Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Chapter 13 Modified
Încărcat de
api-248642018100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
322 vizualizări5 paginiThe branch of physics that deals with the study of static charges is called electrostatics. Electrostatic induction is the rearrangement of charges inside a neutral body when a charged body is brought closer to it. The force of attraction or repulsion between the two charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of charges.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
chapter 13 modified
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThe branch of physics that deals with the study of static charges is called electrostatics. Electrostatic induction is the rearrangement of charges inside a neutral body when a charged body is brought closer to it. The force of attraction or repulsion between the two charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of charges.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
322 vizualizări5 paginiChapter 13 Modified
Încărcat de
api-248642018The branch of physics that deals with the study of static charges is called electrostatics. Electrostatic induction is the rearrangement of charges inside a neutral body when a charged body is brought closer to it. The force of attraction or repulsion between the two charges is directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of charges.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 5
1
Chapter wise Notes by: Mr.
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Naveed Atif
Chapter # 13: Electrostatics
Q#1. Define electrostatics.
Ans: The branch of physics that deals with the study of static charges is called
electrostatics.
Q#2: What is charge?
Ans: It is the property of a material due to which it can attract or repel another material.
Q.3: How an object can be charged by rubbing?
(Ans) Charging by rubbing
A body can be charged by rubbing it with another body. It is because some electrons
from the surface of one body transferred to the surface of other body during rubbing.
For example
When a comb is rubbed with hair, the hair loses an electron and becomes positively
charge while the comb gain electron and becomes negatively charge.
Q.4: What is meant by electrostatic induction?
(Ans) Electrostatic induction
The rearrangement of charges inside a neutral body when a charged body is brought
closer to it is called electrostatic induction. This new arrangement of charges is
temporary and will regain original after the removal of charged body. Electrostatic
induction can take place in both conductors and insulators.
Q#5: What is Electroscope?
Ans: A sensitive device used for the detection and testing of charge is called
Electroscope.
Q#6: State Coulombs law?
(Ans) Statement
This law states that the force of attraction or repulsion between the two charges is
directly proportional to the product of the magnitude of charges and inversely
proportional to the square of the distance between the charges.
F=k q1q2 / r2
Q#7: What is meant by electric field and electric field intensity?
(Ans) Electric field
The region around a charge body in which it can interact another charge is known as
electric field. It is a vector quantity. It is represented by electric lines of force.
Electric field intensity
The strength of the field at any point is known as electric field intensity.
It can also be defined as the electric force exerted per unit positive test charge is
known as electric field intensity. It is denoted by E. It is a vector quantity.
Mathematically
E = k q / r2
This equation shows the electric field intensity of a point charge q.
The SI unit of electric field intensity is Newton/coulomb (N/C).
Chapter wise Notes by: Mr.
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Naveed Atif
Q#8: What are electric lines of force? Describe its characteristics.
(Ans) Eectric lines of force
An electric line of force in general shows the path through which an electric charge
would move. The direction of the lines shows the direction of the field. The number of
electric lines per unit area represents the intensity of the field.
General characteristics of the electric lines of force are as under:
A positive charge always emits lines of force.
A negative charge always absorb lines of force.
W
hen two opposite charges are placed nearer, then the lines of force start from the
positive charge and ends at negative charge. As a result, they attract each other.
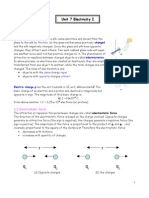
Q#9: Define and explain electric potential and its unit?
(Ans) Electric potential
The work done on a unit positive charge to move it from one place to another against
the electric field is called electric potential. It is denoted by V. Mathematically
V=W/q
Potential difference
The work done on a unit positive charge to move it from point A to point B against
the electric field is called potential difference. OR
The energy supplied by a unit positive charge as it moves from a point of higher
potential to a point of lower potential is called potential difference.
Q#10: Write the practical applications of electrostatics.
