Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Biology Genetic Mutation Notes
Încărcat de
Tiffany GallinaDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Biology Genetic Mutation Notes
Încărcat de
Tiffany GallinaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Genetic Mutation Notes
Mutation: Any change or random error in a DNA sequence
- Mutations can exist in reproductive cells and can therefore be
passed on to offspring
- Mutations can also occur in body cells, and while its not
passed on to the offspring, can impair the functioning of the
cell and can cause problems for the individual (example:
cancer)
Types of mutations:
1. Point Mutation: a change in a single base pair in DNA
- A change in a single nitrogen base can change the entire
structure of a protein because a change in a single amino acid
can affect the shape of the protein.
- Less harmful to organisms than frameshift mutations because
they disrupt only a single codon.
2. Frameshift Mutation: a type of mutation in which a single base is
added or deleted from DNA
- This new sequence would then be transcribed into mRNA. But
the mRNA would be out of position by one base. As a result,
every codon after the deleted base would be different. This
mutation would cause nearly every amino acid in the protein
after the deletion or addition to be changed.
Chromosomal Mutations
Deletion: part of the
chromosome is left
out
Duplication: segment of
a chromosome is
repeated
Inversion: chromosome
becomes orientated in
the reverse of its usual
direction
Translocation: part of
the chromosome
breaks off and attaches
to another
- Few chromosome mutations are passed on to the next generation because
the zygote usually dies. In cases where the zygote survives, it is often sterile
and thus incapable of producing offspring.
Causes of Mutations
- Any agent that can cause a change in DNA is called a mutagen.
Mutagens include high energy radiation, chemicals, and even high
temperatures.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Plasma Proteins V5: Structure, Function, and Genetic ControlDe la EverandThe Plasma Proteins V5: Structure, Function, and Genetic ControlFrank PutnamEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (1)
- 2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription, and TranslationDocument25 pagini2.7 DNA Replication, Transcription, and TranslationJennÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of MutationsDocument11 paginiTypes of MutationsnsjunnarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA NotesDocument26 paginiDNA NotesFight FionaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utation: Big PictureDocument2 paginiUtation: Big PicturehomamunfatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetic MutationDocument23 paginiGenetic MutationKylie GavinneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 6Document60 paginiLecture 6Anthony FajardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gene Expression in Prokaryotes.Document23 paginiGene Expression in Prokaryotes.M.PRASAD NAIDU100% (1)
- Chromosomal Aberrations: Deficiency or DeletionDocument4 paginiChromosomal Aberrations: Deficiency or Deletionvandv printsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generation of Antibody DiversityDocument12 paginiGeneration of Antibody DiversityAltaf khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cell Division: MitosisDocument38 paginiCell Division: MitosisSam RatnamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mutations WorksheetDocument3 paginiMutations Worksheetapi-293001217Încă nu există evaluări
- Protein SynthesisDocument2 paginiProtein SynthesisArlan AbraganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dna Replication and Repair #4Document76 paginiDna Replication and Repair #4Len ArellanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Mendelian GeneticsDocument48 paginiNon Mendelian GeneticsFrank Louie MagadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What is Nucleic Acid? (38Document12 paginiWhat is Nucleic Acid? (38Antonette SolaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supercoiling of DNADocument40 paginiSupercoiling of DNAstevensb055Încă nu există evaluări
