Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Science 9 Outcomes
Încărcat de
api-263902873Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Science 9 Outcomes
Încărcat de
api-263902873Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
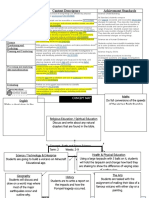
Science 9
General Curriculum Outcomes
STSE
1. Students will develop an understanding of the nature of science and technology, of the
relationships between science and technology, and of the social and environmental contexts of
science and technology.
SKILLS
2. Students will develop the skills required for scientific and technological inquiry, for solving
problems, for communicating scientific ideas and results, for working collaboratively, and for
making informed decisions.
KNOWLEDGE
3. Students will construct knowledge and understandings of concepts in life science, physical
science, and Earth and space science, and apply these understandings to interpret, integrate,
and extend their knowledge.
ATTITUDES
4. Students will be encouraged to develop attitudes that support the responsible acquisition and
application of scientific and technological knowledge to the mutual benefit of self, society, and
the environment.
Specific Curriculum Outcomes
Students will be expected to:
Atoms and Elements (25%)
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHANGES
perform experiments, collect evidence, report findings, and demonstrate a knowledge of
WHMIS standards in the laboratory (209-7, 111-6, 210-11)
investigate materials and describe them in terms of their physical properties (307-12)
describe changes in the properties of materials that result from some common chemical
reactions (307-13)
ATOMIC THEORY
use models in describing the structure and components of atoms and molecules, and
explain the appropriate operational definition (307-14, 208-7)
PERIODIC TABLE
identify examples of common elements, and compare their characteristics and atomic
structure(307-15)
use the periodic table as a classification system and compile data about its structure (2101, 210-2)
identify the elements and number of atoms, given a chemical formula (307-16)
provide examples of scientific knowledge that have resulted in the development of
technologies (111-1)
provide examples of technologies that have enhanced, promoted, or made possible
scientific research (111-4)
explain and provide examples of how societys needs for chemistry incorporate science,
technology, and environment (112-3, 112-8)
Characteristics of Electricity (25%)
ELECTRIC CURRENT
describe the flow of charge in an electrical circuit and explain the factors affecting the
circuit (109-14, 308 16)
investigate, in the laboratory, and compare qualitatively, static electricity and electric
current (210-7, 308-15)
SERIES AND PARALLEL CIRCUITS
describe series and parallel circuits involving varying resistance, voltage, and current
(308-17)
rephrase questions in a testable form and clearly define practical problems (20-1)
use instruments effectively and accurately for collecting data (209-3)
identify and suggest explanations for discrepancies in data and identify potential sources
of error and determine the amount of error in measurement (210-7, 210-10)
ELECTRICITY, ENERGY, AND THE ENVIRONMENT
relate electrical energy to domestic power consumption costs (308-18)
determine quantitatively the efficiency of an electrical appliance that converts electrical
energy to heat energy (308-19)
describe the transfer and conversion of energy from a generating station to the home
(308-20)
make informed decisions and propose a course of action on science, technology, and
social issues, including human and environmental needs for electricity and energy (113-9,
113-13)
Space Exploration (25%)
THE BEGINNINGS
describe theories on the formation of the solar system (312-1)
explain the need for new evidence in order to continually test existing theories about the
composition and origin of our solar system and galaxies (110-6, 210-3)
describe theories on the origin and evolution of the universe (312-3)
THE UNIVERSE
describe and classify the major components of the universe (312-2)
describe and explain the apparent motion of celestial bodies (312-4)
provide and describe examples of how Canadian research projects and careers are
supported through science and technology (112-6, 112-11)
THE SOLAR SYSTEM
describe the composition and characteristics of the components of the solar system (3125)
explain the need for new evidence in order to continually test existing theories and
identify new questions that arise (210-16)
describe the effects of solar phenomena on Earth (312-6)
propose alternative solutions to space life, develop a plan and data, and defend, with a
report, your groups position (208-4, 209-4, 211-1, 211-3, 211-5)
Reproduction (25%)
CELLULAR PROCESSES
illustrate and describe the basic processes of mitosis and meiosis (304-11)
identify major shifts in scientific world views (110-3)
compile and report data and predict values of variables by doing activities on cell