(Ans) The practical applications of electrostatics are as under:
(1) Electropainting
Electrostatics is used in applying paint on the surface of different articles. The body of
the car is earthed. The particles of the paint emerge out of the nozzle of the spray
machine, they aquire a positive charge. As they reached to the body of the car due to
electrostatic induction negative induced on the body of the car. As a result, an
electrostatic force established and firm coating of the paint is formed on the surface of
the car. This method is efficient, effective and cheap.
(2) Dust extraction
Electrostatics is used for the separation of smoke and dust particles from a coal-burning
power station by means of an electroastatic precipitator.
Q.10 What is a capacitor? Describe the capacitance of a capacitor.
(Ans) Capacitor
A device used to store an electric charge is called capacitor.
Construction
A capacitor consists of two parallel metallic plates having a small distance between
them. The medium inside the plates is air or some other insulating material known as
dielectric.
Charging a capacitor
Chapter wise Notes by: Mr.
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Naveed Atif
Consider a charge +Q is transferred to plate A, then by electrostatic induction a -Q
charge is induced on plate B.
A force of attraction is established between the
plates due to which the charges are bound with the
plates and remain stored for long period.
Capacitance of a capacitor
The capacity of a capacitor to store charge is called
capacitance of the capacitor.
Experiments show that the charge store in a
capacitor is directly proportion to the potential
difference across the plates of the capacitor.
Mathematically
Q = Constant V
Q = CV
Where C is costant and is known as capacitance of the capacitor. The SI unit of
capacitance of a capacitor is farad (F).
Farad
It can be defined as the capacitance of a capacitor is one farad if one coulomb charge
is stored by the capacitor providing a potential difference of one volt to their plates.
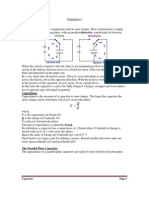
Q.11 How capacitors can be connected in a circuit?
(Ans) There are two basic ways of connecting capacitors in a circuit.
1. Series combination
A type of combination of two or more than two capacitors in
which the capacitors are connected plate to plate is called
series combination of the capacitors.
2. Parallel combination of capacitor
A type of combination of two or more than two capacitors in which
the plates of the capacitors are connected parallel to each other as
shown in figure is called parallel combination of capacitors.
Q.12 Write different types of capacitors.
(Ans) There are two types of capacitors.
1. Fixed capacitors
2. Variable capacitors
1. Fixed capacitors
Those capacitors whose parts are fixed by design and its plates are immovable is called
fixed capacitors. The capacitance of these capacitors does not change (constant).
Examples of these capacitors are paper capacitors and mica capacitors.
2. Variable capacitors
A type of capacitors whose area of the plates can be changed is called variable
capacitors. The capacitance of these capacitors can be changed by increasing or
decreasing the area between the plates. For example
The capacitors used in tuning of a radio frequency.
Chapter wise Notes by: Mr.
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Naveed Atif
SHORT QUESTIONS (EXERCISE)
Q#1: An electrified rod attracts pieces of paper. After a while these pieces fly
away! Why?
Ans:
When electrified rod is brought close to the pieces of paper, by induction an opposite
charge appear on pieces of paper due to which these pieces of paper attracted towards
the rod. But when these pieces of paper touches the charged rod, charge of rod transfer
to the pieces of paper due to which the will be force of repulsion between the rod and
pieces of paper, hence te pieces of paper fly away from the rod.
Q#2: How much negative charge has been removed from a positively charged
electroscope if it has a charge of 7.5 * 10-11 C?
Ans: An electroscope is charged positively means the negative charges are removed
from the electroscope. So, if we remove 2 C charge from electroscope and it is
positively charged means we remove 2 C (-ive) charge from the electroscope to charge
it positively of equal amount i-e 2 C. Hence if an electroscope is charged of an 7.5 * 1011
C positive charge means we have to remove equal amount of negative charge from
electroscope.
Q#3: In What direction will a positively charged particle move in an electric field?
Ans: The whole phenomena depends upon source of electric field if source is positive
charge then electric field will repels and if source charge is negative it attracts the
positively charged particle.
Q#4: Does each capacitor carry equal charge in series combination? Explain.
