Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fluorescent Lamp
Încărcat de
Kantharaj ChinnappaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fluorescent Lamp
Încărcat de
Kantharaj ChinnappaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
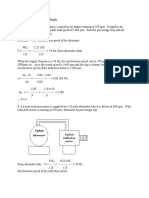
FLUORESCENT LAMP
The fluorescent lamp is an energy saving device. It consumes less power for a given output
lumens when compared to an incandescent lamp.
Construction:
It consists of a long glass tube filled with Argon an inert gas, at low pressure (2.5mm) and a
small amount of mercury. The initial ionization voltage is reduced, as the ionization potential of
argon is low. Two tungsten electrodes are placed at the ends, which are coated with rare earth
oxides. These oxides having a low work function emit the ionizing electrons. A choke is
connected in series with the electrode, which provides the voltage impulse of nearly 1000volts to
start the discharge, and also limits the flow of current through the circuit. It also acts as ballast
when the lamp is ON. The filament is connected to starter switch, a cathode glow lamp that has a
bi-metallic strip as its electrodes. The capacitor C (0.02 F) improves the power factor of the
circuit while the capacitor C1 (4 F ) suppresses the radio interference.
Working:
When the switch is closed the supply voltage comes across the starter electrodes initiating a glow
discharge between them. This heats the bi-metallic strip electrodes, which expand and make
contact completing the circuit. The resulting current flows through the tungsten electrodes and
the electrons are emitted from the oxide coating (low work function), which initiate ionization of
the gas molecules present in the glass tube. At this instant the bi-metallic strip electrodes cool
and the starter opens. Thus there is a sudden interruption of the current, which induces a high
voltage (`1000volts) in the choke.
This impulse strikes an arc between the electrodes lighting the lamp. The vaporized mercury gets
ionized and emits radiations partly in the visible range and partly in ultraviolet range. The
phosphor coating gives the required color and also absorbs the ultra violet light and re-radiates in
the visible spectrum.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Panas LebihDocument51 paginiPanas LebihRinggo Reog100% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Strength of Materials Jan 2018 (2015 Scheme)Document2 paginiStrength of Materials Jan 2018 (2015 Scheme)Kantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Spur Gear Profile PDFDocument8 paginiSpur Gear Profile PDFKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- SFD and BMDDocument278 paginiSFD and BMDRama KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Emissions and Performance Evaluation of DI CI - VCDocument8 paginiEmissions and Performance Evaluation of DI CI - VCKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Yoga Kundalini UpanishadDocument26 paginiYoga Kundalini UpanishadSunil LokeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Strength of Material-Shear Force and Bending MomentsDocument25 paginiStrength of Material-Shear Force and Bending MomentszakeriyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Gear Calculations Rev3Document5 paginiGear Calculations Rev3ghostghost123Încă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
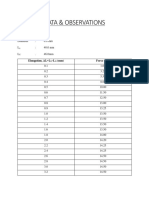
- Data & Observations: BrassDocument4 paginiData & Observations: BrassKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Auto CADDocument61 paginiAuto CADThiru MuruganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data & Observations: BrassDocument4 paginiData & Observations: BrassKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Materials Testing TensileDocument2 paginiMaterials Testing TensileKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data & Observations: BrassDocument4 paginiData & Observations: BrassKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Brief ContentsDocument7 paginiBrief ContentsKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- FuseDocument3 paginiFuseKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Student Progress Check FormDocument1 paginăStudent Progress Check FormKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC MachinesDocument1 paginăDC MachinesKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- DC MachineDocument3 paginiDC MachineKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elec 1Document4 paginiElec 1Kantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worked Examples 1 Induction MotorDocument2 paginiWorked Examples 1 Induction MotorKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Applications of Induction MotorsDocument2 paginiApplications of Induction MotorsKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Protective DevicesDocument4 paginiProtective DevicesKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Induction Motor ADocument2 paginiThree Phase Induction Motor AKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EarthingDocument7 paginiEarthingKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gauss SeidalDocument3 paginiGauss SeidalKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.2 Criteria For Curve FittingDocument5 pagini3.2 Criteria For Curve FittingKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Santhosh Wind Energy Resource Evaluation in A Site of Central Italy by CFD SimulationsDocument1 paginăSanthosh Wind Energy Resource Evaluation in A Site of Central Italy by CFD SimulationsKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- DesignDocument1 paginăDesignKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lee N DuffyDocument1 paginăLee N DuffyKantharaj ChinnappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)