Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lab File Basics of Electronics & Electrical Engg. (For PTU B.Tech. 1st Year)
Încărcat de
CutieTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lab File Basics of Electronics & Electrical Engg. (For PTU B.Tech. 1st Year)
Încărcat de
CutieDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DAVIET
NAME OF LAB: Basic Electrical & Electronics
Engg.
CODE : ELE -103
Laboratory Manual
List of experiments:
1) To find voltage ,current relationship and power factor of a given R-L circuit
2) To connect three identical single phase transformer for three phase power
Transformation through following connection
• Star-Star
• Star-Delta
• Delta- Star
• Delta-star
3) To connect start and reverse the direction of rotation of three-phase induction
motor
4) To find voltage ,phase voltage relationship ,line current, phase current relationship
incase of star –connected & delta connected ,3phase balanced Load circuit
5) To perform open circuit & short circuit tests of a single phase transformer
Also find the transformation ratio &efficiency
6) To perform the block rotor test of a three phase induction motor
7) To study the response of P-N Junction Diode
8) To study the transistor response
9) To analyze the truth tables of various basic digital gates.
10) To study the response of LVDT Transducer
11) To study various measuring instrument
1. Moving iron Instrument – a .Attraction type b. Repulsion type
2. Permanent magnet moving coil instrument
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -1-
DAVIET
3. Dynamometer type instrument
12) To study the use of multimeter.
13) To study the speed control of a dc shunt motor& to draw the speed variations
With respect to:
• Field control
• Armature control
EXPERIMENT NO. 1
AIM: To find voltage, current relationship and power factor of a given R-L circuit.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.NO NAME OF RANGE QUANTITY
APPARATUS
1. VATRIAC(Single 0-260 V 1
Phase)
2. Resistive load 0-10 A 1
3. Inductive load 0-10 A 1
4. AC voltmeter 0-300 V 1
5. AC Ammeter 0-10 A 1
6. Wattmeter(singlephase 0-1 KW 1
)
7. DPIC main switch 32V 1
8. Connecting Leads ----- As per
requirement
THEORY: When only resistive load is connected with AC supply then the power factor
remainsUnity but when inductive load is connected with AC supply then the power factor
reduces,it can be ½ i.e. efficiency of single phase system reduces to 50% which effects our
electricity consumptionas well as AC Efficiency . But many stages RL series circuit is used
for eg. Street light . So when a resistance and an inductor both are connected in series then
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -2-
DAVIET
this type of circuit is called RL Series circuit and total resistance of both is called impedance.
And is denoted by Z and its units are Ohm.
So:-
Current flowing through an AC circuit is given as I=V/Z
Where V is the AC supply voltage and Z is the impedance of the circuit in ohms.
Power factor of an AC supply is given by cosΦ=P/VI
Where P is the power of the given load circuit in watts , V is the voltage applied to the circuit
in the
Volts and I is the current in amperes flowing through the circuit.
And the angle Φ is known as relation between V and I and its value can be calculated by
following
Formula:- Φ = (P/VI)
CIRUCIT DIAGRAM:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -3-
DAVIET
PROCEDURE: Do as follows:
1. Make the connections of Variac, ammeter, wattmeter, voltmeter, load, as shown in circuit
diagram.
2. Connect this circuit to the main single phase supply.
3. Take the readings of ammeter, wattmeter, voltmeter for every 50V setting of Variac in the
Observation table as given below.
4. Note down 5-6 readings.
OBSERVATION AND CALCULATION:
S.NO. VOLTMETER AMMETER POWER(P) COSΦ=P/VI (P/VI)
READING (V) READING(I) WATTS
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
PRECAUTIONS:-1.Connections should be right & tight.
2.Always take accurate reading.
3.Meters used should be without error.
4.Be alert while doing practical.
RESULT:-
1.Current I increases directly in proportion to applied voltage V.
2.Power factor of the circuit is approx. same throughout for a given load.
EXPERIMENT NO. 2
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -4-
DAVIET
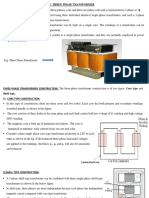
AIM: To connect three identical single phase transformer for three phase power
transformation through following connections:
1. Star-Star
2. Star-Delta
3. Delta-Delta
4. Delta-Star
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.NO. NAME OF THE APPARATUS RANGE QUANTITY
1. Vatriac(3-phase) 0-460V 1
2. Single phase transformer 2KVA 3
3. AC Voltmeter 0-500V 3
4. AC Ammeter 0-10A 3
5. TPIC main switch 32A 1
6. Connecting leads ------ As per reqiurement
THEORY:
When Star connections are done
Line voltage(VL)=√3 X Phase voltage(Vph)
Line current (IL)=Phase current(Iph)
When delta connections are done
Line voltage(VL)=Phase voltage (Vph)
Line Current(IL)=√3 X Phase current(Iph)
CIRUCIT DIAGRAM:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -5-
DAVIET
PROCEDURE: Do as follows:
First find primary & secondary windings of each transformer
Mark all transformer windings polarities by sequence test.
Connect all the three connections in following manner:
1. Star-Star
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -6-
DAVIET
2. Star-Delta
3. Delta-Delta
4. Delta-Star
Take the readings of voltmeter in the observation table as given below:
Note down at least one reading of each.
OBSERVATION AND CALCULATION:
Connections S. No. Voltmeter Voltmeter Ammeter Ammeter
Reading(VL) Reading(Vph) Reading(IL) Reading(Iph)
Star-Star 1.
Star-Delta 2.
Delta-Delta 3.
Delta-Star 4.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Connections should be right & tight.
2. Always take accurate reading.
3. Meters used should be without error.
4. Be alert while doing practical.
RESULT:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -7-
DAVIET
When Star connection are done
Line voltage (VL)=√3 X Phase voltage(Vph)
Line current (IL)=Phase current (Iph)
When Delta connections are done
Line voltage (VL)=Phase voltage(Vph)
Line current (IL)= √3 X Phase current(Iph)
EXPERIMENT NO.3
AIM: To connect, start and reverse the direction of rotation of three-phase induction
Motor.