Ans: Each capacitor has the same charge across series combination because
capacitors are connected side by side so, if battery supply +Q to C 1 due to induction Q
charge is induced on C2. So, total charge remains same.
Q#5: Each capacitor in parallel combination has equal potential difference
between its two plates. Justify the statement.
Ans: In parallel combination potential applied to each capacitor is same so, the
potential difference across capacitor is also same because of direct connection of
capacitor and battery.
Q#6: Is the presence of charge is necessary for the existence of electrostatic
potential?
Ans: Yes, presence of charge is necessary for the existence of electrostatic potential.
Q#7: Rubber tires get charged from friction with road. What is the polarity of the
charge?
Ans: When friction takes place between rubber and road, charge is produced. Then the
rubber become negatively charged and road becomes positively charged.
Q#8: Perhaps you have seen a gasoline truck trailing a metal chain beneath it.
What purpose does the chain serve?
Ans: When the fuel is pumped from the truck to reservoir charge can quickly build up
due to fluid flow. This static charge can create sparks that can cause explosion. So, the
Chapter wise Notes by: Mr.
Expected short questions from theory and exercise
Naveed Atif
metal chain is used since metals are conductors and allow charge to flow in this way ,
by connecting it to ground whole charge transfers to ground.
Q#9: If a high voltage power line fell across your car while you were in the car,
why should you not come out of the car?
Ans: As the tires of the car are totally behaves as insulator so, when a high voltage
power line fell across your car it becomes Faraday cage so, you are perfectly safe
inside. But when you try to come out, you provides a way to current to pass out from
you.
Q#10: Explain why, a glass rod can be charged by rubbing when held by hand but
an iron rod cannot be charged by rubbing, if held by hand?
Ans: The work function of iron is very high so, it doesnt take electrons easily. Also iron
is a good conductor so, it cant take charge because when you apply charge the
electrons in iron flow away.
But the glass is not conductor and it stores a charge for few moments.
1. Why is it not good to seek shelter under a tree during a lightning storm?
A. it is not a good idea to seek shelter under a tree during a lightning storm. Because
when the charge clouds pass over a tree, then an opposite charge is induced on the
tree due to electrostatic induction. The force of attraction is established between the
tree and clouds due to which there is a greater possibility for the lightning discharge to
take place.
2. Define the term volt?
A. Volt is the SI unit of potential difference. It can be defined as if 1 joule work is done
on a charge body of 1 coulomb to move it from one point to another against the electric
field. Mathematically
1 Volt = 1 Joule / 1 Coulomb
3. Why electric charge is produced on bodies by friction?
A. Electric charge is produced on bodies by friction. Because when two bodies rubbed
with each other, transferred of charges occur. As a result, charges are produced on the
objects. For example
When a glass rod is rubbed with silk. The glass rod loses electrons and the silk gain
these electrons. The glass becomes positively charged, while the silk becomes
negatively charged.
4. A chain is hanging from the rear side of petrol supply tanker. What is its
purpose?
