Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Încărcat de
Cyrus De Asis0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
6K vizualizări1 paginăPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
6K vizualizări1 paginăPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Încărcat de
Cyrus De AsisPathophysiology of Diabetic Ketoacidosis
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
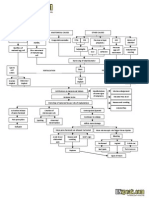
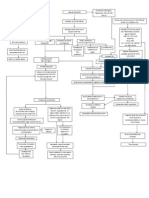
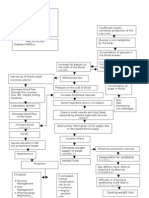
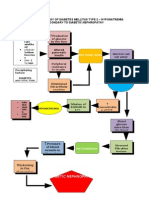
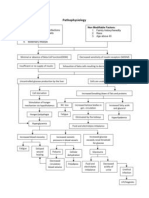
Pathophysiology
Absolute lack of insulin
Transport of glucose to
cells
is impossible
Decreased glucose levels
inside the cell
Increased blood glucose
level: more than 250
mg/dL
Protein breakdown
for fuelling cells
Transport impossible;
glucose stays in the
bloodstream
Fat breakdown (lipolysis)
as source of fuel for cells
Release of ketones as byproduct
Increased ketones in the
blood
Cell hunger/ (-) ATP inside
cells
Cell hunger/ (-) ATP
inside cells
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS
Stimulation of
hypothalamus (hunger
center)
Lungs compensate
through increasing
exhalation of CO2
More breakdown of
carbohydrates into
glucose
Kussmauls respiration
deep, rapid breathing
No insulin to transport
glucose into cells; increase
serum glucose level
Acetone breath
Kidney corrects
metabolic acidosis
Ketonuria - Increased
excretion of ketones in
the urine
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Coronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiCoronary Artery Disease PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis89% (9)
- Cerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlanDocument4 paginiCerebrovascular Accident Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis67% (12)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăEctopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 paginiChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology Schematic Diagramnursing concept maps100% (5)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia Schematic DiagramDocument2 paginiIron Deficiency Anemia Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis83% (12)
- Diarrhea Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiDiarrhea Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis87% (120)
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument3 paginiChronic Renal FailureIvana Yasmin Bulandres100% (2)
- Gestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăGestational Diabetes Mellitus PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Hypertension Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiHypertension Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis93% (14)
- Anaphylactic Shock PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăAnaphylactic Shock PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (3)
- Nursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan Patient EndotrachealCyrus De Asis67% (6)
- Pathophysiology: Precipitating FactorDocument6 paginiPathophysiology: Precipitating FactorMark Anthony YabresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of DM IIDocument6 paginiPathophysiology of DM IIJulie SimaurioÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACS PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiACS PathophysiologyFerliza OblenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of DMDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of DMNicole Louise N. VillanuevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisDocument4 paginiPathophysiology in Liver CirrhosisCyrus Ortalla RobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Heart FailureDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of Heart FailureTiger Knee100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of NephrosclerosisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of NephrosclerosisJessica Damasen Caballero0% (1)
- Final Lung Cancer Concept MapDocument3 paginiFinal Lung Cancer Concept MapKaycee TolingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Weaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaDocument5 paginiWeaknes S/ Fatigue Polyphag IaEwert Hesketh Nillama PaquinganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Chronic Kidney DiseaseKeij AranetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HELLP Concept Map RevisedDocument1 paginăHELLP Concept Map RevisedwandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Document3 paginiPathophysiology of Colon Cancer 1Katherine Clarisse Carvajal Lavarias100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document7 paginiPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2arbyjamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument4 paginiDiabetic KetoacidosisLakshay ChananaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schizophrenia Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăSchizophrenia Schematic DiagramCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăLiver Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Hiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăHiatal Hernia Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Cancer Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăCancer Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (4)
- Hyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăHyperthyroidism Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis67% (9)
- Alzheimer's Disease Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiAlzheimer's Disease Nursing Care PlanCyrus De Asis76% (17)
- Congestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăCongestive Heart Failure Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- The Cardiovascular System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical CollegeDocument125 paginiThe Cardiovascular System: Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical Collegedomo domoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisHelcon John Dela TorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisGeevine CansinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of CVA D/T DMDanielle Marie SamblacenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Diabetic KetoacidosisSuzette PipoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dka Patho DiagramDocument1 paginăDka Patho DiagramGrae TaclobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document1 paginăPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2faula rocamora100% (3)
- Laennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiLaennecs Cirrhosis PathophysiologyTrixie Al Marie100% (3)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Diabetes MellitusJerene67% (3)
- Pathophysiology of StrokeDocument4 paginiPathophysiology of StrokeACe JAyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Renal FailureDocument1 paginăChronic Renal Failurejj_cuttingedges100% (2)
- EsrdDocument3 paginiEsrdRonald Lavada RN100% (1)
- Pathophysiology DMDocument1 paginăPathophysiology DMMJ AmarilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- COPD PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăCOPD Pathophysiologyaj ajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept MapDocument4 paginiConcept Mapdejosep_informaticsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina Pectoris PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiAngina Pectoris PathophysiologyALIANA KIMBERLY MALQUESTOÎncă nu există evaluări
- CKD PathoDocument5 paginiCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology CHFDocument2 paginiPathophysiology CHFPerry Oliver AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology ESRDDocument9 paginiPathophysiology ESRDJaye DangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes PathophysiologyDocument6 paginiDiabetes PathophysiologyKatelyn CherryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 paginăPathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Ards Cmap FinalDocument4 paginiArds Cmap FinalPam Araune67% (3)
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 paginiChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiAcute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyChester NicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiESRD PathophysiologyMark Ronhel Gallardo PerenalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument1 paginăPathophysiology of CVAChristine Joy Ilao PasnoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Hyperthyroidism and Thyroid StormPen MontanteÎncă nu există evaluări
- PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiPathophysiologyCee SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1Document3 paginiPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 1CajRofuli100% (2)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 paginiAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiAcute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyJanica Marinas100% (3)
- CKD PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăCKD Pathophysiologylloyd_santino67% (3)
- Pathophysio CRF RevisedDocument2 paginiPathophysio CRF Revisedroseanne18Încă nu există evaluări
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsDocument9 paginiNon-Modifiable Risk Factors: Modifiable Risk FactorsKimberly Bomediano100% (1)
- Pathophysiology CKD Secondary To CGNDocument1 paginăPathophysiology CKD Secondary To CGNNathan Vince CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- DiabetesDocument2 paginiDiabetespaul andrew laranjo asuncionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ans05 HormonesDocument5 paginiAns05 Hormonesngsuan.2020Încă nu există evaluări
- Ketone BodiesDocument9 paginiKetone BodiesMUTHONI IRERIÎncă nu există evaluări
- InsulinDocument1 paginăInsulincsanjeevanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes KetoacidosisDocument2 paginiDiabetes KetoacidosisJullie Anne SantoyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ketone Bodies: DR Anjali SaxenaDocument3 paginiKetone Bodies: DR Anjali Saxenahirendra patelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetic Ketoacidosis: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument4 paginiDiabetic Ketoacidosis: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaTika Fajar WulandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes Mellitus Type-2Document1 paginăDiabetes Mellitus Type-2Sara SabraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpdprogram Nursing 81718Document301 paginiCpdprogram Nursing 81718PRC BoardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cpdprovider Nursing 81718Document25 paginiCpdprovider Nursing 81718PRC BoardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pregnacy Induced Hypertension - PIH - PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiPregnacy Induced Hypertension - PIH - PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Asthma Pathophysiology and DiagramDocument1 paginăAsthma Pathophysiology and DiagramCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Pregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyDocument1 paginăPregnacy Induced Hypertension PhysiologyCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Major Effects Hormones Pregnant MotherDocument1 paginăMajor Effects Hormones Pregnant MotherCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geriatric Assessment Tool An Application of Core - Care and Cure ModelDocument1 paginăGeriatric Assessment Tool An Application of Core - Care and Cure ModelCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burns Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Risk For InfectionDocument1 paginăBurns Nursing Care Plan - NCP - Risk For InfectionCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Post-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiPost-Throidectomy Nursing Care PlanCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăPreeclampsia Pathophysiology and Schematic DiagramCyrus De Asis80% (10)
