Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
3 Way Speaker
Încărcat de
limboy15Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
3 Way Speaker
Încărcat de
limboy15Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Crossover Network
9 Comments
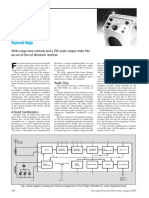
Loudspeaker is a very important component of a hi-fi system.By adding a crossover network to the system of speakers, the
low, high and mid-range frequencies can be separated and fed into a woofer, tweeter and mid-range speaker respectively.
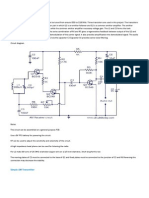
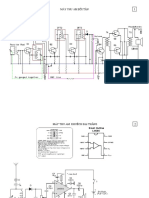
Fig. 1 Wiring diagram for three-way crossover network
PARTS LIST
C1
3.3 f 50v N.P.
C2
4.7 f 50v N.P.
C3
3.3 f 50v N.P.
C4
3.3 f 50v N.P.
C5
0.68 f
C6
1 f 50v N.P.
R1
3.3 2W
R2
4.7 2W
R3
6.8 2W
The given circuit uses four inductances of 0.1, 0.2, 0.3 and 1 mH, each having 70, 100, 120 and 200 turns of 18SWG wire
on the johnson-john adhesive tape bobbins having 2.5 cm length and 2.5 cm dia.The speakers used have an impedance of
8-ohm each, and the circuit can be used for amplifiers with output rating of a maximum of 50 watts RMS per channel.
Fig. 2 air core
The capacitors used are non-polarised type, which can be made by connecting end to end two capacitors of double the
required value, as shown. All the capacitors are 50V type.The crossover frequencies are 500 Hz and 2.5 kHz. All the
inductors are air core type. Resistors are 2W type.
Fig.3 the making of a non-polarised capacitor, using two electrolytic (polarised) capacitor of twice the desired value.
Since a high frequency producing tweeter generally sounds very loud compared to the mellower outputs of a woofer and a
mid-range speaker, the tweeters output can be reduced by introducing the attenuation circuit shown in Fig. 4. Using onepole, four-way switch S1, the tweeters output can be reduced to a desired extent or allowed to pass on unattenuated to the
speaker.
Fig. 4: Tweeter attenuator
Care should be taken to connect the tweeter and the woofer in opposite phase.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Action Plan in ScienceDocument4 paginiAction Plan in ScienceRandy-IanRexLorenzo94% (17)
- Mobile Phone Repairing Testing MethodsDocument3 paginiMobile Phone Repairing Testing Methodslimboy15100% (8)
- AUTO-SF2 (Final Copy)Document97 paginiAUTO-SF2 (Final Copy)limboy15100% (4)
- 4 Channel Programmable FM Remote ControlDocument16 pagini4 Channel Programmable FM Remote ControljpatrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Transistor CircuitsDocument11 paginiPractical Transistor CircuitsFilip Angelovski100% (1)
- Electrostatic Headphones - N. Pollock (Wireless World, Nov 1979)Document5 paginiElectrostatic Headphones - N. Pollock (Wireless World, Nov 1979)jimmy67musicÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Simplest Radio LocatorDocument15 paginiThe Simplest Radio LocatorAlain TabutiauxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple AM Receiver&TransmitterDocument4 paginiSimple AM Receiver&TransmitterGokulk2011100% (2)
- Bereskin 1954 High Quality High Efficiency Power AmplifierDocument7 paginiBereskin 1954 High Quality High Efficiency Power AmplifiererasmeÎncă nu există evaluări
- All India Radio DocumentDocument32 paginiAll India Radio Documentsashi_s2Încă nu există evaluări
- 3V FM TransmitterDocument9 pagini3V FM TransmitterHabib RkÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMSAT Eagle - 70 CM Receiver Circuit DescriptionDocument9 paginiAMSAT Eagle - 70 CM Receiver Circuit Descriptionettore68Încă nu există evaluări
- Matching 50Ω to 75Ω: Minimum-Loss PadDocument6 paginiMatching 50Ω to 75Ω: Minimum-Loss Padvaldesc_tolÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Approach To Audio Frequency Amplifier DesignDocument136 paginiAn Approach To Audio Frequency Amplifier DesignKevin HaworthÎncă nu există evaluări