Apparatus required:
S.NO. Apparatus Required RANGE Quantity
1. 3 ph induction motor 5hp,415V 1
2. Connecting Leads ----- As per
requiremet
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -8-
DAVIET
3. DOL Starter 1
4. TPIC main switch 32 Amp 1
5. AC voltmeter 0-500V 1
6. AC Ammeter 0-20Amp 1
Theory:
When motor is connected to a three-phase supply through a DOL Starter (Direct Online
Starter) or a Star delta Starter, then the motor should run in anticlock wise direction
but/Many times motor runs clockwise. So, it is desired to change its DOL. So, for the same
wehave to interchange any two supply terminal of the motor to make its direction anti-
clockwise.The starter’s main function is to protect the motor from overload condition and it
also provides easy ON-OFF the motor so it is necessary to use a starter. In this practical we
have used a DOL starter,which runs a three-phase 3hp motor.Whose circuit diagram is as
shown.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. -9-
DAVIET
PROCEDURE: Do as follows:
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram-1
2. Now switch on the power supply.
3. The direction of rotation (DOR) should be noted when motors starts.
4. Now if the direction is clockwise or it is required to change the direction of rotation of
motor then the interchange any two phases as shown in diagram-3.
5. Now note the new DOR of motor.
6. Now direction of rotation of the motor is reversed by changing any two phase
terminal.
OBSERVATIONS & CALCULATIONS
S.NO. IN FIRST STAGE IN SECOND STAGE
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 10 -
DAVIET
CONNECTIONS DOR CONNECTIONS DOR
1.
2.
3.
4.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram.
2. Connections should be right & tight.
3. Note the direction of rotation carefully.
4. Do every procedure carefully.
RESULT: Now we have come to know how to change the DOR of any three phase
induction motor by interchanging any two supply terminals.
EXPERIMENT NO. 4
AIM: To find the line voltage, phase voltage relationship,line current,phase current
relationship in case of star – connected & delta connected,3-phase balanced load
circuit.
APPPARTUS REQUIRED
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 11 -
DAVIET
S.NO. NAME OF RANGE QUANTITY
APPARATUS
1. Vatriac(3-phase) 0-460V 1
2. 3-phase Balanced 0-10A 1
Resistive load
3. AC voltmeter 0-500V 3
4. AC Ammeter 0-10A 3
5. TPIC main switch 32A 1
6. Connecting leads ------ As per
requirement
THEORY:
When Star connections are done
Line voltage (VL)=√3 X Phase voltage (Vph)
Line current (IL)=Phase current(Iph)
When Delta connections are done
Line voltage (VL)=Phase voltage(Vph)
Line current(IL)=√3 X Phase current (Iph)
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 12 -
DAVIET
PROCEDURE: Do as follows:
1. Make the connections of variac, ammeter, wattmeter and voltmeter & 3 –ph load, as shown
in diagram.
2. Connect this circuit to the main single phase supply.
3. Take the reading of ammeter,wattmeter and voltmeter in the observation table as given
below.
4. Note down 3-4 readings.
OBSERVATION AND CALCULATION:
Connections S.No. Voltmeter Voltmeter Ammeter Ammeter
reading(Vph reading reading(Iph)
Reading(VL)
) (IL)
1
.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 13 -
DAVIET
STAR 2
.
3
.
4
.
1
.
DELTA
2
.
3
.
4
.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Connections should be right & tight.
2. Always take accurate reading.
3. Meters used should be without error.
4. Be alert while doing practical.
5. Always avoid short circuit & loose connection.
6. Never exceed the permissible value of current , Voltage and
power of any instruments.
7. Check all the connections before switch on the power supply.
RESULT:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 14 -
DAVIET
When Star connections are done
Line voltage (VL)=√3 X Phase voltage (Vph)
Line current(IL)=Phase current(Iph)
When Delta connections are done
Line voltage (VL)=Phase voltage(Vph)
Line current(IL)=√3 X Phase current (Iph)
EXPERIMENT NO. 5
AIM: To perform open circuit & short circuit tests of a single phase transformer. Also
find the transformation ratio & efficiency.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 15 -
DAVIET
A.FOR OPEN CIRCUIT TEST:
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.NO. NAME OF APPARATUS RANGE QUANTITY
1. Vatriac(3-phase) 0-270V 1
2. 1-Phase transformer 2kv A 1
3. AC voltmeter 0-300V 2
4. Wattmeter 0- 1
1000W
5. AC Ammeter 0-1 A 3
6. DPIC main switch 32 A 1
7. Connecting leads ------- As per
requirement
THEORY:
When open circuit test is performed, the secondary side of the transformeris on no
load.The primary is supplied at its rated voltage, since there is no current in the secondary, a
very small current flows through primary. So copper loses are negligible &the wattmeter
gives only iron loses.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 16 -
DAVIET
PROCEDURE: Do as follows:
1. Make the connections of variac ,ammeter,voltmeter&a single-phase transformer
as shown in circuit diagram.
2. Set the Variac to zero position.
3. Switch on the power supply.
4. Increase the variac voltage till rated primary voltage is reached.
5. Take the reading of ammeter,wattmeter,voltmeter in the observation table as given
below.
6. Now find transformation ratio.
7. Also find efficiency of transformer.
OBSERVATION AND CALCULATION
S.N Primar Seconda Transforma
o. y side ry Side tion
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 17 -
DAVIET
Voltage Current Power Voltage Ratio,
Vp Io Wi Vs K=Vs/Vp
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Connections should be right &tight.
2. Always take accurate reading.
3. Meters used should be without error.
4. Be alert while doing practical.
RESULT:
In open circuit test we find iron loses.
