Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Finite Element Methods
Încărcat de
Divya TadepalliDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Finite Element Methods
Încărcat de
Divya TadepalliDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
www.jntuworld.
com
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Code No: D2001
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
www.android.jntuworld.com
R09
Q6
www.jwjobs.net
Q6
Q6
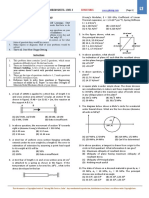
JAWAHARLAL NEHRU TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY HYDERABAD
M.Tech II - SEMESTER EXAMINATIONS, APRIL/MAY-2013
FINITE ELEMENT METHODS
(STRUCTURAL ENGINEERING)
Time: 3hours
Max.Marks:60
Answer any five questions
All questions carry equal marks
Q6
Q6
Q6
1. Consider the
following stateQ6
of strain:
Q6
Q6
---
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
D
L
are constants. Determine whether the compatibility equations are
where
satisfied.
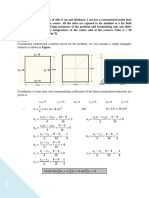
2. Determine the nodal displacements and element stresses by finite element formulation for
the following figure. Use P = 300 kN, A1 = 0.5 m2, A2 = 1 m2; E = 200 GPa.
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
T
N
W
U
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
R
O
Q6
3. Estimate the displacement vector, stresses and reactions for the truss structure as shown
below.
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
A = 250 mm2; E = 200 GPa
Q6
4. A concentrated load P = 50 kN is applied at the center of a fixed beam of length 3 m,
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
depth 200 mm and width 120 mm. Calculate the deflection and slope at the mid point.
Assume E = 2 105 N/mm2.
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
www.jntuworld.com
Q6
Q6
Q6
Contd.2
Q6
Q6
Q6
::2::
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
5. Calculate displacements and stress in a triangular membrane element, fixed along one
www.jntuworld.com
Q6
Q6
Q6
www.android.jntuworld.com
Q6
Q6
Q6
www.jwjobs.net
edge and subjected to concentrated load at its free end. Assume E = 70,000 MPa, t = 10
mm and = 0.3.
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
6. Evaluate the partial derivatives
and
shown in the figure below at the point
of the quadrilateral element
D
L
assuming that the scalar field
variable is approximated by a quadratic interpolation model.
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
R
O
W
U
T
N
7. Consider the differential equation
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
wherea, b, c, and f are known functions of position x. Develop the weak form and the
finite element model of the equation.
8. Determine deflection and stresses at the center of a simply supported rectangular plate as
shown in the figure below subjected to a uniformly distributed load. Use the following
numerical data: 10 5 plate, h = 0.2, E = 106, = 0.3, and q = 10. Take advantage of
symmetry and model one-fourth of the plate using only one element.
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
****
*****
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
Q6
www.jntuworld.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Case ColorscopeDocument7 paginiCase ColorscopeRatin MathurÎncă nu există evaluări
- TB 60 Repair Parts PDFDocument282 paginiTB 60 Repair Parts PDFvatasa100% (2)
- Study Notes - Google Project Management Professional CertificateDocument4 paginiStudy Notes - Google Project Management Professional CertificateSWAPNIL100% (1)
- Numerical Questions - Airbreathing EngineDocument2 paginiNumerical Questions - Airbreathing EngineDhiraj NayakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution CH4Document39 paginiSolution CH4roundstorm1100% (1)
- (Problem Books in Mathematics) Antonio Caminha Muniz Neto - An Excursion Through Elementary Mathematics, Volume III - Discrete Mathematics and Polynomial Algebra (2018, Springer)Document647 pagini(Problem Books in Mathematics) Antonio Caminha Muniz Neto - An Excursion Through Elementary Mathematics, Volume III - Discrete Mathematics and Polynomial Algebra (2018, Springer)Anonymous iH6noeaX7100% (2)
- The New Art of Photographing Nature - ExcerptDocument15 paginiThe New Art of Photographing Nature - ExcerptCrown Publishing GroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW1Document3 paginiHW1Naveen RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Buckling ExamplesDocument5 paginiBuckling ExamplesSrivatsan SampathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Chapter 6Document26 paginiSolution Chapter 6Cara WhiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Distribution Over An AirfoilDocument10 paginiPressure Distribution Over An AirfoilAkash RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Notes Aerospace PropulsionDocument104 paginiLecture Notes Aerospace PropulsionJuan GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PR Closed System 2Document2 paginiPR Closed System 2Mareta DanarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerospace Flywheel DevelopmentDocument12 paginiAerospace Flywheel DevelopmentSunil Pal100% (1)