A. When the petrol supply tanker moves on a road, charge may be induced on its body
due to friction. To avoid these charges a chain is made to hang from the rear side of
petrol supply tanker. This chain works like earth wire and supply these charges to the
earth.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Thermodynamic Analysis of Internal Combustion EnginesDocument26 paginiThermodynamic Analysis of Internal Combustion EnginesKatu2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Abc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesDe la EverandAbc of Capacitors: Basic PrinciplesWürth ElektronikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy 13 NotesDocument5 paginiPhy 13 Notesapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- AP Physics B Notes - Electrostatics EssentialsDocument8 paginiAP Physics B Notes - Electrostatics EssentialsAndy HeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialDocument12 paginiElectric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialMarquee Mae EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Centrifugal PumpDocument36 pagini3 Centrifugal PumpReza Dhony WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy 12 NotesDocument19 paginiPhy 12 Notesapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Psychoacoustic Investigation of Spherical Microphone Array AuralizationDocument109 paginiPsychoacoustic Investigation of Spherical Microphone Array AuralizationGyan Vardhan Singh DikhitÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTROSTATICS FORMULAE AND CONCEPTSDocument24 paginiELECTROSTATICS FORMULAE AND CONCEPTSSankar KumarasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- STEEL STAIR DESIGNDocument4 paginiSTEEL STAIR DESIGNNikki RobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analytic Solution for Torque Between Magnetic DipolesDocument5 paginiAnalytic Solution for Torque Between Magnetic DipolesLee Kar Huo22% (9)
- Table of ContentsDocument120 paginiTable of ContentsBonface Kenani100% (3)
- NPSH CalculationDocument19 paginiNPSH CalculationPatilea Daniela100% (1)
- Assertion and Reasoning Questions Term 1Document37 paginiAssertion and Reasoning Questions Term 1SABARI SRINIVAS AÎncă nu există evaluări
- A and R ElectrostaticsDocument6 paginiA and R ElectrostaticsAkhil SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Chapter 12 & 13 QuestionsDocument51 paginiPhysics Chapter 12 & 13 Questionsqureshi0% (4)
- Learn CBSE Learn CBSEDocument25 paginiLearn CBSE Learn CBSEShivendra KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics With Harshit Srivastava11Document2 paginiPhysics With Harshit Srivastava11adarshtiw787Încă nu există evaluări
- Electric Fields & CapacitorsDocument19 paginiElectric Fields & CapacitorsMohsen SaidiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics XII CH 2 Physics Assertion Reasoning Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceDocument10 paginiPhysics XII CH 2 Physics Assertion Reasoning Electrostatic Potential and CapacitanceNjan KL16么PorottaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitors, Capacitance, and DielectricsDocument57 paginiCapacitors, Capacitance, and DielectricseemylÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions Having One Mark EachDocument11 paginiQuestions Having One Mark EachAshok PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assertion Reasoning QuestionsDocument14 paginiAssertion Reasoning QuestionsPrabhat KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric FieldDocument56 paginiElectric FieldAdivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatic PotentialDocument20 paginiElectrostatic PotentialhiranmayeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Xii 1 ElectrostaticsDocument3 paginiXii 1 Electrostaticsvihaangite18Încă nu există evaluări
- XII Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju HssliveDocument16 paginiXII Physics Chapter 1 - Electric Charges Fields Saju HssliveKanishk Yadav100% (1)
- Static ElectricityDocument6 paginiStatic ElectricityFarjana KabirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics: Ssertion Reason QuestionsDocument3 paginiPhysics: Ssertion Reason QuestionsWilliam MukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoulombsDocument47 paginiCoulombsTrishia LimpinÎncă nu există evaluări
- NotesDocument16 paginiNotesMELODY KINGSÎncă nu există evaluări
- L5 Electricity and MagnetismDocument37 paginiL5 Electricity and Magnetismbussanmugwati2004Încă nu există evaluări
- Physics XII ASS QuestDocument56 paginiPhysics XII ASS Questkanchandosad87Încă nu există evaluări
- LAS BE 10 MELC 1-2 Week 1-2-StudentDocument10 paginiLAS BE 10 MELC 1-2 Week 1-2-StudentKrissa Leigh TrinidadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitance & CapacitorsDocument65 paginiCapacitance & CapacitorsSidhartha ShankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatics: Two Kinds of ChargesDocument37 paginiElectrostatics: Two Kinds of ChargesShajjadul HoqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy Board LatestDocument52 paginiPhy Board LatestChithambaramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phys502 Lect 5Document8 paginiPhys502 Lect 5MaissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Action: C Is The Capacitance in Farads (F) Q Is The Charge in Coulombs (C) V Is The P.D. Between The PlatesDocument10 paginiAction: C Is The Capacitance in Farads (F) Q Is The Charge in Coulombs (C) V Is The P.D. Between The Platesyeeluv99Încă nu există evaluări