B.FOR SHORT CIRCUIT TEST:
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.NO. NAME OF APPARATUS RANGE QUANTITY
1. Vatriac(3-phase) 0-270V 1
2. 1-phase transformer 2kv A 1
3. AC voltmeter 0-300 V 1
4. Wattmeter 0-1000W 1
5. AC Ammeter 0-10a 2
6. DPIC main switch 32A 1
7. Connecting leads ------ As per requirement
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 18 -
DAVIET
THEORY:
When short circuit test is performed , the secondary side of the transformer is
short circuited. The primary is supplied at very less voltage, since there is heavy current in
the secondary, a very large current flows through primary .so copper loses occurs & the
wattmeter gives only copper loses.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
PROCEDURE: Do as follows:
1. Make the connections of variac ,ammeters,voltmeter and a single
phase transformer,as shown in circuit diagram.
2. Set the variac to zero position.
3. Switch on the power supply.
4. Increase the variac voltage till rated secondary current is reached.
5. Take the readings of ammeter,voltmeter, wattmeter, in the
observation table as given below.
6. Now find efficiency of transformer.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 19 -
DAVIET
OBSERVATION AND CALCULATION:
S.NO. Primary side Secondary
Voltage Current Power side
Vsc Isc Wcu Current
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Connection should be right & tight.
2. Always take accurate reading.
3. Meters used should be without error.
4. Be alert while doing practical.
RESULT: In short circuit test we find copper losses.
EXPERIMENT NO.6
AIM: To perform the block rotor test of a three phase induction motor.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.NO. NAME OF RANGE QUANTITY
APPARATUS
1. Vatriac(3-phase) 0-460V 1
2. Three phase induction 3HP 1
motor
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 20 -
DAVIET
3. AC voltmeter 0-500 V 1
4. AC ammeter 0-10A 1
5. Wattmeters 0-1000W 2
6. Break load 0-50 kg 1
7. TPIC main switch 32A 1
8. Connecting Leads ------ As per
requirement
THEORY:
There are generally two types of tests which we perform on a three phase induction
motor.
1. No load test
This test is generally performed for measuring iron loses. In this case
Total power input at no load (Po)=(W1-W2)watts
Copper losses =3 to R watts
Total Constant losses (Pc)=Po-3 to R watts
2. Block rotor test
This test is generally perform for measuring copper losses.In this case
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 21 -
DAVIET
Total power input at break load,(Psc)=(W1+W2)Watts
In case of block rotor,(Psc)=Pcu
Input =Output+Po+Pcu
And efficiency is given by:
Efficiency(η%)=Output x 100/Input
Here W1 & W2 are wattmeters readings: Both the wattmeter find looses in the
Motor . Where as one wattmeter is find cooper looses and another one is find iron
Looses in the three phase induction motor.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
OBSERVATION AND CALCULATION:
S.No. Wattmeter Readings Line Line Total power
Voltage Current
W1 W2 W=W1+W2
V I
1.
2.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 22 -
DAVIET
3.
PROCEDURE:Do as follows:
1. Make the Connections as per circuit diagram.
2. Now block the rotor by tightening the belt so that rotor shouldn’t move.
3. Keep the variac at its minimum value.
4. Switch on the AC input to both the power supplies.
5. Now increase the applied voltage graduately with the of variac until full load current flows
through the motor.
6. Record the reading of wattmeter,ammeter and voltmeter observation table&calculate the
power and efficiency.
7. take 3-4 reading and record the reading of wattmeter ,ammeter&ion voltmeter reading in
observation table and calculate the power and efficiency.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Connections should be tight and right.
2. Always take accurate reading.
3. Meter used should be without error.
4. Be alert while doing practical.
5. Always start from zero voltage.
6. Belt should be so tight so that rotor should not move.
RESULT:
In this experiment we are find the efficiency of the three phase induction motor.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 23 -
DAVIET
EXPERIMENT NO.7
AIM:To Study the response of P-N Junction Diode.
APPARATUS REQUIRED:
S.NO. NAME OF RANGE QUANTITY
APPARATUS
1. Diode Silicon 1 each
Germanium
2. Voltmeters 0- V 1 each
0- V
3. Ammeters 0- mA 1 each
0- μA
4. Resistance
5. Power supply 0- V 1 each
0- V
6. Connecting leads -------- As per
requirement
THEORY:
A p-n junction diode can be realized when a p-type crystals brought in contact with
a n-type crystal structure remains constant.The region around p-n junction is devoid of free
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 24 -
DAVIET
charge carriers.This is known as depletion layer.The act of applying voltage across P-N
junction is known as biasing.There are two ways in which a junction can be biased , one is
forward biased and second is reversed biased.The +ve terminal of the battery is connected to
p side of the junction and –ve to n side.In this set up the conduction across p-n junction
takes place due to migration of majority carriers.
PARAMETERS OF DIODE:
1 KNEE VOLTAGE: It is forward voltage at which the current flowing through the diode
suddenly reaches higher value.
2 REVERSE BREAKDOWN VOLTAGE: The minimum reverse voltage at which the
avalanche breakdown of the p-n junction diode is occurring.
3 IDEAL DIODE: Ideal diode have barrier potential zero.
4 ZENER DIODE: It acts as a voltage regulator.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
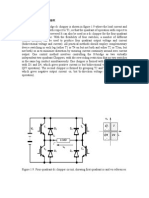
PROCEDURE:
1. Connect the circuit as shown in circuit diagram no.1
2. Bring the variable voltage to the DC source to zero.The current millimeter will also be
zero.
3. Increase the variable voltage DC supply source slowly and in steps.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 25 -
DAVIET
4. Don’t exceed the current rating of the diode.This completes the observation of V-I
characteristics of forward biased diode.
5. Draw the graph for this.
6. Repeat the steps2,3 and draw the graph.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
OBSERVATION & CALCULATIONS
S SILICONDIODE GERMANIUM DIODE
.
N
O
.
FORWARD REVERSE FORWARD REVERSE
CHARACTERISTCS CHARACTERISTCS CHARACTERISTCS
CHARACTERISTCS
If Vf Ir Vr If Vf Ir Vr
1
.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 26 -
DAVIET
.
