Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
16.20 Handout #1
Încărcat de
vishalsinha91370 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
18 vizualizări2 paginiDrepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
18 vizualizări2 pagini16.20 Handout #1
Încărcat de
vishalsinha9137Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
MIT, 16.
20 Fall, 2002
16.20 HANDOUT #1
Fall, 2002
Review of Design Considerations
OVERVIEW OF STRUCTURAL DESIGN PROCESS
Purpose: Assure “structural integrity” while minimizing cost
Structural integrity: “Capability of a structure to carry out the operation for which it
was designed”
Aspects to consider:
• Loads
• Deformations
• Corrosion
• Fatigue/Long life
Factors in Determining cost:
• Material
• Waste amount
• Manufacturing
• Weight
• Subassembly/Assembly
• Durability and maintenance
• Useful life
• Repair
Paul A. Lagace 2002 Handout 1-1
MIT, 16.20 Fall, 2002
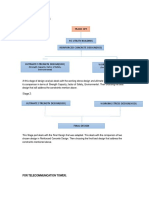
STRUCTURAL DESIGN PROCESS
1. Design restrictions/specifications
2. Determine applied loads and operating
environment to which structure is subjected
3. Layout structural arrangement, select materials,
size components
2
1
4. Determine internal stresses and deflections
5. Determine capability of structure to carry loads
(of box 2) subject to design restrictions (of box 1)
Manufacturing & Maintenance
considered throughout
SOURCES OF APPLED LOADS (and resulting stresses and strains)
• Normal operative environment
• Environmental effects
• Isolated effects/special conditions
TERMINOLOGY
Limit load/stress/condition: maximum load/stress/condition where structure shows no
permanent deformation (operationally defined as maximum condition the structure is
expected to see under normal operation)
Ultimate load/stress/condition: maximum load/stress/condition where structure does not
“fail” (operationally defined as limit condition times factor of safety).
Ultimate Factor of Safety = Ultimate Condition
(design value) Limit Condition
Margin of Safety = Tested Value – Design Value
(experimental reality) Design Value
Definition of “failure” depends on operational requirements.
Paul A. Lagace 2002 Handout 1-2
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Introduction to Design of Building StructuresDe la EverandIntroduction to Design of Building StructuresEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (22)
- RCD1Document24 paginiRCD1Nelle SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metric Handbook - StructureDocument50 paginiMetric Handbook - StructurexufafruitjuiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Design Handout Chapters 1 3Document119 paginiSteel Design Handout Chapters 1 3Hannan Sarrondo VitugÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Design Handout Chapters 1-3Document124 paginiSteel Design Handout Chapters 1-3Kevin Banez100% (1)
- Module 1 Intro To Steel DesignDocument9 paginiModule 1 Intro To Steel DesignAbren DaysoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Steel Structures DesignDocument10 paginiFundamentals of Steel Structures DesignJanice FernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Concept Limit State Design Partial Factor of Safety Types of LoadingsDocument9 paginiBasic Concept Limit State Design Partial Factor of Safety Types of LoadingsRCdesign2012Încă nu există evaluări
- Advance Reinforced Concrete Design To BS 8110-1:1997: F. M. M AbdullahDocument12 paginiAdvance Reinforced Concrete Design To BS 8110-1:1997: F. M. M AbdullahMohamed AbdÎncă nu există evaluări
- W2 L2 Limit State DesignDocument28 paginiW2 L2 Limit State Design木辛耳总Încă nu există evaluări
- PCE 411 Structural Steel Design: ASD vs LRFD PhilosophiesDocument5 paginiPCE 411 Structural Steel Design: ASD vs LRFD PhilosophiesJonathan LlegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module+2 Design+LoadsDocument125 paginiModule+2 Design+LoadsfrnkbartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- No. 106 IACS Guideline For Rule Development - Ship Structure No. 106Document54 paginiNo. 106 IACS Guideline For Rule Development - Ship Structure No. 106Jym GensonÎncă nu există evaluări
- TRADE OFF FlowchatfinalsDocument2 paginiTRADE OFF FlowchatfinalsJoy lauriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Structures Design and Drawing PDFDocument38 paginiSteel Structures Design and Drawing PDFShri100% (5)
- ARCH 415-S&TD - M1 - T1 - W2 - Introduction For Steel and TimberDocument6 paginiARCH 415-S&TD - M1 - T1 - W2 - Introduction For Steel and TimberJomarie AfricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 2: Basic Concepts of DesignDocument18 paginiChapter - 2: Basic Concepts of DesignashenafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Structure Bolted Connections DesignDocument4 paginiSteel Structure Bolted Connections Designramu karriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Limit States Method (Cec402 Assignment of Group3a)Document50 paginiLimit States Method (Cec402 Assignment of Group3a)Kingshuk MukherjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- RCI Chapter 2 ADocument16 paginiRCI Chapter 2 AsasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Lecture 