Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan
Încărcat de
Cyrus De AsisDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan
Încărcat de
Cyrus De AsisDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
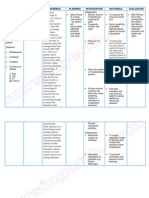
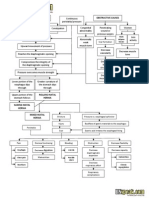
Nursing Diagnosis: Fluid
Volume Deficit
Possible Etiologies:
(Related to)
Goals/ objectives:
Nursing Interventions
Nursing Actions
Uterine Atony
Lacerations
Retained placental
fragments
Disseminated
intravascular
coagulation
Subinvolution of
uterus
Defining characteristics:
(Evidenced by)
Blood loss more
than 500 ml
Heavy lochia flow
Increased
temperature due to
uterine infection
predisposing to
uterine atony
Elevation of pulse
rate indicating
hypovolemia
Sudden drop in
blood pressure
implying
hemorrhage
Pain in the perineal
sutures
Decreased uterine
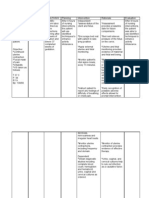
Short term goal:
Rationale
Client will
maintain fluid
volume at a
functional level as
evidenced by
individually
adequate
haemoglobin,
hematocrit
laboratory results,
stable vital signs,
adequate urine
output, good
uterine
contractility, good
skin turgor and
capillary refill
after one week.
Long term goal:
Client will demonstrate
behaviours
Assess uterine
contraction and lochia
flow every 2 hours.
Assess vital signs and
note for peripheral
pulses.
Note clients
physiologic response
to blood loss.
Keep accurate record
of subtotals of
solutions/ blood
products during
replacement therapy.
Maintain bed rest and
schedule activities to
provide undisturbed
rest periods.
Keep fluids within
reach of client.
Teach client perineal
self- care.
Encourage client to
do Kegels exercises
every 4 hours.
Administer fluids/
volume expanders as
indicated.
Replace blood
products as ordered
by the physician.
Administer
That is to note how
much blood loss the
client is
experiencing and to
prompt for
immediate
intervention.
Changes in BP and
pulse may be used
for rough estimate
of blood loss.
Postural
hypotension reflects
a decrease in
circulating volume.
Symptomatology
may be useful in
gauging severity of
bleeding episode.
Potential exists for
over transfusion of
fluids, especially
when volume
expanders are given
prior to blood
transfusion.
Activity may
predispose to further
bleeding.
To encourage fluid
intake
To prevent
development of
perineal infections.
Evaluation
Outcome Criteria:
Clients pulse is
between 80 to 100
beats per min and
blood pressure is
110/60 mmHg,
lochia slows to
moderate amount of
flow with no large
clots, uterus is firm
and haemoglobin
level is above
11g/L.
Client verbalizes
understanding of the
causative factors
and purpose of
interventions and
medication;
participates in
procedures without
hesitations;
attentive and
monitors own vital
signs upon
assessment; and
follows restrictions
applied.
contractility
Drop in the
haemoglobin and
hematocrit
laboratory results
Decreased urine
output
Pallor, easy
fatigability, anxiety
methylergonovine as
prescribed by the
physician.
Monitor laboratory
studies (haemoglobin
and hematocrit,
creatinine/ BUN)
Assist in the
preparation for
surgery specifically
hysterectomy.
It helps improve the
blood supply in the
perineal area.
Fluid replacement
with isotonic
crystalloid solutions
depends on the
degree of
hypovolemia and
duration of bleeding.
Fresh whole blood,
platelets and fresh
frozen plasma are
usually given to
patients depending
on severity of blood
loss.
This drug helps in
the contraction of
the uterus.
Helps in monitoring
the effectiveness of
the therapy;
malfunction in the
kidneys may
indicate major
bleeding episodes.