3
.
4
.
5
.
PRECAUTIONS:
1.All the connections should be tight.
2.The value of the current should be increased slowly.
RESULT:
In this experiment we find the forward & reverse characteristics of the diode.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 27 -
DAVIET
EXPERIMENT NO. 8
AIM:To study the transistor response
APPARATUS REQUIRED
S.NO. NAME OF RANGE QUANTITY
APPARATUS
1. Experiment kit NPN 1
transistor
2 Transistor NPN 1
3. RESISTOR 100Ω,0.5W 1
4. DC AMMETER 0 -A 1 each
0 -A
5. DC VOLTMETER 0 – 1.5V 1 each
0 - 10V
6. Connecting Leads ------- As per
requirement
THEORY:
Transistor is a three semiconducting layers,two junction device,which is used for
weak signal’s amplication .The input is connected in forward biased,whereas the output
junction is reversed biased.
When we draw the curve between collector current and collector emitter voltage with
respect to Ib then following threenregions appear;
(1)Saturation region:
When Vce increases,IC increases from zero to near saturation value of Ib .When Vce is
reduced ,Ic doesnot reduced.In this region input as well as junctions are forward biased .
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 28 -
DAVIET
(2)Active region:
When Vce is increased further output junction is reversed biased . the transistor operates in
active region and Ic increases Vce fiased . the transistor operates in active region and Ic
increases Vce for constant value of Ib.In this region the input junction is forward biased and
output junction is reversed biased.The value of Ic can be changed by changing the value of
Ib.
(3)Cutoff region:
Whwn Ib =0,still some Ic =Iceo flows in the collector region.this is independent of Ib or Vce.
In this region both the junctions are reversed biased.
TRANSISTORS CHARACTERISTICS
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS:
In common base configuration, the curve plotted b/w the emitter current Ie and the emitter
base voltage Veb.At constant collector-base voltage Veb,is called input characteristics. Then
input dynamics resistance:
Ri=∆Veb at constant Veb
∆ Ie
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
In common base configuration ,the curve plotted b/w the collector current Ic and the
collector base voltage Vcb ,at constant emitter current Ie is called Output characteristics.
Then output dynamic resistance:
Ro=∆Vcb at constant Ie
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 29 -
DAVIET
∆Ic
For both the characteristics,we may determine dc and ac current amplification factor:
αac = ∆Ic at constant Vcb
∆Ie
αde = Ic at constant Vcb
Ie
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS:
In common base configuration,the curve plotted b/w collector current Ic and the
collector base voltage Vcb ,at constant emitter current Ie is called is output characteristic then
output dynamic resistance:
Ro = ∆ Vcb at constant Ie
∆Ic
I or both the characteristics,may determine dc and ac current amplification factor:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 30 -
DAVIET
α ae = ∆Ic at constant Vcb
∆Ie
αdc = Ic at constant Vcb
Ie
PROCEDURE:
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram.
2. Set both the power supplies at zero.
3. Switch on the AC input to both the power supplies.
4. For input characteristics fix end voltage Vcb=5V
5. Now increase the Veb voltage in steps of 0.05 V and note down the corresponding
value of emmiter current Ie and record them in the observation table.
6. Draw the input characteristics taking Veb on X axis and Ie on Y axis.
7. Repeat the steps for Vcb=10 V.
8. For output,fix Ie = mA ie , keeps the input circuit open.Change the collector base
voltage Vcb in steps and note down the corresponding values of Ic in observation table.
9. Draw the output characteristics taking Vcb on X axis and Ic on Y axis.
OBSERVATION AND CALCULATION:
A. FOR INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Characteristics S.NO. Vcb=5V Vcb=10V
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 31 -
DAVIET
Voltmeter Ammetr Voltmeter Ammeter
Reading Reading Reading Reading
(Veb)volts (Ie)mA (Veb)Volts (Ie)mA
1.
2.
For input
3.
4.
B.FOR OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Characteristis S.No. Ie=0 mA Ie=2 Ie=4mA
mA
Voltmeter Ammeter Voltmeter Ammeter Vcb Ic
Reading Reading Reading Reading Volts mA
(Vcb)volts (Ic)mA (Veb)Volts (Ie)mA
1.
2.
For output
3.
4.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 32 -
DAVIET
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Connections should be right and tight.
2. Always take accurate reading.
3. Meters used should be without error.
4. Be alert while doing practical.
RESULT:
In this experiment we find the input & output characteristics of the trans
EXPERIMENT NO. 9
AIM: To analyse the truth tables of various basic digital gates.
Apparatus required:
S.NO. APPARATUS RANGE QUANTITY
REQUIRED
1. DC power supply 5V 1
2. Various digital
IC’s
7432 1
a)OR Gate
7408 1
b)AND Gate
7404 1
c)NOT Gate
7400 1
d)NAND Gate
7402 1
e)NOR Gate
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 33 -
DAVIET
3. Connecting leads As per
requirement
4. LED 5
THEORY:
All types of logic gates deals with binary.The binary information is a combination
of binary variables.For this purpose logic circuits which are called gates are used.These gates
are the fundamental building blocks of any digital system.
The important points regarding these gates are:
1.Each logic gate has its own symbol
1.OR GATE
2.AND GATE
3.NOT GATE
4.NAND GATE
5.NOR GATE
PROCEDURE:
Do as follows:
a)FOR OR GATE
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram and connection diagram.
2.Connect the gates,switches A,B,&C and LED with supply (+5V) to 14 no. Pin and pin no. 7
to ground.
3.Now switch on A,B,C in sequence and note down the state of LED in truth table as given
in observation and calculations.
b)FOR AND GATE
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 34 -
DAVIET
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram and connection diagram.
2.Connect the gates,switches A,B,&C and LED with supply (+5V) to 14 no. Pin and pin no. 7
to ground.
3.Now switch on A,B,C in sequence and note down the state of LED in truth table as given
in observation and calculations.
c)FOR NOT GATE
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram and connection diagram.