- RCH Som 01 IntroductionDocument51 paginiRCH Som 01 IntroductionSatish DhanyamrajuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structures - Problem Sheet Level 2Document5 paginiStructures - Problem Sheet Level 2YogendraKumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Known: Comments:: Bending Impact-Effect of Compound SpringsDocument2 paginiKnown: Comments:: Bending Impact-Effect of Compound SpringsGermán EdilbertoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Andrew Pytel, Ferdinand L. Singer - Strength of Materials (1987, Harpercollins College Div) - Libgen - LiDocument606 paginiAndrew Pytel, Ferdinand L. Singer - Strength of Materials (1987, Harpercollins College Div) - Libgen - LiMoshi ULÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr312102 Aircraft PerformanceDocument8 paginiRr312102 Aircraft PerformanceSrinivasa Rao GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aeroelasticity Homework ProblemsDocument1 paginăAeroelasticity Homework Problemslamborghini1991Încă nu există evaluări
- Stress TransformationDocument5 paginiStress TransformationCh TalhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slope Deflection and Moment Distribution MethodDocument33 paginiSlope Deflection and Moment Distribution MethodBari FayzulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document30 paginiChapter 3Victoria JungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expansion Wave Prandti - MEDDocument10 paginiExpansion Wave Prandti - MEDMohammed SalmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuel Technology - Tutorial QuestionsDocument5 paginiFuel Technology - Tutorial QuestionsHisyamAl-MuhammadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics 8th Edition White Solutions ManualDocument25 paginiFluid Mechanics 8th Edition White Solutions ManualHannahMendozajtykÎncă nu există evaluări
- We Have Solutions For Your Book!: See This Answer See This AnswerDocument1 paginăWe Have Solutions For Your Book!: See This Answer See This AnswerNoreen Guiyab TannaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamics ProblemsDocument8 paginiAerodynamics ProblemsPramod GowdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AE2030 - Fatigue and FractureDocument1 paginăAE2030 - Fatigue and FractureArun Raja K K100% (1)
- PIEAS (BS Mechanical CurriculumDocument25 paginiPIEAS (BS Mechanical CurriculumPIEASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamics Test GATE2017Document5 paginiAerodynamics Test GATE2017harishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 Previous Year QuestionsDocument9 paginiModule 2 Previous Year QuestionsnikhilasoknÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Examples Heat TransferDocument9 paginiSolved Examples Heat TransferAshutosh AcharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ae 430 3 PDFDocument14 paginiAe 430 3 PDFcrimelife6100% (1)
- Strength of MaterialsDocument101 paginiStrength of MaterialsLucksy Marcus PalloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Propulsion - II 2 Marks by Nambi RajanDocument12 paginiPropulsion - II 2 Marks by Nambi RajanNambi RajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEM QuizDocument3 paginiFEM Quizmkdev2004Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural Materials: Unit 3Document53 paginiStructural Materials: Unit 3Jayashree MisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statics Chpt.3Document105 paginiStatics Chpt.3safeer_siddickyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tensile Testing of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous AlloyDocument7 paginiTensile Testing of Ferrous and Non-Ferrous Alloyrama100% (1)
- Rizzoni Problemas Capítulo 7Document8 paginiRizzoni Problemas Capítulo 7nicole ortizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experiment 1Document5 paginiExperiment 1Timmy TrinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Force Vibration With Harmonic Excitation: Unit - IvDocument24 paginiForce Vibration With Harmonic Excitation: Unit - IvLathish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Matlab Report1Document2 paginiMatlab Report1Samy MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- A: For The Same HDocument5 paginiA: For The Same HBalaji Himakar100% (1)
- Elastic Pressure TransducersDocument7 paginiElastic Pressure TransducersKrypton HalideÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME302 Assignment Test-1 2019-20Document2 paginiME302 Assignment Test-1 2019-20choudary garuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech4620 Group 12 Report PDFDocument12 paginiMech4620 Group 12 Report PDFAaron Hoytash100% (1)
