Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Y6 t2 Unit 2 Mathematics Term
Încărcat de
api-267136654Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Y6 t2 Unit 2 Mathematics Term
Încărcat de
api-267136654Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Year
6 Mathematics Term: 2 Unit: 2
Strand : Number and Algebra Substrand: Addition and Subtraction 2
Outcomes:
selects and applies appropriate strategies for subtraction with counting numbers of any size MA3-5NA
describes and represents mathematical situations in a variety of ways using mathematical terminology and some conventions MA3-1WM
selects and applies appropriate problem-solving strategies, including the use of digital technologies, in undertaking investigations MA3-2WM
gives a valid reason for supporting one possible solution over another MA3-3WM
Content:
solve
addition
and
subtraction
word
problems
involving
whole
numbers
of
any
size,
including
problems
that
require
more
than
one
operation,
eg
'I
have
saved
$40
000
to
buy
a
new
car.
The
basic
model
costs
$36
118
and
I
add
tinted
windows
for
$860
and
Bluetooth
connectivity
for
$1376.
How
much
money
will
I
have
left
over?'
select
and
apply
appropriate
mental
and
written
strategies,
with
and
without
the
use
of
digital
technologies,
to
solve
unfamiliar
problems
(Problem
Solving)
explain
how
an
answer
was
obtained
for
an
addition
or
subtraction
problem
and
justify
the
selected
calculation
method
(Communicating,
Problem
Solving,
Reasoning)
reflect
on
their
chosen
method
of
solution
for
a
problem,
considering
whether
it
can
be
improved
(Communicating,
Reasoning)
record
the
strategy
used
to
solve
addition
and
subtraction
word
problems
use
selected
words
to
describe
each
step
of
the
solution
process
(Communicating,
Problem
Solving)
Key
Ideas
Teaching and Learning
Resources
Select and apply efficient
mental, written and
calculator strategies to
solve word problems and
record the strategy used
Ignition
Activities
Maths
Starters
http://mathsstarters.net/
Many
good
games
to
promote
mental
computation
Make
100
or
1000
1.The
aim
is
to
score
1000
as
close
as
possible
without
busting
(passing
1000).
2.The
teacher
rolls
the
die
and
announces
the
number.
Students
may
choose
to
multiply
that
number
by
10
or
100
or
score
it
at
face
value,
e.g.
2
may
be
scored
as
2
or
20
or
200.
Once
a
decision
has
been
made
it
cannot
be
changed.
3.The
die
is
rolled
again.
If
the
number
is
(say)
4,
students
decide
to
score
this
as
4
or
40
or
400
and
record
it,
completing
the
progressive
total.
4.This
continues
until
9
rolls
have
been
completed.
Note:
All
rolls
must
be
used.
5.The
student
who
scores
1000
the
number
closest
to
(but
below)
1000
wins.
Variations
(a)Use
a
16
die
or
a
09
die.
Ask
students
how
they
will
vary
their
strategies
if
Maths
Plus
6
p.
2,
30
Language
Differentiation
Assessment
Pre-Assess
Problem:
Peter
collected
568
blue
cards,
392
red
cards
and
175
green
cards.
Sue
had
a
total
of
1534
cards.
How
many
more
cards
did
Sue
have
than
Peter?
Regn
Students should be able
to communicate using the
following language: plus,
sum, add, addition,
increase, m inus, the
difference between,
subtract, subtraction,
decrease, equals, is equal
to, operation, digit
you change from a 16 to a 09 die.
(b)Set a different target.
(i)Target = 200 How will you vary your strategies from the original game?
(Students should realise that they will need to multiply by 10 more often.)
(ii)Target = 1000 and you may multiply by 100 once and once only during the
game.
(c)Allow addition or subtraction of each number rolled.
Explicit Teaching
Missing Addends 1
Write the following problems on the board for students to solve. Before
beginning, discuss with the students all of the possible strategies they could use
to solve addition problems.
List these with examples of each as a reference point.
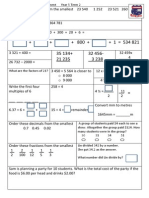
1. 70 + _ + 20 = 1520 2. 421 + 147 + _ = 661
3.