2.Connect the gates,switches A,B,&C and LED with supply (+5V) to 14 no. Pin and pin no. 7
to ground.
3.Now switch on A,B,C in sequence and note down the state of LED in truth table as given
in observation and calculations.
d)FOR NAND GATE
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram and connection diagram.
2.Connect the gates,switches A,B,&C and LED with supply (+5V) to 14 no. Pin and pin no. 7
to ground.
3.Now switch on A,B,C in sequence and note down the state of LED in truth table as given
in observation and calculations.
5)FOR NOR GATE
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram and connection diagram.
2.Connect the gates,switches A,B,&C and LED with supply (+5V) to 14 no. Pin and pin no. 7
to ground.
3. Now switch on A,B,C in sequence and note down the state of LED in truth table as given
in observation and calculations.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 35 -
DAVIET
OBSERVATION & CALCULATIONS:
1.OR GATE
TRUTH TABLE
A B C Y=A+B+C
S.NO.
1. 0 0 0 1
2. 1 0 0 1
3. 0 1 0 1
4. 0 0 1 1
5. 1 1 0 1
6. 1 0 1 1
7. 0 1 1 1
8. 1 1 1 1
9.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 36 -
DAVIET
2.FOR AND GATE
TRUTH TABLE
S.NO. A B C Y=A*B*C
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
9.
3. FOR NOT GATE
S.NO. A Y=A
1.
2.
4.FOR NAND GATE TRUTH TABLE
S.NO. A B C Y=A*B*C X=Y
1.
2.
3.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 37 -
DAVIET
4.
5.
6.
7.
5) FOR NOR GATE
TRUTH TABLE
S.NO. A B C Y=A+B+C X=Y
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Always give positive supply to pin no.14 and ground pin no.7 of any logic gate.
2. Connectivity should be right and tight.
3. Truth table should be accurate.
4. Supply should not be greater than regulated +5V.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 38 -
DAVIET
EXPERIMENT NO. 10
AIM: To study the response of LVDT Transducer
Apparatus required:
1. LVDT kit
2. Connecting Leads
3. Multimeter
THEORY:
LVDT is also known as Linear Variable differential transducer, which is use to
measure displacement fo core. The output voltages of LVDT is a function of core
position. The basic principal behind it is Electro magnetic induction. When the core is
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 39 -
DAVIET
at centre, the rate of change of flux linkages with the windings s-1 and s-2 are the
same. Therefore, the induced EMF in the both windings is of same magnitude and
output is 0 as S-1 &S-2are cross connected. When the position of the core is changed,
different EMF are induced in two windings.And resultant voltage appears across the
output terminals.
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM
PROCEDURE Do as follows
1 Make the connections as per circuit diagram.
2 Connect the instrument such as auto transformer on the primary and voltmeter at
the output are connected
3Now switch on the power supply.
4Give the rated voltage to the primary of the LVDT.
5Now change the core position and record the output.
OBSERVATION & CALCULATIONS
Sr. No. Output Voltage Displacement
Forward Reverse Forward Reverse
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 40 -
DAVIET
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Connections should be right & tight.
2. Observation should be accurate.
RESULT: The curve for displacement (on X-axis) v/s ( On Y- axis) is similar to the
theoretical one
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 41 -
DAVIET
EXPERIMENT NO. 11
AIM: To study various measuring instruments
1. Moving iron instruments-(a) Attraction type (b)Repulsion type
2. Permanent Magnet moving coil instruments
3. Dynamometer type instruments
APPRATUS REQUIRED:
Sr. no. Apparatus required Quantity
1. Moving iron instruments 1 each
Attraction type- AC voltmeter& ammeter
Repulsion type- AC voltmeter& ammeter
2. Permanent Magnet moving coil instruments 1 each
DC voltmeter& ammeter
3. Dynamometer type instruments 1 each
THEORY:
PERMANENT MAGNET TYPE MOVING COIL INSTRUMENT-
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 42 -
DAVIET
These instrument are very sensitive and accurate. These instruments can be used only on d.c.
as voltmeter and ammeter. The pictorial view is shown
The basic principle of permanent type moving coil instrument is that when a current carrying
conductor is placed in a magnetic field, a mechanical force is exerted on the conductor. The
simple view of permanent magnet type moving coil instrument is shown as in fig. In this case
a deflecting coil is placed in a strong magnetic field is produced by permanent magnet when
current flows through the coil, a force is exerted & deflection take place. The controlling
torque is provided with the help of spiral spring where as deflecting torque is provided with
the help of eddy currents as the coil is placed over the aluminum former. This instrument can
be used for DC measurement only. Its scale is uniform.
MOVING COIL INSTRUMENT
It consists of a powerful permanent shoe magnet. A coil of many turns of fine wire wound on
a light aluminium former. An iron core is inserted in between the coil sides to reduce
reluctance for magnetic lines of forces. The coil is mounted on the spindle and acts as moving
element. Two phosphorous bronze spiral hair springs are attached to the spindle. The spring
provide the controlling torque as well as they act as incoming and outgoing leads for the
current. Eddy current damping is provided by the aluminium former. When the instrument is
connected in the circuit, the operating current flows through the coil which is mounted on the
spindle. Since the coil is placed in the strong field of permanent magnets, a force is exerted
on the current carrying conductors of the coil which produces deflecting torque. Thus the
pointer attached to the spindle in deflected over the calibrated scale. If the direction of current
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 43 -
DAVIET
is reversed the direction of deflecting torque is also reversed as field produce by permanent
magnet does not change.
DYNAMOMETER TYPE INSTUMENT:
It consists of two coils, one is called moving coil & other one is called fixed coil. The fixed
coil produces main magnitude field, in which moving coil is placed when current flows
through these coils, a force is exerted & deflection take place in moving coil because when
current carrying conductor is placed in the magnetic field, experiences force. The controlling
torque is provided with the help of spiral spring where as deflecting torque is provided with
the help of air friction. This instruments is costly because special techniques is used for
manufacturing these type of instruments.