- 300 WattsDocument31 pagini300 WattsJosue PazÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1998 - Two-Stage Wideband HF LinearDocument32 pagini1998 - Two-Stage Wideband HF Linearwww.vyeko_.bloger.hrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matching 50Ω to 75ΩDocument7 paginiMatching 50Ω to 75Ωjoyce_caracasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtgDocument8 paginiAtgdarenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rmohn ELEN4314 Project ReportDocument10 paginiRmohn ELEN4314 Project Reportjackal1710Încă nu există evaluări
- CI-01 June06Document1 paginăCI-01 June06indu20mathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DB 4055 56 67 68 71 72 Duplexers InstructionsDocument2 paginiDB 4055 56 67 68 71 72 Duplexers Instructions71177335Încă nu există evaluări
- AM Transmitter'n'receiver CircuitDocument9 paginiAM Transmitter'n'receiver Circuitkapil singh100% (1)
- Lab5: Mixer: Group# Specifications For Mixer 900Mhz, 90-Degree 2Ghz, 90-Degree 3Ghz, 90-Degree 5Ghz, 90-DegreeDocument6 paginiLab5: Mixer: Group# Specifications For Mixer 900Mhz, 90-Degree 2Ghz, 90-Degree 3Ghz, 90-Degree 5Ghz, 90-DegreePaul ShineÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM Receivers With PLLDocument6 paginiFM Receivers With PLLOndrej LomjanskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7MHz CW AM QRP TransmitterDocument3 pagini7MHz CW AM QRP TransmitterVijay MirjeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Amplifier DiagramsDocument104 paginiPractical Amplifier DiagramsLorenzo100% (1)
- Amplificador de Bulbos de Bajo CostoDocument6 paginiAmplificador de Bulbos de Bajo CostoNaelectronic UOÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCMOS Gates Make Frequency MultipliersDocument3 paginiHCMOS Gates Make Frequency MultipliersDefaultAnomolyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2m TransverterDocument6 pagini2m TransverterRanzlerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electret Amplifier Application NoteDocument14 paginiElectret Amplifier Application NoterobkosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Directional Microphone Without Parabolic ReflectorDocument3 paginiDirectional Microphone Without Parabolic Reflectordetroit_me2553Încă nu există evaluări
- CBCC Amp 2Document5 paginiCBCC Amp 2sru_1990Încă nu există evaluări
- 300w tp9383 PDFDocument3 pagini300w tp9383 PDFlu1agp100% (1)
- Audio-Video Systems: AIM: - To Study About Tuner SectionDocument5 paginiAudio-Video Systems: AIM: - To Study About Tuner SectionAtit PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10m NBTV TX ComplDocument2 pagini10m NBTV TX ComplDiego García MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Three: Theoretical Background 3.1 Theory and AnalysisDocument37 paginiChapter Three: Theoretical Background 3.1 Theory and AnalysisNadish FatimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- New PBL CSDocument12 paginiNew PBL CSMalik Ali BiadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3V FM Transmitter 3V FM Transmitter CircuitDocument4 pagini3V FM Transmitter 3V FM Transmitter Circuitpeter.gomes20087216Încă nu există evaluări
- 06 KZ - KL3091 Amplifier Design Class D 2009-09-09Document10 pagini06 KZ - KL3091 Amplifier Design Class D 2009-09-09Rekabentuk DirgantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- By Bob Eckweiler, AF6C: Heathkit of The Month #33Document7 paginiBy Bob Eckweiler, AF6C: Heathkit of The Month #33Nervus NevisÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE3204 D2013 Lab2Document9 paginiECE3204 D2013 Lab2Khalil2097Încă nu există evaluări
- Transmitter and ReceiverDocument9 paginiTransmitter and ReceiverVasu ManikandanÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Electric 802 TV Radio Receiver and PhonografDocument21 paginiGeneral Electric 802 TV Radio Receiver and PhonografRicardo CachorrãoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RFDesign 3Document3 paginiRFDesign 3yel02Încă nu există evaluări
- Các Sơ Đ Do An Mon Hoc KT Thu PhatDocument32 paginiCác Sơ Đ Do An Mon Hoc KT Thu PhatLê ThúyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMOS 1.8GHz VCODocument4 paginiCMOS 1.8GHz VCOsanjeevsoni64Încă nu există evaluări