- 12 Class Physics 1-Chapter Sample Paper PDFDocument9 pagini12 Class Physics 1-Chapter Sample Paper PDFharshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Imp 2019 Sample PapersDocument9 paginiPhysics Imp 2019 Sample PapersharshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12 Class Physics 1-Chapter Sample Paper PDFDocument9 pagini12 Class Physics 1-Chapter Sample Paper PDFharshÎncă nu există evaluări
- 27 Electrostatics IIDocument62 pagini27 Electrostatics IIASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONSÎncă nu există evaluări
- ES191 Electrical and Electronic CircuitsDocument43 paginiES191 Electrical and Electronic CircuitsAbisan ArulananthamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Support Material Class Xii Physics Bhuj Cluster 2020Document67 paginiStudent Support Material Class Xii Physics Bhuj Cluster 2020Debasish GogoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 ElectrostaticsDocument8 paginiLecture 2 ElectrostaticsسیدمحمدفيضانÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTRIC FIELD LINESDocument10 paginiELECTRIC FIELD LINESJohn JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy 12th GyangangaDocument4 paginiPhy 12th GyangangabhartiyaanujÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cbse Class Xii PhysicsDocument30 paginiCbse Class Xii PhysicskumarnpccÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitors: 1) Capacitor and CapacitanceDocument15 paginiCapacitors: 1) Capacitor and CapacitanceAditya NandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 (Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance) UnsolvedDocument8 paginiChapter 2 (Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance) UnsolvedMahendra ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Electric Charge & FieldDocument6 pagini1 - Electric Charge & FieldSamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 PhyDocument58 paginiChapter 2 PhysanjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hiten Parmar: Physics byDocument5 paginiHiten Parmar: Physics byKailas ArunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hiten Parmar: Physics byDocument5 paginiHiten Parmar: Physics byMia JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding ElectrostaticsDocument7 paginiUnderstanding ElectrostaticsMsglowIlustriÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAPACITANCE With Checkpoint 1-18Document40 paginiCAPACITANCE With Checkpoint 1-18chirayuaggarwal2006Încă nu există evaluări
- ELECTROSTATICS KEY CONCEPTSDocument15 paginiELECTROSTATICS KEY CONCEPTSNARRAYANAN ARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy - II PU Impt 1 Mark Qs and AnsDocument12 paginiPhy - II PU Impt 1 Mark Qs and Ansjyoti kudagiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 Electricity IDocument9 paginiUnit 7 Electricity Itwy113Încă nu există evaluări
- Important 1 Mark Questions and AnswersDocument13 paginiImportant 1 Mark Questions and AnswersVishwaradhya KarastalmathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatics: Electric Charges and FieldsDocument21 paginiElectrostatics: Electric Charges and FieldsSONY SAB HDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitance (Lec-1 To 3) XIIDocument13 paginiCapacitance (Lec-1 To 3) XIISushmit GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatic 1Document71 paginiElectrostatic 1emmanuel hauleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Document15 paginiReduced Syllabus Questions (Physics)Saher SaghirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Versatile Notes PHYSICS XII Chapter 01Document36 paginiVersatile Notes PHYSICS XII Chapter 01ShaheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Phy 18 NotesDocument10 paginiPhy 18 Notesapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 15 NotesDocument8 paginiPhy 15 Notesapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 17 NotesDocument12 paginiPhy 17 Notesapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 16 NotesDocument16 paginiPhy 16 Notesapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 14 NotesDocument8 paginiPhy 14 Notesapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 9 30Document1 paginăPhy 9 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 2 30Document1 paginăPhy 2 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 7 30Document1 paginăPhy 7 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 10 NotesDocument9 paginiPhy 10 Notesapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 2 30Document1 paginăPhy 2 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 6 30Document1 paginăPhy 6 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 8 30Document1 paginăPhy 8 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 5 