populations (210-6, 210-4)
REPRODUCTION
identify questions and investigate, in the laboratory, the reproduction of plants and
communicate findings
(208-2, 211-2)
distinguish between sexual and asexual reproduction in representative organisms (305-2)
compare sexual and asexual reproduction in terms of their advantages and disadvantages
(305-3)
GENETICS
provide examples that arise at home, in an industrial setting, or in the environment that
cannot be solved using scientific and technological knowledge (113-10)
discuss factors that may lead to changes in a cells genetic information (305-5)
select and integrate genetics information from various sources and apply criteria for
evaluating evidence and sources of information (209-5, 210-8)
provide examples of science and technology, including Canadian, that have contributed to
and developed genetic knowledge (111-1, 112-12)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Biology 20 Unit A TableDocument4 paginiBiology 20 Unit A Tableapi-236289588Încă nu există evaluări
- Ontario Grade 11 PhysicsDocument14 paginiOntario Grade 11 Physicssandeep_walia14990% (1)
- Bio 20 Unit B - Ecosystem and Population ChangeDocument16 paginiBio 20 Unit B - Ecosystem and Population Changeapi-353447897Încă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Solar RadiationDocument45 paginiEffects of Solar RadiationAkanubong oliverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maximum Adverse ExcursionDocument169 paginiMaximum Adverse ExcursionEriz50% (2)
- Environmental Systems Course Outline-V3Document4 paginiEnvironmental Systems Course Outline-V3anderspnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Education Lesson Plan Format: NGSS Performance ExpectationDocument6 paginiScience Education Lesson Plan Format: NGSS Performance Expectationapi-550329503Încă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Lesson Plan 3Document6 paginiChemistry Lesson Plan 3api-550644778Încă nu există evaluări
- Science Fifth Grade Georgia StandardsDocument3 paginiScience Fifth Grade Georgia Standardsapi-256383094Încă nu există evaluări
- Science Education Lesson Plan FormatDocument6 paginiScience Education Lesson Plan Formatapi-548406117Încă nu există evaluări
- snc1d Ci SheetDocument2 paginisnc1d Ci Sheetapi-275834887Încă nu există evaluări
- Australian CurriculumDocument33 paginiAustralian CurriculumNickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expanding The Fluorine Chemistry of Living Systems Using Engineered Polyketide Synthase PathwaysDocument7 paginiExpanding The Fluorine Chemistry of Living Systems Using Engineered Polyketide Synthase PathwaysJunia Alfa NessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sciencefpd 2Document12 paginiSciencefpd 2api-397568836Încă nu există evaluări
- k12 Curriculum Guides Science Grade9 Unit 2 GRD 9 Science Jan2011Document50 paginik12 Curriculum Guides Science Grade9 Unit 2 GRD 9 Science Jan2011SgsgshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4C's in ScienceDocument7 pagini4C's in ScienceJoel Salwagan jrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Science 2 A/G Semester 1 - Review GuideDocument5 paginiComprehensive Science 2 A/G Semester 1 - Review Guideshivam178Încă nu există evaluări
- Efg 149Document376 paginiEfg 149Prasanna ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science FPDDocument12 paginiScience FPDapi-395537786Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 Science FPDDocument10 paginiYear 6 Science FPDapi-390074616Încă nu există evaluări
- Air ChemistryDocument20 paginiAir Chemistryvictorymichael355Încă nu există evaluări
- Cbems 140aDocument19 paginiCbems 140amdawg467Încă nu există evaluări
- Curric AssDocument2 paginiCurric Assapi-389638207Încă nu există evaluări
- Physical Sciences Ncbts-Based Let 2009 TosDocument7 paginiPhysical Sciences Ncbts-Based Let 2009 TosEngineerEducatorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Grade 3Document3 paginiScience Grade 3Patti Kendrick Whatley100% (1)
- Bio Unit PlanDocument12 paginiBio Unit Planapi-199560874Încă nu există evaluări
- Online Course Syllabus-Sherell JamesDocument9 paginiOnline Course Syllabus-Sherell Jamesapi-665021925Încă nu există evaluări
- TX Essential Knowledge Skills Teks ScienceDocument14 paginiTX Essential Knowledge Skills Teks Scienceapi-197914650Încă nu există evaluări
- Museum Exhibit RubricDocument7 paginiMuseum Exhibit Rubricapi-264532158Încă nu există evaluări
- Physical WorldDocument3 paginiPhysical WorldMarie FaddoulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects of Climate Changes On Water ResourcesDocument2 paginiEffects of Climate Changes On Water ResourcesDawar KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wang 2012Document24 paginiWang 2012magaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Grade 4 Unit 3 2010 GuideDocument179 paginiScience Grade 4 Unit 3 2010 Guidesasnews50% (2)
- Nebraska State Science Standards:: Victoria Freeman Year Long Biology PlanDocument13 paginiNebraska State Science Standards:: Victoria Freeman Year Long Biology Planapi-281582336Încă nu există evaluări