- A4FD1924d01 Wilkinson TheoryDocument4 paginiA4FD1924d01 Wilkinson TheorymrzahzÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM Receiver Using TDA7000 PDFDocument9 paginiFM Receiver Using TDA7000 PDFMuthuraj MuniyappanÎncă nu există evaluări
- AN 01eDocument3 paginiAN 01eluisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3V FM Transmitter CircuitDocument6 pagini3V FM Transmitter CircuitMahmood AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amplificador Final de VálvulasDocument6 paginiAmplificador Final de VálvulasTammy WashingtonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proyecto. CrossoverDocument15 paginiProyecto. CrossoverAppa D. LuffyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atv Transmitter From Microwave OvenDocument5 paginiAtv Transmitter From Microwave Ovensnidely_whiplashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low-Cost 770W Linear Amplifier With 572Bs in Grounded GridDocument5 paginiLow-Cost 770W Linear Amplifier With 572Bs in Grounded Gridjofra_fÎncă nu există evaluări
- DocumentDocument11 paginiDocumentDennis ParkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-Meter Vertical Dipole ArrayDocument15 pagini2-Meter Vertical Dipole ArrayRádioWeb SapucaiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50 W A.F. Amplifier: Uses Only One ICDocument3 pagini50 W A.F. Amplifier: Uses Only One ICSuda KrishnarjunaraoÎncă nu există evaluări
- t2fd 2Document9 paginit2fd 2Daniel Morales PobleteÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20W Hi-Fi Audio Power Amplifier: DescriptionDocument12 pagini20W Hi-Fi Audio Power Amplifier: DescriptionAngel AndersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsDe la EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorDe la Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (2)
- Disciplining Actions Against The Department Teaching and NonDocument7 paginiDisciplining Actions Against The Department Teaching and Nonlimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- Freq. of Scores & Cor. Resp. - GR. 5 and 6Document8 paginiFreq. of Scores & Cor. Resp. - GR. 5 and 6limboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- Almanza Elementary School Ts Cruz AnnexDocument2 paginiAlmanza Elementary School Ts Cruz AnnexEdward TocayonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz On Physical ChangeDocument1 paginăQuiz On Physical Changelimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- Strategic ConversationDocument58 paginiStrategic Conversationlimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Products Assembly and Servicing NC IIDocument85 paginiElectronic Products Assembly and Servicing NC IIlimboy1580% (10)
- IPCRFDocument9 paginiIPCRFlimboy15100% (1)
- Action Research FilDocument19 paginiAction Research Fillimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- 8-1-12 - Blood Vessels - LessonDocument10 pagini8-1-12 - Blood Vessels - Lessonlimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- HomeworkDocument21 paginiHomeworklimboy15100% (1)
- RpmsDocument4 paginiRpmslimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- RPMS Form For Teachers Marice1lDocument3 paginiRPMS Form For Teachers Marice1llimboy1550% (2)
- Friction: Easily As PossibleDocument1 paginăFriction: Easily As Possiblelimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- 8-1-12 - Blood Vessels - LessonDocument10 pagini8-1-12 - Blood Vessels - Lessonlimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- 5 Macro SkillsDocument5 pagini5 Macro Skillslimboy15100% (1)
- SF2 With Complete Formula REVISEDDocument7 paginiSF2 With Complete Formula REVISEDlimboy1564% (14)
- Request FormDocument1 paginăRequest Formlimboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- Big Al'S Music Inventory Analysis For The Year Ended December 31, 2012Document2 paginiBig Al'S Music Inventory Analysis For The Year Ended December 31, 2012limboy15Încă nu există evaluări
- Sf2 Attendance For Sy 2014-2015Document11 paginiSf2 Attendance For Sy 2014-2015limboy15Încă nu există evaluări