It is the most
effective in halting
bleeding especially
an extremely atonic
uterus.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Fluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhageDocument3 paginiFluid Volume Deficit Secondary To Post Partum HemorrhagePatricia Franco100% (1)
- Postpartum Hemorrhage Nursing CareDocument3 paginiPostpartum Hemorrhage Nursing CareClaire Canapi BattadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Postpartum Hemorrhage Concept MapDocument4 paginiPostpartum Hemorrhage Concept MapGCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageLei Ortega95% (21)
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum HemorrhageDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Postpartum Hemorrhagederic100% (60)
- NCP PPHDocument2 paginiNCP PPHmikee-berredo-9975Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Postpartum Care PlanDocument7 paginiNursing Postpartum Care PlanBecky Kipling100% (9)
- Nursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Postpartum HemorrhageDianne Mae100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan - Delivery RoomDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan - Delivery RoomMarivic Misola100% (5)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument7 paginiNursing Care Planrockerespi1283Încă nu există evaluări
- Uterine Atony - NCPDocument17 paginiUterine Atony - NCPMonica BorjaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pain - Post Partum MotherDocument2 paginiPain - Post Partum Motherulrikov91% (11)
- Precipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryDocument7 paginiPrecipitous Labor/Delivery or Unplanned/Out-of-Hospital DeliveryLei Ortega100% (1)
- Acute Pain, Post Partum CareDocument1 paginăAcute Pain, Post Partum Carekbernil83% (18)
- After 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital SignsDocument3 paginiAfter 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital Signsroma_elonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre EclampsiaDocument3 paginiPre EclampsiaJon Sayson100% (1)
- Dysfunctional Labor DystociaDocument8 paginiDysfunctional Labor Dystocianursereview100% (4)
- CA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument13 paginiCA - Amniotic Fluid EmbolismRodelen Maraño100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaDocument13 paginiNursing Care Plans (NCP) of Abruptio PlacentaKath76% (21)
- PTPRETERMDocument2 paginiPTPRETERMJoan Castillo100% (6)
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocument2 paginiAbruptio Placenta NCPNichole Audrey Saavedra100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Postpartum DepressionDocument1 paginăNursing Care Plan Postpartum DepressionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- Painful Abdominal ContractionsDocument4 paginiPainful Abdominal ContractionsKarizza Mae Celis100% (2)
- NCP - Labor PainDocument1 paginăNCP - Labor Painakire12100% (4)
- NCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseDocument9 paginiNCP: Labor Stage 1 Latent PhaseJavieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan of Labor PainDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan of Labor PainKenneth Cole80% (61)
- NCP - Post PartumDocument10 paginiNCP - Post PartumSa Dei91% (22)
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeWann WannÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Post PartumDocument2 paginiNCP Post PartumsteffiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalDocument19 paginiAbruptio Placenta NCP 2 FinalTin100% (1)
- Fluid Volume Excess Nursing Care PlanDocument1 paginăFluid Volume Excess Nursing Care PlanMonica Cruz Dalida74% (23)
- NCP Preeclampsia TissueperfusionDocument2 paginiNCP Preeclampsia TissueperfusionMichael Angelo Seña100% (2)
- NCP (Post-Partum Pain)Document1 paginăNCP (Post-Partum Pain)allure*2083% (6)
- NCP For EclampsiaDocument6 paginiNCP For EclampsiaXtine Soliman Zamora100% (3)
- Nursing Care for Preeclampsia: Monitoring, Education, and Pain ManagementDocument2 paginiNursing Care for Preeclampsia: Monitoring, Education, and Pain ManagementShamoos Alkhusaibi80% (5)
- Final NCP For PostpartumDocument8 paginiFinal NCP For PostpartumJam Ali100% (1)
- NCP For Delivery RoomDocument4 paginiNCP For Delivery RoomGiselle EstoquiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labor Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiLabor Nursing Care PlanGiselle Eclarino100% (9)
- Hemorrhage NCPDocument4 paginiHemorrhage NCPElishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan For Acute Gastrointestinal HemorrhageCyrus De Asis92% (25)
- Eclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionDocument2 paginiEclampsia Nursing Care Plan - Altered Tissue PerfusionCyrus De Asis84% (32)
- Waiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHDocument3 paginiWaiters PATIENT CARE PLAN 2020 For PPHmp1757Încă nu există evaluări
- BOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageDocument4 paginiBOX 17.4 NCP Postpartum HemorrhageJam AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEDocument2 paginiNCP 3 DEFICIT IN FLUID VOLUMEGenEsis CarandangÎncă nu există evaluări
- HemodialysisDocument4 paginiHemodialysisJon Adam Bermudez SamatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP AnemiaDocument1 paginăNCP Anemiamashup100% (3)
- Institute of Health SciencesDocument9 paginiInstitute of Health SciencesFlorygene Kris DisagonÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP LatestDocument6 paginiNCP LatestThirdy AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- IV Fluid TherapyDocument28 paginiIV Fluid TherapyJacinta MaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume DeficitDocument1 paginăDengue Fever Nursing Care Plan-High Risk For Fluid Volume Deficitemman_abz100% (5)
- NCP PancreatitisDocument2 paginiNCP PancreatitisJeanelle GenerosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 paginiAssessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRoMarie AbainzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument9 paginiNursing Diagnosis Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationJezza Sanchez-Rellita VillariasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amniotic Fluid EmbolismDocument51 paginiAmniotic Fluid EmbolismDenyse Mayer Atutubo100% (2)
- NCP - Deficient Fluid VolumeDocument2 paginiNCP - Deficient Fluid VolumerobbychuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Volume ExcessDocument4 paginiFluid Volume ExcessChristine Quirona100% (1)
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument2 paginiPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFA sison100% (1)
- Seminars 2019 PDFDocument200 paginiSeminars 2019 PDFpaingmyintÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Patient with Risk of BleedingDocument11 paginiNursing Care Plan for Patient with Risk of BleedingKimsha ConcepcionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpdprovider Nursing 81718Document25 paginiCpdprovider Nursing 81718PRC BoardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpdprogram Nursing 81718Document301 paginiCpdprogram Nursing 81718PRC BoardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăGestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Major Effects Hormones Pregnant MotherDocument1 paginăMajor Effects Hormones Pregnant MotherCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiCerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis67% (12)
- Cancer Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăCancer Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis89% (9)
- Schizophrenia Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăSchizophrenia Schematic DiagramCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma Pathophysiology and DiagramDocument1 paginăAsthma Pathophysiology and DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Pregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyDocument1 paginăPregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnacy Induced Hypertension - PIH - PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiPregnacy Induced Hypertension - PIH - PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Geriatric Assessment Tool An Application of Core - Care and Cure ModelDocument1 paginăGeriatric Assessment Tool An Application of Core - Care and Cure ModelCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăLiver Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia Schematic DiagramDocument2 paginiIron Deficiency Anemia Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis83% (12)
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis87% (119)
- Anaphylactic Shock PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăAnaphylactic Shock PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăEctopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiHypertension Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis92% (13)
- Burns Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument1 paginăBurns Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Risk For InfectionCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăHiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Hyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăHyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis67% (9)
- Congestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăCongestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealCyrus De Asis67% (6)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDocument2 paginiBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Schematic Diagram of Alcoholic CirrhosisDocument2 paginiSchematic Diagram of Alcoholic CirrhosisCyrus De Asis0% (1)
- Preeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăPreeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis80% (10)
- Hydrocephalus PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăHydrocephalus PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Alzheimer's Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiAlzheimer's Disease Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis76% (17)