2 - Design Loads, ASD Vs LRFDDocument55 paginiSteel Lecture 2 - Design Loads, ASD Vs LRFDSana'a AamirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Manufacturing Guideline For Aerospace CompositesDocument11 paginiDesign and Manufacturing Guideline For Aerospace CompositesBrice_ParmentierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacture of Rocket Motor Cases Using Advanced FilameDocument11 paginiManufacture of Rocket Motor Cases Using Advanced FilameSumithrananthanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Concrete Structures IDocument102 paginiDesign of Concrete Structures IDulanga kameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Final Repord 2076 PDFDocument106 paginiProject Final Repord 2076 PDFPawan Kumar Karki100% (1)
- ULS and SLSDocument4 paginiULS and SLSlolorek100% (8)
- Construction Loads PDFDocument41 paginiConstruction Loads PDFcaner_kurtoglu-1Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Structural Engineering: Steel and Timber Design FundamentalsDocument15 paginiIntroduction to Structural Engineering: Steel and Timber Design FundamentalsKENNETHPAUL HERNANDEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionDocument29 paginiUnit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionOladimeji Ibukun IjaodolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 202210-BDP-Chapter-1BridgeDesign Specifications-A11yDocument15 pagini202210-BDP-Chapter-1BridgeDesign Specifications-A11ydvegaucentralÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory of Structure Reinforced ConcreteDocument2 paginiTheory of Structure Reinforced ConcreteRosaline MainaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Background Theory: Failure CriterionDocument51 pagini1 Background Theory: Failure CriterionAntehun MekonnenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction and Design Overview: Unit 1Document9 paginiIntroduction and Design Overview: Unit 1sabanayagamn1991Încă nu există evaluări
- RCD1 Topic 2Document29 paginiRCD1 Topic 2calchan79Încă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering Design CriteriaDocument32 paginiCivil Engineering Design Criteriacall1986100% (1)
- How Is Working Stress Method (ASD) Different From Limit State Method (LRFD or LFD) - Assumptions, Advantages and Comparisons - CivilDigitalDocument4 paginiHow Is Working Stress Method (ASD) Different From Limit State Method (LRFD or LFD) - Assumptions, Advantages and Comparisons - CivilDigitalStacy JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 7-9 - B.tech V Sem (Civil) Cs-I Ce 15103 - 2022 - LSMDocument37 paginiLect 7-9 - B.tech V Sem (Civil) Cs-I Ce 15103 - 2022 - LSMSandeep MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Based DesignDocument8 paginiPerformance Based Designigunz245200Încă nu există evaluări
- LECTURE NOTE 01 - RCC DesignDocument14 paginiLECTURE NOTE 01 - RCC DesignMohamed AbdÎncă nu există evaluări
- NSCP Chapter 2 Summary FinalDocument2 paginiNSCP Chapter 2 Summary FinalshienellajacildoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shallow Foundations: Understanding Performance RequirementsDocument65 paginiShallow Foundations: Understanding Performance RequirementsCharles Warren GoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionDocument29 paginiUnit No 1: Reinforced Concrete IntroductionAbdur Rasheed RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Notes 2011-6Document68 paginiConcrete Notes 2011-6Kaveesh NCDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Note: Aefac - Tn01Document9 paginiTechnical Note: Aefac - Tn01Anonymous YW5mvpÎncă nu există evaluări
- AE228-222-Lec 5 - Materials 1 PDFDocument8 paginiAE228-222-Lec 5 - Materials 1 PDFjjÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Drift Limits Associated With Different Damage Levels: June 2004Document13 paginiOn Drift Limits Associated With Different Damage Levels: June 2004RaviKanthSrivastavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap-1 (Design Philosophy-Structure) FinalDocument19 paginiChap-1 (Design Philosophy-Structure) FinalAshish SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCI P252 SecureDocument114 paginiSCI P252 SecureDan CiucuÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Basic Principles of Limit State Design MethodDocument57 paginiThe Basic Principles of Limit State Design MethoddavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design codes, safety and behavior of RC structuresDocument23 paginiDesign codes, safety and behavior of RC structuresAhmad Faraz JuttÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Inputs and Structural Engineering LiteratureDocument5 paginiDesign Inputs and Structural Engineering LiteratureMæbēTh CuarterosÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE71 Module 2 2ND SEM 2022Document13 paginiCE71 Module 2 2ND SEM 2022Orland Son FactorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Steel Structures and Design PrinciplesDocument15 paginiTypes of Steel Structures and Design PrinciplesTonymeriÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE30310 Lecture 2Document51 paginiCSE30310 Lecture 2sze yin wongÎncă nu există evaluări