- University of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Document4 paginiUniversity of Bahrain Department of Mechanical Engineering MENG 263 TUTORIAL # 5 (Chapter 5)Vivin MathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eeeb113 Circuit Analysis 1: Chapter 6: Capacitors and Inductors Sharifah Azma Syed MustaffaDocument25 paginiEeeb113 Circuit Analysis 1: Chapter 6: Capacitors and Inductors Sharifah Azma Syed MustaffaSharifah Azma100% (1)
- m01 02 Energy Methods in Structural Analysis Principle of Superposition Strain EnergyDocument21 paginim01 02 Energy Methods in Structural Analysis Principle of Superposition Strain EnergyhorressÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Mechanics - KL - Ramachandran SDocument744 paginiEngineering Mechanics - KL - Ramachandran SFe Fernandez100% (1)
- Dynamics KinematicsDocument32 paginiDynamics Kinematicsวอ แวณÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Experimental Study On Properties of High-Performance Concrete Using Recycled AggregatesDocument5 paginiAn Experimental Study On Properties of High-Performance Concrete Using Recycled Aggregatesnikkimarie cabahugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics in One Complex Variable. (AM-160): (AM-160) - Third EditionDe la EverandDynamics in One Complex Variable. (AM-160): (AM-160) - Third EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of Elasticity and Plasticity (For Structural Engineering)Document1 paginăTheory of Elasticity and Plasticity (For Structural Engineering)prasaad08100% (1)
- AssignmentDocument2 paginiAssignmentD R KumawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mtech. Finite Element AnalysisDocument11 paginiMtech. Finite Element Analysissimalaravi100% (2)
- Analog Ic DesignDocument2 paginiAnalog Ic DesignIbmWasuserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of PlasticityDocument10 paginiTheory of Plasticitybabu1434100% (1)
- FEM 7th Sem NIT Raipur QPaperDocument22 paginiFEM 7th Sem NIT Raipur QPaperShashi Bhushan PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Me 2353 - Finite Element AnalysisDocument4 paginiMe 2353 - Finite Element AnalysiscprabhakaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- P.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya - 571 401Document2 paginiP.E.S. College of Engineering, Mandya - 571 401coolmagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stabilization of An Inverted Pendulum Via Fuzzy Explicit Predictive ControlDocument5 paginiStabilization of An Inverted Pendulum Via Fuzzy Explicit Predictive ControlVirgili0Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-3 Construction Equipment ManagementDocument92 paginiChapter-3 Construction Equipment ManagementDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asian Pacific Heritage MonthDocument12 paginiAsian Pacific Heritage MonthMG CaguladaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 Project ManagementDocument15 pagini9 Project ManagementDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 9 Selection, Planning and Matching of Construction EquipmentDocument9 paginiUnit 9 Selection, Planning and Matching of Construction EquipmentDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4-2 CIVIL R13 SyllabusDocument6 pagini4-2 CIVIL R13 SyllabusDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S1877042813045035 MainDocument10 pagini1 s2.0 S1877042813045035 MainDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estimation NotesDocument32 paginiEstimation NotesSrinivas P50% (2)
- AEE Environmental Engineering NOTESDocument10 paginiAEE Environmental Engineering NOTESVaradharajan SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specific Gravity and Absorption of Coarse AggregateDocument2 paginiSpecific Gravity and Absorption of Coarse AggregateDivya Tadepalli100% (1)
- Cadd VivaDocument5 paginiCadd VivaDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Watershed ManagementDocument46 paginiWatershed ManagementDivya Tadepalli100% (1)
- 1.2 Advantages Types of Pre StressingDocument11 pagini1.2 Advantages Types of Pre StressingcatiexpertÎncă nu există evaluări
- 73 2013 PDFDocument8 pagini73 2013 PDFSoundar PachiappanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIVIL 8.environmental Engineering PDFDocument249 paginiCIVIL 8.environmental Engineering PDFDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Watershed ManagementDocument46 paginiWatershed ManagementDivya Tadepalli100% (1)
- Replacement of Coarse Aggregate by Scrap Tyre RubberDocument6 paginiReplacement of Coarse Aggregate by Scrap Tyre RubberDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experimental Study On Properties of Cement With RHA As Replacement in ConcreteDocument6 paginiExperimental Study On Properties of Cement With RHA As Replacement in ConcreteDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enviromental Lab ManualDocument16 paginiEnviromental Lab ManualDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Replacement of Coarse Aggregate by Scrap Tyre RubberDocument6 paginiReplacement of Coarse Aggregate by Scrap Tyre RubberDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Use of Rice HUsk Ash in Concrete - M.B.G Sameer KumarDocument94 paginiA Study On Use of Rice HUsk Ash in Concrete - M.B.G Sameer KumarNarayan Singhania100% (21)
