Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Unit 3a Vocabulary
Încărcat de
api-296059071Descriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit 3a Vocabulary
Încărcat de
api-296059071Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Mia Ramos
Block 3
Unit 3a Vocabulary
Biological psychology: a branch of psychology concerned with the links between biology and
behavior
Neuron: a nerve cell: the basic building block of the nervous system
Sensory neurons: neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the
brain and spinal cord
Motor neurons: neurons that carry outgoing information from the brain and spinal cord to the
muscles and glands
Interneurons: neurons within the brain and spinal cord that communicate internally and
intervene between the sensory inputs and motor outputs
Dendrite: the bushy, branching extensions of a neuron that receive messages and conduct
impulses toward the cell body
Axon: the extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages
pass to other neurons or to muscles or glands
Myelin sheath: a layer of fatty tissue segmentally encasing the fibers of many neurons; enables
vastly greater transmission speed of neural impulses as the impulse hops from one node to the
next
Action potential: a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
Threshold: the level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse
Synapse: the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite of the cell
body of the receiving neuron. The tiny gap at this junction is called the synaptic gap or synaptic
cleft
Neurotransmitters: chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gaps between neurons. When
released by the sending neuron, the neurotransmitters travel across the synapse and bind to the
receptor sites in the receiving neuron, thereby influencing whether that neuron will generate a
neural impulse
Reuptake: a neurotransmitter's reabsorption by the sending neuron
Endorphins: "morphine within"natural, opiatelike neurotransmitters linked to pain control and
to pleasure
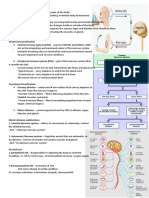
Nervous system: the body's speedy, electrochemical communication network, consisting of all
the nerve cells of the peripheral and central nervous systems
Central nervous system (CNS): the brain and spinal cord
Peripheral nervous system (PNS): the sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS to
the rest of the body
Nerves: bundled axons that form neural "cables" connection the central nervous system with
muscles, glands, and sense organs
Somatic nervous system: the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's
skeletal muscles; skeletal muscle system
Autonomous nervous system: the party of the peripheral nervous system that controls the
glands and the muscles of the internal organs. It's sympathetic division arouses; its
parasympathetic division calms
Sympathetic nervous system: the division of the autonomic nervous system that arouses the
body, mobilizing its energy in stressful situations
Parasympathetic nervous system: the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the
body, conserving its energy
Reflex: a simple, automatic response to a sensory stimulus, such as the knee-jerk response
Endocrine system: the body's "slow" chemical communication system; a set of glands that
secrete hormones into the bloodstream
Hormones: chemical messengers that are manufactured by the endocrine glands, travel through
the bloodstream, and affect other tissues
Adrenal gland: a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones
(epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress
Pituitary gland: the endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the
hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- General Psychology - Biological FoundationDocument55 paginiGeneral Psychology - Biological FoundationKomala PodapatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functions of The Nervous SystemDocument5 paginiFunctions of The Nervous SystemJungkookie BaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordination and Response BiologyDocument2 paginiCoordination and Response BiologyChrispin MsofeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemDocument32 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Nervous SystemLouise Murphy100% (1)
- Nervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterDocument25 paginiNervous System: Science 6 - Second QuarterRegin BaguioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lect 12Document70 paginiLect 12fatima shahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2Document8 paginiChapter 2itxkazimÎncă nu există evaluări
