atoms
Section 1
Thomsons Plum Pudding Model
Thomson believed the electrons in an atom are randomly
scattered within a positive cloud. No Nucleus in this
model.
Atoms
Section 1
Rutherfords Model of the Atom
What is Rutherfords atomic model?
Rutherford proposed that most of the mass of
the atom was concentrated at the atoms center.
Atoms
Section 1
Rutherfords Model of the Atom,
continued
Rutherford conducted the gold-foil experiment.
Rutherford discovered the
nucleus.
nucleus: an atoms central
region, which is made up of
protons and neutrons
Atoms
Section 1
Visual Concept: Rutherfords Gold Foil
Experiment
Atoms
Section 1
Atoms
Section 1
Atoms
Section 1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Week 12Document1 paginăWeek 12api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 11Document1 paginăWeek 11api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 13Document1 paginăWeek 13api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 10Document1 paginăWeek 10api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 10Document1 paginăWeek 10api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 13Document1 paginăWeek 13api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 12Document1 paginăWeek 12api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 9Document1 paginăWeek 9api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 9Document1 paginăWeek 9api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 6Document1 paginăWeek 6api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 7Document1 paginăWeek 7api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 8Document1 paginăWeek 8api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 8Document1 paginăWeek 8api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 6Document1 paginăWeek 6api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 7Document1 paginăWeek 7api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 8Document1 paginăWeek 8api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 6Document1 paginăWeek 6api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 9Document1 paginăWeek 9api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 5Document1 paginăWeek 5api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- Week 5Document1 paginăWeek 5api-261372832Încă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- G8 Science Q3 Adm Module For PrintingDocument36 paginiG8 Science Q3 Adm Module For PrintingJenn ElardeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems 2Document8 paginiProblems 2Jaider MárquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Revision Notes AQA GCSE (9 1) ChemistryDocument9 paginiMy Revision Notes AQA GCSE (9 1) ChemistrySaad Javeed AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science8 q3 Mod3 Week5-6 Subatomic-Particles v5Document28 paginiScience8 q3 Mod3 Week5-6 Subatomic-Particles v5Lawrence Bianes100% (1)
- Atomic Models - TheoryDocument109 paginiAtomic Models - TheoryDr-Walid FemtosecondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thomson's Model of AtomDocument16 paginiThomson's Model of AtomGurjyot Uppal100% (1)
- Atomic Theories and ModelsDocument12 paginiAtomic Theories and ModelsJhana Kate Falculan100% (1)
- AQA - Chemistry - Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - KnowIT - GCSEDocument86 paginiAQA - Chemistry - Atomic Structure and The Periodic Table - KnowIT - GCSEAlwayne SappletonÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLP Extra On Formation of ElementsDocument9 paginiDLP Extra On Formation of ElementsDaniah AllemaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science8 Q3 Week5Document20 paginiScience8 Q3 Week5Kathrina De SenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psma PrelimsDocument42 paginiPsma PrelimsPrincess Rose GamboaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 A Simple Atomic Model QPDocument38 pagini1.1 A Simple Atomic Model QPV LawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Project Fa 4 On ModelsDocument16 paginiChemistry Project Fa 4 On ModelsVARIGALA SAI CHARAN GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phet SimulationDocument4 paginiPhet SimulationPierre FilerioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rutherford and Bohr's Atomic ModelDocument101 paginiRutherford and Bohr's Atomic Modelthrivikram100% (1)
- Day 2Document6 paginiDay 2Kinberly AnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Atom ProjectDocument21 paginiStructure of Atom ProjectJaisam JÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Science ReviewerDocument8 paginiPhysical Science ReviewerAliana FemiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Structure of The Atom - Thomson ModelDocument34 pagini1 - Structure of The Atom - Thomson ModelBahaa GhirbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Postulates of Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument5 paginiPostulates of Dalton's Atomic TheoryVenugopal RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chem QuizDocument2 paginiChem Quizmisganamarcos10Încă nu există evaluări
- CH 4 Test Review sheet-KEYDocument4 paginiCH 4 Test Review sheet-KEYNaomi HeywardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aqa 7404 7405 Collins SampleDocument33 paginiAqa 7404 7405 Collins SampleJustin HadinataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Document7 paginiAtomic ST 8 IIT Class ...Venugopal RÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12Ch2 Atom ModelsDocument31 pagini12Ch2 Atom ModelsSarah SaeedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Theory WebQuestDocument92 paginiAtomic Theory WebQuestTamara Baez FloresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic Structure and The Subatomic ParticlesDocument7 paginiAtomic Structure and The Subatomic ParticlesDaniel ClementeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discovering The AtomsDocument59 paginiDiscovering The AtomsyoroshikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Investigating Atoms and Atomic TheoryDocument34 paginiInvestigating Atoms and Atomic Theorysophia luÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project On Atomic StructureDocument13 paginiProject On Atomic Structureswati0611Încă nu există evaluări