+ 110 + 339 = 451
4. 25 + _ + 747 = 1586
5. 771 + + 43 = 1166
6. 441 + 1 +_ = 470
7. 894 + + 826 = 1725 8. _ + 262 + 81 = 984
9. 941 + 339 + = 1334 10. 623 + 83 +
= 1456
11. 607 + 431 + = 1137 12. + 498 + 253 = 763
13. + 126 + 351 = 535 14. 711 + 505 +
= 1293
15. 989 + + 930 = 1981 16. + 137 + 19 = 359
When students have completed the problems and answers have been checked.
Invite students to explain which strategy they used for solving the problems.
Ask them:
- Do you think that was the best strategy? Why/why not?
- What alternate strategy could you have used?
Missing Addends 2
Using the strategy list from the previous lesson, have students choose a suitable
strategy to solve the following. Write the following examples on the board:
1. 15 + 31 +
_ + 49 + 2600 = 2819 2. + 91 + 86 + 151 + 2000 =2337
3. 6 + 10 + 68 + _ + 2900 = 3146 4.
+ 800 + 80 + 147 + 11 =1043
5.
+ 76 + 39 + 111 + 300 = 531
6. 168 + 49 + + 1500 = 1768
Invite students to explain what their strategy was and whether they felt it was
effective.
Working in pairs have students create 5 addends each for their partner to solve.
Check and discuss answers with each other.
Adjust
the
difficulty
of
the
sums
based
on
ability
level
Advanced
Primary
Post
Assess
Maths
p.6,
79
Addition of 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6 digit Numbers With Trading
Revise place value lining up with numbers of different sizes e.g
234
65
+9402
Missing addends
3567_
+ 6_ _2
4_1 31
Year 6 Mathematics Term: 2 Unit: 2
Strand: Statistics and Probability Substrand : Data 2
Outcomes:
describes and represents mathematical situations in a variety of ways using mathematical terminology and some conventions MA3- 1WM
gives a valid reason for supporting one possible solution over another MA3-3WM
uses appropriate methods to collect data and constructs, interprets and evaluates data displays, including dot plots, line graphs and two-way tables MA3-18SP
Content:
Interpret and compare a range of data displays, including side-by-side column graphs for two categorical variables (ACMSP147)
interpret data presented in two-way tables
create a two-way table to organise data involving two categorical variables, eg
Key Ideas
Interpret and create two-
way tables in digital
media and elsewhere
Language
Students should be able to
communicate using the
following language: data,
collect, category, display,
table, column graph, scale,
axes, two-way table, side-
by-side column graph,
misleading, bias.
Teaching and Learning
Explicit Teaching
Two-Way Tables
Activities found at syllabus bites site:
http://lrrpublic.cli.det.nsw.edu.au/lrrSecure/Sites/LRRView/14118/14118_03.htm
Gathering
Data
Discuss
variables
and
how
to
ask
questions
that
specify
the
variables.
Targeting
Maths
6
p.194
Hands
On
Collecting
Data
Activities
Nelson
Maths
6
p.80,81,82.
Students
collect
data
and
rule
tables
to
display
data
Resources
Targeting
Maths
6
p.194
Nelson
Maths
6
p.80,81,82
Assessment
Pre-Assess
Post
Assess
Regn
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Year 6 T2u5Document5 paginiYear 6 T2u5api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 8Document6 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 8api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Tenambit Ps Maths Key Ideas Ass Yr5 t2Document3 paginiTenambit Ps Maths Key Ideas Ass Yr5 t2api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 T2u3 Mathematics TermDocument6 paginiYear 6 T2u3 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 10Document5 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 10api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 5 Mathematics TermDocument5 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 5 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Editing t2-2Document22 paginiEditing t2-2api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 7 Mathematics TermDocument5 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 7 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Speaking and Listening Tasks t2-3Document2 paginiSpeaking and Listening Tasks t2-3api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 2 Mathematics TermDocument8 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 2 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 9Document4 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 9api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 6 Mathematics TermDocument6 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 6 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 6Document10 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 6api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 3 Mathematics TermDocument6 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 3 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit1 Mathematics TermDocument5 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit1 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 7Document4 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 7api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 t1 Unit 4 Mathematics TermDocument6 paginiYear 6 t1 Unit 4 Mathematics Termapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 8Document6 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 8api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 10Document5 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 10api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 