Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Aids
Încărcat de
api-299693592Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Aids
Încărcat de
api-299693592Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
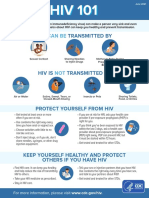
AIDS
HOW TO PREVENT
AIDS
Anyone can get HIV, but you can take steps to protect yourself from HIV infection.
Get tested and know your partners HIV status. Talk to your partner about HIV testing and get tested before you
have sex.
Have less risky sex. Oral sex is much less risky than anal or vaginal sex. Anal sex is the most risky type of sex for
HIV transmission.
Use condoms. Use a condom correctlyevery time you have vaginal, anal, or oral sex. Read this fact sheet from the
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)on how to use condoms correctly.
Limit your number of sexual partners. The more partners you have, the more likely you are to have a partner with
HIV whose HIV is not well controlled or to have a partner with a sexually transmitted disease (STD). Both of these
factors can increase the risk of HIV transmission. If you have more than one sexual partner, get tested for HIV
regularly.
Get tested and treated for STDs. Insist that your partners get tested and treatedtoo. Having an STD can increase
your risk of becoming infected with HIVor spreading it to others.
Talk to your health care provider about pre-exposure prophylaxis (PrEP).PrEP is an HIV prevention option for
people who dont have HIV but who are at high risk of becoming infected with HIV. PrEPinvolves taking a
specificHIV medicine every day. PrEP should always be combined with other prevention options, such as condoms.
Dont inject drugs. But if you do, use onlysterile drug injection equipment and water and never share your
equipment with others.
HOW HIV IS SPREAD
HIV can spread only incertain body fluids from a person infected with HIV:
Blood
Semen
Pre-seminal fluids
Rectal fluids
Vaginal fluids
Breast milk
The spread of HIV (called HIV transmission) is only possible if these fluids come in contact with a mucous membrane or damaged
tissue or are directly injected into the bloodstream (from a needle or syringe). Mucous membranes are found inside the rectum,
the vagina, the opening of the penis, and the mouth.
In the United States, HIV is spread mainly by having sex or sharing injection drug equipment, such as needles, with someone who
has HIV.
HIV can also spread from an HIV-infected woman to her child during pregnancy, childbirth (also called labor and delivery), or
breastfeeding. This spread of HIV is called mother-to-child transmission of HIV.
In the past, some people were infected with HIV after receiving a blood transfusion or organ or tissuetransplant from an HIVinfected donor. Today, this risk is very low because donated blood, organs, and tissues arecarefully tested in the United States.
SIGNS AND SYMTONS OF AIDS
Within2-4 weeksafter HIV infection, many, but not all, people experience flu-like symptoms, often described as the
worst flu ever. This is called acute retroviral syndrome (ARS) and its the bodys natural response to the HIV infection.
Symptoms can include:
Fever (this is the most common symptom)
Swollen glands
Fatigue
Muscle and joint aches and pains
Headache
These symptoms can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks.
You should not assume you have HIV just because you have any of these symptoms. Each of these symptoms can be
caused by other illnesses.And some people who have HIVdo not show any symptoms at allfor 10 years or more.
If you think you may have been exposed to HIV, get an HIV test. Most HIV tests detect antibodies (proteins your body
makes against HIV), not HIV itself. But it takes a few weeks for your body to produce these antibodies, so if you test too
early, you might not get an accurate test result. A new HIV test is available that can detect HIV directly during this early
stage of infection. So be sure to let your testing site know if you think you may have been recently infected with HIV.
You are at high risk of transmitting HIV to others during this early stage, even if you have no symptoms. For this reason, it
is very important to take steps to reduce your risk of transmission.
