Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Actuators Definitions
Încărcat de
api-2964992450 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
19 vizualizări2 paginiElectric actuators are often the solution of choice for repeatedly moving a load. Linear actuators are also used to control the rate of acceleration. RotaryA rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque.
Descriere originală:
Titlu original
actuators definitions
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentElectric actuators are often the solution of choice for repeatedly moving a load. Linear actuators are also used to control the rate of acceleration. RotaryA rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
19 vizualizări2 paginiActuators Definitions
Încărcat de
api-296499245Electric actuators are often the solution of choice for repeatedly moving a load. Linear actuators are also used to control the rate of acceleration. RotaryA rotary actuator is an actuator that produces a rotary motion or torque.
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Explain and define the following
actuators, including their most
appropriate applications:
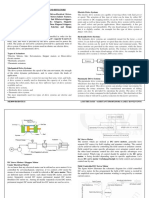
LinearA linear actuator is a mechanical device that
converts energy (power from air, electricity or liquid) to
create motion in a straight line; contrasted with circular
motion of a conventional electric motor. It can also be
used to apply a force.
Repeated Linear Movement
Electric actuators are often the solution of choice for repeatedly
moving a loador several loadsto a consistent locationor
locationsin a continuous fashion. Repeated linear movement
sometimes requires synchronizing multiple axes to facilitate
coordinated moves. If you need to repeat motion continuously
and consistently, as well as coordinate several different motions
simultaneously, this type of actuator is often the best solution.
Adaptable Movement
Linear motion that changes or adaptsfrequently referred to as
adaptable movement is another important application.
Whenever load, positions, or the very nature of the motion itself
changesas often is necessary for synchronizing movements with
other machine operationsyou can use these actuators to control
and facilitate adaptable movement.
Controlled Precision Movement
Precisely controlled motionthe accuracy of which is beyond the
capabilities of an actual person without exhibiting human erroris
another important electric actuator use. With these linear
actuators, you can control position with extreme levels of
precision, duplicate and repeat precise movements within the full
stroke, and even reprogram or reconfigure precise motions to
support multiple applications.
Acceleration Controlled Movement
Electric linear actuators are also used to control the rate of
acceleration. Because you can precisely control speed, position,
and torque, you can make the actuator accelerate or decelerate
as quickly and as often as you need.
RotationalA rotary actuator is an actuator that produces
a rotary motion or torque. The simplest actuator is purely
mechanical, where linear motion in one direction gives rise
to rotation. The most common actuators though are electrically
powered.
The rotary actuator became the steering and bearing system,
providing the strength and flexibility the vehicle required without
unnecessary weight, complexity, and maintenance of mechanical
linkages.
By: Cody Winsor
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Regenerative Elevator DrivesDocument7 paginiRegenerative Elevator DrivesPierre Hoyos AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actuators Lecture NotesDocument47 paginiActuators Lecture Notesdanilopangatungan8Încă nu există evaluări
- ACTUATORSDocument16 paginiACTUATORSGaga GogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actuators: Definition, Types & Examples: DR - Devender KumarDocument19 paginiActuators: Definition, Types & Examples: DR - Devender KumarEditor IRBJÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is An Actuator?Document2 paginiWhat Is An Actuator?Adam DinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sand Ramming FullDocument15 paginiSand Ramming FullAlmubeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microactuator 1Document21 paginiMicroactuator 1Anonymous P85UrA0FATÎncă nu există evaluări
- NEE 4101 - Bautista Control ValveDocument2 paginiNEE 4101 - Bautista Control ValveJETTDOMINIC BAUTISTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Key Words:: Motion Control Is Required in Large No of Industrial and Domestic Applications LikeDocument11 paginiKey Words:: Motion Control Is Required in Large No of Industrial and Domestic Applications LikeVijay BhaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC DrivesDocument10 paginiDC DrivesEuoshy HussainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Motion ControlDocument7 paginiMotion Controlla.wajeehakhurshidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Libro 2 PDFDocument18 paginiLibro 2 PDFCésar MaravíÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSD Unit 1Document24 paginiSSD Unit 1Shashank SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid State Motor ControDocument22 paginiSolid State Motor ControJesse Jones SeraspeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation & Robotics (RME078) : Lecture Notes OnDocument10 paginiAutomation & Robotics (RME078) : Lecture Notes Onمقدس ألم Μυφυαδδας ΑιαΜÎncă nu există evaluări