- 2020 Physics Subject Assessment AdviceDocument11 pagini2020 Physics Subject Assessment AdviceMaan PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objectives For Lesson 1: Cyclones and The Coriolis EffectDocument4 paginiObjectives For Lesson 1: Cyclones and The Coriolis EffectEagle NavÎncă nu există evaluări
- WAssce Physics SyllabusDocument24 paginiWAssce Physics SyllabusIkedi UcheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essentials of Modern Physics h3Document16 paginiEssentials of Modern Physics h3Wang Si QiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum LinksDocument4 paginiCurriculum Linksapi-391216982Încă nu există evaluări
- Standard 9 - ArtifactDocument28 paginiStandard 9 - ArtifactSarah BurnettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Year 6 Overview-2Document2 paginiYear 6 Overview-2api-350585868Încă nu există evaluări
- Science: Planning Document University of Notre DameDocument15 paginiScience: Planning Document University of Notre Dameapi-319889786Încă nu există evaluări
- SNC 1 PDocument2 paginiSNC 1 Papi-275834887Încă nu există evaluări
- 5E Lesson Plan Explore Explain2Document11 pagini5E Lesson Plan Explore Explain2Alyssa FranciscoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Grade 4 Light Optical DevicesDocument2 paginiScience Grade 4 Light Optical DevicesMary-Rose CasuyonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th Grade Ngss StandardsDocument8 pagini4th Grade Ngss Standardsapi-261541929Încă nu există evaluări
- Year 6Document1 paginăYear 6api-450945881Încă nu există evaluări
- Science Physical Science Georgia StandardsDocument5 paginiScience Physical Science Georgia Standardsapi-491081853Încă nu există evaluări
- Primary Science FPD 5esDocument11 paginiPrimary Science FPD 5esapi-525582472Încă nu există evaluări
- Biondi 2012 Validation of Hydrological Models CDocument7 paginiBiondi 2012 Validation of Hydrological Models CJesús RealesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 1257158Document4 paginiScience 12571581592162022Încă nu există evaluări
- Primary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)Document12 paginiPrimary Science FPD: Australian Curriculum: Science (Year 6)api-479877445Încă nu există evaluări
- HS - Earth's SystemsDocument2 paginiHS - Earth's Systemsapi-3189379420% (1)
- A Reconciled Estimate of Ice-Sheet Mass Balance Shepherd Et Al 2012Document8 paginiA Reconciled Estimate of Ice-Sheet Mass Balance Shepherd Et Al 2012silvabussoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline SPH4UDocument6 paginiCourse Outline SPH4UKaXin CheahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry, Beginning With School Year 2010-2011 (One Credit)Document4 paginiChemistry, Beginning With School Year 2010-2011 (One Credit)Jo ContrerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science TeksDocument1 paginăScience Teksapi-25564329Încă nu există evaluări
- 10-20-17 III J Non-Substantive Changes To Math Ela Science Standards Attachment 3 - ScienceDocument4 pagini10-20-17 III J Non-Substantive Changes To Math Ela Science Standards Attachment 3 - Scienceapi-470241740Încă nu există evaluări
- ITEEA Stdrs TEDocument6 paginiITEEA Stdrs TEDo NhamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modeling of Resistivity and Acoustic Borehole Logging Measurements Using Finite Element MethodsDe la EverandModeling of Resistivity and Acoustic Borehole Logging Measurements Using Finite Element MethodsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pavement Materials for Heat Island Mitigation: Design and Management StrategiesDe la EverandPavement Materials for Heat Island Mitigation: Design and Management StrategiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wanted Poster Exemplar BariumDocument2 paginiWanted Poster Exemplar Bariumapi-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 Course Outline 2015Document2 paginiScience 9 Course Outline 2015api-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- New Grade 9 Specific Curriculum OutcomesDocument9 paginiNew Grade 9 Specific Curriculum Outcomesapi-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- Math 9 Course Outline 2015Document2 paginiMath 9 Course Outline 2015api-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Outcomes For Mathematics 8 2014Document2 paginiCurriculum Outcomes For Mathematics 8 2014api-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- Healthy Living 9 OutcomesDocument2 paginiHealthy Living 9 Outcomesapi-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum Outcomes For Mathematics 7 2014Document3 paginiCurriculum Outcomes For Mathematics 7 2014api-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- Math 8 Course Outline 2014 v2Document2 paginiMath 8 Course Outline 2014 v2api-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- Math 8 Course Outline 2014 v2Document2 paginiMath 8 Course Outline 2014 v2api-263902873Încă nu există evaluări