- SSYA1013 Chapter 3 BiologicalDocument27 paginiSSYA1013 Chapter 3 BiologicalPing Ping TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)Document7 paginiChapter 12 - An Introduction To The Nervous System: Peripheral Nerves)tomorrow.today.yesterday .yesterdayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyDocument101 paginiUnit III Nervous System and ElectromyographyakshayÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3A Neurology FlashcardsDocument14 pagini3A Neurology FlashcardsJustin ChangÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH. 2 PsychologyDocument2 paginiCH. 2 PsychologySirena GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument14 paginiNervous SystemJose-Miguel HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordination and ControlDocument5 paginiCoordination and Controltracy lettÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument55 paginiNervous SystemJhemDelfinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument26 paginiNervous SystemAe-jay CacalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ini SarafDocument6 paginiIni SarafIvanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled DocumentDocument16 paginiUntitled Documentpierre TritzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument28 paginiNervous SystemPhoebe dane M PandayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument48 paginiOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous SystemDocument69 paginiThe Nervous SystemKilles SmileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology of MindOK1Document120 paginiBiology of MindOK16130019037 FATCHUR RIZQI HAMZAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oral Exam ReviewerDocument39 paginiOral Exam ReviewerFayena JoseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Group 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Document24 paginiGroup 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Tara DolotaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument34 paginiNervous SystemAlmiah Alfarouk100% (1)
- Module 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDocument43 paginiModule 2 Biological Foundations of Behaviour - Student OutlineDweep BajajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument57 paginiBiological Basis of BehaviorJAMES ALDRIN CALVEZ PAMPOSAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1-Nervous SystemDocument39 paginiLesson 1-Nervous SystemLouise Yvonne ManaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument7 paginiNervous SystemJavi OceansoulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous Sys BiologyDocument6 paginiNervous Sys Biologyalviayaan807Încă nu există evaluări
- File 1476322561Document31 paginiFile 1476322561Maria Tricia Desiree ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinDocument43 paginiPertemuan 8 - Sistem Saraf MinErsha PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology 30 Final VocabularyDocument30 paginiBiology 30 Final VocabularyJose EstradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myer's AP Psychology 8th Edition Chapter 2 VocabDocument4 paginiMyer's AP Psychology 8th Edition Chapter 2 Vocabcardenass100% (3)
- Nervous SystemDocument25 paginiNervous SystemRocky MrRockyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous SystemDocument10 paginiNervous SystemPogi BearÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain or EncephalonDocument6 paginiBrain or EncephalonPredescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Document3 paginiStructure of Brain Nervous System-20-04-2020Jethalal GadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pagini3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyDocument85 paginiThe Nervous System: Anatomy & PhysiologyJamie Bagundol100% (3)
- Nervous SystemDocument6 paginiNervous Systemapi-390021179Încă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous System: Chapter 25 Section 1Document34 paginiThe Nervous System: Chapter 25 Section 1thegedusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Nervous SystemDocument18 paginiCentral Nervous SystemAnne Dominique VenturaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Terms DefDocument3 paginiBio Terms Defapi-31355470Încă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahDocument24 paginiThe Nervous System: DR - Arshad Ali DPT Ipm&R Kmu Ms NMPT RiphahAzhar MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neuropsychology Summary BookletDocument12 paginiNeuropsychology Summary Bookletapi-642709499Încă nu există evaluări
- Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology: Nature or NurtureDocument43 paginiPsychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology: Nature or Nurtureapi-293070066Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3.10 Neurons: Structure of A NeuronDocument5 paginiUnit 3.10 Neurons: Structure of A NeuronNeville Cheong (SPC)Încă nu există evaluări
