Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35
Încărcat de
JUSASB50%(2)50% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
38 vizualizări1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
50%(2)50% au considerat acest document util (2 voturi)
38 vizualizări1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35
Încărcat de
JUSASBToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 35
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
NP35 Nephrology
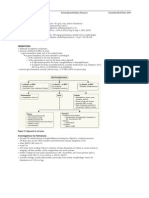
Chronic Kidney Disease/End Stage Renal Disease
Essential Med Notes 2015
Prevention of Progression
as above
control of HTN, DM, cardiovascular risk factors (e.g. smoking cessation)
avoid nephrotoxins
address reversible causes of AKI
End Stage Renal Disease
end stage renal disease represents a decline in kidney function which can occur over days to
weeks (AKI), over months to years (CKD), or as a combination of the two
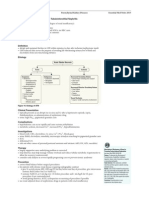
Presentation of End Stage Renal Disease
1. Volume Overload
due to increase in total body Na+ content
signs: weight gain, HTN, pulmonary or peripheral edema
2. Electrolyte Abnormalities
high
K+ (decreased renal excretion, increased tissue breakdown)
PO43- (decreased renal excretion, increased tissue breakdown)
Ca2+ (rare; happens during recovery phase after rhabdomyolysis-induced AKI or in
settings where hypercalcemia contributes to renal failure, such as in multiple myeloma or
sarcoidosis)
uric acid
low
Na+ (failure to excrete excessive water intake)
Ca2+ (decreased Vit D activation, hyperphosphatemia, hypoalbuminemia)
HCO3 (especially with sepsis or severe heart failure)
3. Uremic Syndrome
manifestations result from retention of urea and other metabolites as well as hormone deficiencies
CNS: headache, lethargy, somnolence,
confusion, asterixis, hyporeflexia
PNS:
wrist drop
GI: decreased taste
RESPIRATORY: shortness of
breath, pleuritic chest pain
PNS:
foot drop
CVS: pericardial
friction rub
ENDOCRINE: weight loss,
amenorrhea,
decreased libido
GI: anorexia,
nausea, vomiting
GU: irritative and/or
obstructive urinary tact
symptoms, hematuria,
palpable bladder
MSK: nocturnal muscle
cramps, muscle weakness
Figure 19. Signs and symptoms of end stage renal disease
PNS:
glove and
stocking
neuropathy
Alice Zheng 2014
SKIN: pruritus, pallor,
yellow discoloration
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nephrology - Dr. Allam 2021Document42 paginiNephrology - Dr. Allam 2021Alokh Saha RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology MRCP1Document174 paginiNephrology MRCP1Raouf Ra'fat Soliman100% (3)
- Nephrology PDFDocument55 paginiNephrology PDFPolito Soyti100% (2)
- Nephrology FormulasDocument3 paginiNephrology FormulasM Patel0% (1)
- Step 3 Nephrology Part 1 of 3Document7 paginiStep 3 Nephrology Part 1 of 3Bhavin ChoksiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology: Edward F. Foote, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPSDocument32 paginiNephrology: Edward F. Foote, Pharm.D., FCCP, BCPSandirio7486Încă nu există evaluări
- ACCP 2018 NephrologyDocument31 paginiACCP 2018 NephrologyMonica Febri Andari100% (1)
- Nephrology DR ZeinabDocument101 paginiNephrology DR ZeinabZeinab Muhammad100% (1)
- Renal Chart 2Document21 paginiRenal Chart 2fortheloveofmedicineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology Review NotesDocument6 paginiNephrology Review NotesEdilberto HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00 NephrologyDocument98 pagini00 Nephrologyeryxsp0% (1)
- Anemia in CKD: Ppds Sp1 Divisi Ginjal Hipertensi Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Rsup Dr. Mohammad Hoesin Palembang 2021Document31 paginiAnemia in CKD: Ppds Sp1 Divisi Ginjal Hipertensi Bagian Ilmu Penyakit Dalam Rsup Dr. Mohammad Hoesin Palembang 2021Richard 151289Încă nu există evaluări
- Top 10 Nephro Slides in Board ExamsDocument223 paginiTop 10 Nephro Slides in Board ExamsMirza Shaharyar Baig100% (2)
- ACP Board Review Nephrology 20052ndDocument35 paginiACP Board Review Nephrology 20052nddoctormido2010100% (1)
- Clinical Approach To RPRF PDFDocument6 paginiClinical Approach To RPRF PDFshankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Co Nephrology CurriculumDocument130 paginiOn Co Nephrology CurriculumPopy TheresiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NephSAP HTNDocument88 paginiNephSAP HTNAditya JayaramanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Nephrology Dialysis and TransplantationDocument1.539 paginiClinical Nephrology Dialysis and Transplantationalrafeek1050100% (1)
- Hepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHepatorenal Syndrome, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology PDFDocument38 paginiNephrology PDFOmar AyashÎncă nu există evaluări
- NephroTube Nephrology Synopsis of Glomerulonephritis 2010-2019Document41 paginiNephroTube Nephrology Synopsis of Glomerulonephritis 2010-2019Selena GajićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antipsychotics - FactsheetDocument12 paginiAntipsychotics - FactsheetColonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Clinical Nephrology 4th Editionl PDFDocument4 paginiComprehensive Clinical Nephrology 4th Editionl PDFJenniferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vital Nephrology - $86.04Document106 paginiVital Nephrology - $86.04Abdallah Bouleghraif100% (1)
- 17 - Toronto Notes 2011 - NephrologyDocument92 pagini17 - Toronto Notes 2011 - NephrologyKhairulsani Yusof100% (2)