- HCL CDC Project Report FinalDocument68 paginiHCL CDC Project Report Finalshahinnocent100% (1)
- Thesis Chapter 2 Review of Related Literature FormatDocument8 paginiThesis Chapter 2 Review of Related Literature Formatc5rqq644Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Proposal PotatoDocument17 paginiFinal Proposal PotatoAbhishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Related LiteratureDocument4 paginiReview of Related LiteratureKaren Roldan RosalejosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good Research ProblemDocument30 paginiGood Research ProblemSurvivalgirlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stat Research-ProposalDocument15 paginiStat Research-ProposalJuly Grace CasinilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Technology SocietyDocument17 paginiScience Technology SocietyRenz CarpioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choosing Where To Work at Work - Towards A Theoretical Model of Benefits and Risks of Activity-Based Flexible OfficesDocument53 paginiChoosing Where To Work at Work - Towards A Theoretical Model of Benefits and Risks of Activity-Based Flexible OfficesElla SetyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of Literature of Medicinal PlantsDocument8 paginiReview of Literature of Medicinal Plantsgrgdazukg100% (1)
- Correlation Research Design - PRESENTASIDocument62 paginiCorrelation Research Design - PRESENTASIDiah Retno Widowati100% (1)
- 4th Draft - Data GatheringDocument6 pagini4th Draft - Data GatheringFatima GuinidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flecha - Critical Communicative MethodologyDocument11 paginiFlecha - Critical Communicative MethodologyAny RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human FlourishingDocument21 paginiHuman Flourishinggerald romero100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Bio EthicsDocument3 paginiLesson 1 Bio EthicsRandom TvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laboratory Response Checklist For Infectious Disease Outbreaks-Preparedness and Response Considerations For Emerging ThreatsDocument11 paginiLaboratory Response Checklist For Infectious Disease Outbreaks-Preparedness and Response Considerations For Emerging ThreatsamabelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educational Research An Introduction 7th Edition by Meredith D Gall Walter R Borg Joyce P GallDocument9 paginiEducational Research An Introduction 7th Edition by Meredith D Gall Walter R Borg Joyce P GallAyuni DwismÎncă nu există evaluări
- APA Format and Style 7th Ed - ACC FIN-1Document128 paginiAPA Format and Style 7th Ed - ACC FIN-1Diego MondragonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Research Essentials 9th Edition Mcdaniel Solutions ManualDocument13 paginiMarketing Research Essentials 9th Edition Mcdaniel Solutions Manualadamcarlsonkesjgzaxby100% (18)
- A Study On The Career Preferences of EdisonDocument29 paginiA Study On The Career Preferences of EdisonJoshua Dalmacio80% (15)
- EdrhodgDocument8 paginiEdrhodgJonahJunior50% (2)
- 2018 - Dobbs - Escobedo - Urban Ecosystem Services in Latin America Mismatch Between Global Concepts and Regional Realities Urban EcosystemsDocument15 pagini2018 - Dobbs - Escobedo - Urban Ecosystem Services in Latin America Mismatch Between Global Concepts and Regional Realities Urban EcosystemsfabianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantitative Techniques & Operations Research: Ankit Sharma Neha Rathod Suraj Bairagi Vaibhav ThammanDocument12 paginiQuantitative Techniques & Operations Research: Ankit Sharma Neha Rathod Suraj Bairagi Vaibhav ThammanAbhijeet SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sudha Milk DairyDocument62 paginiSudha Milk Dairyimamitanand83% (6)
- The Effect of Cost Control and Reduction Practices On Transport Companies Profitability (Case Study of Jihan Freighters Limited)Document32 paginiThe Effect of Cost Control and Reduction Practices On Transport Companies Profitability (Case Study of Jihan Freighters Limited)OSCAR AHINAMPONGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Factors Associated With Students' Performance in English in The Implementation of Spiral ProgressionDocument26 paginiFactors Associated With Students' Performance in English in The Implementation of Spiral ProgressionGlobal Research and Development ServicesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dorothea Orem PowerpointDocument35 paginiDorothea Orem Powerpointapi-486954490Încă nu există evaluări
- 1920 Meng Electronic Engineering With Pathways 4436 4438 4439 4440 4441 4476 6043Document37 pagini1920 Meng Electronic Engineering With Pathways 4436 4438 4439 4440 4441 4476 6043Mwaisa BangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- f16 - Anth Soc 301a Environmental Sociology - KanDocument7 paginif16 - Anth Soc 301a Environmental Sociology - KanNowrin MohineeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frequency of Visit To Doctor and Health PDFDocument9 paginiFrequency of Visit To Doctor and Health PDFAnkur VishalÎncă nu există evaluări