- Genbio - Unit 2 - Genetics - l1 Mendelian and Post Mendelian GeneticsDocument40 paginiGenbio - Unit 2 - Genetics - l1 Mendelian and Post Mendelian GeneticsErika Jane BulanhaguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bacterial PlasmidsDocument9 paginiBacterial PlasmidsspanishinqÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 10 Practice TestDocument3 paginiCH 10 Practice Testrylee graceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Dogma Molecular Genetics FlowDocument3 paginiCentral Dogma Molecular Genetics FlowDiana RomeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gene Regulation of Prokaryotic TranscriptionDocument17 paginiGene Regulation of Prokaryotic TranscriptionAyu Tri AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- CRISPR: A Defense Mechanism in MicroorganismsDocument11 paginiCRISPR: A Defense Mechanism in MicroorganismsRaissa E. FedoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genetic Control of Protein Structure & FunctionDocument60 paginiGenetic Control of Protein Structure & Functionathirah100% (1)
- Nucleosome Model PDFDocument26 paginiNucleosome Model PDFpenny singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organelle targeting motifs quizDocument6 paginiOrganelle targeting motifs quizJeevikaGoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
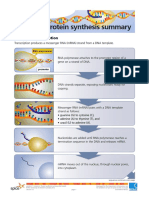
- Protein Synthesis SummaryDocument2 paginiProtein Synthesis SummaryTrinitee Wesner100% (1)
- Polymerase Chain ReactionDocument22 paginiPolymerase Chain ReactionPoornaBasuri100% (1)
- Red Biotechnology PPT 2021Document12 paginiRed Biotechnology PPT 2021Vanessa SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio 106 Lecture 5 Chemical Basis of Heredit1Document16 paginiBio 106 Lecture 5 Chemical Basis of Heredit1Evan Jane JumamilÎncă nu există evaluări
- MeiosisDocument10 paginiMeiosisNoor Hafezah Mohd MokhtiarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Plasmid Is A Small DNA Molecule Within A Cell That Is Physically Separated From A Chromosomal DNA and Can Replicate IndependentlyDocument5 paginiA Plasmid Is A Small DNA Molecule Within A Cell That Is Physically Separated From A Chromosomal DNA and Can Replicate Independentlyyaqoob008Încă nu există evaluări
- Mitosis and MeiosisDocument56 paginiMitosis and MeiosisJaime Soriano100% (2)
- Inheritance Biology EDUNCLEDocument54 paginiInheritance Biology EDUNCLEEvita Almeida100% (1)
- 5.3 Understanding Genes and ChromosomesDocument11 pagini5.3 Understanding Genes and ChromosomesNoor Hidayah SambliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biotechnology CorrectdDocument7 paginiBiotechnology CorrectdKalyan ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCB 102 DNA Problem SetDocument5 paginiMCB 102 DNA Problem SetSadab KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 02: Bacterial Genetics, Metabolism, and Structure Test BankDocument8 paginiChapter 02: Bacterial Genetics, Metabolism, and Structure Test BankroeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mutation PowerpointDocument34 paginiMutation PowerpointErick BercÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final KeyDocument11 paginiFinal KeyAbhinandan ChakrabortyÎncă nu există evaluări
- FCB 7-GeneticsDocument15 paginiFCB 7-GeneticsYuri PaderesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sex-Linked Traits Practice ProblemsDocument2 paginiSex-Linked Traits Practice ProblemsLaila MahmudahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Pedigree AnalysisDocument48 pagini4 Pedigree AnalysisBiologistAhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOT643 Midterm Exam Summer 2016Document4 paginiBIOT643 Midterm Exam Summer 2016JayÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA To Protein Worksheet: Directions: Below Are Five (5) Different DNA SequencesDocument2 paginiDNA To Protein Worksheet: Directions: Below Are Five (5) Different DNA SequencesJuju Zenemij0% (2)
- Lecture 1 (DNA - The Genetic Material)Document43 paginiLecture 1 (DNA - The Genetic Material)M Luqman HakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gene Silencing Gene Silencing: Niranjana.S.Karandikar Msc-I Roll No.12Document21 paginiGene Silencing Gene Silencing: Niranjana.S.Karandikar Msc-I Roll No.12Niranjana KarandikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linkage and crossing over: Genetic recombination between genes on homologous chromosomesDocument34 paginiLinkage and crossing over: Genetic recombination between genes on homologous chromosomesDhungana Surya RdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quiz 5 Scin130Document11 paginiQuiz 5 Scin130new rhondaldÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus in Chemical Biology III (Biomolecules) (TCB3)Document12 paginiSyllabus in Chemical Biology III (Biomolecules) (TCB3)Yuri PaderesÎncă nu există evaluări
- DNA and RNA Structure and Function Test ReviewDocument3 paginiDNA and RNA Structure and Function Test ReviewEjaz KazmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disorders and DiseasesDocument5 paginiDisorders and DiseasesMhariane MabborangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linkage and Recombination PDFDocument44 paginiLinkage and Recombination PDFVenkatesh JelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Tools TechniquesDocument10 paginiBiological Tools TechniquesAzmi Rahman50% (2)