SKIN WHEN INFECTED
WITH AIDS
HIV AND AIDS
While HIV is a virus that may cause an infection, AIDS is a condition or a
syndrome. Being infected with HIV can lead to having AIDS, which stands for
Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome. AIDS develops when HIV has caused
serious damage to the immune system.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Maths Project 1Document4 paginiMaths Project 1api-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- Finance Project ADocument4 paginiFinance Project Aapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- Collins Barracks 1Document1 paginăCollins Barracks 1api-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- Careers 1Document8 paginiCareers 1api-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- It Is Not Just For Geeks 1Document1 paginăIt Is Not Just For Geeks 1api-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- Work ExDocument1 paginăWork Exapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- Public Access To LawDocument1 paginăPublic Access To Lawapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- ConcussionsDocument3 paginiConcussionsapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- Book ReviewDocument1 paginăBook Reviewapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- CalcutaDocument1 paginăCalcutaapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- BullbearingsDocument3 paginiBullbearingsapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- La SuisseDocument8 paginiLa Suisseapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- Quebec SportsDocument2 paginiQuebec Sportsapi-299693592Încă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Who Is at Risk For HIV Infection?: Sexually Transmitted DiseaseDocument2 paginiWho Is at Risk For HIV Infection?: Sexually Transmitted Diseasevscolegit shoppeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtDocument49 paginiDHQ Flowcharts v2 1 Prep Pep ArtNatasha MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kenya ARV Guidelines 2018Document230 paginiKenya ARV Guidelines 2018Felix Wafula MusibiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comp ART Training Manual March 2020 PDFDocument472 paginiComp ART Training Manual March 2020 PDFStricker ManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Polling Booth Survey ReportDocument128 paginiPolling Booth Survey ReportArtful Eyes ProductionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- WHO Recommendations On Maternal and Newborn Care For A Positive Postnatal ExperienceDocument242 paginiWHO Recommendations On Maternal and Newborn Care For A Positive Postnatal Experiencearum pratiwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trans Women's Safer Sex GuideDocument36 paginiTrans Women's Safer Sex GuideHenry JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harvard Doctor's Secrets For Better Sleep: HealthDocument17 paginiHarvard Doctor's Secrets For Better Sleep: HealthContra_hourÎncă nu există evaluări
- UN AIDS Miles-To-Go - enDocument268 paginiUN AIDS Miles-To-Go - ensofiabloem100% (1)
- 2019 HIV Drug ChartDocument5 pagini2019 HIV Drug ChartETÎncă nu există evaluări
- Access To Hiv Testing and Prevention Services Among Female Sex Workers in Ibesikpo Asutan Local Government Area of Akwa Ibom State.Document6 paginiAccess To Hiv Testing and Prevention Services Among Female Sex Workers in Ibesikpo Asutan Local Government Area of Akwa Ibom State.ErimmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summary Sugar Swee SetDocument1.037 paginiSummary Sugar Swee SetDPK Rumkit Bhayangkara Tk IÎncă nu există evaluări
- HIV and AIDS - Basic Facts: GeneralDocument18 paginiHIV and AIDS - Basic Facts: GeneralBudoy WashupapiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CDC Hiv Consumer Info Sheet Hiv 101Document2 paginiCDC Hiv Consumer Info Sheet Hiv 101Sandy AguilarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Job Announcement-NewDocument31 paginiJob Announcement-NewErick MkomwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023 Planning EvidenceDocument30 pagini2023 Planning EvidenceChimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stevenson National Health Act Guide 2019 1Document207 paginiStevenson National Health Act Guide 2019 1Godfrey OyakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical: GuidelinesDocument58 paginiClinical: Guidelinesdonovandube8235Încă nu există evaluări
- 2020 HivDocument1 pagină2020 HivhenkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 250621Document184 paginiScience 250621gÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prep Guidance For Karp Health Care ProvidersDocument3 paginiPrep Guidance For Karp Health Care ProvidersMigori Art DataÎncă nu există evaluări
- AFAO On Demand PrEP Fact Sheet Oct 2019Document1 paginăAFAO On Demand PrEP Fact Sheet Oct 2019Procesos Selección de PersonasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Consolidated Hiv-Aids Guidelines-2022Document380 paginiFinal Consolidated Hiv-Aids Guidelines-2022Odulusi DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexual Transmited DiseaseDocument22 paginiSexual Transmited DiseasehanifiahanumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capstone Noreen 1Document45 paginiCapstone Noreen 1api-560728162Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Studies - HIVDocument2 paginiCase Studies - HIVclonewars222Încă nu există evaluări
- Proposal TemplateDocument34 paginiProposal TemplateYonas D. EbrenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Communities at The Centre - A Global Aids Update 2019Document316 paginiCommunities at The Centre - A Global Aids Update 2019Mayeth MacedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brunette Eloise A. Cesa - April 15, 2022Document12 paginiBrunette Eloise A. Cesa - April 15, 2022Jackielou MaquisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disparity in HIV Service Interruption in The Outbreak of COVID 19 in South CarolinaDocument9 paginiDisparity in HIV Service Interruption in The Outbreak of COVID 19 in South CarolinaBisma SyahrizalÎncă nu există evaluări