- Nephrology: Omar K MRCP IrelandDocument54 paginiNephrology: Omar K MRCP IrelandManmeet SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 10JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 5JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 3JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Murray CaseStudiesInNephrologyDocument179 paginiMurray CaseStudiesInNephrologyAdil BilaeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 21JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- NephrologyDocument9 paginiNephrologyRohit BharadwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Physiology For The BoardsDocument37 paginiRenal Physiology For The BoardsRainy Day100% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 7Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 7JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Pearls in NephrologyDocument5 paginiClinical Pearls in NephrologyEdmilson R. LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lange Nephrology EssentialsDocument9 paginiLange Nephrology EssentialsAlejandro GarcíaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 12JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- IgA Nep PDFDocument10 paginiIgA Nep PDFNarinder SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemodiafiltration KuhlmannDocument31 paginiHemodiafiltration Kuhlmanntigercat100% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology DR Osama Mahmoud PDFDocument83 paginiNephrology DR Osama Mahmoud PDFMaria PatituÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revise Nephrology Manipal - CME BrochureDocument2 paginiRevise Nephrology Manipal - CME BrochureLydia IsaacÎncă nu există evaluări
- References: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015Document1 paginăReferences: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Give Grand RoundsDocument12 paginiHow To Give Grand RoundsNephrology On-DemandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigDocument29 paginiIntra and Intradialytic Hypotension and Hypertension InrigMonica HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesDocument7 paginiManagement of Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children: Children's Services Medical GuidelinesdaypranitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology Notes 2015Document81 paginiNephrology Notes 2015Mahmoud Hussien100% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Writing The Home Hemodialysis PrescriptionDocument22 paginiWriting The Home Hemodialysis Prescriptionstudent_physicianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glomerulonephritis Dwi Fin PDFDocument108 paginiGlomerulonephritis Dwi Fin PDFOvyanda Eka MItraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nephrology Curriculum - الزمالة المصرية للكليDocument60 paginiNephrology Curriculum - الزمالة المصرية للكليbook1man100% (1)
- Nephrology ExamsDocument30 paginiNephrology Examsdhianne_garcia2001100% (1)
- Nephrology Guide for Common Kidney ConditionsDocument19 paginiNephrology Guide for Common Kidney ConditionseuncieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 38JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- COMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesDocument5 paginiCOMLEX Normal Adult Laboratory ValuesJUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antipsychotics Factsheet pg2Document1 paginăAntipsychotics Factsheet pg2JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- FA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesDocument2 paginiFA 2016 Step 1 - Reference ValuesJUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 36JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 37JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 33JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 39JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- References: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015Document1 paginăReferences: NP40 Nephrology Landmark Nephrology Trials/References Essential Med Notes 2015JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 27JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 28JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 30Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 30JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 26JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 34JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 31JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 22JUSASB0% (1)
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 29Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 29JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 24Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 24JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 32JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 17Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 17JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 23JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 20JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 18Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 18JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 14Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 14JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 25Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 25JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toronto Notes Nephrology 2015 15Document1 paginăToronto Notes Nephrology 2015 15JUSASBÎncă nu există evaluări