PRECAUTIONS:
1. Study the instruments dial carefully.
2. Don’t touch pointer & spiral spring.
3. Remove every part carefully.
EXPERIMENT NO. 12
AIM: To study the use of multimeter
APPRATUS
Sr.no. Name of Apparatus Range Quantity
1. Digital multimeter ------- 1
2. Connecting leads ------- As per requirement
Theory: A multimeter is basically a permanent magnet moving galvanometer. There is an
iron core pivoted on two jeweled bearings. The coil is wounded on an aluminium former
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 44 -
DAVIET
which is free to rotate in the field of permanent magnet. An aluminium pointer is attached to
the coil and it moves over the gradual scale. There are two spiral springs providing path to
current as well as restoring torque. It can measure voltage, current and resistance for which
its galvanometer is converted to voltmeter, ammeter and ohmmeter with the help of suitable
circuit incorporated in it.There are basically two types of multimeter
1. Digital multimeter
2. Analog multimeter
DIGITAL MULTIMETER- It display the a.c. or d.c. voltages being measured as discrete
numerals in the decimal number system. It limits observational errors. Its use increase the
speed with which readings are taken.
2. ANALOG MULTIMETER- It gives the reading by deflecting its needle. In it
chances of occurring error are more as reading is to be taken from deflecting needle. The
pictorial view of analog multimeter as shown below-
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 45 -
DAVIET
Above all DMM is better than AMM, as it display the reading in digits therefore chances of
error occurring are very less.
EXPERIMENT 13
AIM: To study the speed control of a dc shunt motor & to draw the speed variation with
respect to
1. Field Control
2. Armature Control
APPARATUS REQUIRED :
S.No. Name of Apparatus Range Quantity
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 46 -
DAVIET
1. DC SHUNT MOTOR 5 HP, 220V 1
2. DC VOLTMETER 0-300V 1
3. DC AMMETER 0-10A 1
4. RHEOSTATC 0-1500Ω, .75A 1
5. CONNECTING LEADS ---- AS PER REQUIREMENT
6. RHEOSTATE 0-20Ω, 16A 1
7. DPIC MAIN SWITCH 32A 1
8. TACHOMETER ---- 1
THEORY
A DC shunt motor consist of two parts, one movable & other static. The movable part is
called ARMATURE & static is called filed. Field winding is connected in parallel with
armature & it has very high resistance as compared to armature.
The speed of shunt motor can be calculated with following relation:
N=k =k
Hence the speed either changing the shunt fie motor can be changed by either changing the
shunt field current ish by inserting an external resistance in field circuit or by changing the
back emf, Eb by inserting an external resistance in armature circuit.
i.e V-laRa
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 47 -
DAVIET
Armature Control
FIELD CONTROl
PROCEDURE: Do as follows:
1. Make the connections as per circuit diagram.
2. Set the rheostat at zero position.
3. Switch on the DC power supply.
4. Now change the rheostat of filed & corresponding note down RPMs & field current.
5. Take 5-6 readings and note in the observation table.
6. Similarly vary the armature resistance & correspondingly note down in observation
table as given below:
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 48 -
DAVIET
OBSERVATION:
S. NO. CONTROL FIELD RPM
CURRENT ISH N
FIELD 1.1A
1 0.85 A
2 0.725 A
3 0.625 A
4 0.625 A
5 0.575 A
ARMATURE BACK EMF EB RPM N
1 220 V 1500 RPM
2 200 V 1400 RPM
3 180 V 1300 RPM
4 160 V 1200 RPM
5 150 V 1100 RPM
PRECAUTIONS:
1. The current, voltage should be in limit.
2. Do not touch any live wire.
3. Connections should be write & tight.
RESULTS
1. By increasing resistance of the field current decreases, thus speed increases.
2. By increasing resistance of the armature voltage drop in armature increases, thus back
emf Eb decreases, thus speed decreases.
Basic Electrical and Electronic Engg. - 49 -
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Reference Practicle File For RDBMS-IIDocument41 paginiReference Practicle File For RDBMS-IIkingsofleon18200% (1)
- Electrical VivaDocument5 paginiElectrical VivaHari KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- R-L Circuit Analysis and Power Factor DeterminationDocument5 paginiR-L Circuit Analysis and Power Factor DeterminationDemoin GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluorescent Lamp WiringDocument2 paginiFluorescent Lamp WiringEngr. Raheel khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ED LAB ManualDocument31 paginiED LAB Manualmanoj kumar100% (1)
- Sample Question Paper Basic Electrical & Electronics EngineeringDocument4 paginiSample Question Paper Basic Electrical & Electronics Engineeringsachin tupeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSC141 Lab Manual Introduction to ProgrammingDocument87 paginiCSC141 Lab Manual Introduction to ProgrammingiamneonkingÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEEE Lab Manual - BT104 - Readings - 1625301921Document8 paginiBEEE Lab Manual - BT104 - Readings - 1625301921sid mankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minimizing Industrial Power Penalties with APFCDocument5 paginiMinimizing Industrial Power Penalties with APFCZeeshan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eec-553 Cad of Electronics Lab FileDocument21 paginiEec-553 Cad of Electronics Lab FileShitansh Nigam33% (3)
- DC Motor (P)Document16 paginiDC Motor (P)Ankit KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Lab Manual for WorkshopsDocument25 paginiElectrical Lab Manual for Workshopsjaythakar888775% (4)
- Anderson Bridge: User ManualDocument12 paginiAnderson Bridge: User Manualaa_nilawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control System Lab Manual 18EEL66Document70 paginiControl System Lab Manual 18EEL66ADARSH SHINDE100% (1)
- Drives and Control Lab ManualDocument36 paginiDrives and Control Lab ManualKabilanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Regulated Power SupplyDocument18 paginiDesign of Regulated Power SupplyDanish KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateDocument60 paginiMagnetization Characteristics of A D.C. Shunt Generator: Exp. No: DateSuyash SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Root Locus ExperimentDocument2 paginiRoot Locus Experimentnishantkothari77Încă nu există evaluări