- NGMA DesignDocument17 paginiNGMA DesignJames LawsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture On Limit State Design by Manish BhutaniDocument27 paginiLecture On Limit State Design by Manish BhutaniTarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Design Methodology-1Document9 pagini03 Design Methodology-1Abdul RehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.1 Intended Learning Outcomes: Structural DesignDocument6 pagini1.1 Intended Learning Outcomes: Structural DesignJenevive Tumacder100% (1)
- Effective Time ManagementDocument61 paginiEffective Time ManagementTafadzwa94% (16)
- Concept Page - Using Vagrant On Your Personal Computer - Holberton Intranet PDFDocument7 paginiConcept Page - Using Vagrant On Your Personal Computer - Holberton Intranet PDFJeffery James DoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acuity Assessment in Obstetrical TriageDocument9 paginiAcuity Assessment in Obstetrical TriageFikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Apu Trilogy - Robin Wood PDFDocument48 paginiThe Apu Trilogy - Robin Wood PDFSamkush100% (1)
- KINETIC THEORY OF GASES TUTORIALDocument6 paginiKINETIC THEORY OF GASES TUTORIALMat SyafiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Are Hypomineralized Primary Molars and Canines Associated With Molar-Incisor HypomineralizationDocument5 paginiAre Hypomineralized Primary Molars and Canines Associated With Molar-Incisor HypomineralizationDr Chevyndra100% (1)
- Baseline Program Rev 3A Presentation 25 July 2020Document24 paginiBaseline Program Rev 3A Presentation 25 July 2020Shakti Sourava RautrayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arm BathDocument18 paginiArm Bathddivyasharma12Încă nu există evaluări
- AI Model Sentiment AnalysisDocument6 paginiAI Model Sentiment AnalysisNeeraja RanjithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Casio AP-80R Service ManualDocument41 paginiCasio AP-80R Service ManualEngkiong Go100% (1)
- WK 43 - Half-Past-TwoDocument2 paginiWK 43 - Half-Past-TwoKulin RanaweeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection 2: WHAT DOES It Mean To Be A Pacific Islander Today and in The Future To Me?Document5 paginiReflection 2: WHAT DOES It Mean To Be A Pacific Islander Today and in The Future To Me?Trishika NamrataÎncă nu există evaluări
- ROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDocument20 paginiROMUS 2012 Flooring CatalogueDan George IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indian Patents. 232467 - THE SYNERGISTIC MINERAL MIXTURE FOR INCREASING MILK YIELD IN CATTLEDocument9 paginiIndian Patents. 232467 - THE SYNERGISTIC MINERAL MIXTURE FOR INCREASING MILK YIELD IN CATTLEHemlata LodhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sibuyan Island ResiliencyDocument12 paginiSibuyan Island ResiliencyEndangeredSpeciesÎncă nu există evaluări
- STS Chapter 1 ReviewerDocument4 paginiSTS Chapter 1 ReviewerEunice AdagioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caterpillar Ep15krtDocument37 paginiCaterpillar Ep15krtIvan MajikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct From: 1St Quarter 2020Document23 paginiDirect From: 1St Quarter 2020JeanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisDocument12 paginiWho will buy electric vehicles Segmenting the young Indian buyers using cluster analysisbhasker sharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lightwave Maya 3D TutorialsDocument8 paginiLightwave Maya 3D TutorialsrandfranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem SolutionsDocument5 paginiProblem SolutionskkappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Brewing Log Sheet PDFDocument2 paginiHome Brewing Log Sheet PDFStefanita0% (1)
- Oecumenius’ Exegetical Method in His Commentary on the RevelationDocument10 paginiOecumenius’ Exegetical Method in His Commentary on the RevelationMichał WojciechowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aortic Stenosis, Mitral Regurgitation, Pulmonary Stenosis, and Tricuspid Regurgitation: Causes, Symptoms, Signs, and TreatmentDocument7 paginiAortic Stenosis, Mitral Regurgitation, Pulmonary Stenosis, and Tricuspid Regurgitation: Causes, Symptoms, Signs, and TreatmentChuu Suen TayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure Personal CareDocument38 paginiBrochure Personal CarechayanunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liquid Out, Temperature 25.5 °C Tube: M/gs P / WDocument7 paginiLiquid Out, Temperature 25.5 °C Tube: M/gs P / WGianra RadityaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors With Phased Array ImagingDocument16 paginiAdvanced Ultrasonic Flaw Detectors With Phased Array ImagingDebye101Încă nu există evaluări
- Entrepreneurship Project On Jam, Jelly & PicklesDocument24 paginiEntrepreneurship Project On Jam, Jelly & Picklesashish karshinkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyclograph User ManualDocument15 paginiCyclograph User ManualPeter BateÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1010 PDS WLBP 170601-EN PDFDocument4 pagini1010 PDS WLBP 170601-EN PDFIan WoodsÎncă nu există evaluări