- ActuatorsDocument6 paginiActuatorsFam ChumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Ii Robot Drive Systems and End Effectors.Document11 paginiUnit Ii Robot Drive Systems and End Effectors.Akash PrasanthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture Three Actuators ObjectivesDocument5 paginiLecture Three Actuators ObjectivesKenani SaningaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Termpaper: Different Mechanism Used in Industries CODE:MEC101Document13 paginiTermpaper: Different Mechanism Used in Industries CODE:MEC101Tejpal SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industrial Drives and Control - ReviewerDocument10 paginiIndustrial Drives and Control - Reviewer21-09696Încă nu există evaluări
- Motion and Power Transmission SystemsDocument6 paginiMotion and Power Transmission Systemscompras.seaagsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Robotic Sensors: Robot Actuators - Different TypesDocument4 paginiRobotic Sensors: Robot Actuators - Different Typesmohan_rapaka100% (1)
- CHAPTER 1 - Actuators in Automation SystemDocument18 paginiCHAPTER 1 - Actuators in Automation SystemnurliyanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jian Moleta CTEDocument5 paginiJian Moleta CTETristan Jay AranasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final PDF EditedDocument6 paginiFinal PDF EditedFirdous NaazÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELX-321-MODULE-2-Drive System and End EffectorDocument14 paginiELX-321-MODULE-2-Drive System and End EffectorErvert SoteraniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity No. 2: Motor and Electric DrivesDocument17 paginiActivity No. 2: Motor and Electric DrivesAldrian BarachinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric ActuatorsDocument2 paginiElectric ActuatorsCair Euromatic AutomationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Screw: Leadscrew, Screw Jack, Ball Screw and Roller Screw Actuators All Operate On TheDocument3 paginiScrew: Leadscrew, Screw Jack, Ball Screw and Roller Screw Actuators All Operate On ThedheenadhyalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- VFD SDocument25 paginiVFD Svasanth11kvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation and Robotic Lec 2Document9 paginiAutomation and Robotic Lec 2Josh Sam Rindai MhlangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solid State Drives - 02 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inDocument141 paginiSolid State Drives - 02 - by WWW - Learnengineering.inRAJESHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Servo Drive: FunctionDocument2 paginiServo Drive: FunctionBrahmanand SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- M2-Robotics - Classfication by Power SourceDocument8 paginiM2-Robotics - Classfication by Power SourceSam ShekhawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1: 1.1 Suspension SystemDocument31 paginiChapter-1: 1.1 Suspension SystemPritiprajna MohantyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full AutomationDocument16 paginiFull AutomationunimkeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Ii PDFDocument17 paginiUnit Ii PDFManojKumar MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-II Drive SystemDocument84 paginiUnit-II Drive SystemSatheesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-II: Robot Drive Systems and End EffectorsDocument81 paginiUnit-II: Robot Drive Systems and End EffectorsSatheesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automation in Manufacturing 101-200Document100 paginiAutomation in Manufacturing 101-200MsÎncă nu există evaluări
- BMED423 - Final Project - Endoscopic Robotic SolutionsDocument24 paginiBMED423 - Final Project - Endoscopic Robotic SolutionsRazan Al AzzamÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC and AC Motor ControlDocument6 paginiDC and AC Motor Controldes tosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mach L 1Document34 paginiMach L 1abdul bariÎncă nu există evaluări
- ActuatorDocument21 paginiActuatorkylechristiansarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part Ii: Electrical Drives Chapter TenDocument37 paginiPart Ii: Electrical Drives Chapter TenDawit Shimeles TesfayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Creative Technologies 10Document3 paginiCreative Technologies 10Peter Hisu-anÎncă nu există evaluări
- MJET Engg. CollegeDocument74 paginiMJET Engg. CollegePiyush AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Balancing Drive SystemsDocument13 paginiBalancing Drive Systemsismail çakmakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kgi Spec Sheet Multi Axle Steeringv4 PrintDocument2 paginiKgi Spec Sheet Multi Axle Steeringv4 Printyongjun xiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actuators For Robots: A Presentation OnDocument26 paginiActuators For Robots: A Presentation OnreezmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document29 paginiUnit 2VELIVELA LAKSHMIKANTHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit-2, PPT 1Document29 paginiUnit-2, PPT 1VELIVELA LAKSHMIKANTHÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Traction Using A Chopper - 20bee008Document4 paginiDC Traction Using A Chopper - 20bee008Sujith RohitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 1Document7 paginiPaper 1EADummyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsDe la EverandElectric Motor Control: DC, AC, and BLDC MotorsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (19)