- Biotech Principles: Genetic Engineering & Microbial GrowthDocument6 paginiBiotech Principles: Genetic Engineering & Microbial GrowthIndrajith MjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crispr Cas HajarDocument21 paginiCrispr Cas HajarHajira Fatima100% (1)
- Replication, Transcription, Translation and Its Regulation: By, University of Agricultural Sciences, DharwadDocument42 paginiReplication, Transcription, Translation and Its Regulation: By, University of Agricultural Sciences, DharwadTabada NickyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Gene RegulationDocument35 paginiProkaryotic and Eukaryotic Gene RegulationDrew TaryeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- RNA and Protein Synthesis Problems KEYDocument4 paginiRNA and Protein Synthesis Problems KEYnona wayne dela peña100% (1)
- Gene MutationDocument20 paginiGene Mutationdheeresh aggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tiffs GA EOCT American Lit CondensedDocument16 paginiTiffs GA EOCT American Lit CondensedTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geometry ReviewDocument6 paginiGeometry ReviewTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- APUSH Review ChartDocument22 paginiAPUSH Review ChartTiffany Gallina100% (1)
- Chemistry - Chart To ID CompoundsDocument1 paginăChemistry - Chart To ID CompoundsTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tiff's GA EOCT Condensed US HistoryDocument26 paginiTiff's GA EOCT Condensed US HistoryTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Calculating The Element's ChargeDocument2 paginiChemistry - Calculating The Element's ChargeTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Ion Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiChemistry Ion Cheat SheetTiffany Gallina100% (4)
- Tiffs GA EOCT 9th Grade Lit CondensedDocument13 paginiTiffs GA EOCT 9th Grade Lit CondensedTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry: Writing Ionic Formulas For CompoundsDocument5 paginiChemistry: Writing Ionic Formulas For CompoundsTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fill in Blank Biology Eoct Study Guide Based On 2008Document9 paginiFill in Blank Biology Eoct Study Guide Based On 2008Tiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Calculating The Element's ChargeDocument2 paginiChemistry - Calculating The Element's ChargeTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Psych Myers Chapter 7 Review Chart of DrugsDocument1 paginăAP Psych Myers Chapter 7 Review Chart of DrugsTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Single Replacement Reactions NotesDocument1 paginăChemistry - Single Replacement Reactions NotesTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fill in Blank Biology Eoct Study Guide Based On 2008Document9 paginiFill in Blank Biology Eoct Study Guide Based On 2008Tiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Nuclear Chemistry NotesDocument4 paginiChemistry - Nuclear Chemistry NotesTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Naming Hydrocarbons NotesDocument1 paginăChemistry - Naming Hydrocarbons NotesTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Significant Number NotesDocument1 paginăChemistry - Significant Number NotesTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Psych Anatomy The Brain - Coloring Worksheet - Visual MapDocument2 paginiAP Psych Anatomy The Brain - Coloring Worksheet - Visual MapTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Atomic Structure NotesDocument2 paginiChemistry - Atomic Structure NotesTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig The Unit Circle in Radian and DegreesDocument1 paginăTrig The Unit Circle in Radian and DegreesTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP Psych Chart of Freud's Stages Psychology MyersDocument1 paginăAP Psych Chart of Freud's Stages Psychology MyersTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myers AP Psych Important Psychologists CondensedDocument1 paginăMyers AP Psych Important Psychologists CondensedTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry - Half-Life NotesDocument1 paginăChemistry - Half-Life NotesTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AP PSYCH Major Structures of The Brain Review Chart MyersDocument2 paginiAP PSYCH Major Structures of The Brain Review Chart MyersTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigonometry Summary Unit Circle RatiosDocument1 paginăTrigonometry Summary Unit Circle Ratiosteachopensource100% (2)