- Post-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiPost-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Girl, Interrupted Film Analysis Diana Fox Molloy CollegeDocument5 paginiGirl, Interrupted Film Analysis Diana Fox Molloy CollegeDiana Fox100% (1)
- Malang Batu Tour Package Itinerary 2 Days 1 NightDocument3 paginiMalang Batu Tour Package Itinerary 2 Days 1 NightSepta SuryadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Consensus On Non Cirrhotic Portal FibrosisDocument41 paginiNew Consensus On Non Cirrhotic Portal Fibrosisramesh5889Încă nu există evaluări
- Fibre Cement Slates Fixing GuideDocument26 paginiFibre Cement Slates Fixing GuideMuhammad HafizuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Your Body Speaks Your Mind by Deb ShapiroDocument315 paginiYour Body Speaks Your Mind by Deb Shapiroisidora milosevic100% (2)
- STERILE PARENTERAL FORMULATIONSDocument85 paginiSTERILE PARENTERAL FORMULATIONSShalimashalu100% (1)
- Vulvovaginal Atrophy in The CRETA Study The Healthcare Professionals PerceptionDocument7 paginiVulvovaginal Atrophy in The CRETA Study The Healthcare Professionals PerceptionHugo GutiérrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- MKWD Lwua Adb Package 2 AnnexesDocument199 paginiMKWD Lwua Adb Package 2 AnnexesRoland AnaumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paragraph TypesDocument4 paginiParagraph TypesZayb EhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pq-Unocal Csms '03Document15 paginiPq-Unocal Csms '03Ismail Hamzah Azmatkhan Al-husainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of GuidanceDocument13 paginiTypes of GuidanceJomar Gasilla Navarro100% (1)
- Snodgrass (1980) A Standardized Set of 260 Pictures. Norms For Name Agreement, Image Agreement, Familiarity, and Visual ComplexityDocument42 paginiSnodgrass (1980) A Standardized Set of 260 Pictures. Norms For Name Agreement, Image Agreement, Familiarity, and Visual ComplexityΜακίν Ξηροί ΚαρποίÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Dissociation and What To Do About It?Document2 paginiWhat Is Dissociation and What To Do About It?Tommy ThompsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Definition of Sexual Abuse of ChildrenDocument2 paginiDefinition of Sexual Abuse of ChildrenRadhika RathoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hematology Lecture - AnemiaDocument10 paginiHematology Lecture - AnemiaKimberly EspaldonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Donald A. Neumann-Kinesiology of The Musculoskeletal SystemDocument607 paginiDonald A. Neumann-Kinesiology of The Musculoskeletal SystemLuciano Klapisch81% (16)
- Introduction of PhobiaDocument2 paginiIntroduction of PhobiawoodenskyÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ultimate Guide To Anxiety DisordersDocument66 paginiThe Ultimate Guide To Anxiety Disordersnajaxx100% (2)
- Elanco Parvovirus DXTX GDocument2 paginiElanco Parvovirus DXTX Gazamkhan60Încă nu există evaluări
- Benefits of Effective Lifting ProgramDocument30 paginiBenefits of Effective Lifting ProgramMoradeke OnasanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Disparities BrochureDocument2 paginiHealth Disparities Brochureapi-276375030100% (1)
- Manuale Advantage 350Document50 paginiManuale Advantage 350PaulmankeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inflammation - The Silent Killer - Terra Health EssentialsDocument6 paginiInflammation - The Silent Killer - Terra Health EssentialshighlanderoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Commentary: Novel Application For G Protein - Biased Mu Opioid Receptor Agonists in Opioid Relapse PreventionDocument2 paginiCommentary: Novel Application For G Protein - Biased Mu Opioid Receptor Agonists in Opioid Relapse PreventionIntan AyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Middle Childhood Physical Development (6-11 YearsDocument13 paginiMiddle Childhood Physical Development (6-11 YearsAngela YlaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brosur SucofindoDocument14 paginiBrosur SucofindoJay Van BuurninkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Process in Drug TherapyDocument60 paginiNursing Process in Drug TherapyYra JhaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training Session Evaluation Form InstructionsDocument8 paginiTraining Session Evaluation Form Instructionsaaronjules100% (1)
- Less Adaptive or More Maladaptive? A Meta-Analytic Investigation of Procrastination and CopingDocument12 paginiLess Adaptive or More Maladaptive? A Meta-Analytic Investigation of Procrastination and CopingVALERIA BUSTAMANTE ALBERCOÎncă nu există evaluări
- NO Kodebarang Satuan Pakai Stock Awal Masuk Keluar Stock Akhir Harga KeteranganDocument4 paginiNO Kodebarang Satuan Pakai Stock Awal Masuk Keluar Stock Akhir Harga Keteranganruang belajar farmasiÎncă nu există evaluări