- Scott Connection of Transformers TitleDocument6 paginiScott Connection of Transformers TitleSheri Abhishek ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two-Way Staircase Lighting ControlDocument3 paginiTwo-Way Staircase Lighting Controlshubhika gupta100% (1)
- Unit-4 Static Relays (Switchgear and Protection)Document54 paginiUnit-4 Static Relays (Switchgear and Protection)sujithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ministry of Education Laboratory StandardsDocument95 paginiMinistry of Education Laboratory Standardssekin0% (1)
- Use of Laboratory Log BooksDocument2 paginiUse of Laboratory Log BookshamoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3 Cycloid Inclined ConstructionDocument2 pagini1.3 Cycloid Inclined ConstructionMartin De Boras Pragash100% (1)
- EE8711 Power System Simulation Lab ManualDocument162 paginiEE8711 Power System Simulation Lab ManualAbdul YaseenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Food Serving RobotDocument3 paginiFood Serving RobotSonia MohapatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open CircuitedDocument35 paginiOpen Circuitedgirishkumardarisi254Încă nu există evaluări
- DC Machines Lab ManualDocument56 paginiDC Machines Lab ManualRockstar RichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Four Quadrant Chopper OperationDocument5 paginiFour Quadrant Chopper OperationSAIKAT100% (1)
- Phase-Controlled AC-DC Converters TutorialDocument3 paginiPhase-Controlled AC-DC Converters TutorialChangyuFuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment No 4Document5 paginiExperiment No 4Kush GoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bee Viva QueDocument3 paginiBee Viva QueVijayramraj Mocherla40% (5)
- 3 Point StarterDocument16 pagini3 Point StarterSameer Sharma0% (1)
- Self Inductance ProjectDocument10 paginiSelf Inductance Projecthackerhack2021centuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus: Module 3A-Transducers & PLCDocument24 paginiSyllabus: Module 3A-Transducers & PLCRaja G VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy Project FileDocument16 paginiPhy Project FileCadever Y.T100% (1)
- Experiment - 12: Power Angle Curve of Syncronous MachineDocument3 paginiExperiment - 12: Power Angle Curve of Syncronous MachinesanjuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aim of ExperimentDocument6 paginiAim of ExperimentPrabhu Dev50% (2)
- CPP 03 PDFDocument1 paginăCPP 03 PDFbhuvangatesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hve Unit 4Document3 paginiHve Unit 4Arikesari100% (1)
- Experiment No. 4 Drawing of Floor Plan of Building Using Autocad ObjectiveDocument2 paginiExperiment No. 4 Drawing of Floor Plan of Building Using Autocad ObjectiveM. Ahmad RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab ReportDocument26 paginiLab Reportsanjana972Încă nu există evaluări
- Report On TransformerDocument40 paginiReport On Transformerashish suraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primitive Network and Graph Theory PDFDocument12 paginiPrimitive Network and Graph Theory PDFDhavalVoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Switching TransientsDocument16 paginiSwitching TransientsvenkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pspice Simulation of Single-Phase Full Converter With Rle Load and Single-Phase Ac Voltage Controller Using Rle LoadsDocument3 paginiPspice Simulation of Single-Phase Full Converter With Rle Load and Single-Phase Ac Voltage Controller Using Rle LoadsSai Sadiq100% (1)
- Edc Unit 1Document62 paginiEdc Unit 1raghul100% (1)
- UNIT-2 Three Phase TransformerDocument24 paginiUNIT-2 Three Phase Transformerkaran nirmala gajanan shindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Lab Manual With LogoDocument69 paginiPower Electronics Lab Manual With LogoPunith Gowda M BÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Tech Mini Project Report GuidelinesDocument11 paginiB.Tech Mini Project Report GuidelinesPranay PranayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1. DC CircuitDocument1 paginăChapter 1. DC CircuitBhavik PrajapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- M.E. PseDocument23 paginiM.E. PseKRAJ315Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab # 01 To Study The Transient Response of RL Series Circuit MaterialsDocument4 paginiLab # 01 To Study The Transient Response of RL Series Circuit MaterialsYasir100% (1)
- DSP 18eel67 FinalDocument94 paginiDSP 18eel67 FinalBlackopsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mini-Project I-Led Flasher ReportDocument8 paginiMini-Project I-Led Flasher ReportAtiqMarwatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation Capacitor Start Motor (Group 4)Document14 paginiPresentation Capacitor Start Motor (Group 4)Surajit ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Report On The "3-Phase Line Fault Detector" Ee344 Minor Project - IDocument34 paginiA Report On The "3-Phase Line Fault Detector" Ee344 Minor Project - IDhruv PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Implementation of A Microcontroller Based 5 KVA Automatic Voltage StabilizerDocument8 paginiImplementation of A Microcontroller Based 5 KVA Automatic Voltage StabilizerMawunyo100% (1)
- Laboratory ManualDocument23 paginiLaboratory ManualAnmol AhsaasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Java File PGDCA Second SemesterDocument84 paginiJava File PGDCA Second SemesterCutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Anti Frost Irrigator Using Embedded SystemDocument64 paginiDesign of Anti Frost Irrigator Using Embedded SystemCutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Report On Computer NetworksDocument45 paginiProject Report On Computer NetworksCutie81% (59)
- Database Administrator File MCA Semester 3Document70 paginiDatabase Administrator File MCA Semester 3CutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab File - Micro Controllers (8051) & Embedded SystemsDocument17 paginiLab File - Micro Controllers (8051) & Embedded SystemsCutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Network Operating Systems (File)Document8 paginiNetwork Operating Systems (File)CutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab File - Digital Signal Processing Using MATLABDocument32 paginiLab File - Digital Signal Processing Using MATLABCutie100% (2)