- APWH Gender Difference Chart by CultureDocument1 paginăAPWH Gender Difference Chart by CultureTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- APUSH AP US History Glossary - IDSDocument47 paginiAPUSH AP US History Glossary - IDSTiffany Gallina88% (8)
- Apush Supreme Court Cases / Decisions US HistoryDocument5 paginiApush Supreme Court Cases / Decisions US HistoryTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trig Properties of Sine and Cosine - Graphing NotesDocument2 paginiTrig Properties of Sine and Cosine - Graphing NotesTiffany GallinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vehicon (Prime) - Transformers WikiDocument13 paginiVehicon (Prime) - Transformers Wikiamos_evaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joycie 4-7Document2 paginiJoycie 4-7Jay VillasotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toyota Vehicle Glossary TermsDocument31 paginiToyota Vehicle Glossary TermsEdward Ugochukwu AdighibeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 10Document19 paginiLecture 10Sara AlwehrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluation of Plant Extracts Against Two Spotted Spider MiteDocument7 paginiEvaluation of Plant Extracts Against Two Spotted Spider MiteAnkaranaRenvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motor ManualDocument4 paginiMotor ManualRemezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum MapDocument3 paginiCurriculum MapSem PerezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Occupation Certificate DocumentsDocument1 paginăOccupation Certificate Documentsarungupta366Încă nu există evaluări
- F 25 Sensor Family Miniature Sensors for Precision DetectionDocument34 paginiF 25 Sensor Family Miniature Sensors for Precision DetectionAlex GarduñoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conceptual SLDDocument1 paginăConceptual SLDakhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- SynonymsDocument14 paginiSynonymsMursal IbrahimiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noun Form Answers PDFDocument11 paginiNoun Form Answers PDFChinna LingamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pages From 0625 - s16 - QP - 42 - 01Document2 paginiPages From 0625 - s16 - QP - 42 - 01lelon ongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Attachment at Meghna Knit Composite Ltd.Document137 paginiIndustrial Attachment at Meghna Knit Composite Ltd.Riasat Alam50% (2)
- Is 1726 1991Document17 paginiIs 1726 1991RaykochiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Company ProfileDocument10 paginiCompany Profile1anupma0Încă nu există evaluări
- Predicting Iron Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials With Arbitrary Voltage Supply An Engineering ApproachDocument9 paginiPredicting Iron Losses in Soft Magnetic Materials With Arbitrary Voltage Supply An Engineering Approachmayur isameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Public List Programs by Specialty 460Document9 paginiPublic List Programs by Specialty 460Enta SyngÎncă nu există evaluări
- S6000-Operation-Manual SkyliftDocument50 paginiS6000-Operation-Manual SkyliftSetiawan Tuhu basukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidelines For Dengue Surveillance Edition2.PDF WHODocument115 paginiGuidelines For Dengue Surveillance Edition2.PDF WHOFebyan Kuan Lu Hap100% (1)
- Water Transport Studies in Stone Masonry With Soil Cement MortarDocument10 paginiWater Transport Studies in Stone Masonry With Soil Cement MortarTJPRC PublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIST of Tools-BartenderDocument5 paginiLIST of Tools-BartenderLegal DepartmentÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bushings BrochureDocument14 paginiBushings Brochurebpd21Încă nu există evaluări
- MANAURITE XM Material PDFDocument8 paginiMANAURITE XM Material PDFkbc404Încă nu există evaluări
- Suvarnaprashan Sanskar EnglishDocument4 paginiSuvarnaprashan Sanskar EnglishLifecare Ayurveda Drnikul PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASME B36.10M-2004 Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe StandardDocument2 paginiASME B36.10M-2004 Welded and Seamless Wrought Steel Pipe StandardAmit BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- KFS Ut U3Document5 paginiKFS Ut U3Ana DuarteÎncă nu există evaluări
- FIITJEE SAMPLE PAPER – 2018 (Big Bang Edge Test / Talent Recognition Exam) for Class 10 (Paper 2Document17 paginiFIITJEE SAMPLE PAPER – 2018 (Big Bang Edge Test / Talent Recognition Exam) for Class 10 (Paper 2msreddy86Încă nu există evaluări
- Men FootwearDocument442 paginiMen FootwearAbhishekÎncă nu există evaluări
- SR-21 SniperDocument6 paginiSR-21 SniperBaba HeadquaterÎncă nu există evaluări