- Methods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesDe la EverandMethods for Increasing the Quality and Reliability of Power System Using FACTS DevicesÎncă nu există evaluări
- InterfacesDocument2 paginiInterfacesapi-296499245Încă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3 Parameters of A CircuitDocument2 paginiTopic 3 Parameters of A Circuitapi-296499245Încă nu există evaluări
- Ac Vs DCDocument2 paginiAc Vs DCapi-296499245Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 DefinitionsDocument2 paginiUnit 2 Definitionsapi-296499245Încă nu există evaluări
- Circuit DiagramsDocument3 paginiCircuit Diagramsapi-296499245Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document7 paginiUnit 2api-296499245Încă nu există evaluări
- Differentiating Methods of Energy Transfer Within Robotics Systems Robotics Jonathon English Cody WinsorDocument5 paginiDifferentiating Methods of Energy Transfer Within Robotics Systems Robotics Jonathon English Cody Winsorapi-296499245Încă nu există evaluări
- Sensor DefinitionsDocument6 paginiSensor Definitionsapi-296499245Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Drives Ans ControlsDocument40 paginiElectrical Drives Ans Controlsjeyasaravanan77Încă nu există evaluări
- Caliper Volovo Euro 4Document72 paginiCaliper Volovo Euro 4Car PartsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Catalogue 2015: IvecoDocument3 paginiProduct Catalogue 2015: IvecoAnita MiljkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mek General AnwarDocument98 paginiMek General AnwarRaktim Kumar SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- QSK60G Temp Control GuidelinesDocument4 paginiQSK60G Temp Control GuidelinesMuhammad IshfaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carrier CatalogoDocument100 paginiCarrier CatalogoRafael CubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RFQ Dan PoDocument17 paginiRFQ Dan Pore altairÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Frame Plunger Pump: Model Gearbox ModelDocument4 pagini5 Frame Plunger Pump: Model Gearbox ModeljulioramcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speeduino ManualDocument35 paginiSpeeduino ManualCarlosOlivierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tipicos Tuberia Ecopetrol PDFDocument141 paginiTipicos Tuberia Ecopetrol PDFJunior Oña OrdoñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Method Statement For Testing Precommissioning & Commissioning of Fuel Oil PumpsDocument3 paginiMethod Statement For Testing Precommissioning & Commissioning of Fuel Oil Pumpsvin ssÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shimano Hub Type Maintenance-Manual PDFDocument5 paginiShimano Hub Type Maintenance-Manual PDFArmandSorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- QSI-335i/370i QSI-440i/500i: Parts ManualDocument88 paginiQSI-335i/370i QSI-440i/500i: Parts ManualJ&CÎncă nu există evaluări
- White Fork Lift My60 Parts Operation Maintenance Manual S 407Document20 paginiWhite Fork Lift My60 Parts Operation Maintenance Manual S 407billie100% (44)
- Safety Precautions . . .. ..2 About U600 . .. . ..4Document32 paginiSafety Precautions . . .. ..2 About U600 . .. . ..4NablabsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Price List PDFDocument36 paginiPrice List PDFanon_758223626100% (1)
- KVS 300 - EA RemakeDocument6 paginiKVS 300 - EA RemakePhương Hoàng NgọcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fuel InjectorsDocument2 paginiFuel InjectorsxLibelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Battle GasDocument36 paginiBattle Gaspsn_kylmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Cooled Water ChillerDocument28 paginiWater Cooled Water ChillerHENRYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assemblies: Numbering and Identification For Turbocompressors and Turbines 800 450 98Document7 paginiAssemblies: Numbering and Identification For Turbocompressors and Turbines 800 450 98SreekanthMylavarapuÎncă nu există evaluări
- AutoSam-3.23 Manual ENGDocument89 paginiAutoSam-3.23 Manual ENGМаксим АминовÎncă nu există evaluări
- CL-PG 28-Jun08Document1 paginăCL-PG 28-Jun08Gary GodffreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service: Polo/Vento 2014-2018Document294 paginiService: Polo/Vento 2014-2018hiramfgarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- JP Balancing MachineDocument11 paginiJP Balancing MachineJames JamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pumps Tech Data SheetDocument3 paginiPumps Tech Data SheetSumedha LiyanageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Especificaciones Tecnicas Deep Sea 501 - EspañolDocument2 paginiEspecificaciones Tecnicas Deep Sea 501 - EspañolMH..2023Încă nu există evaluări
- Atb461 Isuzu 4l30-E Delays ForwardDocument1 paginăAtb461 Isuzu 4l30-E Delays ForwardAleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gasoline GeneratorDocument1 paginăGasoline GeneratormuhammadnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Inbuilt Hydraulic JackDocument12 paginiDesign of Inbuilt Hydraulic JackAnonymous L9fB0XU100% (4)