30Document1 paginăPhy 5 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 2 30Document1 paginăPhy 2 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 4 30Document1 paginăPhy 4 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 2 30Document1 paginăPhy 2 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- U15 QuestionsDocument2 paginiU15 Questionsapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 16 35Document1 paginăPhy 16 35api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 15 35Document1 paginăPhy 15 35api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 ModifiedDocument6 paginiChapter 12 Modifiedapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 2 30Document1 paginăPhy 2 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 14 35Document1 paginăPhy 14 35api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 2 30Document1 paginăPhy 2 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 2 30Document1 paginăPhy 2 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy 1 30Document1 paginăPhy 1 30api-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 11 ModifiedDocument5 paginiChapter 11 Modifiedapi-248642018100% (2)
- Chapter 14 ModifiedDocument8 paginiChapter 14 Modifiedapi-248642018Încă nu există evaluări
- Shell and Tube Heat ExchangersDocument13 paginiShell and Tube Heat ExchangersLieu Dinh PhungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 107 ConcreteDocument44 pagini107 Concretenoadspls2029Încă nu există evaluări
- Antenna Theory - Beam Width - TutorialspointDocument4 paginiAntenna Theory - Beam Width - TutorialspointSukhada Deshpande.Încă nu există evaluări
- ClassNotes 94 853 Production of Propagation of WavesDocument6 paginiClassNotes 94 853 Production of Propagation of WavesPatrick Chukwunonso A.Încă nu există evaluări
- Nlewis65,+105 108 Laboratory Edwards 44 No 2 SPRING 2010 CEEDocument4 paginiNlewis65,+105 108 Laboratory Edwards 44 No 2 SPRING 2010 CEEMariel RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ballistic CoefficientDocument7 paginiThe Ballistic Coefficientjvs57Încă nu există evaluări
- De-Broglie Hypothesis - Grade 12 Physics Notes - NEB NotesDocument2 paginiDe-Broglie Hypothesis - Grade 12 Physics Notes - NEB NotesDahanyakage WickramathungaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow liquefaction simulation using combined effective stress and total stress modelsDocument8 paginiFlow liquefaction simulation using combined effective stress and total stress modelsClaudia Victoria Vallejos CatalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moment of Inertia of Flywheel (Theory) - Mechanics Virtual Lab (Pilot) - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabDocument4 paginiMoment of Inertia of Flywheel (Theory) - Mechanics Virtual Lab (Pilot) - Physical Sciences - Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham Virtual LabkulvindermimitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Mechanical Engineering: Credit & Contact Hours: Course Code: Course Level: Prerequisite(s)Document2 paginiBasic Mechanical Engineering: Credit & Contact Hours: Course Code: Course Level: Prerequisite(s)Ahad MunawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel IAL Mechanics MDocument28 paginiEdexcel IAL Mechanics MDima MurjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aeroelasticity20202021 Ex9Document2 paginiAeroelasticity20202021 Ex9Arianna PascaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refractive Index of TissuesDocument140 paginiRefractive Index of TissuesNag28raj100% (1)
- งานและพลังงาน StudentDocument28 paginiงานและพลังงาน StudentSumitta KonglaithongÎncă nu există evaluări
- CON4335 Structural Analysis B PastPaper 2015Document6 paginiCON4335 Structural Analysis B PastPaper 2015Trevor LingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Lateral Load Resisting System FDocument33 pagini3 Lateral Load Resisting System FUd BsecÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018tut6 PDFDocument1 pagină2018tut6 PDFsudheerÎncă nu există evaluări
- HKDSE Physics Book 2 Ch.1 Question BankDocument14 paginiHKDSE Physics Book 2 Ch.1 Question Bankorlando LiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Throttling Characteristics of Multi-Hole Orifice in Multi Stage AssemblyDocument13 paginiThrottling Characteristics of Multi-Hole Orifice in Multi Stage AssemblyGuglielmoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ives Keir Bassey Hamad Vol 10 Iss 1Document10 paginiIves Keir Bassey Hamad Vol 10 Iss 1RomizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optoelectronics Polarization Optics ChapterDocument20 paginiOptoelectronics Polarization Optics ChapterEngAya R ElmetwallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- IJCE v12n4p281 enDocument11 paginiIJCE v12n4p281 entaw1021966mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Explained in 40 CharactersDocument21 paginiThermodynamics Explained in 40 CharactersAlexander Gordon InesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canned Goods Math Problem SolvedDocument6 paginiCanned Goods Math Problem SolvedbreimanangÎncă nu există evaluări