9Document6 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 9api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 5Document10 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 5api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 4Document8 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 4api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 1Document5 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 1api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 2Document10 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 2api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 t1 Unit 3Document10 paginiYear 5 t1 Unit 3api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 5 Mathematics Portfolio AboveDocument34 paginiYear 5 Mathematics Portfolio Aboveapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Teaching Measurement s2 and s3 Volume and Capacity and MassDocument64 paginiTeaching Measurement s2 and s3 Volume and Capacity and Massapi-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 Mathematics Term 2 Unit 1Document5 paginiYear 6 Mathematics Term 2 Unit 1api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- Estimation Sum Difference 3Document2 paginiEstimation Sum Difference 3api-267136654Încă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Line Follower Robot ProjectDocument8 paginiLine Follower Robot ProjectPuneeth ShettigarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Netflix Business Model Canvas Highlights Key StrategiesDocument1 paginăNetflix Business Model Canvas Highlights Key StrategiesNemo SecretÎncă nu există evaluări
- Luccon PflegehinweisEDocument2 paginiLuccon PflegehinweisEDejana Lazarus Lufkin MarosÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV - Sanjana DhaidwalDocument1 paginăCV - Sanjana DhaidwalPayal KathiawadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- How to love and understand the independent ISTP personality typeDocument4 paginiHow to love and understand the independent ISTP personality typeKingwaKamencuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gambar Tata Ruang Landscape PDFDocument11 paginiGambar Tata Ruang Landscape PDFmhaiqalÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Franziska Bieri) From Blood Diamonds To The KimbeDocument226 pagini(Franziska Bieri) From Blood Diamonds To The KimbeMona SaidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antipsychotic DrugsDocument2 paginiAntipsychotic DrugsDana Mae AfanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BusseDocument12 paginiBusseGabriel FerreiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enterprise Performance Management - Performance ManagementDocument40 paginiEnterprise Performance Management - Performance ManagementKhushali OzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anticharm 2Document15 paginiAnticharm 2api-3697331100% (1)
- BE Semester-VIII (Civil Engineering) Question Bank (Design of Steel Structures)Document2 paginiBE Semester-VIII (Civil Engineering) Question Bank (Design of Steel Structures)Suresh RajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Mounting and LabelingDocument1 pagină12 Mounting and LabelingEunice AndradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automating Network Slicing Operations in The 5G Core With OrchestrationDocument18 paginiAutomating Network Slicing Operations in The 5G Core With OrchestrationmorganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erin Alles BipDocument39 paginiErin Alles Bipapi-270220688Încă nu există evaluări
- CeaDocument28 paginiCeaPong YasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Paper Final Report PDFDocument3 paginiThesis Paper Final Report PDFFiraol NegasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tac71 09Document32 paginiTac71 09TateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hurdle TechnologyDocument26 paginiHurdle TechnologyPradeep Kumar93% (14)
- Shaheen Public H/S School Mirpur Mathelo CH # 07 Work Power and Energy By: Laghari Zoheb HassanDocument40 paginiShaheen Public H/S School Mirpur Mathelo CH # 07 Work Power and Energy By: Laghari Zoheb HassanLaghari Hassan XohebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Social and Economic History of East Africa P2102Document137 paginiSocial and Economic History of East Africa P2102Sserwanja Emmanuel100% (9)
- Design and Construction of A Tower Crane: June 2009Document6 paginiDesign and Construction of A Tower Crane: June 2009Beza GetachewÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Philippine Tourism Master Plan 1991-2010Document7 paginiThe Philippine Tourism Master Plan 1991-2010Zcephra MalsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Electric Motor PDFDocument89 paginiBasics of Electric Motor PDFRajeevAgrawal100% (3)
- Maint - N00272a2Document76 paginiMaint - N00272a2bobbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSP FlexDocument4 paginiCSP FlexBhoomaiah Sunkenapalli100% (1)
- PSK Questions and AnswersDocument5 paginiPSK Questions and AnswersMiraj Sheikh50% (2)
- Air Compressor Trouble Shooting Guide - 4Document6 paginiAir Compressor Trouble Shooting Guide - 4Ashwin NarayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beechtree ISCDocument6 paginiBeechtree ISCWinterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Study of HospitalDocument18 paginiLiterature Study of HospitalJasleen KaurÎncă nu există evaluări