- Important Definitions: Nervous SystemDocument4 paginiImportant Definitions: Nervous SystemValeri LopezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System ReportDocument24 paginiNervous System ReportChelo Jan GeronimoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 16 The Nervous SystemDocument10 paginiLab 16 The Nervous Systemrhycelayon304Încă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System - Cabil (G6)Document96 paginiNervous System - Cabil (G6)Lady Ann CabilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21-Spinal Cord TractsDocument23 pagini21-Spinal Cord TractsALFAHRUL CAHYADIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System Part 1Document6 paginiNervous System Part 1rb YangzonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Nervous SystemDocument11 paginiHuman Nervous SystemridwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Describe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous SystemDocument29 paginiDescribe The Structure and Function of Each Component of The Nervous Systemsiska yantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous SystemDocument12 paginiThe Nervous SystemJoyce ElizaldeÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Nervous SystemDocument71 paginiThe Nervous SystemDennis Limosnero MayorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.De la EverandMind at Rest: How Neuron Structure Evolves in the Sleep Cycle.Încă nu există evaluări
- Gale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyDe la EverandGale Researcher Guide for: Overview of Physiology and NeuropsychologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CatcherintheryeessayDocument3 paginiCatcherintheryeessayapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Top 10 Online Businesses - Mia RamosDocument11 paginiTop 10 Online Businesses - Mia Ramosapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- SiddharthaessayDocument3 paginiSiddharthaessayapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- MacbethDocument2 paginiMacbethapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Shakespeareansonnet 2Document1 paginăShakespeareansonnet 2api-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- SavethebananafishDocument1 paginăSavethebananafishapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- SoliloquyDocument1 paginăSoliloquyapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- 3C Genetics and Evolution: Unit QuestionsDocument1 pagină3C Genetics and Evolution: Unit Questionsapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 BthebrainDocument2 pagini3 Bthebrainapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Assessment Executivebranch-MialucilleramosDocument3 paginiAssessment Executivebranch-Mialucilleramosapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- 3B The Brain: Unit Questions: Mia Ramos Block-2Document2 pagini3B The Brain: Unit Questions: Mia Ramos Block-2api-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3c Vocab: Genetics and EvolutionDocument1 paginăUnit 3c Vocab: Genetics and Evolutionapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 AquestionsDocument1 paginăUnit 3 Aquestionsapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Cbaessay 2Document1 paginăCbaessay 2api-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- 7 AmemoryDocument2 pagini7 Amemoryapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Research Methods: Mia Ramos Block 2Document3 paginiUnit 2 Research Methods: Mia Ramos Block 2api-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- 7 AmemoryquestionsDocument2 pagini7 Amemoryquestionsapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Mia Ramos Block 2 7B Thinking, Problem Solving, Creativity, and Language: Unit QuestionsDocument2 paginiMia Ramos Block 2 7B Thinking, Problem Solving, Creativity, and Language: Unit Questionsapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- 7B Cognition Vocab: Mia Ramos Block 2Document2 pagini7B Cognition Vocab: Mia Ramos Block 2api-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 QuestionsDocument2 paginiUnit 2 Questionsapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- SiddharthaessayDocument3 paginiSiddharthaessayapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- SoliloquyDocument1 paginăSoliloquyapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- GuitarautobiographyDocument1 paginăGuitarautobiographyapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Period 6-Ramos Mia-Emelynes Secret EmporiumDocument1 paginăPeriod 6-Ramos Mia-Emelynes Secret Emporiumapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Period 6-Ramos Mia-Razor Sharp Scooter 3rd Quarter ExpensesDocument1 paginăPeriod 6-Ramos Mia-Razor Sharp Scooter 3rd Quarter Expensesapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Period 6-Ramos Mia-Mayors ElectionDocument2 paginiPeriod 6-Ramos Mia-Mayors Electionapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Period 6-Ramos Mia - Kylies Pet ShopDocument2 paginiPeriod 6-Ramos Mia - Kylies Pet Shopapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Period 6-Ramos Mia - Computer Discount SalesDocument2 paginiPeriod 6-Ramos Mia - Computer Discount Salesapi-296059071Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Upper LimbDocument112 paginiAnatomy of Upper LimbUzma KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planilha Resultado 2019 Ensino Medio Am InstitutofederaldeeducaocinciaetecnologiadoamazonascampusmanauscentroDocument1.540 paginiPlanilha Resultado 2019 Ensino Medio Am InstitutofederaldeeducaocinciaetecnologiadoamazonascampusmanauscentroChiara GrazziotinÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Health and Safety Guideline For Your Workplace - Manual Materials HandlingDocument6 paginiA Health and Safety Guideline For Your Workplace - Manual Materials HandlingJames UgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Request For MeetingDocument6 paginiRequest For MeetingMARY JUSTINE SIENNE D. CORPORALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Work Word Problem Worksheet 2 PDFDocument2 paginiWork Word Problem Worksheet 2 PDFJaya Porsche Ignacio AlegarbesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saab 900 Convertible 86 93 (Opt)Document4 paginiSaab 900 Convertible 86 93 (Opt)mnbvqwertÎncă nu există evaluări
- Push Pull Legs FreeDocument10 paginiPush Pull Legs FreePanos MisiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 VGV S18 CDocument81 pagini9 VGV S18 CEugenio Hernán100% (1)
- Baki Workout Program 2Document7 paginiBaki Workout Program 2Plamen PetkovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grooming : Edited For Educational Purpose by Dr. Sujal PathakDocument24 paginiGrooming : Edited For Educational Purpose by Dr. Sujal PathakAnimaion SlidesÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Ultimate Lifestyle Guide The Bodyweight MasterDocument46 paginiThe Ultimate Lifestyle Guide The Bodyweight MasterRahul75% (4)
- Ruffled Shawl-Cape by Linda Kaye SmithDocument4 paginiRuffled Shawl-Cape by Linda Kaye SmithTragaluzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elizabeth Hansen MejiaDocument34 paginiElizabeth Hansen MejiaIvan Vargas100% (1)
- YMA Chu Tanpui Ngaite Tanpuitu A NiDocument4 paginiYMA Chu Tanpui Ngaite Tanpuitu A NibawihpuiapaÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Yield Anatomy Notes For FCPS Part 1 (MUST HAVE)Document12 paginiHigh-Yield Anatomy Notes For FCPS Part 1 (MUST HAVE)Dr-Sanjay SinghaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kinetic Chain Exercises - Open Versus ClosedDocument4 paginiKinetic Chain Exercises - Open Versus Closedamirreza jmÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States Patent (19) : 11 Patent Number: 4,541,152 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 1985Document8 paginiUnited States Patent (19) : 11 Patent Number: 4,541,152 45) Date of Patent: Sep. 17, 1985Shubham KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Book: Automotive TechnicalDocument1 paginăData Book: Automotive TechnicalW̶i̶l̶l̶i̶a̶m̶ Valer Yoi KoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moto3™: QNB Grand Prix of Qatar Official Starting GridDocument2 paginiMoto3™: QNB Grand Prix of Qatar Official Starting GridHerik HamzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intimidate Rogue BuildDocument6 paginiIntimidate Rogue BuildThomas McKleranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drone Guide 101Document26 paginiDrone Guide 101acomicbookguyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Log 2Document2 paginiLog 2Emanuela MarinescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- England Abc BookDocument28 paginiEngland Abc Bookapi-251681514Încă nu există evaluări
- The Blackmar-Diemer Gambit (1 d4 d5 2 E4) - Lane, G - 1995Document130 paginiThe Blackmar-Diemer Gambit (1 d4 d5 2 E4) - Lane, G - 1995mpollinni50% (2)
- MargaiaStairClimbTest PDFDocument2 paginiMargaiaStairClimbTest PDFMohd Afiq100% (1)
- The Elder Scrolls IV: Oblivion: Character Build FAQ by PapaGamerDocument66 paginiThe Elder Scrolls IV: Oblivion: Character Build FAQ by PapaGamervictorbb4694Încă nu există evaluări
- Allontherebound1 1Document250 paginiAllontherebound1 1maxguevarax100% (1)
- Mess Bill For April 2023Document10 paginiMess Bill For April 2023Tarang GajbhiyeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chrysler Scan Tool Flash AvailabilityDocument733 paginiChrysler Scan Tool Flash AvailabilityAlbert0% (1)
- Sato ManualDocument1 paginăSato ManualJonÎncă nu există evaluări