- Hydrocephalus PathophysiologyDocument1 paginăHydrocephalus PathophysiologyCyrus De Asis100% (1)
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPDocument2 paginiBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia NCPCyrus De Asis100% (2)
- Schematic Diagram of Alcoholic CirrhosisDocument2 paginiSchematic Diagram of Alcoholic CirrhosisCyrus De Asis0% (1)
- Departemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraDocument23 paginiDepartemen Fisiologi Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas Sumatera UtaraLoshseniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Integumentary Changes in AgingDocument1 paginăIntegumentary Changes in AgingJonathan R. YadaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015 The ECG Handbook of Contemporary Challenges PDFDocument246 pagini2015 The ECG Handbook of Contemporary Challenges PDFFercho MedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise 9 Act 4Document4 paginiExercise 9 Act 4Abigail YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-17-叶伟玉 Acupuncture and Tuina Report 1. (With Table)Document17 pagini1-17-叶伟玉 Acupuncture and Tuina Report 1. (With Table)Virda Izzah PermatasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Respiratory Part 2Document23 paginiRespiratory Part 2api-26938624Încă nu există evaluări
- Human Physiology From Cells To Systems Sherwood 9th Edition Test BankDocument15 paginiHuman Physiology From Cells To Systems Sherwood 9th Edition Test BankWillis Sanchez100% (34)
- Test Bank For Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Mary C TownsendDocument15 paginiTest Bank For Essentials of Psychiatric Mental Health Nursing 7th Edition Mary C TownsendVanessa Martin100% (31)
- General BIology 1 Q2 M5 SCDocument10 paginiGeneral BIology 1 Q2 M5 SCAldrin James DafunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pato Insomnia PDFDocument14 paginiPato Insomnia PDFdilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group Presentation (A) Group Presentation : Health Science (Gen. Nursing) Biochemistry Gluconeogenesis DR SujuudDocument31 paginiGroup Presentation (A) Group Presentation : Health Science (Gen. Nursing) Biochemistry Gluconeogenesis DR SujuudIbrahim WarsameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple-Choice Questions Cardiology Questions For (UK) : The MRCP ExaminationDocument6 paginiMultiple-Choice Questions Cardiology Questions For (UK) : The MRCP ExaminationDr.vidyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQDocument19 paginiMCQMohamed Shaban faroukÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson PlanDocument2 paginiLesson PlanBryanAngelo Laguilles100% (1)
- Active Transport MechanismDocument3 paginiActive Transport MechanismDaren jay GeneraleÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENDOCRINE FinalDocument68 paginiENDOCRINE FinalJerick Sevilla SearesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Based Learning of Blood Oxygen TransportDocument14 paginiCase Based Learning of Blood Oxygen TransportElena Delfin0% (1)
- ECG Interpretation in Small AnimalsDocument10 paginiECG Interpretation in Small Animalsgacf1974Încă nu există evaluări
- Science 9 - Week 1Document8 paginiScience 9 - Week 1MICAH NORADAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2013 ESH/ESC Practice Guidelines For The Management of Arterial HypertensionDocument14 pagini2013 ESH/ESC Practice Guidelines For The Management of Arterial HypertensionReski Melinia PatinggiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ecf and Icf PDFDocument55 paginiEcf and Icf PDFChidera EmmanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical ExaminationDocument10 paginiPhysical ExaminationKeneth Dave AglibutÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Radial Path of Ion Movement Through RootsDocument2 paginiThe Radial Path of Ion Movement Through RootsAtika AnggrainiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCLEX Mark K NotesDocument131 paginiNCLEX Mark K NotesRhika Mae ObraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intra-Arterial Balloon Pump: A Primer & Some Evidence: Andrea Tsai September 24, 2019Document54 paginiIntra-Arterial Balloon Pump: A Primer & Some Evidence: Andrea Tsai September 24, 2019JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handout 6 CardioVascular DisordersDocument15 paginiHandout 6 CardioVascular DisordersAllysa Megan OrpillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 101 High Intensity Workouts For Fast ResultsDocument159 pagini101 High Intensity Workouts For Fast ResultsLynseyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Photorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarDocument11 paginiPhotorespiration: The Assignment Submitted by Mumtahin Ul KousarJunaid MushtaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- L3 Anatomy and Physiology Learner Workbook 1A Mar12Document84 paginiL3 Anatomy and Physiology Learner Workbook 1A Mar12markÎncă nu există evaluări