- Implementation of Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Using VHDLDocument71 paginiImplementation of Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) Using VHDLCutie93% (30)
- Mechanical Engineering - Training ReportDocument39 paginiMechanical Engineering - Training ReportCutie72% (32)
- Completely Organize Your Room or HouseDocument4 paginiCompletely Organize Your Room or HouseCutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Sockets in Unix: A Concise GuideDocument8 paginiIntroduction to Sockets in Unix: A Concise GuideCutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- The TeacherDocument1 paginăThe TeacherCutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pspice TutorialDocument56 paginiPspice TutorialCutie0% (1)
- Physics ExperimentDocument3 paginiPhysics ExperimentCutie50% (2)
- Why MBA ? "Want To Be An MBA ?"Document11 paginiWhy MBA ? "Want To Be An MBA ?"CutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Structures & System Programming Lab FileDocument29 paginiData Structures & System Programming Lab FileCutie0% (1)
- FCPIT File (For PTU B.Tech 1st Yr Students)Document105 paginiFCPIT File (For PTU B.Tech 1st Yr Students)Cutie83% (6)
- DebateDocument2 paginiDebateCutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus For PTU ECE Branch (All Sems)Document66 paginiSyllabus For PTU ECE Branch (All Sems)Cutie0% (2)
- Speaker Style and ResponsibilitiesDocument7 paginiSpeaker Style and ResponsibilitiesCutieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Design in 7 DaysDocument69 paginiWeb Design in 7 DaysCutie100% (2)
- Basic Electronic Components (Post 1st Year Training ECE)Document23 paginiBasic Electronic Components (Post 1st Year Training ECE)Cutie100% (4)
- Rack+product+brochure SAFT 31032020 PDFDocument8 paginiRack+product+brochure SAFT 31032020 PDFanarang15Încă nu există evaluări
- Stal9781607500315 1088Document3 paginiStal9781607500315 1088Tariq SufianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 - Part 2: DC-DC ConverterDocument15 paginiChapter 2 - Part 2: DC-DC ConverterWeehao SiowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newton's Laws of Motion Summative Test Science 8Document20 paginiNewton's Laws of Motion Summative Test Science 8lie villote100% (1)
- AltuglasDocument8 paginiAltuglasLUCACOMP1974Încă nu există evaluări
- Isc BD263: Isc Silicon NPN Darlington Power TransistorDocument2 paginiIsc BD263: Isc Silicon NPN Darlington Power TransistorAndrewÎncă nu există evaluări
- DP1 Practice 2: MarkschemeDocument17 paginiDP1 Practice 2: MarkschemeaurennosÎncă nu există evaluări
- LE13-038-R04a (TECHNICAL SHEET)Document83 paginiLE13-038-R04a (TECHNICAL SHEET)Sermchart PakumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge IGCSEDocument20 paginiCambridge IGCSEVarvaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam SolutDocument12 paginiExam Solutnunulovin911Încă nu există evaluări
- 16-CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM - 01-TheoryDocument15 pagini16-CONSERVATION OF LINEAR MOMENTUM - 01-TheoryRaju SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elements of Practical Aerodynamics by B. Jones (Scanned Copy)Document456 paginiElements of Practical Aerodynamics by B. Jones (Scanned Copy)Kier Dela RosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- En J02.DAI.73 Daikin RZAG N Technical Data RZAG NV1 Data BookDocument51 paginiEn J02.DAI.73 Daikin RZAG N Technical Data RZAG NV1 Data BookTheEngineer - المهندسÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSS SP-75 2004Document31 paginiMSS SP-75 2004Argenis Daniel Nieves BerroetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV BaxterDocument3 paginiCV BaxterGYANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry: A Timeline of The Development On The Field of GeometryDocument25 paginiGeometry: A Timeline of The Development On The Field of GeometryARIANNE JASMINE ADRIANOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise-01 Check Your Grasp: K Cro Dil. HCLDocument20 paginiExercise-01 Check Your Grasp: K Cro Dil. HCLAkashGauravÎncă nu există evaluări
- Owners Manual: 3000 SERIES Electric Hot Food Holding UnitsDocument15 paginiOwners Manual: 3000 SERIES Electric Hot Food Holding UnitsAdeRorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chords Arcs Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesDocument11 paginiChords Arcs Central Angles and Inscribed AnglesMaylieh MayÎncă nu există evaluări
- OTC 21228 Emergency Pipeline Repair Equipment: Site Integration Tests and Post SIT EngineeringDocument5 paginiOTC 21228 Emergency Pipeline Repair Equipment: Site Integration Tests and Post SIT EngineeringRasheed YusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mooring Design AnalysisDocument41 paginiMooring Design AnalysisRaghu Nath100% (1)
- Positive Displacement Meter SpecificationsDocument3 paginiPositive Displacement Meter SpecificationsYohanes AzzisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ophthalmic and Diagnostic Instruments: Ophthalmoscope / Retinoscope / OtoscopeDocument37 paginiOphthalmic and Diagnostic Instruments: Ophthalmoscope / Retinoscope / OtoscopeKhelifa RadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-Representing Real-Life Situations Using Logarithmic FunctionsDocument29 pagini5-Representing Real-Life Situations Using Logarithmic FunctionsEllen DadivasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Safety Syllabus Anna UnivDocument20 paginiIndustrial Safety Syllabus Anna UnivSourabh DuttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S0927024815001075 MainDocument8 pagini1 s2.0 S0927024815001075 MainPEDRO REYNALDO MARTINEZ MANUELÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotel RB 1080 Service ManualDocument6 paginiRotel RB 1080 Service Manualsandy nÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2D E Tray Sorter with Contactless Energy SupplyDocument8 pagini2D E Tray Sorter with Contactless Energy Supplystg44Încă nu există evaluări
- BC 640Document5 paginiBC 640Miguel AngelÎncă nu există evaluări
- LKPB Practice Test Four Section 1Document27 paginiLKPB Practice Test Four Section 1Bintana CahyaÎncă nu există evaluări