- Enviromental Lab ManualDocument16 paginiEnviromental Lab ManualDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soils ConsolidationDocument41 paginiSoils ConsolidationDavid CastañoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project On Partial Replacement of Cement With Marble PowderDocument11 paginiProject On Partial Replacement of Cement With Marble PowderSaurabh Pandey100% (2)
- Enviromental Lab ManualDocument16 paginiEnviromental Lab ManualDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural DynamicsDocument1 paginăStructural DynamicsDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Theodolite PDFDocument9 paginiNotes Theodolite PDFAshok_sth71% (7)
- Surveying Previous Question PaperDocument2 paginiSurveying Previous Question PaperDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- CTDocument8 paginiCTDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Mix Design Is MethodDocument29 paginiConcrete Mix Design Is MethodChirag TanavalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Foundation EngineeringDocument3 paginiAdvanced Foundation EngineeringDivya TadepalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sage TutorialDocument115 paginiSage TutorialChhakuli GiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kiraan Supply Mesin AutomotifDocument6 paginiKiraan Supply Mesin Automotifjamali sadatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethical Hacking IdDocument24 paginiEthical Hacking IdSilvester Dian Handy PermanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ty Baf TaxationDocument4 paginiTy Baf TaxationAkki GalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Previews 1633186 PreDocument11 paginiPreviews 1633186 PreDavid MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Initial Police Report: Calamba City Police Station Brgy Real, Calamba City, Laguna E-Mail: 545-1694/545-6789 Loc 8071Document1 paginăInitial Police Report: Calamba City Police Station Brgy Real, Calamba City, Laguna E-Mail: 545-1694/545-6789 Loc 8071Jurish BunggoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bharti Airtel Strategy FinalDocument39 paginiBharti Airtel Strategy FinalniksforloveuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6int 2008 Dec ADocument6 pagini6int 2008 Dec ACharles_Leong_3417Încă nu există evaluări
- Physiol Toric Calculator: With Abulafia-Koch Regression FormulaDocument1 paginăPhysiol Toric Calculator: With Abulafia-Koch Regression FormuladeliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Education Deteriorating - EditedDocument3 paginiPhilippine Education Deteriorating - EditedRukimi Yamato100% (1)
- Experiment 2 HORSEPOWER EFFICIENCY GEAR RATIO AND SPEED RATIODocument10 paginiExperiment 2 HORSEPOWER EFFICIENCY GEAR RATIO AND SPEED RATIOJake Polo SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 7 NSTP 1Document55 paginiModule 7 NSTP 1PanJan BalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Level of Organisation of Protein StructureDocument18 paginiLevel of Organisation of Protein Structureyinghui94Încă nu există evaluări
- WSD M1a283 B50Document9 paginiWSD M1a283 B50'Lampa'Încă nu există evaluări
- JMC MSDS Puraspec 1173 (GB)Document10 paginiJMC MSDS Puraspec 1173 (GB)Benny Samsul B.Încă nu există evaluări
- Acute Suppurative Otitis MediaDocument41 paginiAcute Suppurative Otitis Mediarani suwadjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pepsico SDM ProjectDocument6 paginiPepsico SDM ProjectJemini GanatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forensic IR-UV-ALS Directional Reflected Photography Light Source Lab Equipment OR-GZP1000Document3 paginiForensic IR-UV-ALS Directional Reflected Photography Light Source Lab Equipment OR-GZP1000Zhou JoyceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics 11 02566Document13 paginiElectronics 11 02566卓七越Încă nu există evaluări
- Driver Drowsiness Detection System Using Raspberry PiDocument7 paginiDriver Drowsiness Detection System Using Raspberry PiIJRASETPublicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 19 Code Standards and ReviewDocument27 paginiLecture 19 Code Standards and ReviewAdhil Ashik vÎncă nu există evaluări
- Army Aviation Digest - Apr 1971Document68 paginiArmy Aviation Digest - Apr 1971Aviation/Space History LibraryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Communication at Mahabharatha WarDocument19 paginiRole of Communication at Mahabharatha WarAmit Kalita50% (2)
- MegaMacho Drums BT READ MEDocument14 paginiMegaMacho Drums BT READ MEMirkoSashaGoggoÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The PCB Shelf Life Extending The Life of PCBsDocument9 paginiWhat Is The PCB Shelf Life Extending The Life of PCBsjackÎncă nu există evaluări